Personal genome sequencing assesses the status of all of your genes at one time, just as if the Human Genome Project
Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the sequence of nucleotide base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying and mapping all of the genes of the human genome from both a physical and a functional standpoint…
Full Answer
What is personal genome sequencing?
What is personal genome sequencing? Personal genome sequencing assesses the status of all of your genes at one time, just as if the Human Genome Project were conducted specifically on you. The completion of the Human Genome Project was a great advance for medical research, providing us with part of the blueprint that makes us human.
How much of the human genome is sequenced by whole genome sequencing?
In addition, whole genome sequencing should not be confused with methods that sequence specific subsets of the genome - such methods include whole exome sequencing (1% of the genome) or SNP genotyping (<0.1% of the genome). As of 2017 there were no complete genomes for any mammals, including humans.
What is the difference between HGP and genome sequencing?
Sequencing an individual's 'personal' genome actually involves establishing the identity and order of ~6 billion bases of DNA (rather than a ~3-billion-base 'reference' sequence; see above). Thus, the generation of a person's genome sequence is a notably different endeavor than what the HGP did.
What is a Human Genome Reference Sequence?
A human genome reference sequence is an accepted representation of the human genome sequence that is used by researchers as a standard for comparison to DNA sequences generated in their studies.
What is human genome sequence?
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome.
How does personal genome sequencing work?
Electrodes are placed at either end of the gel and an electrical current is applied, causing the DNA molecules to move through the gel. Smaller molecules move through the gel more rapidly, so the DNA molecules become separated into different bands according to their size.
What is an individual's genome?
A genome is all of the genetic material in an organism. It is made of DNA (or RNA in some viruses) and includes genes and other elements that control the activity of those genes.
How do I find my genome sequence?
To find the gene coding sequence, look at the Genomic regions, transcripts, and products section or the NCBI Reference Sequences (RefSeq) section of the Gene record: Clicking on the GenBank link displays the GenBank record in the Nucleotide database.
How much does full genome sequencing cost?
Whole Genome Sequencing Cost in the USA There are many providers that offer whole genome sequencing tests in the United States; many of them offer prices that range from $999 to as low as $399.
How long does it take to sequence a human genome?
A research effort led by Stanford scientists set the first Guinness World Record for the fastest DNA sequencing technique, which was used to sequence a human genome in just 5 hours and 2 minutes.
What is the difference between genome and DNA?
A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA. If the DNA code is a set of instructions that's carefully organised into paragraphs (genes) and chapters (chromosomes), then the entire manual from start to finish would be the genome. Almost every human's genome, chromosomes and genes are organised in the same way.
How many genomes do we have in our body?
The diploid human genome is thus composed of 46 DNA molecules of 24 distinct types. Because human chromosomes exist in pairs that are almost identical, only 3 billion nucleotide pairs (the haploid genome) need to be sequenced to gain complete information concerning a representative human genome.
Can two people have the same DNA?
Identical twins are born when one zygote (formed by a sperm and an egg cell) splits into two foetuses. That's why these rare cases are known as monozygotic twins: the two children are formed by the same gametes, inherit the same genes, and therefore have identical DNA test results.
What is the most common DNA sequencing process still in use today?
Although genomes are now typically sequenced using other methods that are faster and less expensive, Sanger sequencing is still in wide use for the sequencing of individual pieces of DNA, such as fragments used in DNA cloning or generated through polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
What is whole genome sequencing test?
Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) is a comprehensive method for analyzing entire genomes. Genomic information has been instrumental in identifying inherited disorders, characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression, and tracking disease outbreaks.
How do you identify an unknown gene?
For modern biology, the sequences around unknown genes are always known; therefore, genome walking methods based on PCR amplification are the major techniques employed for exploring unknown genes.
Can you sequence your own genome?
Whole genome sequencing is available to anyone.
Does 23andMe sequence your whole genome?
No, their DNA tests do not sequence your genome. The type of testing technology used by 23andMe, Ancestry.com, and similar companies test less than 0.1% of your genome. Their tests, which are called genotyping microarray tests, do not sequence your genes and do not test your whole genome.
What is genome sequencing and how is it done?
(jeh-NOH-mik SEE-kwen-sing) A laboratory method that is used to determine the entire genetic makeup of a specific organism or cell type. This method can be used to find changes in areas of the genome. These changes may help scientists understand how specific diseases, such as cancer, form.
How does automated DNA sequencing work?
Automated DNA sequencing uses a PCR-type reaction to sequence DNA. In PCR sequencing, or cycle sequencing, the template DNA with unknown sequence is amplified by Taq polymerase as any normal PCR reaction.
What is a genome test?
Genome tests often identify sequence variants associated with adult-onset disorders. While this knowledge may, in adulthood, assist with medical care, it could be a profound and premature psychological burden to parents and children.
What does a whole genome test reveal?
Whole-genome tests may reveal that your child has a change in a gene predisposing him or her to a disease, such as autism. “This does not mean that your child will become autistic,” says Hudgins. “It means that, in large population studies, specific changes in that gene were associated with an increased risk of autism.
Is personal genome sequencing specific?
But personal genome sequencing is not specific —it gathers all genetic data into one enormous report, with little or no context. Buyers are presented with a trove of genetic information that may be difficult or even impossible to understand—and possibly difficult to cope with.
Who is the author of the statement on direct to consumer genetic testing?
For parents who may want to purchase direct-to-consumer, whole-genome testing, Dr. Hudgins encourages careful consideration of the following issues for their children, as well as those outlined in the American College of Medical Genetics Statement on Direct-to-Consumer Genetic Testing, which was co-authored by Dr. Hudgins:
Is whole genome sequencing accurate?
The study also showed that the current technology used for whole-genome sequencing is not yet as accurate as it needs to be . In a research setting, whole-genome sequencing has the potential to decode our personal mysteries through millions of genetic clues.
How is the genome sequenced?
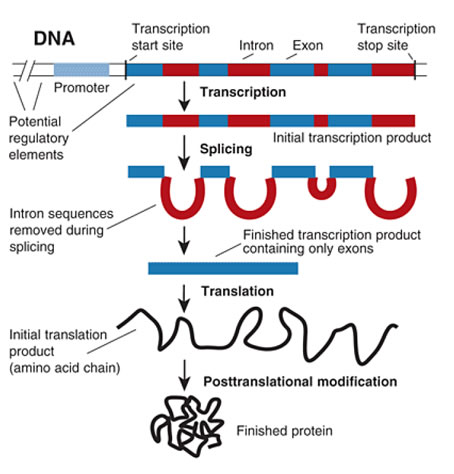
Rather, to sequence a genome, its DNA must first be broken down into smaller pieces, with each resulting piece then subjected to chemical reactions that allow the identity and order of its bases to be deduced . The established base order derived from each piece of DNA is often called a 'sequence read,' and the collection of the resulting set of sequence reads (often numbering in the billions) is then computationally assembled back together to deduce the sequence of the starting genome. Sequencing human genomes are nowadays aided by the availability of available 'reference' sequences of the human genome, which play an important role in the computational assembly process. Historically, the process of breaking down genomes, sequencing the individual pieces of DNA, and then reassembling the individual sequence reads to generate a sequence of the starting genome was called 'shotgun sequencing' (although this terminology is used less frequently today). When an entire genome is being sequenced, the process is called 'whole-genome sequencing.' See Figure 2 for a comparison of human genome sequencing methods during the time of the Human Genome Project and circa ~ 2016.
What is the driver of the costs associated with generating genome sequences?
Another important driver of the costs associated with generating genome sequences relates to data quality. That quality is heavily dependent upon the average number of times each base in the genome is actually 'read' during the sequencing process.
Why was the HGP necessary?
The former was required at the time because there was otherwise no 'framework' for organizing the actual sequencing or the resulting sequence data. The maps of the human genome served as 'scaffolds' on which to connect individual segments of assembled DNA sequence. These genome-mapping efforts were quite expensive, but were essential at the time for generating an accurate genome sequence. It is difficult to estimate the costs associated with the 'human genome mapping phase' of the HGP, but it was certainly in the many tens of millions of dollars (and probably hundreds of millions of dollars).
What is the process of sequencing DNA?
Historically, the process of breaking down genomes , sequencing the individual pieces of DNA, and then reassembling the individual sequence reads to generate a sequence of the starting genome was called 'shotgun sequencing' (although this terminology is used less frequently today).
What is the alternative to whole genome sequencing?
An alternative to whole-genome sequencing is the targeted sequencing of part of a genome. Most often, this involves just sequencing the protein-coding regions of a genome, which reside within DNA segments called 'exons' and reflect the currently 'best understood' part of most genomes.
How much did it cost to complete the human genome?
The estimated cost for advancing the 'draft' human genome sequence to the 'finished' sequence is ~ $150 million worldwide. Of note, generating the final human genome sequence by the HGP also relied on the sequences of small targeted regions of the human genome that were generated before the HGP's main production-sequencing phase; it is impossible to estimate the costs associated with these various other genome-sequencing efforts, but they likely total in the tens of millions of dollars.
How long did it take to get the human genome?
Once significant human genome sequencing began for the HGP, a 'draft' human genome sequence (as described above) was produced over a 15-month period (from April 1999 to June 2000). The estimated cost for generating that initial 'draft' human genome sequence is ~ $300 million worldwide, of which NIH provided roughly 50-60%.
What is whole genome sequencing?
Unlike all other genetic tests, whole genome sequencing is exactly that, sequencing of your entire genome. And at Veritas this means sequencing at clinical grade (30X coverage) the gold standard of sequencing quality. Watch Video.
How many genes are actionable?
In this clinical section of your report, over 59 genes deemed medically actionable by leading experts in the field of genetics. These genes are associated with Cardiovascular, Cancer and Metabolic and others.
Why do we go back to our genome?
Your genome is a resource for life. You can go back to your genomic data at any time to look for additional insights if new medical concerns arise in the future.
How many genes are associated with autosomal recessive disorder?
Screening for 24 genes associated with several autosomal recessive conditions. These genes were selected by leading experts in the field to to help guide family planning.
What is the DNA sequence?
Your genome sequence contains all your genetic information so that your DNA can be constantly replicated to create new cells and keep your organism running properly. Your DNA is made up of nucleotides — adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine — which bind together to create base pairs.
Where Can I Get My Genome Sequenced?
There are several companies that offer DNA testing, but not all of them perform whole genome sequencing. Many popular DNA testing providers offer other tests that are less comprehensive than WGS and only inspect certain portions of your DNA. These results may be accurate, but they won’t be as extensive as the ones you’ll receive through WGS.
What was the $1,000 genome era?
Everyone from small startups to global companies devotes funds to the development of these new sequencing services, which resulted in what is now called the “$1,000 genome” era.
What is the Human Genome Project?
The Human Genome Project was groundbreaking for its time. It used sequencing methods that were amazingly innovative then but have fallen out of use over time, such as Sanger sequencing. Sanger sequencing , along with other first-generation sequencing methods, were time-consuming and expensive since they were only able to sequence small DNA fragments. This technique has since been improved upon, and while it’s still used for very specific purposes, it would be practically impossible to make genetic testing widely available if other techniques hadn’t been developed.
What companies offer whole genome sequencing?
Companies such as Illumina, Pacific Biosciences, Full Genomes Corp., 454 Life Sciences, Veritas Genetics, Dante Labs, and Solexa started working towards the development of sequencing platforms that would allow them to offer whole genome sequencing for $1,000 or less.
How much did the Human Genome Project cost?
By the time the Human Genome Project was completed, it had cost nearly $3 billion. But as modern sequencing platforms became available, the cost of having your personal genome sequenced has steadily decreased.
Why do people use genome sequencing?
Some people choose to get their genome sequenced to learn more about their ancestry, whereas others want to have more control and knowledge over their potential health risks . Genetic information can also be used by prospective parents for genetic counseling or prenatal testing. Sequencing data can also be used to achieve a personalized approach to healthcare, and to create public health programs that are tailored to each community’s requirements.
What is the process of sequencing the genome?
Whole genome sequencing ( WGS ), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in ...
When was the first genome sequenced?
The first bacterial and archaeal genomes, including that of H. influenzae, were sequenced by Shotgun sequencing. In 1996 the first eukaryotic genome ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae) was sequenced. S. cerevisiae, a model organism in biology has a genome of only around 12 million nucleotide pairs, and was the first unicellular eukaryote to have its whole genome sequenced. The first multicellular eukaryote, and animal, to have its whole genome sequenced was the nematode worm: Caenorhabditis elegans in 1998. Eukaryotic genomes are sequenced by several methods including Shotgun sequencing of short DNA fragments and sequencing of larger DNA clones from DNA libraries such as bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs).
Why is genome sequencing important?
In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response.
How much does it cost to sequence a human genome?
In June 2009, Illumina announced that they were launching their own Personal Full Genome Sequencing Service at a depth of 30× for $48,000 per genome. In August, the founder of Helicos Biosciences, Stephen Quake, stated that using the company's Single Molecule Sequencer he sequenced his own full genome for less than $50,000. In November, Complete Genomics published a peer-reviewed paper in Science demonstrating its ability to sequence a complete human genome for $1,700.
What was the DNA sequencing method used in the 1970s?
The DNA sequencing methods used in the 1970s and 1980s were manual , for example Maxam-Gilbert sequencing and Sanger sequencing. Several whole bacteriophage and animal viral genomes were sequenced by these techniques, but the shift to more rapid, automated sequencing methods in the 1990s facilitated the sequencing of the larger bacterial and eukaryotic genomes.
Why are mutation rates higher in cancer?
In cancer, mutation frequencies are much higher, due to genome instability. This frequency can further depend on patient age, exposure to DNA damaging agents (such as UV-irradiation or components of tobacco smoke) and the activity/inactivity of DNA repair mechanisms. Furthermore, mutation frequency can vary between cancer types: in germline cells, mutation rates occur at approximately 0.023 mutations per megabase, but this number is much higher in breast cancer (1.18-1.66 somatic mutations per Mb), in lung cancer (17.7) or in melanomas (≈33). Since the haploid human genome consists of approximately 3,200 megabases, this translates into about 74 mutations (mostly in noncoding regions) in germline DNA per generation, but 3,776-5,312 somatic mutations per haploid genome in breast cancer, 56,640 in lung cancer and 105,600 in melanomas.
How long did it take to sequence the mouse genome?
The genome of the lab mouse Mus musculus was published in 2002. It took 10 years and 50 scientists spanning the globe to sequence the genome of Elaeis guineensis ( oil palm ). This genome was particularly difficult to sequence because it had many repeated sequences which are difficult to organise.
Why is the Personal Genome Project important?
“ The Personal Genome Project could help scientists learn more about how genetic and environmental factors interact to cause disease.
What is personal genomics?
Personal genomics is an area of genomics focusing specifically on the sequencing and analysis of one person’s genome, and then giving them their genomic information.
How can genomics be used to predict genetic disease?
Personal genomics can also be used to predict or confirm a genetic disease?. By looking at an individual’s genome it is possible to identify genetic variants? that may increase the likelihood of an individual having a genetic disease later on in life. For example, it can be used to tell a woman if she carries the BRCA1 breast cancer gene? and, if so, how much it increases the probability of her having breast cancer during her lifetime. This gives the individual the option of taking preventative measures, for example, if a woman finds her risk of breast cancer is high she may decide to have an operation to remove breast tissue (mastectomy).
Why do doctors use genetic information?
The genetic information from an individual can, in some cases, be used to select the most appropriate drug to prescribe to a patient. This helps doctors to ensure that the drug has the maximum effect while minimising any potential side effects.
Why is it important to know about our genes?
This is important as the more we know about our individual genes and disease risk the more easily we will be able to take lifestyle choices that lessen the likelihood of developing these diseases, or delay their onset.
Can we learn more about genetics?
Ultimately, we can only learn more about genetic risks by comparing many genomes in research studies. With this in mind, some people with personal genome sequences may choose to participate in research projects and allow scientists to study their genomic data to help advance knowledge in the field.
Can you be a carrier of a genetic disorder?
For example, it is possible to be a ‘carrier’ of a genetic disorder? such as cystic fibrosis?, which means that an individual has one of the two genes for the disorder but does not exhibit symptoms. However, if their partner is also a carrier the chance of their child having the full disorder is dramatically increased.
