
What is a negative inducible operon? Negative inducible operons is a process where the active regulator protein binds to the operator which prevents RNA polymerase RNA polymerase, abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, officially DNA-directed RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of R…RNA polymerase
Full Answer
What is the difference between negative and repressible operons?
Operons can be under negative or positive control. Negative control involves turning off the operon in the presence of a repressor; this can be either repressible or inducible. A repressible operon is one that is usually on but which can be repressed in the presence of a repressor molecule.
What is positive control of an operon?
Positive control of an operon is when gene expression is stimulated by the presence of a regulatory protein. The Lac operon is the classic operon example, and is responsible for the degradation of the milk protein lactose. The Lac operon is an inducible operon; in the absence of lactose the operator is blocked by a repressor protein.
What is an inducible operon?
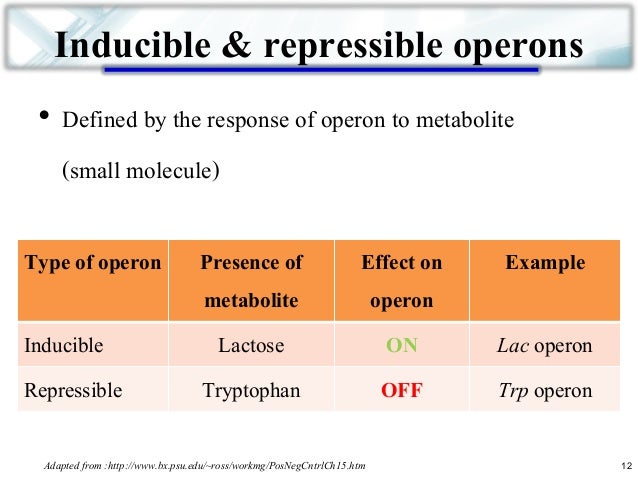
An inducible operon is one whose expression increases quantitatively in response to an enhancer, an inducer, or a positive regulator. The lac operon is a classic example of an inducible operon and is induced by lactose and its structural analogs: isopropyl beta-D-1 thiogalactopyranoside(IPTG) and thiomethyl galactoside(TMG). [2][3]
When are operons turned on or turned off?
These operons are turned on when the gene products are needed. Operons can be under negative or positive control. Negative control involves turning off the operon in the presence of a repressor; this can be either repressible or inducible.
.PNG)
What is negative inducible regulation?
In inducible negative regulation, the default state of gene transcription is “on.” The regulatory protein on its own binds to the operator site to block transcription, turning it off.
What is the difference between positive and negative control what is the difference between inducible and repressible operons?
Positive/Negative and Repressible/Inducible gene regulation Positive control- The regulator of the operon acts as an activator and is required in its active form for transcription. Negative control- The regulator of the operon acts as a repressor that prevents transcription when it is active.
What is negative inducible?
Negative inducible operons is a process where the active regulator protein binds to the operator which prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing. If precursor five is present, it acts as and inducer altering the shape of the regulator protein disabling it to bind to DNA, and transcription can occur.
What is a positive inducible operon?
The clustering of genes allows coordinated regulation and expression of the genes and provides rapid adaptation to various environmental changes. An inducible operon is one whose expression increases quantitatively in response to an enhancer, an inducer, or a positive regulator.
Why is the lac operon negative inducible?
The lac operon exhibits both systems. It is a negative control system because expression is typically blocked by an active repressor (the lac repressor) that turns off transcription. The lac repressor binds to the operator region and negatively controls (prevents) transcription.
What is positive and negative control in operon?
Regulation of the lac Operon The activity of the promoter that controls the expression of the lac operon is regulated by two different proteins. One of the proteins prevents the RNA polymerase from transcribing (negative control), the other enhances the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter (positive control).
Is the lac operon negative inducible?
Allolactose is an example of an inducer, a small molecule that triggers expression of a gene or operon. The lac operon is considered an inducible operon because it is usually turned off (repressed), but can be turned on in the presence of the inducer allolactose.
Is an inducible operon negatively regulated?
2:5413:59Repressible/Inducible Gene Regulation - Positive/NegativeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBut you can force a negatively regulated gene to be off if a DNA repressor protein binds to thatMoreBut you can force a negatively regulated gene to be off if a DNA repressor protein binds to that gene. The terms were pressable. And inducible they describe the cells perspective.
What is the difference between positive and negative regulation?
Positive gene regulation refers to the type of gene regulation that enables the expression of genes, while negative gene regulation refers to the type of gene regulation that prevents the gene expression. Hence, this is the main difference between positive and negative gene regulation.
What does negative regulation mean?
It is the process of regulating gene expression by inhibiting the expression of that specific gene. The repressor (a substance that can inhibit the expression of a gene) gets attached to the operator and inhibits the further process of gene expression.
Is a inducer positive or negative control?
(A) Negative control: induction is achieved when an inducer inactivates a repressor protein allowing the expression of the gene of interest. (B) Positive control: induction is achieved when an inducer activates an activator protein.
What is positive and negative control in gene expression?
positive control - when transcription is under positive control, a protein known as an activator binds to the DNA in order for transcription to take place. negative control - when transcription is under negative control, a protein known as a repressor binds to the DNA and blocks transcription.
What is the difference between inducible and repressible operons?
The main difference between inducible and repressible operons is that the inducible operons are turned off under normal conditions while the repressible operons are turned on under normal conditions.
What is the difference between inducible and repressible regulation?
Some operons are inducible, meaning that they can be turned on by the presence of a particular small molecule. Others are repressible, meaning that they are on by default but can be turned off by a small molecule.
What is the difference between positive and negative control of gene expression?
Positive gene regulation refers to the type of gene regulation that enables the expression of genes, while negative gene regulation refers to the type of gene regulation that prevents the gene expression. Hence, this is the main difference between positive and negative gene regulation.
What do you mean by inducible and repressible operon cite example?
Inducible operon is regulated by a substrate present in the metabolic pathway while repressible operon is regulated by the presence of a metabolic end product known as a co-repressor. This is the main difference between inducible and repressor operon.
Need more help understanding negative, inducible control?
Which factor (s) contribute to the expression of phenotypic variation within populations? Environmental factors contribute soley to phenotypic variation Genetic factors contribute soley to phenotypic variation Neither...
Get the most out of Chegg Study
In science there are many key concepts and terms that are crucial for students to know and understand. Often it can be hard to determine what the most important science concepts and terms are, and even once you’ve identified them you still need to understand what they mean.
What is the difference between repressible and inducible operons?
Repressible operons are generally involved in anabolic pathways, or the synthesis of an essential component, while inducible operons are generally involved in catabolic pathways, or the breakdown of a nutrient. Positive control of an operon is when gene expression is stimulated by the presence of a regulatory protein.
What is the inducer molecule for the Lac operon?
In order for the Lac operon to be turned on, an inducer molecule must inactivate the repressor protein. The inducer molecule in this system is allolactose, an isomer of lactose. When lactose and its isomer are present in the cell, allolactose will bind to allosteric sites on the repressor protein, changing its conformation and rendering it inactive. As the repressor protein detaches from the operator, RNA polymerase can bind to the promoter, transcription can occur, and the three lactose degradation genes can be synthesized.
How does the Lac operon regulate gene expression?
The level of gene expression is controlled by the amount of the preferred energy source, glucose, in the cell. This control is regulated by an allosteric regulatory protein, catabolite activator protein (CAP). When glucose levels in the cell are low, the organic molecule cyclic AMP is in high concentration. Cyclic AMP activates CAP by binding to the allosteric sites, causing CAP to attach to the Lac operon promoter. Unlike the repressor proteins, binding of CAP to the Lac operon stimulates gene expression. When the cell glucose levels increase, the cyclic AMP levels in the cell decrease, and the activator protein will disassociate from the promoter. Transcription will return to low levels, or will turn off if the repressor protein reattaches.
What is the function of the lac operon?
The Lac operon is the classic operon example, and is responsible for the degradation of the milk protein lactose. The Lac operon is an inducible operon; in the absence of lactose the operator is blocked by a repressor protein. The operon is made up of a promoter with operator, and three genes (lacZ, lacY, and lacA) which encode β-galactosidase, permease, and transacetylase. The three genes are involved in the breakdown of lactose into its metabolites: β-galactosidase breaks lactose down into glucose and galactose, while the other two proteins aid in the metabolic process. The expression of the Lac operon is controlled by the regulatory gene lacI, located immediately adjacent to the promoter region. LacI encodes an allosteric repressor protein that keep the Lac operon “off”.
How is the Lac operon controlled?
The Lac operon is controlled by both positive and negative regulation. For positive regulation it requires the presence of an activator protein, CAP, for transcription to occur at more than very low levels. For negative regulation it requires the removal of the repressor protein by the inducer molecule, allolactose. 3.
What happens when the repressor protein detaches from the operator?
As the repressor protein detaches from the operator, RNA polymerase can bind to the promoter, transcription can occur , and the three lactose degradation genes can be synthesized. The figure shows the structure of the Lac operon and the adjacent lacR repressor gene. The Lac operon is also under positive gene regulation.
Where is the lac operon located?
The expression of the Lac operon is controlled by the regulatory gene lacI, located immediately adjacent to the promoter region. LacI encodes an allosteric repressor protein that keep the Lac operon “off”. In order for the Lac operon to be turned on, an inducer molecule must inactivate the repressor protein.
Which operon is known to operate by both negative repressible regulation of operator and attenuation?
The trp operon is known to operate by both negative repressible regulation of operator and attenuation. Which of the following does NOT support the reason as to why dual control exists to regulate the operon?
What is an operon?
Positive inducible. An operon is controlled by a repressor. When the repressor binds to a small molecule, it binds to DNA near the operon. The operon is constitutively expressed if a mutation prevents the repressor from binding to the small molecule. The type of control illustrated is.
How is an operon controlled?
An operon is controlled by a repressor. When the repressor binds to a small molecule, it is released from binding to DNA near the operon. The operon is never expressed if a mutation prevents the repressor from binding to the small molecule. The type of control illustrated is.
Why is the structural gene constitutively expressed?
The structural gene will be constitutively expressed due to the lack of negative inducible control.
Which site of the operon blocks the binding of RNA polymerase?
the repressor-binding site overlaps the promoter site of the operon, allowing it to physically block the binding of RNA polymerase.
Why is transcription turned off?
As the transcription will require an activator protein, the transcription will be turned off.
Operon Definition
Operon Structure
- Operons are regions of DNA that contain clusters of related genes. They are made up of a promoter region, an operator, and multiple related genes. The operator can be located either within the promoter or between the promoter and the genes. RNA polymerase initiates transcription by binding to the promoter region. The location of the operator is important as its r…
Operon Function
- An operon is a complete package for gene expression and synthesis of polypeptides. By combining the related genes, all polypeptides required for a specific function are synthesized in response to a single stimulus. For example, the bacterium Escherichia coli contains a number of genes clustered into operons and regulons: the Lac operonwhich is involved in lactose degradati…
Lac Operon
- The Lac operon is the classic operon example, and is responsible for the degradation of the milk protein lactose. The Lac operon is an inducible operon; in the absence of lactose the operator is blocked by a repressor protein. The operon is made up of a promoter with operator, and three genes (lacZ, lacY, and lacA) which encode β-galactosidase, per...
TRP Operon
- The Trp operon is responsible for synthesis of the amino acid trytophan when it is not available in the environment. The Trp operon is made up of a promoter with an operator, and five genes that encode enzymes for tryptophan synthesis. The Trp operon is regulated by the regulatory gene trpR, a gene that is located at a distance from the Trp operon. The Trp operon is an example of …
Quiz
- 1. Which of the following organisms contain operons? A. yeast B. bivalves C. trees D.archaea 2. How is the Lac operon regulated? A. positive control B. negative control C. inducible D.all of the above 3. Are repressible operons under positive or negative control? A. positive B.negative