Percutaneous Approach. A procedure performed via a percutaneous approach (character value 3) is one in which there is entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure.
What is the difference between open approach and percutaneous?
Percutaneous endoscopic-assisted procedures are coded to the open approach as stated above. Percutaneous approach is entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and/or any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure.
What are percutaneous techniques?
In surgery, a percutaneous procedure is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using an "open" approach where inner organs or tissue are exposed (typically with the use of a scalpel).
What does percutaneous mean in ICD-10-PCS?
Percutaneous Endoscopic Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the. skin or mucous membrane and/or any other body layers necessary. to reach and visualize the site of the procedure. Via Natural or Artificial. Opening.
Is laparoscopic considered percutaneous or percutaneous endoscopic?
Percutaneous Endoscopic Approach The access location for this approach is the skin or mucous membrane with visualization instrumentation being used to reach the operative site. Laparoscopy with ablation of endometriosis of the endometrium is performed via a percutaneous endoscopic approach.
What is an example of a percutaneous?
Percutaneous: Through the skin. For example, a percutaneous biopsy is a biopsy that is obtained by putting a needle through the skin in order to obtain tissue within the body for examination.
What is the importance of percutaneous approach in surgery?
Percutaneous drainage represents an efficient and safe alternative to open surgical drainage. When it is not curative, percutaneous treatment may allow the stabilization of the patient until the curative intervention.
Is a catheter percutaneous?
A percutaneous nephrostomy is the placement of a small, flexible rubber tube (catheter) through your skin into your kidney to drain your urine. It is inserted through your back or flank.
Is a burr hole open or percutaneous?
The term “burr hole” is almost always indicative of a percutaneous procedure. However, in some cases, the surgeon will make multiple burr holes and then remove the skull bone that is between the burr holes (like in a triangle) to get down to the operative site of the brain.
Is Thoracostomy open or percutaneous?
Chest tube placement CPT code (thoracostomy) Open procedures. There is only one revised code in this Procedure. CPT code 32551 is earlier used for percutaneous procedure for chest tube placement. But, with the new updates this codes has been revised and now it should be used only for open procedure.
What is the difference between endoscopic and percutaneous?
Endoscopic approaches are a subset of percutaneous approaches that use one or more small puncture sites and a thin video instrument with a small camera at the tip.
What is a percutaneous endoscopic procedure?
What is a PEG? PEG stands for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, a procedure in which a flexible feeding tube is placed through the abdominal wall and into the stomach. PEG allows nutrition, fluids and/or medications to be put directly into the stomach, bypassing the mouth and esophagus.
What is meant by percutaneous implant?
INTRODUCTION. Our definition of a percutaneous implant is an object foreign to the body placed through the skin such that a permanent defect is created.
Which are examples of percutaneous medications?
Percutaneous (medications are absorbed directly through the skin into the bloodstream. Some birth control pills and hormone replacements are administered by patches that are absorbed slowly and evenly through the skin, for example.)
What does percutaneous mean in medical terms?
Passing through the skin(per-kyoo-TAY-nee-us) Passing through the skin, as an injection or a topical medicine.
What are percutaneous devices?
A percutaneous device (PD) constitutes a foreign material penetrating through the skin. It provides a connection between an internal organ or cavity and an extracorporeal device. PDs serving a multitude of clinical and research purposes are described.
What is the difference between percutaneous and subcutaneous?
Subcutaneous refers to being below the skin (as in a penetrating injury, injection or intravenous line). Percutaneous refers to being passed, done or effected through the skin. For example, some materials pass through exposed skin, causing poisoning.
What is endoscopic approach?
Endoscopic approaches are a subset of percutaneous approaches that use one or more small puncture sites and a thin video instrument with a small camera at the tip. This scope transmits a picture of the internal organs on a video monitor to give the surgeon a close-up view of the surgical area as he performs the procedure.
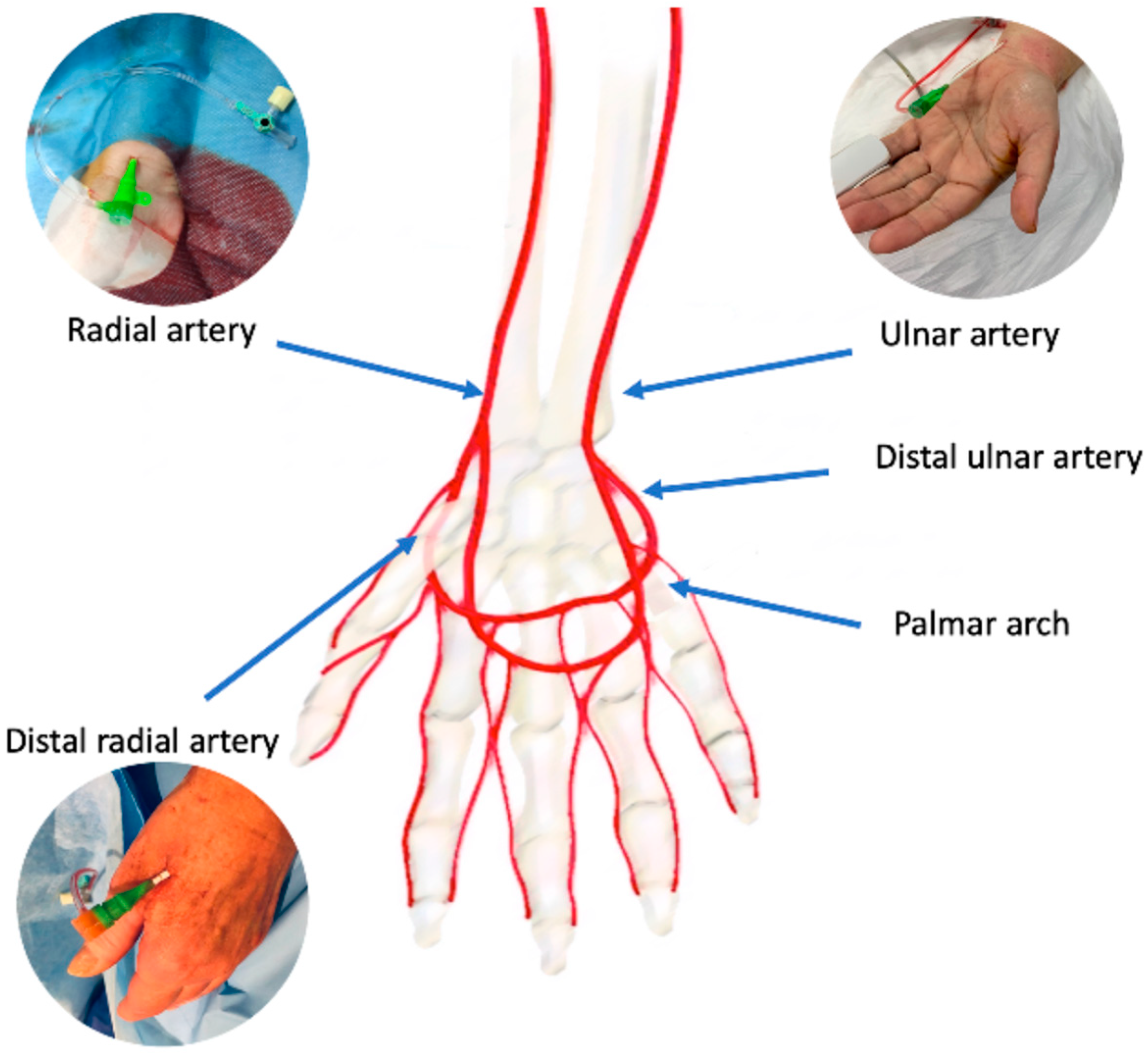
What is percutaneous approach?
Instead of the large incision required for traditional heart or vascular surgery, percutaneous approaches use special catheters and devices to treat the problem through one or more small puncture sites through the skin.
What is endoscopic lead placement?
Endoscopic lead placement for defibrillator or pacemaker devices. Endoscopic radial artery and saphenous vein harvesting for bypass surgery. Learn more about minimally invasive thoracic and cardiovascular surgery.
Is percutaneous surgery considered non-surgical?
As cardiologists and heart surgeons search for new techniques to treat heart and vascular disease in less invasive ways, many new percutaneous (also called endovascular) procedures are evolving that will provide non-surg ical treatment options for patients in the future.
Overview
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (nef-roe-lih-THOT-uh-me) is a procedure used to remove kidney stones from the body when they can't pass on their own. A scope is inserted through a small incision in your back to remove the kidney stones.
Why it's done
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is typically recommended in the following situations:
Risks
The most common risks from percutaneous nephrolithotomy include the following:
How you prepare
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is usually performed in the hospital under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep during the procedure and not feel any pain.
What you can expect
Before the procedure, your surgeon may have you go to the radiology department, where a radiologist will use CT, ultrasound or X-ray imaging to guide access to the kidney. This is done with a local anesthetic, meaning you will be awake but will not feel any pain. You will then be transferred to the operating room for the actual procedure.
Results
Your doctor probably will want to see you again after four to six weeks. At that visit, your doctor may use ultrasound or X-rays to check for any stones that may be left and to make sure that urine is draining normally from the kidney.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
