
Policy Tools
- Open Market Operations
- Discount Window and Discount Rate
- Reserve Requirements
- Interest on Reserve Balances
- Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreement Facility
- Term Deposit Facility
- Central Bank Liquidity Swaps
- Foreign and International Monetary Authorities (FIMA) Repo Facility
What are the 3 tools of the Federal Reserve?
The Fed uses three main tools to accomplish these goals:
- A change in reserve requirements,
- A change in the discount rate, and.
- Open market operations.
Is a tool of monetary policy in which the Federal Reserve buys and sells?
The Fed uses open market operations as its primary tool to influence the supply of bank reserves. This tool consists of Federal Reserve purchases and sales of financial instruments, usually securities issued by the U.S. Treasury, Federal agencies and government-sponsored enterprises.
How does Federal Reserve regulate money?
How does the Federal Reserve control the supply of money? The Fed controls the supply of money by increasing or decreasing the monetary base. The monetary base is related to the size of the Fed's balance sheet; specifically, it is currency in circulation plus the deposit balances that depository institutions hold with the Federal Reserve.
What policy is the Federal Reserve System in charge of?
The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the United States. It performs five general functions to promote the effective operation of the U.S. economy and, more generally, the public interest. The Federal Reserve. conducts the nation’s monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates ...
See more
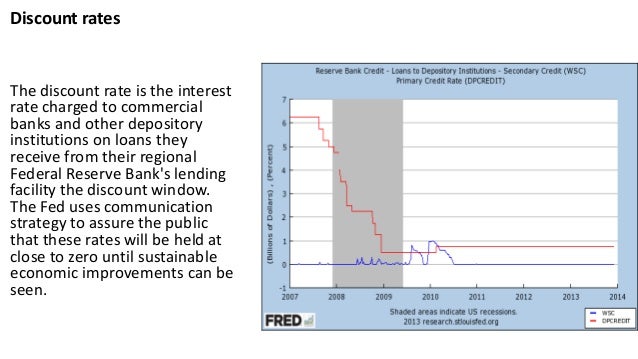
What is the most used Federal Reserve tool?
IORB is the Fed's primary tool for guiding the federal funds rate. The overnight reverse repurchase agreement (ON RRP) rate is the interest rate that a broad set of financial institutions can earn on deposits with the Fed.
What tool does the Federal Reserve use to influence?
The Fed uses its monetary policy tools to influence the supply of money and credit in the economy. It does this primarily by using daily open market operations. When the Fed buys or sells U.S. government securities, it increases or decreases the level (or supply) of reserves in the banking system.
What are the 4 monetary policy tools the Fed uses?
How the Fed Implements Monetary Policy with Its ToolsInterest on Reserve Balances: The Primary New Monetary Policy Tool. ... Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreement Facility: The Supplementary Tool. ... Discount Rate: Setting a Ceiling for the Federal Funds Rate. ... Open Market Operations: Maintaining Ample Reserves.
What are the 3 tools of the Fed?
The Federal Reserve controls the three tools of monetary policy--open market operations, the discount rate, and reserve requirements.
Which is not a policy tool used by the Fed?
b. Deposit insurance is not a basic monetary policy tool used by the Fed.
How many monetary policy tools are there?
The 6 tools of monetary policy are reverse Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate, Open Market Operations, Bank Rate policy (discount rate), cash reserve ratio (CRR), Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR). You can read about the Monetary Policy – Objectives, Role, Instruments in the given link.
Which of the following is not a tool of monetary policy?
Out of the given options, deficit financing is not a monetary tool.
What is the Fed's most important monetary policy tool quizlet?
Open market operations are by far the most important and most often used monetary policy tool. Through bond SALES, the Fed REMOVES RESERVES from the banking system.
What tool does the Federal Reserve used to influence the volume of money in the economy by buying and selling government securities?
Permanent open market operations (POMO)Permanent open market operations (POMO) refers to the Fed (or any central bank) constantly using the open market to buy and sell securities in order to adjust the money supply. POMO has been one of the tools used by the Federal Reserve to implement monetary policy and influence the American economy.
What tool does the Federal Reserve uses to influence the volume of money in the economy?
The primary tool the Federal Reserve uses to conduct monetary policy is the federal funds rate—the rate that banks pay for overnight borrowing in the federal funds market.
What tool does the Federal Reserve use to influence the volume of money in the economy by buying and selling?
open market operationsThe Federal Reserve buys and sells government securities to control the money supply and interest rates. This activity is called open market operations.
What is the Federal Reserve's monetary policy?
The Federal Reserve currently uses several tools to implement monetary policy in support of its statutory mandate to foster maximum employment and stable prices. The Federal Reserve conducts open market operations (OMOs) in domestic markets. OMOs can be permanent, including the outright purchase and sale of Treasury securities, ...
What is the Federal Reserve's liquidity arrangement?
The Federal Reserve provides short-term liquidity to domestic banks and other depository institutions through the discount window. In addition, because of the global nature of bank funding markets, the Federal Reserve has established liquidity arrangements with foreign central banks (FCBs) as part of coordinated international efforts.
What is a repo loan?
A repo is the economic equivalent of a collateralized loan from the Federal Reserve to a primary dealer (the Federal Reserve counterparty in repo operations) and increases bank reserves while the trade is outstanding. The difference between the purchase and sale prices reflects the interest on the loan.
When did the FRBNY start conducting reverse repos?
In December 2009, the FRBNY began conducting small-scale reverse repo test operations with primary dealers as a matter of prudent advance planning. Reverse repo test operations were gradually expanded to include a larger group of counterparties (which is described in more detail below), and terms varying from overnight up to about four weeks. From September 2013 to December 2015, the FRBNY conducted a series of overnight reserve repos as a technical exercise for the purpose of further assessing the appropriate structure of such operations in supporting the implementation of monetary policy during normalization. Since the commencement of the monetary policy normalization process in December 2015, the FOMC has authorized the FRBNY to conduct OMOs, including reverse repos, as necessary to maintain the federal funds rate in its target range. Additional information is available at https://www.newyorkfed.org/markets/rrp_op_policies.html and https://www.newyorkfed.org/markets/rrp_faq.html, and the results of the operations are available at https://www.newyorkfed.org/markets/omo/dmm/temp.cfm.
How does reducing the Federal Reserve's securities holdings affect the balance sheet?
Gradually reducing the Federal Reserve's securities holdings will result in a declining supply of reserve balances. Decreasing the size of the balance sheet in a gradual and predictable manner will limit the volume of securities that private investors will have to absorb and will guard against outsized moves in interest rates and other potential market strains. The FOMC anticipates reducing the quantity of reserve balances, over time, to a level appreciably below that seen in recent years but larger than before the financial crisis, and intends to continue to implement monetary policy in a regime in which an ample supply of reserves ensures that control over the level of the federal funds rate and other short-term interest rates is exercised primarily through the setting of the Federal Reserve's administered rates, and in which active management of the supply of reserves is not required.
How are term deposits awarded?
Term deposits may be awarded either through (1) a competitive single-price auction with a noncompetitive bidding option (which allows institutions to place small deposits at the rate determined in the competitive portion of the operation), (2) a fixed-rate format with full allotment up to a maximum tender amount at an interest rate specified in advance, or (3) a floating-rate format with full allotment up to a maximum tender amount at an interest rate set equal to the sum of the interest rate paid on excess reserves plus a fixed spread. Since September 2014, term deposits have incorporated an early withdrawal feature that allows depositors to obtain a return of funds prior to the maturity date subject to an early withdrawal penalty.
What is a TDF deposit?
The Term Deposit Facility (TDF) is a program through which the Federal Reserve Banks offer interest-bearing term deposits to eligible institutions. A term deposit is a deposit at a Federal Reserve Bank with a specific maturity date. The TDF was established to facilitate the conduct of monetary policy by providing a tool that may be used to manage the aggregate quantity of reserve balances held by depository institutions and, in particular (as with reverse repos), to support a reduction in monetary accommodation at the appropriate time. An increase in term deposits outstanding drains reserve balances because funds to pay for them are removed from the accounts of participating institutions for the life of the term deposit.
How does the Fed affect monetary policy?
The Fed is able to affect monetary policy by changing reserve requirements. When the Fed wants to decrease the amount of money in the system, it raises the reserve requirements for banks. This forces banks to pull money out of circulation and put it into reserve. When the Fed wants to increase the amount of money in the system, it lowers the reserve requirements for banks. This allows banks to pull money out of reserve and put it back into circulation.
Who sets the discount rate?
The Federal Reserve is responsible for setting the discount rate—the interest rate the Fed charges banks to borrow money at the Discount Window. The Discount Window is a facility where banks can borrow money directly from the Fed to meet reserve requirements or increase the amount of money they have available to lend to customers.
How does OMO affect the economy?
If the Fed buys bonds in the open market, it increases the money supply in the economy by swapping out bonds in exchange for cash to the general public. Conversely, if the Fed sells bonds, it decreases the money supply by removing cash from the economy in exchange for bonds. Therefore, OMO has a direct effect on money supply. OMO also affects interest rates because if the Fed buys bonds, prices are pushed higher and interest rates decrease; if the Fed sells bonds, it pushes prices down and rates increase.
How does the Fed increase the money supply?
If the Fed buys bonds in the open market, it increases the money supply in the economy by swapping out bonds in exchange for cash to the general public. Conversely, if the Fed sells bonds, it decreases the money supply by removing cash from the economy in exchange for bonds.
Why did the Fed create term auction facilities?
The Fed was tasked with bolstering credit markets and investors' perceptions thereof and encouraging institutions to lend in spite of worsening conditions in the economy and credit markets. To accomplish this, the Fed created the term auction facilities and term securities lending facilities. Let's take a closer look at these two items:
What can the Fed do when the economy falters?
When the economy is faltering, the Fed can use these tools to enact expansionary monetary policy. If that fails it can use unconventional policy such as quantitative easing.
What is the Fed manipulating interest rates?
Manipulating Interest Rates. The first tool used by the Fed, as well as central banks around the world, is the manipulation of short-term interest rates. Put simply, this practice involves raising/lowering interest rates to slow/spur economic activity and control inflation. The mechanics are relatively simple.
Why is it called an auction?
5 The reason it was called an auction is that firms would bid on the interest rate they would pay to borrow cash. This differs from the discount window, which makes an institution's need for cash public information, potentially leading to solvency concerns on the part of depositors, which only exacerbate concerns about economic stability.
How does the Federal Reserve work?
In the U.S., The Federal Reserve (The Fed) exists to maintain a stable and growing economy through price stability and full employment – its two legislated mandates. 1 Historically, the Fed has done this by manipulating short-term interest rates, engaging in open market operations (OMO) and adjusting reserve requirements.
What is the federal funds market?
These loans take place in a private financial market called the federal funds market.
What is the discount rate?
Banks also can borrow reserves directly from the Federal Reserve Banks at their “discount windows,” and the discount rate is the rate that financially sound banks must pay for this “primary credit.” The Boards of Directors of the Reserve Banks set these rates, subject to the review and determination of the Federal Reserve Board. (“Secondary credit” is offered at higher interest rates and on more restrictive terms to institutions that do not qualify for primary credit.) Since January 2003, the discount rate has been set 100 basis points above the funds rate target, though the difference between the two rates could vary in principle. Setting the discount rate higher than the funds rate is designed to keep banks from turning to this source before they have exhausted other less expensive alternatives. At the same time, the (relatively) easy availability of reserves at this rate effectively places a ceiling on the funds rate.
What is the interest rate on overnight borrowing of reserves called?
The interest rate on the overnight borrowing of reserves is called the federal funds rate or simply the “funds rate.”. It adjusts to balance the supply of and demand for reserves.
What happens when the Fed wants the funds rate to rise?
When the Fed wants the funds rate to rise, it does the reverse, that is, it sells government securities. The Fed receives payment in reserves from banks, which lowers the supply of reserves in the banking system, and the funds rate rises.
How does the Fed pay for government securities?
To do this, it buys government securities from a bank. The Fed then pays for the securities by increasing that bank’s reserves. As a result, the bank now has more reserves than it wants. So the bank can lend these unwanted reserves to another bank in the federal funds market.
What is the process of keeping intervention from affecting reserves and the funds rate called?
The process of keeping intervention from affecting reserves and the funds rate is called the “sterilization” of exchange market operations. As such, these operations are not used as a tool of monetary policy.
What is the Fed's main tool?
The major tool the Fed uses to affect the supply of reserves in the banking system is open market operations —that is, the Fed buys and sells government securities on the open market. These operations are conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
What is the effect of a higher reserve requirement on the economy?
A higher reserve requirement results in a tighter monetary supply, as it restrains banks’ ability to make loans. Tighter monetary supply acts as a brake on the speed of the economy. The discount rate is the interest rate charged by the 12 Federal Reserve Banks to the member banks who borrow funds from the Fed.
How does the Fed control the amount of money banks borrow?
The Fed controls the amount banks borrow by increasing or decreasing the cost to borrow funds. Banks may also borrow money from other banks, rather than from the 12 Reserve Banks, at a rate known as the federal funds rate. The federal funds rate is typically lower and is a more attractive option for bank borrowing.
How does the Fed tighten the monetary supply?
To tighten the monetary supply and slow the economy, the Fed sells securities. When banks purchase the securities, the Fed collects the funds from the purchase and removes the money from the economy, which reduces the amount of money banks can loan and aids in the goal of increasing interest rates. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) ...
How does the Fed control the supply of money?
The Federal Reserve controls the supply of money by buying and selling U.S. Treasury securities. If the Fed wishes to stimulate the economy and promote growth, it purchases securities from a bank or dealer. By paying for the securities, the Fed provides assets to the bank that it can then loan to businesses and consumers. Usually, the result is increased spending and lower interest rates. To tighten the monetary supply and slow the economy, the Fed sells securities. When banks purchase the securities, the Fed collects the funds from the purchase and removes the money from the economy, which reduces the amount of money banks can loan and aids in the goal of increasing interest rates.
What is reserve requirement?
The reserve requirement is the portion of deposits that banks must refrain from loaning to borrowers and keep in reserves at the bank. For example, if the reserve requirement is set at 5%, the bank must retain $5,000 of every $100,000 in deposits.
What is the term used to describe the actions taken by the Fed to increase or decrease the size of the nation's?
Monetary policy is the term used to describe the actions taken by the Fed to increase or decrease the size of the nation’s money supply. By adjusting money supply, the Fed attempts to maintain a steadier trajectory in the economy.
What is the role of the Federal Reserve in the financial system?
The Federal Reserve is tasked with determining and controlling the United States’ monetary policy.
What are the tools that the Fed uses to conduct monetary policy?
The Fed has traditionally used three tools to conduct monetary policy: reserve requirements, the discount rate, and open market operations. In 2008, the Fed added paying interest on reserve balances held at Reserve Banks to its monetary policy toolkit.
What is the inflation rate for 2020?
In its 2020 “Statement on Longer-Run Goals and Monetary Policy Strategy,” the FOMC changed that goal to inflation that averages 2 percent over time, in contrast to aiming for 2 percent at any given time. So, following periods when inflation has persisted below 2 percent, the Fed strives for inflation to be moderately above 2 percent for some time.
How does the Federal Funds Rate affect the economy?
Changes in the federal funds rate tend to cause changes in other short-term interest rates, which ultimately affect the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers, the total amount of money and credit in the economy, and employment and inflation. To keep price inflation in check, the Fed can use its monetary policy tools to raise ...
How does the Fed influence the Federal Funds Rate?
The Fed implements monetary policy primarily by influencing the federal funds rate, the interest rate that financial institutions charge each other for loans in the overnight market for reserves. Fed monetary policy actions, described below, affect the level of the federal funds rate. Changes in the federal funds rate tend to cause changes in other ...
What is the Fed's monetary policy?
The Fed, as the nation’s monetary policy authority, influences the availability and cost of money and credit to promote a healthy economy. Congress has given the Fed two coequal goals for monetary policy: first, maximum employment; and, second, stable prices, meaning low, stable inflation. This “dual mandate” implies a third, lesser-known goal ...
Why did the Fed add to reserve balances?
Because the Fed added to reserve balances, banks had more reserves that they could then convert into loans, putting more money into circulation in the economy. At the same time, the increase in the supply of reserves put downward pressure on the federal funds rate according to the basic principle of supply and demand.
Why did the Fed open a series of special lending facilities?
In addition, the Fed opened a series of special lending facilities to provide much-needed liquidity to the financial system. The Fed also announced policy plans and strategies to the public, in the form of “forward guidance.”. All of these efforts were designed to help the economy through a difficult period.

Permanent Open Market Operations
Temporary Open Market Operations and Other Reserve Management Tools
- Recent Developments 1. On April 24, 2019, outstanding reverse repurchase agreements (RRPs or reverse repos) conducted under OMOs totaled $9.5 billion. This amount is shown in table 1 as reverse repurchase agreements with others. Outstanding RRPs from these operations ranged from less than $50 million to $9.5 billion during the period from February ...
Discount Window Lending
- Recent Developments 1. Credit provided to depository institutions through the discount window generally remained around its usual level. As presented in table 5, discount window credit outstanding on April 24, 2019, was less than $50 million, and the lendable value of collateral pledged by borrowing institutions on that date was $0.3 billion. Background The discount windo…
Liquidity Arrangements with Foreign Central Banks
- Recent Developments 1. As presented in table 7, as of April 24, 2019, dollar liquidity extended under the central bank liquidity swap arrangements totaled $0.1 billion. Detailed information about swap operations is available at https://apps.newyorkfed.org/markets/autorates/fxswap. Background Because of the global character of bank funding markets, the Federal Reserve has …
The Monetary Policy Tools of The Federal Reserve
- Congress—along with giving the Fed goals that it has to accomplish—gave the Fed tools and authorities to enable it to meet its goals. Let’s take a look at the following primary tools the Fed uses to affect monetary policy: – Reserve requirements – Discount rate – Federal funds rate
Reserve Requirements
- The Federal Reserve is responsible for setting the reserve requirements for banks. Reserve requirements specify what percentage of a bank’s deposits the bank has to keep on reserve with the Fed. For instance, if the Fed sets the reserve requirement at 10 percent and a bank has $10 billion in deposits, the bank is required to keep $1 billion on reserve at the Fed. The Fed is able t…
Discount Rate
- The Federal Reserve is responsible for setting the discount rate—the interest rate the Fed charges banks to borrow money at the Discount Window. The Discount Window is a facility where banks can borrow money directly from the Fed to meet reserve requirements or increase the amount of money they have available to lend to customers. The Fed is able to affect monetary p…
Federal Funds Rate
- The Federal Reserve is responsible for setting a target for the federal funds rate—the interest rate banks charge each other to lend and borrow money on reserve at the Fed (also known as federal funds). You see, as banks deposits change, the amount of money they have to have on reserve at the Fed also changes. Sometimes banks have excess reserves, and sometimes banks have res…
Manipulating Interest Rates
Open Market Operations
- The other major tool available to the Fed is open market operations (OMO), which involves the Fed buying or selling Treasury bonds in the open market. This practice is akin to directly manipulating interest rates in that OMO can increase or decrease the total supply of money and also affect interest rates. Again, the logic of this process is rather...
Reserve Requirements
- The Federal Reserve also has the ability to adjust banks' reserve requirements, which determines the level of reserves a bank must hold in comparison to specified deposit liabilities. Based on the required reserve ratio, the bank must hold a percentage of the specified deposits in vault cash or deposits with the Federal Reserve banks. By adjusting the reserve ratios applied to depository i…
Influencing Market Perceptions
- The final tool used by the Fed to affect markets an influence on market perceptions. This tool is a bit more complicated because it rests on the concept of influencing investors' perceptions, which is not an easy task given the transparency of our economy. Practically speaking, this encompasses any sort of public announcement from the Fed regarding the economy. For exam…
Term Auction Facility/Term Securities Lending Facility
- In 2007 and 2008, the Fed was faced with another factor that strongly influences the economy – the credit markets. With the recent interest rate increases and the subsequent meltdown in values of subprime-backed collateralized debt obligations (CDOs), investors were provided an unexpected and sharp reminder of the potential downside of taking credit risk.4 Although mos…
Quantitative Easing
- Sometimes, the Fed's toolkit is simply not enough to spur economic activity in a severe crisis. Quantitative easing (QE) is a form of unconventional monetary policy in which a central bank purchases longer-term government securities or other types of securities from the open market in order to increase the money supply and encourage lending and investment.8Buying these secur…
The Bottom Line
- Overall, monetary policy is constantly in a state of flux but still relies on the basic concept of manipulating interest rates and, therefore, money supply, economic activity, and inflation. It is important to understand why the Fed institutes certain policies and how those policies could potentially play out in the economy. This is because the ebbs and flows of economic cycles offe…