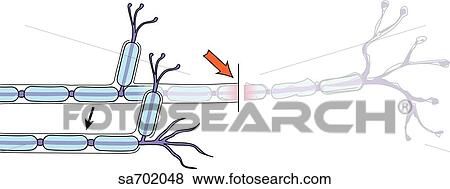
Is it neurotmesis or axonotmesis?
With Seddon's classification of nerve injuries, it is often tough to identify whether a particular nerve injury is neurotmesis, or axonotmesis, which has damage to the nerve fibres but preservation of the nerve trunk.
Why is neurotmesis the worst degree of peripheral nerve damage?
It is the worst degree of peripheral nerve because the components of the nerve are completely disrupted. If neurotmesis occurs in a particular nerve, it produces a complete sensory deficit to the skin and muscles innervated by the injured nerve.
What is neuromuscular neurotmesis?
Neurotmesis occurs in the peripheral nervous system and most often in the upper-limb (arms), accounting for 73.5% of all peripheral nerve injury cases. Of these cases, the ulnar nerve was most often injured. Peripheral nerves are structured so that the axons are surrounded by most often a myelinated sheath and then an endoneurium.
What are the symptoms of neurotmesis?
Symptoms of neurotmesis include but are not limited to pain, dysesthesias (uncomfortable sensations), and complete loss of sensory and motor function of the affected nerve. Neurotmesis occurs in the peripheral nervous system and most often in the upper-limb (arms), accounting for 73.5% of all peripheral nerve injury cases.
How do you get neurotmesis?
Neurotmesis is most commonly caused by a serious injury with forceful impact and, in a lot of instances, a laceration that cuts through the nerve. Whenever there is either an axonotmesis or a neurotmesis there is a Tinel sign.
How do you know if you have neurotmesis?
The only way to know for sure if a nerve injury is in fact neurotmesis is to allow for the normal progression of nerve regeneration to take place (nerves regenerate at a rate of approximately 2–4 mm/day proximal to the lesion), and if, after that time, there is still profound muscle paralysis and degeneration in these ...
What is Neuropraxia axonotmesis and neurotmesis?
The second degree in which the axon is damaged but the surrounding connecting tissue remains intact is called axonotmesis. The last degree in which both the axon and connective tissue are damaged is called neurotmesis.
How long does neurotmesis take to heal?
Nerve conduction is preserved both proximal and distal to the lesion but not across the lesion. Complete recovery occurs within 12 weeks.
Does neurotmesis heal?
Neurotmesis will produce complete sensory and motor deficits to the skin and muscles innervated by the injured nerve. Spontaneous recovery of function is extremely suboptimal without surgical intervention.
What is the most severe nerve injury?
The most severe form of injury is called neurotmesis, which is a full transection of the axons and connective tissue layers wherein complete discontinuity of the nerve is observed.
What are the 3 types of nerve injuries?
Seddon2 classified nerve injuries into three broad categories; neurapraxia, axonotmesis, and neurotmesis.
What type of injury is axonotmesis?
A second-degree injury (axonotmesis) is a nerve fiber injury in which the distal fibers undergo wallerian degeneration, but the endoneurial tubes remain open and in continuity. Recovery is complete, occurs at a rate of 1 mm/day, and may be followed by an advancing Tinel's sign.
What are the three different types of nerve damage?
Classification of Nerve Injuries. When assessing peripheral nerve damage, most physicians use Seddon's classification of nerve injury. This divides nerve damage into three types: neurapraxia, axonotmesis, and neurotmesis.
Do nerves grow back after surgery?
Successful nerve growth to the neuromuscular endplate may take as long as 6-12 months after surgery. After this period, nerve maturation and initial muscle recovery may take 12-18 months. Remember our body is hard at work healing before any electrical recovery can even be detected in the growing nerve fibers!
How do I know if nerve damage is healing?
How do I know the nerve is recovering? As your nerve recovers, the area the nerve supplies may feel quite unpleasant and tingly. This may be accompanied by an electric shock sensation at the level of the growing nerve fibres; the location of this sensation should move as the nerve heals and grows.
What does Neuropraxia feel like?
In neuropraxia, an injury to your peripheral nerve(s) causes symptoms like burning, stinging and pain. These mild nerve injuries typically heal on their own with rest and time. Wearing protective equipment during contact sports and physical activities like cycling can help reduce your risk of neuropraxia.
How long can Neuropraxia last?
Neurapraxia has an excellent prognosis. It is a non-axonal injury, and most patients experience recovery within 2–3 months.
What injuries cause nerve damage?
Injury to the peripheral nerve network can happen through:Laceration (a cut or tear in the nerve tissue)Severe bruising (contusion)Gunshot wounds.Stretching (traction)Drug injection injury.Electrical injury.
Is Axonotmesis reversible?
The prognosis of axonotmesis relies on the underlying condition of the patient and the nature of the injury. In the best circumstances, the nerve can regenerate within a timely manner by axonal branching or through the expansion of the proximal segment of the damaged nerve.
What causes Axonotmesis?
This injury can be caused by direct blunt injury, fractures, dislocations, contusions, or stretch or crush injuries and can result in motor, sensory, or autonomic paralysis in the autonomous distribution of the nerve.
What is neurotmesis in neurology?
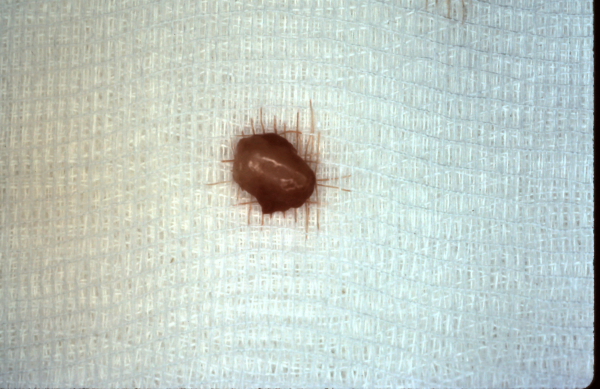
Neurotmesis is defined as an injury in which the nerve is completely divided. This results in complete paralysis, the resultant atrophy of muscles innervated by the nerve, and total anesthesia of the nerve’s cutaneous distribution. Physical examination may reveal a tender mass, a neuroma, at the distal stump of the amputated nerve. Clinicians should assume that a neurological dysfunction referable to a nerve injury resulting from a laceration is a neurotmetic injury, unless there is evidence to the contrary.
What happens after neurotmesis?
After neurotmesis, nonviable tissue must be removed and then the nerve must regenerate. First, within hours of the injury, chromatolysis, with breakdown of rough endoplasmic reticulum, occurs in the injured part of the nerve.
What is the most severe level of injury characterized by complete axonal disruption and discontinuity of some or all?
Neurotmesis is the most severe level of injury, characterized by complete axonal disruption and discontinuity of some or all of the surrounding connective tissue. From: Imaging of Arthritis and Metabolic Bone Disease, 2009. Download as PDF. About this page.
What is the term for a mass at the distal stump of the amputated nerve?
Physical examination may reveal a tender mass, a neuroma , at the distal stump of the amputated nerve. Clinicians should assume that a neurological dysfunction referable to a nerve injury resulting from a laceration is a neurotmetic injury, unless there is evidence to the contrary.
What is the result of a severe crush or traumatic division of the nerve?
Loss of continuity of axons and connective tissue components result in neurotmesis. This usually is a consequence of an acute stretching of the nerve, a severe crush or traumatic division. Sunderland has subdivided these more severe lesions into three types:
Where do motor neurons grow?
Studies have shown that nerve axons preferentially grow toward distal nerve stumps rather than toward other soft tissues and toward their own distal stump rather than other distal nerve stumps and that motor neurons grow toward denervated muscle rather than toward innervated muscle. 116 There are several proposed mechanisms for these patterns of regeneration. The growth cone and filopodia are attracted to negatively charged proteins present in the basement membrane of the distal nerve stump, thus axon sprouts are directed toward the distal nerve segment, specifically the basement membrane. When one axon, from a single growth cone, reaches the basement membrane of the distal segment of the same nerve a protein known as actin, found in the growth cone, attaches to the basement membrane of that distal segment and the other nerve sprouts in that growth cone degenerate. In addition, a protein called neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) that is expressed by muscle attracts motor nerves, and for other nerves, axonal regeneration and myelinization are promoted by the nerve connecting with an end-organ. 114
Which protein is expressed by muscle and stimulates motor nerves?
In addition, a protein called neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) that is expressed by muscle attracts motor nerves, and for other nerves, axonal regeneration and myelinization are promoted by the nerve connecting with an end-organ. 114.
Which sports are associated with neurotmesis?
Neurotmesis affecting the upper and lower limbs are being recognized with increasing frequency in sports, such as football and rugby.
What is the term for destruction of both nerves and connecting tissues?
Neurotmesis; destruction of both nerves and connecting tissues.
What is the worst form of peripheral nerve injury?
Neurotmesis is a severe form of peripheral nerve injury where there is a complete transection of the nerve fiber, that is, the entire nerve is completely severed, avulsed, or crushed. It is the worst degree of peripheral nerve because the components of the nerve are completely disrupted.
What is the best treatment for nerve pain?
Neuropathic drugs such as serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants help you with the pains as a result of the nerve damage.
How long does it take for a nerve to regenerate?
The time to regenerate a nerve depends on the type of nerve injury you received. A slight bruise or damage not affecting connective tissue may take 6 to 12 weeks. But for neurotmesis, the nerve can take months to regenerate because when a nerv e is cut, it grows at 1mm per day.
What is the role of nerves in the body?
They are a group of fibers in the body whose primary role is to provide a pathway to conduct sensory impulses throughout the body. It essentially relays information from one part of the body to another. The nerve just like the “telephone wiring” system carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body.
Why do nerves sustain injury?
The nerve is said to sustain injury when the cells (neurons) that make up its units are damaged. The damage can result from too much pressure, stretching, or a cut.
What are the mechanisms of nerve injury?
Some of the major mechanisms behind nerve injury are discussed below. Mechanical injury resulting from a tourniquet or other causes of external pressure can lead to nerve compression and therefore injury.
What is nerve injury?
Nerve Injury (Neuropraxia, Axonotmesis, Neurotmesis) and Healing. Acute nerve injuries are very common and may be associated with different types of trauma. Injury to the peripheral nerve (nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord) may result from blunt force, fractures, crush injuries, stretch, penetrating or cut injuries.
What is a partial cut of the axon?
Partial or complete severance (cut) of the axons and the sheath is referred to as neurotmesis. It is the most severe form of nerve injury. However, a clean cut has scope for immediate repair and faster recovery.
What is the least severe type of nerve injury?
Neuropraxia is the least severe type of nerve injury. It results in complete block of nerve transmission despite intact nerve fibers. Neither the axon nor the sheath are cut. Sudden stretching of nerves in fractures and dislocations can lead to neuropraxia.
What is the difference between sensory and motor nerve injury?
Motor nerve injury affect motor function (muscle movement) while sensory nerve injury results in impairment of the senses. The muscular function impairment may be in the form of weakness or paralysis. The sensory impairment can present as loss of sensations, abnormal sensations (parasthesias) or pain. The symptoms of nerve injury also depend on the ...
What is nerve repair?
The nerve repair process involves degeneration of the nerve followed by regeneration. The degeneration of nerve is called Wallerian degeneration. The process involves phagocytosis of the damaged segment of the nerve beyond the site of nerve injury.
What is sensory impairment?
The sensory impairment can present as loss of sensations, abnormal sensations (parasthesias) or pain. The symptoms of nerve injury also depend on the nerve injured and the site of nerve injury. In many patients the injury may not present with such specific or clear signs and symptoms.
What is neurotmesis in neurology?
Neurotmesis is part of Seddon's classification scheme used to classify nerve damage. It is the most serious nerve injury in the scheme. In this type of injury, both the nerve and the nerve sheath are disrupted. While partial recovery may occur, complete recovery is impossible. With Seddon's classification of nerve injuries it is often tough to identify whether a particular nerve injury is neurotmesis, or axonotmesis, which has damage to the nerve fibres but preservation of the nerve trunk. Due to the damage involved in both of these conditions they will both show paralysis of muscles that are supplied by nerves below the site of the lesion, and will have sensory deficits in accordance with the individual nerves that are damaged. The only way to know for sure if a nerve injury is in fact neurotmesis is to allow for the normal progression of nerve regeneration to take place and if after that time there is still resound muscle paralysis and degeneration in these areas then it is likely to have been a neurotmesis injury.
What is the numerical value of neurotmesis in Chaldean numerology?
The numerical value of neurotmesis in Chaldean Numerology is: 9