
Periosteal reactions are caused by trauma to the outer layer of bone (periosteum) and are associated with systemic infection and inflammation. To obtain the cross-sectional cortical bone region, a periosteal contour was first segmented by delineating mineralized bone and extra-osseal soft tissue. Medical browser ? Full browser ?
What is a periosteal reaction in a fracture?
Periosteal reaction. Periosteal reaction on a healing supracondylar fracture. Specialty. Orthopedics. A periosteal reaction is the formation of new bone in response to injury or other stimuli of the periosteum surrounding the bone. It is most often identified on X-ray films of the bones.
What is a periosteal reaction Quizlet?
Periosteal reaction. Jump to navigation Jump to search. A periosteal reaction is the formation of new bone in response to injury or other stimuli of the periosteum surrounding the bone.
What is aggressive periosteal reaction?
Aggressive periosteal reaction is likely the result of disorganized new bone in response to a destructive process. New bone formation cannot keep pace with the accelerated rate of bone destruction. In response to a rapidly destructive process, new bone formation along the periosteum produces several characteristic patterns.
What is the meaning of periosteal?
per·i·os·te·al re·ac·tion radiographically detectable new subperiosteal bone formed as a reaction to soft tissue or osseous disease. pertaining to or emanating from the periosteum. a stage in the development of bone to replace existing cartilage; periosteal bud formation results in the removal of calcified cartilage.
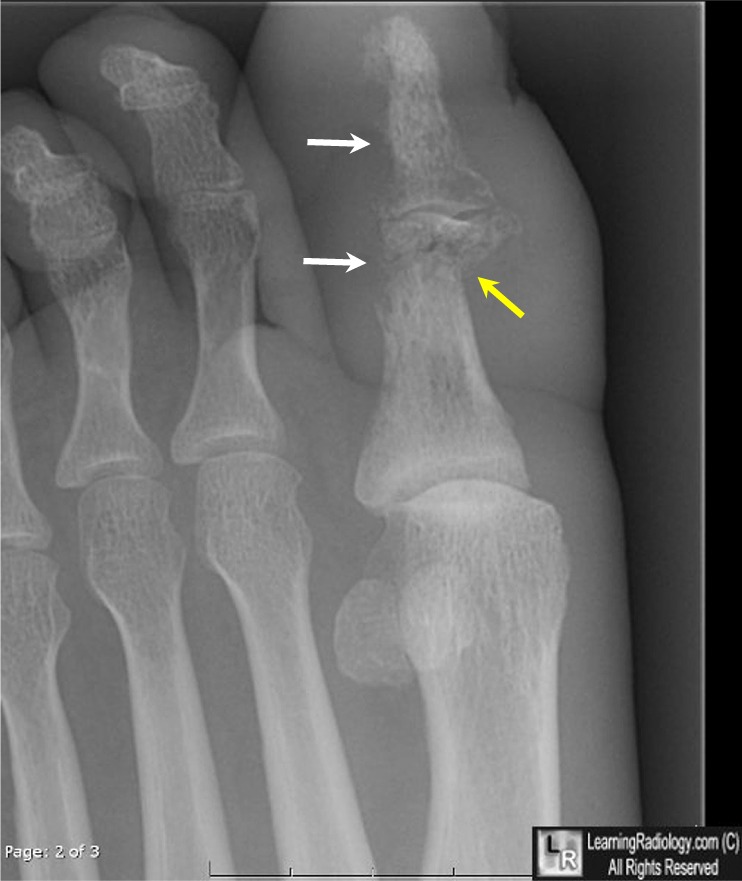
What does a periosteal reaction mean?
Periosteal reaction is a nonspecific radiographic finding that indicates new bone formation in reaction to the abnormal stimulants. Periosteal reactions may be broadly characterized as benign or aggressive, or more specifically categorized by pattern.
How is periosteal reaction treated?
Take a break from high-impact activities, such as running or jumping. Try going with more low-impact exercises, such as biking or swimming. Applying ice can bring down swelling and reduce inflammation. Taking an anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil), may also help.
How long does periosteal reaction take?
Periosteal reaction was first seen at day 5 and was present in 62% of the films obtained between 15 and 35 days after the fracture. Soft callus was first seen at day 12 and was prevalent in 41% between 22 and 35 days.
What is periosteal inflammation?
Periostitis is a condition that many runners are familiar with. It is caused by inflammation of the periosteum, a layer of connective tissue that surrounds bone. The condition is generally chronic and needs to be differentiated from stress fracture or shin splints.
Is periosteal reaction Bad?
In this reaction, the periosteum has been lifted from the cortex and new bone is filling the space in a uniform manner. This reaction may be thick or thin, straight or undulating, variable in opacity, and have distinct or indistinct margins. These reactions are generally benign and usually signify benign disease.
What causes a periosteal reaction?
Periosteal reaction results when cortical bone reacts to one of many possible insults. Tumor, infection, trauma, certain drugs, and some arthritic conditions can elevate the periosteum from the cortex and form various patterns of periosteal reaction (Fig.
Which type of periosteal reaction shows aggressiveness of tumor?
The spiculated pattern is an aggressive form of periosteal reaction that includes both hair- on-end and sunburst subtypes. Spicules of bone form perpendicular to the periosteal surface in the hair-on-end subtype (Figs. 4 and 5), which is highly suggestive of Ewing's sarcoma.
Can a bone heal in 2 weeks?
How Long Does a Fracture Take to Heal? Most fractures heal in 6-8 weeks, but this varies tremendously from bone to bone and in each person based on many of the factors discussed above. Hand and wrist fractures often heal in 4-6 weeks whereas a tibia fracture may take 20 weeks or more.
Where is the periosteum located in the bone?
The periosteum is a thin layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of a bone in all places except at joints (which are protected by articular cartilage).
How do you recover from periostitis?
Step 1 Ice packs, pain relief, felt or orthotic footwear correction. Step 2 Myofascial release and muscle rehabilitation. Step 3 Continue swimming and cycling, and only restart running after at least two weeks when symptoms have settled. Start on grass initially.
Is periostitis an infection?
Periostitis is an inflammation of your periosteum. It can be infectious, but usually, it is a chronic condition caused by impact or injury to an area of bone. Your bone may swell or become inflamed if you have periostitis. The impact of exercise can lead to chronic periostitis.
Why is pain felt over areas where there is periosteum?
The nerves of the periosteum register pain when the tissue is injured or damaged. Some of the nerves of the periosteum travel alongside the blood vessels into the bone, although many remain in the outer layer of the periosteum.
Which type of periosteal reaction shows aggressiveness of tumor?
The spiculated pattern is an aggressive form of periosteal reaction that includes both hair- on-end and sunburst subtypes. Spicules of bone form perpendicular to the periosteal surface in the hair-on-end subtype (Figs. 4 and 5), which is highly suggestive of Ewing's sarcoma.
Where is the periosteum located in the bone?
The periosteum is the sheath outside your bones that supplies them with blood, nerves and the cells that help them grow and heal. The endosteum is a membrane that lines the center of your bones that contain bone marrow. The perichondrium is very similar to the periosteum.
What is dental periosteum?
The periosteum is a specialized connective tissue that forms a fibrovascular membrane covering all bone surfaces except for that of articular cartilage, muscle, and tendon insertions and sesamoid bones.
What is periosteal reaction?
Periosteal reaction, also known as periostitis or periosteitis, is a nonspecific radiographic finding that indicates periosteal irritation. Periosteal reactions may be broadly characterized as benign or aggressive, or more specifically categorized by pattern.
Can callus formation be seen in periosteal reaction?
Benign periosteal reactions can be seen in callus formation in a fracture or with slowly growing tumors.
Is periosteal reaction benign or aggressive?
Benign versus aggressive. Periosteal reaction may be classified as benign or aggressive (note: not benign and malignant) based on the time course of the initiating process.
What is periosteal reaction?
Orthopedics. A periosteal reaction is the formation of new bone in response to injury or other stimuli of the periosteum surrounding the bone. It is most often identified on X-ray films of the bones.
What causes periosteal hematomas?
A periosteal reaction can result from a large number of causes, including injury and chronic irritation due to a medical condition such as hypertrophic osteopathy, bone healing in response to fracture, chronic stress injuries, subperiosteal hematomas, osteomyelitis, and cancer of the bone. It may also occur as part ...
What is an active periosteal reaction?
An active periosteal reaction is a feature of many aggressive bone lesions and is one where the margin of the periosteal reaction is irregular, not smooth. There are various degrees of periosteal reactivity and almost innumerable specific appearances of an active periosteal reaction. The presence of an irregular margin is the clue ...
What is the reaction of the periosteum?
The periosteum may react to irritation by the production of new bone. The type of periosteal reaction is often indicative of the severity of the lesion provoking it. In its earliest form it appears as a fine irregular reaction giving the bone a blurred or indistinct margin at the site of the lesion.
What is focal anaerobic osteomyelitis?
Bacterial – often solitary and associated with an open wound (trauma, surgery); focal anaerobic osteomyelitis occurs following bite wounds, with a small central sequestrum surrounded by a raised, ring-like periosteal reaction. May be multifocal if haematogenous spread. b.
What is the Palisade reaction?
Palisade reaction: New bone is formed extending in columns outward at right angles from the cortex. The new bone forms a solid continuum. This type of reaction is seen with hypertrophic osteopathy and sometimes osteomyelitis.
What is the reaction of new bone?
Palisade reaction: New bone is formed extending in columns outward at right angles from the cortex. The new bone forms a solid continuum. This type of reaction is seen with hypertrophic osteopathy and sometimes osteomyelitis. Spicular: Thin spicules of new bone are formed radiating outward from a lesion in the bone.
What is a spicule in bone?
Spicular: Thin spicules of new bone are formed radiating outward from a lesion in the bone. This type of reaction is indicative of an aggressive process and is often seen with malignant bone tumors. The term “sunburst” is sometimes given to an exuberant type of this reaction.
Is a smooth periosteal reaction aggressive?
The finding of a smooth periosteal reaction does not mean that the lesion is not aggressive, because there may be another finding that makes the lesion aggressive. Thus, a lesion with a smooth periosteal reaction but an indistinct transition zone will still be aggressive (see Fig. 17.18 ). View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What is the histological appearance of a periosteal reaction?
Histological appearance was characterised by a nearly circumferential periosteal reaction, reactive new bone formation, occasional sequester formation, and drastic infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with occasional microabscesses.
What reaction was present in the control group accompanying the newly formed bone?
There was also a periosteal reactionin the control group accompanying the newly formed bone which represented the continuation of the healing process.
Why is it difficult to differentiate SAPHO syndrome from suppurative osteomyelitis?
It is difficult to differentiate SAPHO syndrome from suppurative osteomyelitis because of its nonspecific findings, such as bone marrow edema and periosteal reaction. Suei et al.
What is a thin periosteal reaction?
A thin periosteal reaction might represent an early stage of a highly aggressive bone lesion or a chronic, benign process ( Fig. 3. 1 ). On the other hand, a thick periosteal reaction usually suggests a benign condition.
How long does it take for a periosteal reaction to be diagnosed?
After an acute incidence, it usually takes three weeks before a periosteal reaction can be diagnosed radiographically.
What is the term for a calcified periosteum?
A local elevation of the periosteum that is calcified at the site of its bone insertion is known as “Codman’s triangle” ( Fig. 3. 3b ). Originally considered as a sign of a malignant bone neoplasm, it has been recognized that it can also occur with benign processes such as osteomyelitis, subperiosteal hemorrhage, and fracture. When the periosteal reaction eventually blends with the adjacent cortex, cortical thickening occurs. However, cortical thickening may also develop by excessive endosteal or periosteal new bone formation without stripping the periosteum away from the cortex. The differential diagnoses of various bone lesions with periosteal reactions are discussed in Table 3. 1.
Where is periostitis found?
Under a variety of degenerative, traumatic and inflammatory conditions, a periostitis is found at the insertions of many tendons and ligaments causing the appearance of “whiskering” ( Fig. 3. 4 ). The most common location is the pelvis, where the iliac crests, the ischial tuberosities and the ischiopubic rami are affected.
What are the patterns of periosteal reaction?
Periosteal reaction may also be grouped into several patterns: smooth, solid or thick, and aggressive (laminar, sunburst, Codman triangle, and cloaking). Smooth periosteal reaction consists of one or multiple unbroken layers of ossified periosteum along the cortical surface.
What is the periosteal response?
Periosteal Reaction. The periosteum is a membrane that covers the majority of bone except at locations at and near cartilage. How periosteum responds to stimuli (e.g., trauma, infection, metabolic process, and neoplasm) can often give clues to the etiology of the underlying stimulus. An aggressive or destructive process will often greatly alter ...
What is the difference between a nonaggressive and aggressive periosteal reaction?
An aggressive or destructive process will often greatly alter the periosteum, whereas a nonaggressive process usually gives the periosteum the opportunity to remodel with a more orderly architecture. The distribution of periosteal reaction (focal or diffuse) may give clues to the underlying process.
What causes periosteal cloaking?
Rapidly growing bones appear to be predisposed to producing cloaking in response to injury. Trauma and infection are the most common causes of cloaking.
How long does it take for subperiosteal cortical hyperostosis to resolve?
Subperiosteal cortical hyperostosis. Epiphyses spared. Fever and soft-tissue swelling adjacent to involved bones. Rarely appears after 5 mo and usually resolves spontaneously by 2 y. Imaging appearance will depend on phase of disease.
What is the early stage of subperiosteal bone formation?
Early stage: symmetri c subperiosteal new bone formation along the diaphyses of the extremities, hands, and feet. Advanced stage: diffuse subperiosteal bone formation, ossification of ligaments and tendons, ankylosis, acroosteolysis.
Which bones are symmetric periostitis?
Symmetric periostitis of the radius and ulna > femur, humerus, metacarpals, and metatarsals.
What does it mean when you have a periosteal reaction?
If you have a periosteal reaction, it doesn’t mean there’s a crack in the bone, but it does mean that you’ve had irritation to the bone. Now, obviously your doctor is going to make sure that you don’t have other things like a bone tumor or a bone infection or something worrisome. But, in most runners, this is pretty simple.
How long does it take for periosteal reaction to show up on x-ray?
But, there’s a very wide timeframe from less than a couple of weeks to actually more than several weeks before the periosteal reaction shows up on an x-ray, or you see a bone callus forming on the x-ray where you’re actually getting calcium deposited in that area, that little hazy cloud around the bone.
How to tell if you have periostitis?
The symptoms of acute periostitis can include: 1 intense pain 2 difficulty bearing weight on the affected limb 3 pus formation 4 fever 5 chills 6 swelling of the tissue surrounding the bone
How long does it take for periostitis to heal?
If you have surgery to treat acute periostitis, you’ll probably get antibiotics intravenously, or through your veins, for 4 to 6 weeks. A few weeks of oral antibiotic treatment may follow. After that, your recovery will depend on the nature of the bone surgery.
What are the two types of periostitis?
The two types of periostitis are chronic and acute. Infection of the bone can lead to acute periostitis, which is a painful condition. This may lead to necrosis, which is death of the living tissue surrounding the bone. Chronic periostitis can result from trauma and stress to the bones. Shin splints from running are an example.
How to treat chronic periostitis?
For shin splints and similar stress-related injuries, try rest and ice. Take a break from high-impact activities, such as running or jumping. Try going with more low-impact exercises, such as biking or swimming. Applying ice can bring down swelling and reduce inflammation.
What is the cause of acute periostitis?
Acute periostitis can develop from a variety of infections in other parts of your body.
Is periostitis a serious condition?
Periostitis is usually benign and well tolerated. It can also take other forms, though, including an infectious condition that’s much more serious and may require intensiv e therapy .
Is periostitis more common in children?
Certain other noninfectious forms of periostitis, such as Osgood-Schlatter disease, are more common in growing children.
How does periostitis treatment work?
Periostitis treatment involves a healing period and rehabilitation. During healing, the treatment focuses on controlling the symptoms. When the time comes for you to participate in rehabilitation, the aim is to rebuild the affected area and minimize the risk of the condition reoccurring.
What is the best definition of periostitis?
Periostitis symptoms. The best periostitis definition is simply inflammation of the membrane enveloping a bone. If you are a runner, it may be easy to blame your pain on this condition, but as mentioned above, you can get it from other types of movement. Knowing the symptoms will help you identify the problem.
What causes periostitis?
The cause of your periostitis depends on whether it’s acute or chronic. In acute cases, it can develop from infections in other parts of the body. It may sound odd, but a UTI or STI can lead to periostitis. You can also get it from a cut that doesn’t heal.
What is the name of the condition where periostitis grows?
Suppurative —the periostitis grows when there is an infection. Fever and extreme pain and swelling occur.
What does a doctor look for in a periostitis patient?
Is very effective in confirming periostitis. A physician will look for tenderness, swelling, and redness along with the different diagnostic tests. A detailed review of patient medical history can also help in coming to a final diagnosis.
What are the risk factors for acute periostitis?
Risk factors for acute periostitis include having any systemic infection, joint replacement surgery, poor circulation, and having an open fracture where the bone pierces through the skin.
How to diagnose periostitis?
There are different ways to diagnose periostitis. As your doctor conducts a physical exam, they will rule out other conditions such as fracture, Lyme disease, arthritis, Hypertrophic Pulmonary Osteoarthropathy, Caffey’s disease, and other potential ailments.
