Common Causes
Red flags associated with otalgia include[4]:
- Dysphagia, odynophagia, dysphonia, or hemoptysis
- Loss of vision or black spots
- Unintended weight loss
Related Conditions
The best products for ear pain
- EarPlanes. EarPlanes brand earplugs are a common sight among frequent flyers for preventing ear pain before it starts.
- PUR Chewing Gum. This is a classic technique for travelers: chewing gum. ...
- YumEarth Organic Lollipops. For those looking for a tasty and helpful tool when alleviating ear pain, turn to a childhood treat.
Which conditions are associated with otalgia?
The 3 most common ear diseases
- Otitis. Otitis is a bacterial or viral infection that can affect both the middle ear and the outer ear. ...
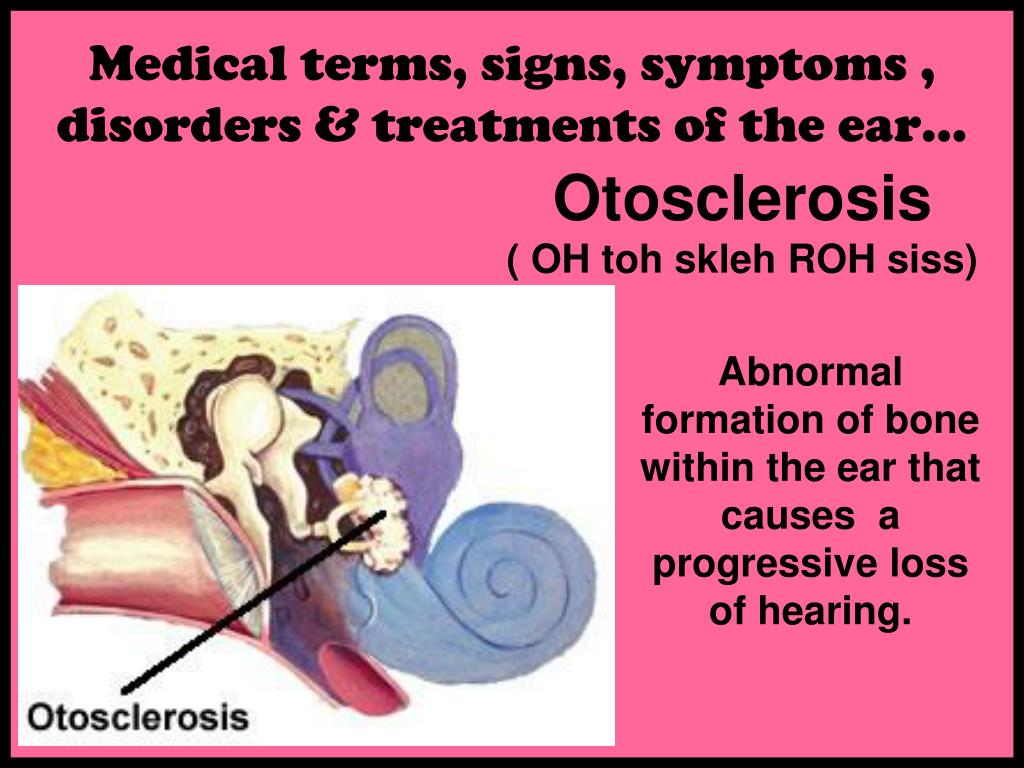
- Otosclerosis. This is a disease that affects young adults, and is one of the main causes of hearing loss within this age group.
- Ménière’s disease. The last pathology on our list of the most common ear diseases is Ménière’s disease. ...
How to relieve ear pain?
TMJ-related ear pain is most often felt in front of or below the ear. With ear infections, the pain is often inside the ear. If the pain sharpens when you move your mouth, this may also indicate a TMJ disorder is resulting in ear pain. Also, check for the TMJ disorder symptoms below, or see our TMJ disorder symptoms page.
What is the most common ear disease?
Is there actually a link between TMJ and ear pain?

What is the most common cause of otalgia?
Pain that originates from the ear is called primary otalgia, and the most common causes are otitis media and otitis externa. Examination of the ear usually reveals abnormal findings in patients with primary otalgia.
How do you treat otalgia?
Once determined, most causes of referred otalgia can be readily treated. Use antibiotics in treating various types of infections (eg, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis). Use antivirals if the causative agent is suspected to be viral, such as in cases associated with herpes zoster or shingles.
What are the symptoms of otalgia?
The most common of these signs and symptoms are ear fullness sensation, tinnitus, ear pain and vertigo with nystagmus. The group of all these muscle, articular and ear alterations was called Costen's Syndrome(10).
What does the term otalgia mean?
Otalgia is defined as ear pain. Two separate and distinct types of otalgia exist. Pain that originates within the ear is primary otalgia; pain that originates outside the ear is referred otalgia. [1, 2] Typical sources of primary otalgia are external otitis, otitis media, mastoiditis, and auricular infections.
Why do I have ear pain but no infection?
Earaches can happen without an infection. This can occur when air and fluid build up behind the eardrum, causing pain and reduced hearing. This is called serous otitis media. It means fluid in the middle ear.
How should I sleep with ear pain?
Sleep position Rest with your head on two or more pillows, so your affected ear is higher than the rest of your body. Or if your left ear has an infection, sleep on your right side. Less pressure equals less ear pain. It could be effective, though a few inches may not make a big difference in pressure measurement.
Does otalgia cause hearing loss?
Primary otalgia is frequently accompanied by hearing loss and otorrhea. The combination of these symptoms may indicate common self-limited disease such as otitis media or externa.
Is otalgia a diagnosis?
Otalgia is the sensation of pain in the ear, while referred otalgia is pain felt in the ear but originating from a nonotologic source. Ear pain is a diagnostic problem when examination of the ear shows no pathology. Pain in the ear can be caused by inflammation of the external meatus or the middle ear.
Can stress cause ear pain?
Stress and ear pressure Ears pop because of the difference in the air pressure in your middle ear and the air pressure outside. As stress heightens and persists, so can the ear popping and pressure symptoms.
What is the type of otalgia?
Otalgia can be classified into 2 types. Otogenic otalgia originates from diseases of the external, middle and inner ear, whereas referred otalgia arises from pathologies outside the ear [4,5].
What is otalgia of both ears?
Otalgia is the medical word for ear ache or ear pain. It may be burning, stabbing, dull, sharp, sore, full, or clogged.
Can a pinched nerve cause an earache?
What is Geniculate Neuralgia? Geniculate neuralgia is a condition that is caused by a small nerve (the nervus intermedius) being compressed by a blood vessel. Geniculate neuralgia results in severe, deep ear pain which is usually sharp—often described as an "ice pick in the ear"—but may also be dull and burning.
What is the type of otalgia?
Otalgia can be classified into 2 types. Otogenic otalgia originates from diseases of the external, middle and inner ear, whereas referred otalgia arises from pathologies outside the ear [4,5].
Which drops is best for ear infection?
Ciprofloxacin and dexamethasone combination ear drops is used to treat ear infections, such as acute otitis externa and acute otitis media.
What is the first line treatment for otitis media?
Most patients can be treated effectively with an analgesic such as a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medication or acetaminophen. Choice of initial antibiotic — Our choice for first-line therapy is amoxicillin-clavulanate. In most adults, the dose is amoxicillin 875 mg with clavulanate 125 mg orally twice daily.
Why does the cartilage in my ear hurt when I sleep?
It's most likely down to sleeping on the same side for too long, on a pillow that's too firm. The ear cartilage gets a constant pressure or gets folded against the pillow and this irritates the pain receptors.
What is the condition that causes otalgia?
Patients with abnormal vital signs who present initially with otalgia may have a serious infection, such as meningitis or sepsis, or serious traumatic injury, such as epidural hematoma. Patients with ear pain and abnormal mental status must be evaluated for traumatic injury, epidural infection, and osteomyelitis 37).
What are the symptoms of otalgia?
Symptoms such as ear discharge (otorrhea), tympanic membrane fullness, and vertigo suggest primary otalgia 30), whereas pain with chewing, sinusitis, dental procedures, and a history of gastroesophageal reflux suggest referred ear pain (secondary otalgia) 31). In adults, the absence of hearing loss is a cardinal finding associated with non-ear disease 32). The character of pain also provides important clues. Pain that is continuous and progressively worsens is more likely to be associated with infection and primary otalgia. Intermittent pain is likely to be associated with referred ear pain (secondary otalgia) 33).
What nerves are involved in ear pain?
The complex embryologic development of the ear results in neural connections to several cranial and cervical nerves. These nerves provide sensory innervation to regions of the head, neck, chest, and abdomen, which can result in referred pain to the ear (Figure 2 and Table 2) 18). Referred ear pain from the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) is the most common source of secondary otalgia stemming from temporomandibular joint syndrome, dental infections, trigeminal neuralgia, sinusitis, and mandibular osteomyelitis or tumor 19). Herpes zoster can affect cranial nerve VII to a lesser degree than in Ramsay Hunt syndrome, which can also cause ear pain associated with Bell palsy and an unremarkable ear examination 20). Cranial nerve IX can refer pain caused by tonsillitis, pharyngitis, pharyngeal tumor, or glossopharyngeal neuromas 21). The vagus nerve affects many systems as inferior as the colon and can be activated by any vagal stimulation. Otalgia has been reported as the presenting symptom of myocardial ischemia from irritation of the vagus nerve 22).
What is the difference between primary and secondary otalgia?
Pain that originates from the ear is known as primary otalgia, whereas pain that originates outside the ear is secondary otalgia (referred ear pain) 1) . A comprehensive history and physical examination are essential to determine the cause of primary otalgia or secondary otalgia (referred ear pain).
What is the term for ear pain?
Otalgia. Otalgia is a medical term for an ear pain that can be a sharp, dull, or burning pain in one or both ears. Otalgia may last a short time or be ongoing. Otalgia is a common complaint, especially in children and is generally caused by a middle ear infection (otitis media). Ear pain in adults is less likely to be from an ear infection.
Why does my ear hurt?
External ear pain can be due to several factors , including trauma, sunburn, acute folliculitis, contact dermatitis, shingles, and other skin conditions. When trauma is suspected, the temporal and parietal regions of the skull should be assessed and appropriate imaging ordered. Disorders of the external auditory canal that may cause pain include cerumen impaction, foreign bodies, and, most commonly, infection of the canal.
What is the pain in the ear called?
Pain that originates from the ear is called primary otalgia, and the most common causes are otitis media and otitis externa. Examination of the ear usually reveals abnormal findings in patients with primary otalgia.
What is secondary otalgia?
Secondary or referred otalgia occurs as a result of the complex cranial nerve network that innervates the ear. These cranial nerves have a shared connection between the ear and organs outside of the ear. One theoretical mechanism of referred otalgia is the convergence-projection theory, which states that these nerves converge onto a shared neural pathway.[9] Given the extent of different organs that share innervation pathways with the ear, secondary otalgia can arise from many different organs.
What is the difference between otalgia and ear pain?
Otalgia (ear pain) divides into two broad categories: primary and secondary otalgia. Primary otalgia is ear pain that arises directly from pathology within the inner, middle, or external ear. Secondary or referred otalgia is ear pain that occurs from pathology located outside the ear. A complex neural network innervates the ear as a result of complex embryologic development. The ear shares this neural network with other organs, which leads to numerous potential causes of referred ear pain.[1]
What causes otitis media in children?
Primary otalgia occurs most commonly from infection. Acute otitis media (AOM) ranks as the number one cause of primary otalgia in children. The disease is typically associated with an upper respiratory tract infection that causes congestion and swelling of the eustachian tube. Between the middle ear and the eustachian tube, there is a narrowing of the eustachian tube called the bony-cartilaginous junction or isthmus. The swelling of the eustachian tube at this location can prevent the middle ear drainage. This collection of middle ear secretions can initially generate an effusion, leading to obstruction and potential bacterial growth.[12] In adults, chronic otitis media is the most common primary disease. Its pathophysiology is the same as AOM and can result from upper respiratory infections or allergic rhinitis. Infections can also directly affect the auricle or ear canal in perichondritis or otitis externa, respectively. If the infection spreads to adjacent bone, it can cause petrous apicitis, mastoiditis, or malignant otitis externa.
What causes otalgia in women?
While primary causes tend to be more common, two studies stated that secondary causes account for nearly 50% of cases of otalgia. [1][9]Adults and women with otalgia are more likely to have a secondary cause. [5][3][4][6]While the literature is inconsistent, temporomandibular, and dental pathology tends to get cited as the most common causes of secondary otalgia. [1][4][6]While dental pathology tends to get cited as the most common cause, one article published in Ireland mentioned that mechanical disorders of the neck and jaw were much more common.[10] Patients over 65 years of age are more likely to experience otalgia from cervical spine disease.[2] Women 20 to 40 years old are more likely to experience temporomandibular joint disease.[11] Malignancies or distant secondary causes such as thyroid cardiac, gastrointestinal, or lung pathology are rare. Other secondary etiologies, such as petrous apicitis, malignant otitis externa, and Eagle syndrome, are also uncommon.
Where is the otalgia point located?
Of note, 1 case series noted "the otalgia point," located at the apex of the jugulodigastric region. The case series included 32 patients who pointed to this location, who also had normal physical examinations, tympanogram, and age-appropriate audiograms. This point was found to correlate more with symptom relief after either myringotomy or nasal steroid usage. [14]
Why does my ear feel full?
Ear fullness rather than ear pain may be more associated with cholesteatomas.
Is otalgia a pain?
Otalgia is ear pain and breaks down into two categories of primary otalgia and secondary otalgia. Primary otalgia is pain coming directly from the ear where secondary otalgia is referred pain from somewhere outside the ear. This activity reviews the broad differential diagnosis and workup for both types of otalgia and highlights the role of the interprofessional workforce in treating otalgia.
What is the difference between primary and secondary otalgia?
Secondary or referred otalgia is ear pain that occurs from pathology located outside the ear. A complex neur …
Which nerve innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, sublingual, and submandib?
Cranial nerve VII (facial) innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, sublingual, and submandibular salivary glands. It also innervates the muscles of facial expression.
Which nerves innervate the ear?
Cranial nerves V (trigeminal), VII (facial), IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), and branches from the cervical plexus (C2 and C3) all innervate the ear.
Which nerve innervates the tympanic membrane?
The tympanic membrane is innervated by cranial nerves VII, IX, and X.
How to treat referred otalgia?
Once determined, most causes of referred otalgia can be readily treated. Use antibiotics in treating various types of infections ( eg, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis). Use antivirals if the causative agent is suspected to be viral , such as in cases associated with herpes zoster or shingles.
What is the pain in the ear called?
Pain that originates within the ear is primary otalgia; pain that originates outside the ear is referred otalgia. [ 1, 2] Typical sources of primary otalgia are external otitis, otitis media, mastoiditis, and auricular infections. Most physicians are well trained in the diagnosis of these conditions.
What is aural fullness secondary to Eustachian tube dysfunction?
In the absence of obvious fluid within the middle ear, aural fullness secondary to Eustachian tube dysfunction may manifest with a practically imperceptible bulging or retraction of the tympanic membrane. If autoinsufflation is not effective in relieving this pressure, consider a diagnostic myringotomy.
What is aural fullness?
The perception of aural fullness may be described as ear pain and is observed in conditions associated with endolymphatic hydrops and Eustachian tube dysfunction. [ 3]
Is otalgia more common in women than in children?
In a Korean study of 294 patients with otalgia, the prevalence of primary otalgia was found to be higher in children than in adults and in men than in women, while referred otalgia was more likely to occur in adults in general and in women in particular. The study, by Kim et al, also found that neuralgia occurred more frequently in women than in men with referred otalgia. [ 5]
Is otalgia a dental origin?
Frequently, the workup suggests that otalgia may be a problem of dental origin.
Can otalgia cause ear pain?
Referred o talgia is a topic unto itself. Although many entities can cause referred otalgia, their relationship to ear pain must be identified. A categorical discussion of the workup, treatment, prognosis, demographics, and other issues is impossible because the various pathologies responsible for creating referred otalgia are so diverse.
