How does a negative feedback loop respond to a variable?
Jul 30, 2017 · Feedback allows the product of a pathway to control the switch. Sometimes referred to as a “negative feedback loop”, negative feedback occurs when the product of a pathway turns the biochemical pathway off. Positive feedback, the opposite of negative feedback, is found in other biological pathways in which the product increases the pathway.
What is the difference between positive and negative feedback?
Jul 09, 2015 · Negative feedback is a regulatory mechanism in which a 'stimulus' causes an opposite 'output' in order to maintain an ideal level of whatever is being regulated. Negative feedback loops occur in a...
How does negative feedback loop work in the body?
Jul 25, 2021 · A negative feedback loop is a biological process that occurs within our bodies that causes a decrease in the function of that pathway. A …
What are some examples of negative feedback?
Mar 01, 2022 · Negative Feedback Loops. A negative feedback loop occurs in biology when the product of a reaction leads to a decrease in that reaction. In this way, a negative feedback loop brings a system closer to a target of stability or homeostasis. Negative feedback loops are responsible for the stabilization of a system, and ensure the maintenance of a steady, stable …

What is an example of a negative feedback loop?
What is biology negative feedback?
What is a negative feedback loop in homeostasis?
What is negative feedback in biology for dummies?
What is a negative feedback loop quizlet?
What is a negative feedback loop kids?
What is a feedback loop in the body?
What are negative and positive feedback loops?
What are some examples of negative feedback loops?
Another common example of a negative feedback loop in biology is thyroid regulation of metabolism, which you can see in this diagram. This is a negative feedback loop that controls the release of thyroid hormones T3 and T4, which stimulate metabolic activity.
What is negative feedback?
Negative feedback is a regulatory mechanism in which a 'stimulus' causes an opposite 'output' in order to maintain an ideal level of whatever is being regulated. Negative feedback loops occur in a series of steps. You have a stimulus, in which a change occurs. You have a sensor, or the change is detected.
What happens if the temperature drops down?
If the temperature were to keep dropping down until it is too cold, then the process would repeat itself, but this time, the response (or control) would be to increase the temperature to bring it back to normal. A negative feedback loop serves to keep a certain variable in check, temperature in this case.
What happens when you have a stimulus?
You have a stimulus, in which a change occurs. In this case, the temperature in the house increases.
Which structure controls homeostasis?
The controller of homeostasis in most animals is the hypothalamus. Without this structure in the brain, organisms would have great difficulty functioning normally. There are many negative feedback pathways in biological systems, including: Temperature regulation. Blood pressure regulation.
Is there an effector in a response?
There's an effector, or the effect of the response.
Is a thermostat a negative feedback?
The thermostat is a prime example of negative feedback, and we see the same thing happen in the bioche mistry of living things. Negative feedback is a regulatory mechanism in which a 'stimulus' causes an opposite 'output' in order to maintain an ideal level of whatever is being regulated.
Why are feedback loops negative?
Negative feedback loops within the body are meant to keep the body within homeostasis. However, not every situation is able to do so. For example, in the situation of Type 1 diabetes, where there is no insulin production from the pancreas, homeostasis cannot be achieved when there is an increase in high blood sugar. Ideally, the high blood sugar should activate the beta cells in the pancreas to secrete insulin which will then decrease the glucose in the bloodstream by storing it as glucagon in the liver. However, this feedback loop does not function in the situation of diabetes because high blood sugar will not lead to the secretion of insulin. This is why those with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin injections to directly inject insulin into their bloodstream.
What are some examples of negative feedback loops?
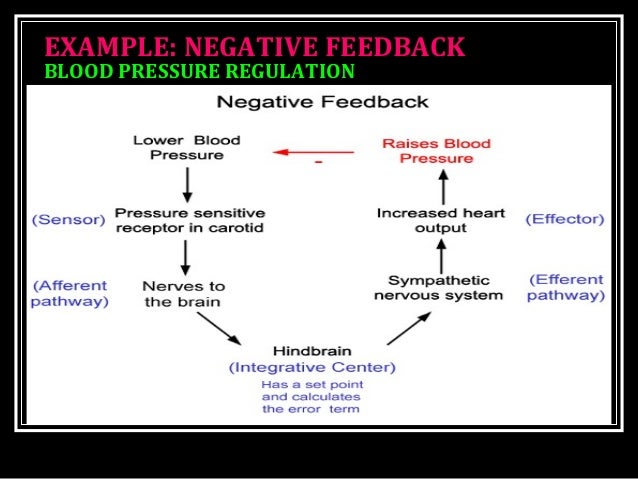
An example of a negative feedback loop within the body is the regulation of blood pressure. When blood pressure falls out of normal limits, depending on the situation, either the sympathetic or parasympathetic nerves are stimulated and the kidneys either excrete more water or retain more water in an effort to bring the blood pressure back to normal.
What is negative feedback?
A negative feedback loop is a biological process that occurs within our bodies that causes a decrease in the function of that pathway. A negative feedback loop is in place to ensure that the body has an off switch. This mechanism allows the body to make enough of wh
How does the pathway work?
Essentially, how the mechanism works is that there is a signal that causes the pathway to be turned on. The pathway goes through the steps necessary to create an end product. When enough of that end product is made, either the end product or the effect the end product has on the body acts as an off switch to shut off the pathway. This allows the body to return to normal and restore homeostasis.
How does the hypothalamus maintain homeostasis?
When this happens, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the body to start shivering which is a way to increase internal body temperature. Once internal body temperature has been restored back to normal, the shivering will stop.
What is negative feedback loop?
A negative feedback loop occurs in biology when the product of a reaction leads to a decrease in that reaction. In this way, a negative feedback loop brings a system closer to a target of stability or homeostasis. Negative feedback loops are responsible for the stabilization of a system, and ensure the maintenance of a steady, stable state.
When does a positive feedback loop occur?
A positive feedback loop occurs in nature when the product of a reaction leads to an increase in that reaction. If we look at a system in homeostasis, a positive feedback loop moves a system further away from the target of equilibrium.
How does feedback work in an ecosystem?
Feedback loops can also occur to a larger degree: at the ecosystem level, a form of homeostasis is maintained . A good example of this is in the cycle of predator and prey populations: a boom in prey population will mean more food for predators, which will increase predator numbers. This will then lead to over predation, and the prey population will again decline. The predator population will decline in response, releasing the pressure on the prey population and allowing it to bounce back. See figure 1. Another example is what is known as the “evolutionary arms race,” wherein a predator and its prey are continually trying to out compete each other. One such relationship is that of nectarivorous birds and the flowers on which they feed. The birds evolve long beaks to gain access to the nectar within the flower. In response, the flower develops a longer and longer trumpet-like shape, in an attempt at preventing the bird from getting to the nectar. The bird responds by developing an even longer beak. And so it continues.
Why is feedback loop important?
Feedback loops are important because they allow living organisms to maintain homeostasis.
Is temperature regulation a negative feedback loop?
Figure 5: The process of temperature regulation in humans is a negative feedback loop.
Is the process of apples ripening a positive feedback loop?
Figure 2: The process of apples ripening is a positive feedback loop.
Can homeostasis be achieved without feedback?
Without feedback, homeostasis cannot occur. This means that an organism loses the ability to self-regulate its body. Negative feedback mechanisms are more common in homeostasis, but positive feedback loops are also important. Changes in feedback loops can lead to various issues, including diabetes mellitus.
What is the difference between positive and negative feedback loops?
Positive feedback loops enhance or amplify changes; this tends to move a system away from its equilibrium state and make it more unstable. Negative feedbacks tend to dampen or buffer changes; this tends to hold a system to some equilibrium state making it more stable.
What is a feedback loop in biology?
what is a feedback loop in biology? Feedback loops are therefore the process whereby a change to the system results in an alarm which will trigger a certain result. A feedback loop is a biological occurrence wherein the output of a system amplifies the system (positive feedback) or inhibits the system (negative feedback).
What is homeostasis in biology?
Definition: Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a constant internal environment in response to environmental changes. It is a unifying principle of biology. The nervous and endocrine systems control homeostasis in the body through feedback mechanisms involving various organs and organ systems.
What is negative feedback?
Negative feedback is a reaction that causes a decrease in function. It occurs in response to some kind of stimulus. Often it causes the output of a system to be lessened; so, the feedback tends to stabilize the system. This can be referred to as homeostatis, as in biology, or equilibrium, as in mechanics.
Does blood pressure change with negative feedback?
In a negative feedback system some factor, such as blood pressure, changes. The change is detected by a sensor. The brain will cause the heart to beat slower and thus decrease the blood pressure. Decreasing heart rate has a negative effect on blood pressure.
What are the positive and negative feedback loops?
Positive and Negative Feedback 1 Childbirth is a positive feedback loop. During childbirth, the uterus will contract until the child is born. 2 Blood clotting is another example because platelets will continue to be released to the injury site until the bleeding has stopped.
What is negative feedback?
A negative feedback loop is a reaction that causes a decrease in function. It occurs in response to some kind of stimulus. Often, it causes the output of a system to be lessened; so, the feedback tends to stabilize the system. This can be referred to as homeostasis, as in biology, or equilibrium, as in mechanics.
What is the feedback loop in childbirth?
Childbirth is a positive feedback loop. During childbirth, the uterus will contract until the child is born.
Does negative feedback decrease or increases?
So to simplify, negative feedback decreases while positive feedback increases a function until a specific outcome is reached.
Is mechanics a negative feedback loop?
Mechanics is also full of different physical negative feedback loops. Here are a few examples.
What is the difference between positive and negative feedback loops?
The main difference between positive and negative feedback loops is that the positive feedback loops amplify the initiating stimulus, moving the system away from its equilibrium whereas the negative feedback loops counteract the changes of the system, maintaining them in a set point. Furthermore, positive feedback loops result in more products ...
What is positive feedback loop?
Definition. Positive feedback loops refer to a feedback mechanism resulting in the amplification or growth of the output signal while negative feedback loops refer to a feedback mechanism resulting in the inhibition or the slowing down of a process.
Which loops maintain homeostasis?
Furthermore, the positive feedback loops breakdown the homeostasis of the system while the negative feedback loops always maintain the conditions of homeostasis.
What is negative feedback?
Negative feedback loops are responsible for reversing the change by activating the opposite responses. This means this type of feedback mechanisms stabilize biological systems maintained under homeostatic conditions, important for a constant internal environment. Some examples of negative feedback loops are described below.
What are the two mechanisms that affect homeostasis?
Positive and negative feedback loops are the two mechanisms that affect homeostasis, which refers to the tendency to maintain a relatively stable environment in biological systems.
What are some examples of negative feedback loops?
Other examples of negative feedback loops include the regulation of blood sugar, blood pressure, blood gases, blood pH, fluid balance, and erythropoiesis.
What are the components of a feedback loop?
Feedback loops have three components—the sensors, the control, and the effector. Sensors are also called receptors and they monitor conditions inside and outside the body. Some examples are thermoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. The control center, often in the brain, compares the value the sensor receives to the values in the range.
Why is positive feedback important?
Instead of reversing it, positive feedback encourages and intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition, actually driving it farther out of the normal range. This type of feedback is normal for the body, provided there is a definite endpoint.
Why is thermoregulation the primary reaction?
This type of thermoregulation is the primary reaction because the effects will occur faster than the physiological mechanisms. It is important to realize that this feedback mechanism is based on controlling heat loss or heat gain in the body.
What is homeostasis in biology?
Last Updated: April 15, 2018. Homeostasis refers to the steady state of internal conditions maintained by living organisms. Humans have control centers in the brain and other parts of the body that constantly monitor conditions like temperature, pressure, and blood and tissue chemistry. When any condition gets out of balance, ...
What happens when a condition is out of balance?
When any condition gets out of balance, feedback loops return the body to homeostasis. This is a natural response to changes in the optimal conditions for the body to function. To sense when things are out of balance, bodily functions have set points around which normal values fluctuate within a range. For example, normal human body temperature set ...