What are amniotes?
Amniotes are a group of higher vertebrates who have an extra-embryonic membrane called amnion during the embryonic stage. This group includes animals such as reptiles, birds, and mammals.
What is the difference between amniotes and vertebrates?
While amniotes share a number of other characteristics in general (being vertebrates, tetrapods, etc.), they all developed from a common ancestor which developed the amnion character. The amnion is seen within egg-laying species, such as birds and reptiles, as well as in mammals.
What is the amnion in vertebrates?
Amniotes are vertebrate organisms which have a fetal tissue known as the amnion. The amnion is a membrane derived from fetal tissue which surrounds and protects the fetus. The amnion can be found within the egg, as in lizards and birds, or the amnion can simply enclose the fetus within the uterus.
What are amniote embryos and how are they protected?
Amniote embryos, whether laid as eggs or carried by the female, are protected and aided by several extensive membranes. In eutherian mammals (such as humans), these membranes include the amniotic sac that surrounds the fetus.
What is not an Amniote?
Answer and Explanation: The animal that is NOT an amniote is A) bullfrog. Amniotes are vertebrates that are within an amnion during embryonic or fetal development. Mammals (e.g. humans), reptiles (e.g. coral snake), and birds (e.g. bald eagle) are amniotes.
What is an Amniote?
Definition of amniote : any of a group (Amniota) of vertebrates that undergo embryonic or fetal development within an amnion and include the birds, reptiles, and mammals.
What organisms are amniotes?
The amniotes—reptiles, birds, and mammals—are distinguished from amphibians by their terrestrially adapted egg, which is protected by amniotic membranes.
What makes an animal an Amniote?
Amniotes contain reptiles (including birds) and mammals. While most mammals do not lay eggs (except for monotremes like the platypus), they are still amniotes because their embryo is still covered by an amnion.
Which animals are not amniotes?
The anamniotes are an informal group comprising the fishes and the amphibians which lay their eggs in water. They are distinguished from the amniotes (reptiles, birds and mammals), which lay their eggs on land or retain the fertilized egg within the mother.
What does non amniotic egg mean?
Birds, reptiles, and mammals have amniotic eggs. Because amphibian eggs don't have an amnion, the eggs would dry out if they were laid on the land, so amphibians lay their eggs in water. The larvae of most amphibians have gills and look like fish when they are born.
What are amniotes give four examples?
Amniota, a group of limbed vertebrates that includes all living reptiles (class Reptilia), birds (class Aves), mammals (class Mammalia), and their extinct relatives and ancestors.
Is a dog an amniote?
Reptiles, birds, and mammals are all amniotes.
Is Elephant a amniote?
Elephants do not have amniotic eggs. An example of an amniotic egg is a chicken egg. Elephants are placental mammals, which means their young grow inside of the mother and are fed through a placenta that is attached to her body.
Are humans Amniote?
Identify characteristics of amniotes In eutherian mammals (such as humans), these membranes include the amniotic sac that surrounds the fetus. These embryonic membranes and the lack of a larval stage distinguish amniotes from tetrapod amphibians.
Do all mammals have amnion?
The amnion is a feature of the vertebrate clade Amniota, which includes reptiles, birds, and mammals. Amphibians and fish are not amniotes and thus lack the amnion. The amnion stems from the extra-embryonic somatic mesoderm on the outer side and the extra-embryonic ectoderm or trophoblast on the inner side.
Do all amniotes lay eggs?
Because reptiles, birds, and mammals all have amniotic eggs, they are called amniotes. The duck-billed platypus and some other mammals also lay eggs. But most mammals have evolved amniotic eggs that develop inside the mother's womb, or uterus, and so lack a shell.
What is amnion in biology?
amnion, in reptiles, birds, and mammals, a membrane forming a fluid-filled cavity (the amniotic sac) that encloses the embryo. The amniotic sac and the fluid it contains are sometimes referred to as the bag of waters.
Is a human an amniote?
Identify characteristics of amniotes In eutherian mammals (such as humans), these membranes include the amniotic sac that surrounds the fetus. These embryonic membranes and the lack of a larval stage distinguish amniotes from tetrapod amphibians.
What are amniotes give four examples of them?
Examples of amniotes are reptiles, birds, and mammals. The reptiles and birds lay eggs on land where the latter hatch in time....AmnioteKingdom: Animalia.Phylum: Chordata.Superclass: Tetrapoda.Clade: Reptiliomorpha.Clade: Amniota 1866.
Do all amniotes lay eggs?
Because reptiles, birds, and mammals all have amniotic eggs, they are called amniotes. The duck-billed platypus and some other mammals also lay eggs. But most mammals have evolved amniotic eggs that develop inside the mother's womb, or uterus, and so lack a shell.
What are Amniotes?
Amniotes are a group of higher vertebrates who have an extra-embryonic membrane called amnion during the embryonic stage. This group includes animals such as reptiles, birds, and mammals. They are tetrapods, meaning they have four limbs. Amniotes do not lay eggs in water instead they lay eggs on lands or they keep fertilized eggs within the mother organism.
What is the difference between anamniotes and amniotes?
The key difference between Amniotes and Anamniotes is that Amniotes are higher vertebrates including reptiles, birds, and mammals while anamniotes are lower vertebrates including fishes and amphibians. Classification is the systematic grouping of organisms based on their morphological, structural, ...
What is the characteristic feature that is used to separate higher vertebrates from lower vertebrates?
Figure 01: Amniotes. The presence of the amnion is the characteristic feature that is used to separate higher vertebrates from lower vertebrates. The group Amniota was first introduced by Ernst Haeckel in 1866.
What are the two groups of animals that are considered anamniotes?
Anamniotes are lower vertebrates. Included Animal Groups. Amniotes include reptiles, birds and mammals. Anamniotes include fishes and amphibians. Presence of Gills. Amniotes do not bear gills. Anamniotes have gills during their lifetime. Presence of Amnion during the Embryonic stage.
Do anamniotes need water?
Amniotes are not needed to go to water for reproduction. Anamniotes are required to go to water for reproduction. Laying Eggs. Amniotes lay eggs on land or keep the fertilized egg within the mother body. Anamniotes lay eggs in water.
Do anamniotes have amnion?
Anamniotes are a group of lower vertebrates who do not have an amnion during their embryonic stage. Anamniotes depend on water for reproduction. They lay eggs in water. Figure 02: Anamniotes. Moreover, they possess a permeable skin that is used to diffuse water and gasses.
What are the characteristics of amniotes?
Features of amniotes evolved for survival on land include a sturdy but porous leathery or hard eggshell and an allantois that facilitates respiration while providing a reservoir for disposal of wastes. Their kidneys and large intestines are also well-suited to water retention.
Where does the term "amniote" come from?
The term amniote comes from the Greek ἀμνίον amnion, "membrane surrounding the fetus", and earlier "bowl in which the blood of sacrificed animals was caught", from ἀμνός amnos, "lamb". The amnion comprises several extensive membranes.
Why are amniotes unique?
The unique embryonic features of amniotes may reflect specializations for eggs to survive drier environments; or the increase in size and yolk content of eggs may have permitted, and coevolved with , direct development of the embryo to a large size .
Why is the amnion important?
The amnion is a critical divergence within vertebrates that allows the embryos to survive out of the water. This enabled amniotes to reproduce on land and so move into drier environments—free of the need to return to water for reproduction as amphibians.
What is the next major breakthrough in the amniote ancestry?
After internal fertilization and the habit of laying eggs in terrestrial environments became a reproduction strategy amongst the amniote ancestors, the next major breakthrough appears to have involved a gradual replacement of the gelatinous coating covering the amphibian egg with a fibrous shell membrane.
When did the first amniotes evolve?
The first amniotes, referred to as "basal amniotes", resembled small lizards and evolved from the amphibian reptiliomorphs about 312 million years ago , in the Carboniferous geologic period.
Who first described the amniota?
Definition and classification. Amniota was first formally described by the embryologist Ernst Haeckel in 1866 on the presence of the amnion, hence the name. A problem with this definition is that the trait ( apomorphy) in question does not fossilize, and the status of fossil forms has to be inferred from other traits.
What is an amniote?
: any of a group (Amniota) of vertebrates that undergo embryonic or fetal development within an amnion and include the birds, reptiles, and mammals. Other Words from amniote Example Sentences Learn More About amniote. Keep scrolling for more.
What are some examples of amniotes?
Examples of amniote in a Sentence. Recent Examples on the Web This new kind of animal, that Dawson would name Hylonomus lyelli, remains the earliest amniote in the fossil record. — Hillary Maddin, Smithsonian, 18 July 2019.
What are the two main groups of amniotes?
Sauropsid Amniotes. There are two main divisions of amniotes, the sauropsid amniotes and the synapsid amniotes. The sauropsid amniotes include the reptiles and birds. Formally, this constitutes many different groups, but the sauropsid amniotes share many derived characteristics which separate them from the synapsids.
Where are amniotes found?
The amnion is a membrane derived from fetal tissue which surrounds and protects the fetus. The amnion can be found within the egg, as in lizards and birds, or the amnion can simply enclose the fetus within the uterus.
What is the synapsid amniote?
Synapsid Amniotes. The synapsid amniotes do things slightly different, since they separated from the sauropsids millions of years ago. The synapsid strategy for expelling waste, for instance, is typically all urea. Urea can be concentrated in the synapsid kidney, and excreted with small bits of water.
What is the difference between anamniotes and fish?
Amniotes include most of the vertebrates, excluding fish and amphibians. Fish and amphibians are anamniotes, meaning “without an amnion”. The eggs of these species are often laid in water, which protects them from being damaged or squished. Most amniotes, by contrast, are terrestrial and require the amnion to protect the developing fetus under ...
What is the role of placental mammals in the synapsid amniote?
These animals use a placenta, or oxygen and nutrient passing maternal membrane, to feed and nourish offspring within the womb. At birth, offspring of these animals are the largest of all amniotes comparatively.
What are the three membranes of an amniote?
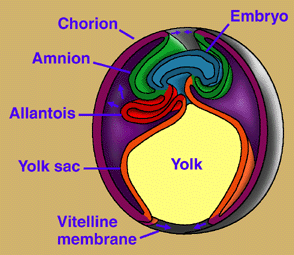
All amniotes have three membranes surrounding the fetus of one offspring. These membranes are the amnion, or protective layer, the top chorion layer, and the waste-absorbing allantois. These layers can be seen in the image of a chicken egg, below.
When did the amniotes emerge?
This likely occurred in the Devonian period, around 400 million years ago.
What are the names of amniotes?
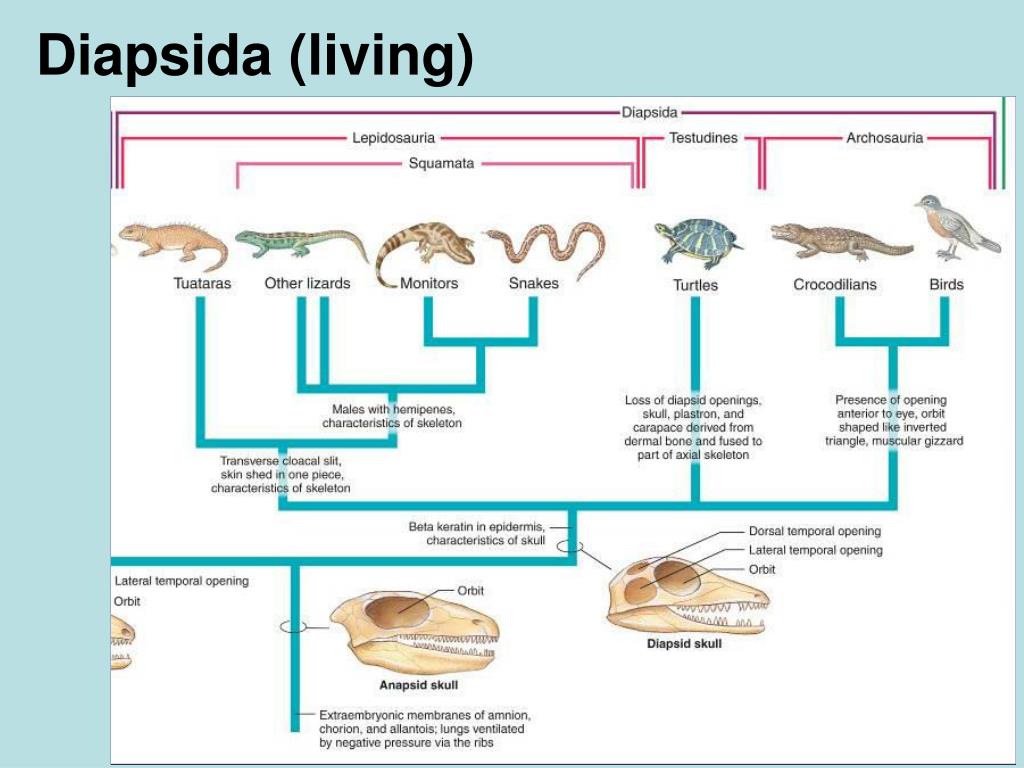
For much of the past century, the classification of amniotes closely reflected fenestration; and hence Anapsida, Diapsida, Euryapsida, and Synapsida were used as formal names for amniote radiations. More recently, however, we have realized that while the pattern of fenestration does broadly reflect amniote evolution, it is not tied as strictly to phylogeny as was once presumed. At least two of these groups, Diapsida (includes archosauromorphs and lepidosauromorphs) and Synapsida (includes mammals), are still considered monophyletic, but for the former we recognize that at least the earliest basal members of the clade had anapsid skulls.
How are amniotes named?
The Amniota derives its name from the amniotic egg, a synapomorphy shared by all members ( Fig. 1.12 and Fig. 1.13). Other stem amniotes may have had amniotic eggs, although they are not classified as amniotes. A fossil taxon cannot be identified as an amniote or anamniote by structure of its egg, because few fossil eggs of anthracosaurs have been found. Further, no eggs have been found in association with an adult’s skeleton or with a fossil embryo showing extra-embryonic membranes. Bony traits must be used to determine which taxa are amniotes and which ones are not, and there is no unanimity in which bony traits define an amniote. Indeed, amniotes are commonly defined by content; for example, Amniota comprise the most recent common ancestor of mammals and reptiles and all of its descendants.
What is the temporal region of an amniote skull?
Amniote Skulls and Classification. Amniotes have long been subdivided on the condition of the temporal region of the skull, that portion posterior to the orbit. This region can either be solid or have openings, termed temporal fenestrae (from the Latin, fenestra, window).
How is an amniote diagnosed?
Amniota is diagnosed by a suite of characters, including presence of an amniote egg (see below), caniniform teeth, two or more vertebrae in contact with the pelvic girdle, internal fertilization, and keratin (a protein that acts as the building block for scales, nails, hooves, hair, and feathers).
What are bony traits?
Bony traits must be used to determine which taxa are amniotes and which ones are not, and there is no unanimity in which bony traits define an amniote. Indeed, amniotes are commonly defined by content; for example, Amniota comprise the most recent common ancestor of mammals and reptiles and all of its descendants.
What is the most recent common ancestor of Reptilia and Mammalia?
Amniota is defined as the most recent common ancestor of Reptilia and Mammalia, and all of that ancestor's descendants. Amniota is diagnosed by a suite of characters, including presence of an amniote egg (see below), caniniform teeth, two or more vertebrae in contact with the pelvic girdle, internal fertilization, and keratin (a protein that acts as the building block for scales, nails, hooves, hair, and feathers). The amniote egg includes a series of extraembryonic membranes that surround the developing embryo and provide all the nutritional, waste disposal, and gas exchange requirements during development. In reptiles (including birds) and the Monotremata (basal mammals), the embryo and extraembryonic membranes are encapsulated in an egg with either a leathery exterior or a hard shell. Because this is a self-contained fluid-filled system, eggs can be laid away from water. Although fishes, amphibians, and most reptiles are often referred to as “cold-blooded,” many species in these groups manage to maintain elevated body temperature at a constant level. This is achieved by shuttling between heat sources and heat sinks (ectothermy). However, birds and mammals generally maintain a constant temperature by changing the basal metabolic rate (endothermy). There is substantial evidence suggesting that some of the fossil reptiles did maintain body temperatures above the level of the environment. There has been much argument about the question of whether the mechanism by which this was achieved was ectothermy or endothermy. The earliest known members of the Amniota appear in the fossil record during the Pennsylvanian period.
What are the stages of amniote neurulation?
Amniote neurulation occurs in at least four stages: (i) the acquisition of a neural fate , (ii) the elevation of the neural folds , (iii) the bending of the neural plate, and (iv) the meeting of the neural folds at the midline and fusion that forms the closed neural tube (Figure 27.2 ).

About Amniota
Description
Adaptation For Terrestrial Living
The Egg Membranes
Amniote Traits
Traditional Classification
The Eggs of Amniotes
Non-Amniotic Egg
- The amniotic egg contains numerous distinct structures. At the egg's innermost part, the embryo is suspended by the amniotic fluid that is surrounded by a membrane known as the amnion. The allantois deals with the waste and gas exchange and also, together with the nutritious egg yolk, connects to and partially surrounds the embryo. The chorion surr...
Did You Know?
Conclusion