Animal mating systems
- promiscuous. In monogamous systems, one male and one female are paired for at least one breeding season. ...
- Polygamy. When one male mating with multiple females, called polygyny (“many females”), the female takes responsibility for most of the parental care as the single male is not capable of ...
- Promiscuous. ...
What is polygynous mating?
reproductive success by inseminating more females) or where males are able to monopolize more than one female (if females or the resources they require are spatially clumped). Mammalian mating systems are predominantly polygynous, in part because young develop within and are then nursed by the female.
What is a promiscuous mating system?
Promiscuous mating systems occur when females mate with multiple males, and males mate with multiple females.
What is polygamy?
(adjective) Polygamous describes the behavior of mating with several partners during a single breeding season, generally when one male mates with several females.
What is the mating system of a mammal?
Mammalian mating systems are predominantly polygynous, in part because young develop within and are then nursed by the female. In polyandry ( andros means "male"), some females mate with more than one male during the breeding season.

What happens in a polygyny type of polygamous mating system?
Polygynous mating refers to one male mating with multiple females. In these situations, the female must be responsible for most of the parental care as the single male is not capable of providing care to that many offspring. In resourced-based polygyny, males compete for territories with the best resources.
What are the four types of mating systems?
A mating system involves the structure of an animal society in terms of sexual reproduction and (sometimes) pair bond behavior. There are four mating systems: monogamy, polyandry, polygyny, and polygynandry. Monogamy is a mating system in which two partners mate exclusively with each other.
What is a polyandry mating system?
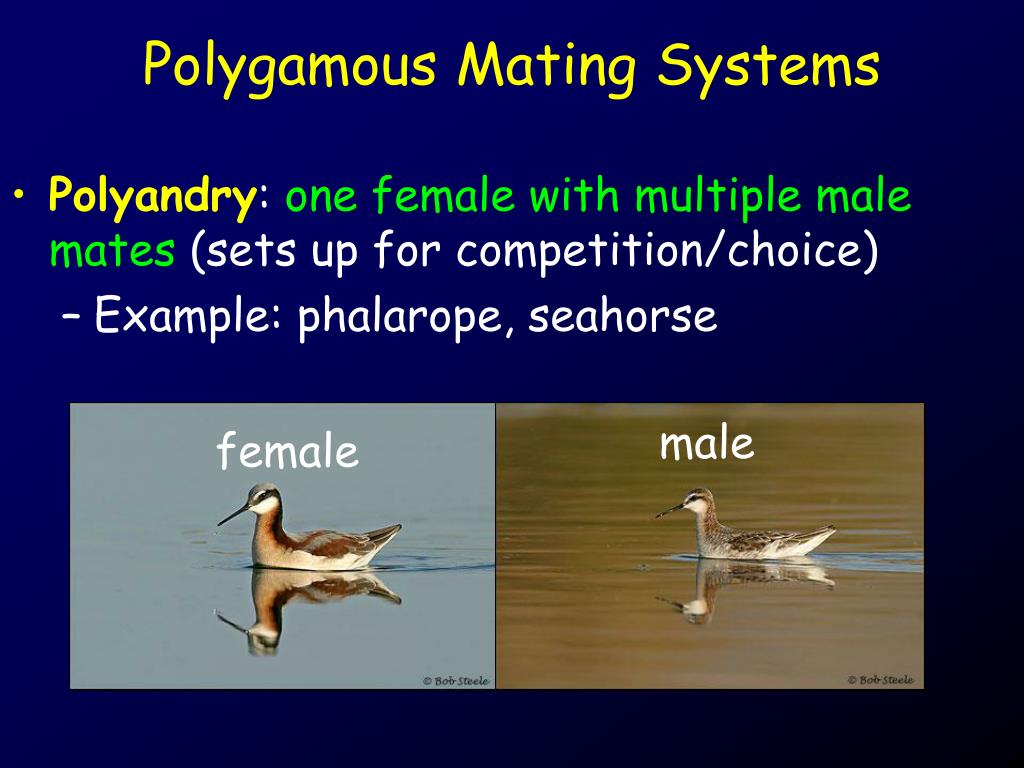
The mating of one female with more than one male while each male mates with only one female is known as polyandry (literally, "many males"). It is a rare mating system, occurring in less than one percent of all bird species, and is found mostly in shorebirds.
What is polygamous behavior?
In animal social behaviour: Social interactions involving sex. Although polygamy also involves mating with multiple partners, it often refers to cases in which individuals form relatively stable associations with two or more mates. Most such species exhibit polygyny, in which males have multiple partners.
Why do females mate with multiple males?
First, females compete for access to the highest quality males and once mated, those males are no longer available. In that case, females can breed with an available male and engage in extra-pair copulations with their preferred male (Møller, 1992).
What are the advantages of polygamy in animals?
Polygyny is beneficial in particular to the male, because he has a greater increase in fitness and reproductive success. This increase consequently reduces the genetic diversity of the community, often leading to increased inbreeding.
What's the difference between polygamy and polyandry?
Anthropologically, polygamy is defined as marriage between one person and two or more spouses simultaneously. It exists in two main forms: polygyny, where one man is married to several women, and polyandry, where one woman is married to several men.
What is a female polygamist called?
Table of Contents. polyandry, marriage of a woman to two or more men at the same time; the term derives from the Greek polys, “many,” and anēr, andros, “man.” When the husbands in a polyandrous marriage are brothers or are said to be brothers, the institution is called adelphic, or fraternal, polyandry.
Do female animals mate with multiple males?
It has been argued that in addition to direct benefits, such as nuptial gifts or an adequate sperm supply, females may gain genetic benefits from mating with different males. Females of the scorpionfly Panorpa cognata mate with several males during their lifetime.
What are the advantages of polygamy?
In general, polygamy allows you to have a bigger selection of partners at the same time and in case one partner annoys you quite a lot, you can simply spend your time with your other spouses and neglect the annoying spouse for a while Thus, a bigger variety of different partners can make your life easier in the sense ...
Is polygamy still illegal?
Polygamy is illegal and criminalized in every country in North and South America, including all 50 U.S. states. However, in February 2020, the Utah House and Senate reduced the punishment for consensual polygamy, which had previously been classified as a felony, to roughly equivalent to a traffic ticket.
Is polygamy a mental disorder?
They have also shown that polygamy is associated with mental illness (in particular, depression and anxiety) among women and children[15,16]. Chaleby[14] has found a disproportionate number of women in polygamous marriages (mostly senior wives) among psychiatric outpatient and inpatient populations in Kuwait.
What are two different mating systems?
By classifying social interactions, scientists have been able to identify different types of mating systems, such as monogamy and polygyny. The mating systems described in this article represent a variety of strategies to achieve reproductive success.
What is mating system in plants?
The primary mating systems in plants are outcrossing (cross-fertilisation), autogamy (self-fertilisation) and apomixis (asexual reproduction without fertilization, but only when arising by modification of sexual function). Mixed mating systems, in which plants use two or even all three mating systems, are not uncommon.
What is the human mating system?
Humans exhibit a wide range of marriage systems and mating practices within and among societies, including monogamy (one individual of each sex), polygyny (one male and multiple females), polyandry (one female and multiple males), polygynandry (multiple males and females) as well as same-sex relationships.
What is an example of mating?
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. Fertilization is the fusion of two gametes. Copulation is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization.
Why are mammalian mating systems polygynous?
Mammalian mating systems are predominantly polygynous, in part because young develop within and are then nursed by the female. In polyandry ( andros means "male"), some females mate with more than one male during the breeding season. This is the rarest type of mating system.
What is mating system?
Mating Systems. Mating systems are descriptions of who mates with whom in the animal world. In simplest terms, definitions of mating systems are based on how many mates an individual acquires during the breeding season. In monogamy, both males and females have only one mate at a time. This type of mating system often occurs in species in which ...
What is it called when a male mate has more than one female?
When males in the population mate with more than one female, it is called polygyny ( poly means "many," and gyne means "female").
What are some examples of males competing for females?
Males compete for females, and this leads to strong selection for traits that either attract females (for example, elaborate songs or calls, bright coloration, and courtship display s) or allow males to compete effectively with other males (for example, aggressiveness, large size, and fighting aids such as antlers).
Can a male have more than one mate?
Evidence from deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) studies of birds, mammals, and other species has shown that extra-pair copulations can result in fertilized eggs so that a presumably "monogamous" male or female may in fact have more than one mate.
Is a dunnock a monogamous pair?
Within a single population of dunnocks, there may be monogamous pairs as well as birds in polygynous and polyandrous relationships. Because of differences in the amount of energy invested in producing gametes (eggs are costly, sperm are not), finding a mate, and rearing offspring, the costs and benefits of a particular mating system may be ...
What is mating system?
A mating system is a way in which a group is structured in relation to sexual behaviour. The precise meaning depends upon the context. With respect to animals, the term describes which males and females mate under which circumstances.
What is the primary mating system in plants?
The primary mating systems in plants are outcrossing (cross-fertilisation), autogamy (self-fertilisation) and apomixis (asexual reproduction without fertilization, but only when arising by modification of sexual function). Mixed mating systems, in which plants use two or even all three mating systems, are not uncommon.
What are the three types of polygamy?
Polygamy: Three types are recognized: Polygyny (the most common polygamous mating system in vertebrates so far studied): One male has an exclusive relationship with two or more females. This is associated with one-male, multi-female group compositions.
Why is polygyny important?
Polygyny is also associated with greater environmental variability in the form of variability of rainfall. This may increase the differences in the resources available to men. An important association is that polygyny is associated with a higher pathogen load in an area which may make having good genes in a male increasingly important. A high pathogen load also decreases the relative importance of sororal polygyny which may be because it becomes increasingly important to have genetic variability in the offspring (See Major histocompatibility complex and sexual selection ).
What is the process of mating in archaea?
In several species of archaea, mating is mediated by formation of cellular aggregates. Halobacterium volcanii, an extreme halophilic archaeon, forms cytoplasmic bridges between cells that appear to be used for transfer of DNA from one cell to another in either direction.
What is the relationship between a male and a female?
Monogamy: One male and one female have an exclusive mating relationship. The term " pair bonding " often implies this. This is associated with one-male, one-female group compositions. There are two types of monogamy: type 1, which is facultative, and type 2, which is obligate.
What is the basic model of mating?
A number of models have been used to describe the parameters of plant mating systems. The basic model is the mixed mating model, which is based on the assumption that every fertilisation is either self-fertilisation or completely random cross-fertilisation. More complex models relax this assumption; for example, the effective selfing model recognises that mating may be more common between pairs of closely related plants than between pairs of distantly related plants.
What is the difference between monogamy and polygamy?
Monogamy polygamy and promiscuity. There are five basic types of animal mating systems (Table 6.1). Monogamy involves a pair-bond between one male and one female, whereas in polygamy, which includes polygyny, polyandry and polygynandry, social bonds involve multiple males and/or females.
Why do polygyny occur?
In many species this occurs when resources such as food are distributed patchily, because males can then defend high quality territories that will each attract multiple females. In Gunnison's prairie dogs (Cynomys gunnisoni) for example, monogamy prevails when resources are uniformly distributed whereas polygyny or polygynandry is often found when resources are distributed in patches that are guarded by one or several males (Travis, Slobodchikoff and Keim, 1995).
What is polygynandry in biology?
Polygynandry refers to the situation in which two or more males within a group are bonded socially with two or more females. This differs from promiscuity, a system in which any female can mate with any male without any social ties being formed. Differentiating between polygynandry and promiscuity may require a detailed study of a particular social group, and in fact the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Promiscuity is very common in mammals, occurring in at least 133 mammalian species (Wolff and Macdonald, 2004). It has also been documented in birds such as sage grouse (Centrocercus urophasianus) (Wiley, 1973) and in a number of fish species including guppies (Poecilia reticulata) (Endler, 1983). Promiscuity can have high fitness benefits to males if they can fertilize multiple females. Females may also benefit from promiscuous mating, as illustrated by field experiments on a number of species, including adders (Vipera berus) (Madsen et al., 1992) and crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) (Tregenza and Wedell, 1998), that have shown increased offspring survival when females mated with multiple males. This may result from one or more of a number of factors, including genetically variable offspring, increased parental investment and a reduced risk of male infanticide.
What is the mating system of jacanas?
This mating system is known as polyandry, of which the American jacana (Jacana spinosa) is a well-studied example. In this species the female defends large territories on a pond or lake, and in each territory several males will each defend their own floating nest and incubate the eggs that the female lays there.
Why are birds more likely to be biparental?
This is known as biparental care and is generally more common in birds than in mammals because both male and female birds can incubate eggs and bring food to nestlings, whereas gestation and lactation in mammals mean that much of the parental care is performed by females.
Do female squid have multiple clutches?
If, however, females simultaneously lay multiple clutches and a proportion of these survive, the female will increase her fitness. Although males appear to be disadvantaged by this mating system, they may have little choice in the matter when there is such strong competition for suitable nest sites.
Do females benefit from promiscuous mating?
Females may also benefit from promiscuous mating, as illustrated by field experiments on a number of species, including adders (Vipera berus) (Madsen et al., 1992) and crickets (Gryllus bimaculatus) (Tregenza and Wedell, 1998), that have shown increased offspring survival when females mated with multiple males.
What is promiscuity mating?
Promiscuous mating systems occur when females mate with multiple males, and males mate with multiple females. Promiscuity generally occurs when a single male is unable to sexually monopolize a group of females, either because the females range more widely than the territory size of a single male, so they interact with multiple males (eg, the maximum territory size a male can defend is smaller than the females’ ranges), or because males and females live together in large social groups that a single male cannot monopolize.
What is it called when a male mate has multiple females?
Polygamy refers to either one male mating with multiple females or one female mates with many males. When one male mating with multiple females, called polygyny (“many females”), the female takes responsibility for most of the parental care as the single male is not capable of providing care to that many offspring.
What is the difference between sexual monogamy and social monogamy?
True monogamy, also called sexual monogamy, is where both partners mate only with each other; true monogamy is exceedingly rare. Much more common is social monogamy, where two individuals partner together to rear their offspring , but also engage in “extra-pair copulations,” or matings with other individual (in human social parlance, we would call this “infidelity”). Social monogamy has both advantages and disadvantages for each partner. You can imagine the advantage for a male in this scenario: he helps rear offspring with his social partner, increasing the likely survival of those offspring, but he also mates with other females, thus increasing his total number of offspring (assuming any of these other offspring also survive).
How does social monogamy affect a female?
Social monogamy can also be advantageous for the female: she has help from a social partner in raising her offspring, but she can also mate with other males who may be genetically “better.” The disadvantage for the male in this scenario is that he is most likely helping to raise offspring that are not his own. The disadvantage for the female is that the male may abandon her – and her offspring – if he detects that she has mated with another male. The vast majority of songbirds demonstrate social monogamy, where up to 40% of the offspring in a mating pair’s nest were not actually fathered by the male partner.
What does the arrow mean in a mating system?
A schematic of the types of animal mating systems. Arrows indicate matings between individuals. Based on Wolff and Macdonald, TRENDS in Ecology and Evolution 2004.
How is mating influenced by competition?
Mating systems are influenced by competition for mates, and competition for mates is influenced by mating system. Except in the case of sexual (true) monogamy, there is always competition for fertilization. What differs in different mating systems is whether the competition occurs before mating (direct male competition) or after mating ...
Do pipefish compete with each other?
In contrast to seahorses, pipefish tends to live in very dense populations in resource-rich environments. Because the male’s pouches, rather than the female’s eggs, are the limiting resource in reproduction, females compete with each other for access to males. Promiscuous mating systems occur when females mate with multiple males, ...
What Is a Mating System?
As humans, it's easy to get wrapped up in the way that we live, especially in terms of our social relationships. While many humans may have multiple romantic partners in their lifetimes, there is a strong tendency towards settling on a single, monogamous relationship. We have moral systems, legal partnerships, and societal norms surrounding this behavior. But humans are only one animal species on planet Earth and not all animals behave the same way.
What is the difference between monogamy and polygyny?
Monogamy is a mating system in which two partners mate exclusively with each other. In polyandry, one female gets mating rights to many males. In polygyny, one male gets mating rights to many females. Polygynandry involves multiple males mating with multiple females in an animal group.
What is the meaning of monogamy?
Monogamy is a system in which two animals mate with only one another. The prefix in monogamy— mono —comes from a Greek word that means one. Polyandry, polygyny and polygynandry are all different types of polygamy. Polygamy is a mating system in which the animals in a partnership mate with multiple partners.
What is polyandry in fish?
Polyandry is a mating system in which one female gets mating rights to multiple males. This is also quite rare, but has been found in multiple species. Perhaps the most famous example is that of the mating habits of the female deep sea anglerfish. The small male anglerfish finds a female and bites her, which releases a chemical that combines the two bodies. The male then dies and his body is gradually eaten and absorbed by the female.
How many partners does monogamy have?
Let's go through each of the four mating systems one at a time. As mentioned, monogamy involves two partners, usually a single male who mates with a single female; however, homosexual monogamous partnerships have been documented in some species as well.
What happens when eggs are released by females?
Eggs are then released by females. As a result, random combinations of egg and sperm cause unique offspring. One result of this mating system, and all other polygamy mating systems, is incredible genetic diversity. Lesson Summary.
Why do bonobos have sex?
Bonobos use sex for reproduction, pair bonding, and to aid with social conflict. This system is also common among some fish species such as herring. Male herring release sperm in the water and it spreads throughout the habitat. Eggs are then released by females.
What is the most common mating system?
Across a broad range of human cultures, the most common mating systems are monogamy and polygyny ; the latter occurs when a male has multiple female mates (sometimes this is called a harem mating system ). However, from a lifetime perspective, both males and females are likely to have multiple mates, and serial monogamy—pair bonds that are nonpermanent—is a common mating system in humans. Extrapair copulations—sexual encounters outside a pair bond—are certainly frequent in humans. Extrapair copulations may allow a person to produce genetically diverse offspring while avoiding the costs of parental care.
Why do animals have nonmonogamous mating systems?
Animals with nonmonogamous mating systems may suffer from the effects of parasites and venereal diseases for two different reasons: (a) the risk of contracting diseases and parasites increases during sexual contact; and (b) animals with particular mating systems are more susceptible to infections.
What is social monogamy in shrimp?
As in birds, social monogamy in certain coral-reef dwelling caridean shrimps has evolved into territorial cooperation and extended mate guarding by the male partner. In many crustaceans, mating occurs in the fresh moult stage when the female is receptive to males. Hence a new behavioural trait, namely pre-copulatory mate guarding by the males has evolved as a physiological necessity. Interestingly, in the sponge-dwelling snapping shrimp Synalpheus, social monogamy has given origin to advanced social systems, such as eusociality. Among other invertebrates, reproductive division of labour and cooperative care of young, resulting in eusocial condition has been well-defined only in social insects like honey bees and termite ants.
How does mating affect sexual selection?
Mating systems determine the skew in mating success among individuals and, hence, the strength of sexual selection. If the mating system is adaptive, this skew ensures that individuals best adapted to local environmental conditions reproduce and pass on their genes to the following generation, which is important for ensuring a viable population. However, if changes to the mating system distort the correlation between mating success and individual quality, then population viability may be endangered. For instance, as we already have discussed, environmental changes that interfere with animal communication – and the efficacy of sexual signals – can prevent individuals from making adaptive mate choice decisions and result in the production of fewer offspring or those that are less well adapted to the environment.
What is the classification of mating systems?
Mating system classification differs between plants and animals. In animals, the classification is based on how many mates can be monopolized, how mates are acquired, characteristics of a pair bond, and patterns of parental care (Table 2; Emlen and Oring, 1977 ). In plants, the classification of the mating system is based on the amount of selfing and inbreeding depression ( Table 3; Sakai and Westneat, 2001 ).
How does environmental change affect mating systems?
Changes in mating systems – because of environmental change – can consequently alter the demography and genetic-make up of populations. This can have serious consequences for the viability and persistence of populations, and, ultimately, for the structure and function of ecosystems.
What are the mating systems of mammals?
Mating systems are a critical part of the life history of all animals, including mammals. Across 21 orders of Mammalia, the patterns for mating are highly varied, both within and between orders. The major mating types are polygyny, polyandry, and promiscuity, each having several subcategories.
Why is polygamy out of place?
The most important reason that polygamy is out of place in the modern world is that it works best in agricultural societies where children contributeto farm labor and care of livestock (4).
Why do birds have polygyny?
There are three basic reasons for polygyny in birds. First, there may be a scarcity of adult males. Second, some males may have much better genes than others which is particularly important for populations where there is a heavy load of diseases and parasites to which resistance is genetically heritable.
Why do developed countries hate polygamy?
Why the developed world hates polygamy. At least three factors are critical. First, instead of a scarcity of males, developed countries have an excess, thanks to better public health that saves more males than females.
Why do humans marry multiple birds?
So humans turn to multiple marriage for the same three basic reasons that birds do (scarcity of males, selection for disease-resistant genes, and defense of breeding territory and its economic equivalents.)
Which president's father was a polygamist?
Both candidates for the presidency owe their very existenceto polygamy (1). President Obama ’s father belonged to the polygamous Luo tribe. Mitt Romney’s paternal great grandfathers moved to Mexico to continue the Mormon practice of polygamy then outlawed in the U.S. So the time is ripe to ask what advantages polygamy has over monogamy.
Did Romney's Mormon ancestors practice polygamy?
Romney’s Mormon ancestors practiced polygamy but it was mainly confined to members of the church hierarchy who were wealthier than others in terms of land holdings and could maintain multiple households (bird reason number three). Obama’s Luo ancestors likely practiced polygamy for all three bird reasons.
Does multiple marriage have anything to do with poverty?
Contrary to popular assumptions, multiple marriage had nothing to do with poverty, backwardness, or oppression of women (e.g., acceptance of wife-beating) in my study. Of course, that begs the question as to why polygamy survives mostly in underdeveloped countries close to the equator and why it is so unpopular in developed countries(4, see map.)
What is mating system?
A mating system describes how males and females pair when choosing a mate. Males and females differ greatly in the investment each makes to reproduce, and may therefore approach mating with differing strategies. To study these differences, scientists observe mating systems and describe how males and females come together.
Why do cichlids have multiple matings?
Criticisms of Bateman's theory focus on the generality of the predictions. Contrary to the predictions of Bateman's principle, there are several possible advantages to female multiple matings. The female cichlid fish Pseudotropheus spiliopterusmates with any male they meet because they have a high risk of getting predated and a small population. This often leads to multiple matings by a single female (Kellogg et al.1998). Mating with any male that is seen ensures that these cichlids have a chance at producing offspring. The female Malawi blue cichlid has a high population but still participates in multiple matings. In this case multiple matings occur to avoid inbreeding and increase genetic diversity among the offspring (Kellogg et al. 1998). Additionally, multiple matings by females may increase the likelihood that they will find a compatible mate, one that is not sterile, or even help prevent infanticide.
Why is mate choice important?
The importance of male mate choice is controversial. Older theory predicts that male mate choice should be less common in animals. However it plays an important role in many mating systems, and the cost of mating for males may have been underestimated in earlier studies. Male mate choice occurs most often when males are substantially involved in caring for their offspring, or when there is great variation in the quality of the females as mates within a population. If males are choosy about their mate, then over time females may evolve ornamentation or coloration that is subject to sexual selection.
How does Bateman's principle help animals?
A key element of the study of mating systems is understanding how many mates an animal has in its lifetime. Bateman's principlehelps to make predictions about mating success and number of mates. Bateman's principle postulates that varianceamong females in mating success is low, whereas variance among males in mating success is high. This stems from the fact that one mating in females should be enough to fertilize all their eggs whereas in males reproductive success is based on the number of times they have mated. In other words, nearly all females in a population mate and have offspring, but relatively few males mate successfully (Figure 2). Those males that do mate tend to mate with many females-thus a few males have very high reproductive output, but many males have little or no reproductive output (Bateman 1948). This leads to the prediction that sexual selection should act more strongly on males, leading to greater elaboration of behavior and structures used in attracting mates in males than in females.
How do animals transfer their genes to the next generation?
To transfer their genes to the next generation successfully, animals need to choose a suitable mate. Failure to do so leads to low or no reproductive success — that is, poor fitness. But reproductive success can also hinge on the number of mates, and on social interactions that extend beyond mating. By classifying social interactions, scientists have been able to identify different types of mating systems, such as monogamy and polygyny. The mating systems described in this article represent a variety of strategies to achieve reproductive success. The diversity of mating systems in animals is a fascinating example of the incredible variety of solutions that a complex evolutionary problem can yield.
What is the process of creating allelic variation in offspring by exchanging DNA?
genetic recombination: The process of creating allelic variation in offspring by exchanging DNA; typically happens during sexual reproduction.
Why do aphids reproduce sexually?
When the environment is going to turn cold, most species of aphids reproduce sexually, because sexual reproduction produces eggs that are freeze tolerant and can diapause during the winter (Simon et al. 2002). Genetic diversity may also lead to evolved defenses against parasites and disease.

Overview
In animals
The following are some of the mating systems generally recognized in animals:
• Monogamy: One male and one female have an exclusive mating relationship. The term "pair bonding" often implies this. This is associated with one-male, one-female group compositions. There are two types of monogamy: type 1, which is facultative, and type 2, which is obligate. Facultative monogamy occu…
In plants
The primary mating systems in plants are outcrossing (cross-fertilisation), autogamy (self-fertilisation) and apomixis (asexual reproduction without fertilization, but only when arising by modification of sexual function). Mixed mating systems, in which plants use two or even all three mating systems, are not uncommon.
A number of models have been used to describe the parameters of plant mating systems. The b…
In microorganisms
Mating in bacteria involves transfer of DNA from one cell to another and incorporation of the transferred DNA into the recipient bacteria's genome by homologous recombination. Transfer of DNA between bacterial cells can occur in three main ways. First, a bacterium can take up exogenous DNA released into the intervening medium from another bacterium by a process called transformation. DNA can also be transferred from one bacterium to another by the process of tra…
In arthropods
Fruit flies like A. suspensa have demonstrated polygamy. The males often attract females through marking where they will perch and release air-borne pheromones from the tip of their abdomen to mark and defend individual leaves.
See also
• Heterosexuality
• Assortative mating
• r/K selection theory
• Monocotyledon reproduction
• Sexual reproduction
Further reading
• Marlowe, F.W. (2003). "The Mating System of Foragers in the Standard Cross-Cultural Sample" (PDF). Cross-Cultural Research. 37 (3): 282–306. doi:10.1177/1069397103254008. S2CID 145482562. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-09-01.