
A positive Lachman test or pivot test is strong evidence of an existing anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, and a negative Lachman test is fairly good evidence against that injury. Although widely used, the anterior drawer is the least helpful maneuver for diagnosing an ACL tear.
What does a positive Lachman test mean?
The movement is a combination of axial load and valgus force, applied by the examiner, during a knee flexion from an extended position. When the test is positive, it indicates an injury of the anterior cruciate ligament.
What is a normal Lachman test?
This test is done by bending the hip 45 degrees and the knee 90 degrees, then pulling the knee forward with a sudden jerk to test the leg's range of motion. If it moves 6 mm beyond its normal range of motion, then you may have an ACL tear or injury.
How is the Lachman test graded?
Grading of Lachman Test Grade 1 (mild): 3-5 mm more translation of the tibia on the femur. Grade 2 (moderate): 5-10 mm more translation of the tibia on the femur. Grade 3 (severe): >10 mm more translation of the tibia on the femur.
What is a positive drawer test?
This test is done on your uninjured knee first to compare and check for differences. If the tibia, or shinbone, has more movement, or if the ligament is loose compared with the other knee, the anterior drawer test is considered to be positive.
How do you tell if ACL is torn or sprained?
Signs and symptoms of an ACL injury usually include:A loud "popping" in the knee.Severe pain.Rapid swelling.Loss of range of motion.Knee instability where the knee feels like it will buckle and cannot support the weight.
How can u tell if u tore your ACL?
When you've torn your ACL you will lose a range of motion. Try bending your knee and then straightening it out. If you can't bend your knee to a 90 degree angle or straighten out your leg because of pain, stiffness and swelling, then it is likely that you've torn your ACL. Set an appointment with your doctor.
Do all ACL tears require surgery?
While complete ACL tears almost always require surgery, partial ACL tears may be treated effectively with nonsurgical methods. ACL tears are graded by severity and are called sprains (a sprain is a stretch or tear in a ligament). A grade 1 ACL sprain occurs when your ACL is overstretched, but not torn.
What is the difference between an ACL rupture and tear?
An ACL injury may be diagnosed when the ligament is overstretched or torn. The tear may be partial or complete; a complete tear of the ACL is also known as an ACL rupture.
Can you walk on a torn ACL?
Can you walk with a torn ACL? The short answer is yes. After the pain and swelling subsides and if there is no other injury to your knee, you may be able to walk in straight lines, go up and down stairs and even potentially jog in a straight line.
What is the difference between Lachman and anterior drawer test?
Lachman's test is more sensitive than is the anterior drawer sign. One reason may be that it is difficult for the patient to contract his hamstrings and thus prevent forward sliding of the tibia when the knee is in only 20 degrees - 30 degrees of flexion.
Is the Lachman test accurate?
Conclusion. The prone Lachman test is a reliable evaluation technique that can be used to confirm the presence of an ACL tear; however, the test should not be used as the sole criterion to rule out the presence of the injury.
How do you know if you have a PCL tear?
People with PCL injuries may experience a wide range of symptoms, including: Pain that worsens over time. Swelling and inflammation. A feeling of instability in the knee.
What does a negative Lachman test mean?
This review by Scholten et al suggests that during the physical examination of the knee, a negative Lachman test would indicate no anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, whereas a positive pivot shift test would indicate an ACL tear.
What is a Lachman test of knee?
The Lachman test is a physical examination maneuver used to assess the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament in a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test is used to evaluate the anterior translation of the tibia in relation to the femur and is considered a variant of the anterior drawer test.
What is the difference between an ACL rupture and tear?
An ACL injury may be diagnosed when the ligament is overstretched or torn. The tear may be partial or complete; a complete tear of the ACL is also known as an ACL rupture.
What are the 2 most popular tests for the ACL?
The anterior Lachman test, anterior drawer test and the pivot shift test, which are summarised in Table 1, are the most commonly known physical tests used to assess the integrity of the ACL (Benjaminse 2006; Leblanc 2015; Malanga 2003; Scholten 2003; Solomon 2001).
What is the function of the ACL?
The primary function of the ACL is to control anterior movement of the tibia and inhibit extreme ranges of tibial rotation. The ACL consists of 2 major bundles; the posterolateral bundle and the anteromedial bundle, which are named based on their tibial insertion. The bundles originate on the posteromedial side of the lateral femoral condyle and insert just anterior to the intercondylar tibial eminence. The Lachman test directly assesses the integrity of this anatomical relation. [2]
How to diagnose anterior cruciate ligament tear?
Diagnosis of an anterior cruciate ligament tear is definitively made by diagnostic imaging (MRI) or knee arthroscopy, but most often, the patient's history and physical presentation can reliably establish the diagnosis. Suggestive clinical findings of an ACL rupture include an acute knee effusion with positive Lachman, pivot shift, and/or anterior drawer tests. [4]
What is the Lachman test?
The Lachman test is a physical examination maneuver used to assess the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament in a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test is used to evaluate the anterior translation of the tibia in relation to the femur and is considered a variant of the anterior drawer test. Multiple studies have shown that the Lachman test is the most sensitive and specific in the diagnosis of acute ACL tears, and generally superior to both the anterior drawer test and the pivot shift test.[1]
What is physical examination?
Physical examination includes inspection, palpation, testing of mobility, strength, and stability, and performance of special tests of ACL integrity. One should always examine the unaffected knee for comparison as patients have a baseline increased laxity with Lachman testing that is not due to injury. It is often best to examine the patient immediately after the injury or at least within several hours for a suspected ACL injury to avoid evaluating a knee with significant swelling and hemarthrosis, which may lead to patient guarding and negatively impact testing accuracy. [3][4]
What causes knee to pop?
The clinician should ask about the timing of the injury, the mechanism, joint swelling, functional ability, joint instability, and associated injuries while performing an appropriate history and physical exam in a patient with a suspected ACL injury. Non-contact injuries most commonly cause ACL tears, and historical cues prompting an ACL evaluation include a sudden change of direction or awkward landing, causing the knee to "pop" or give way, resulting in knee pain, swelling or instability.
What is considered a positive endpoint?
The test is considered positive if there is excessive anterior translation of the proximal tibia greater than the uninjured side and also a lack of a firm endpoint. Endpoints are graded from “hard” to “soft,” and have been nominally classified as A (firm, hard endpoint) or B (absent, soft endpoint).[6] A hard endpoint is appreciated when there is an abrupt endpoint preventing further anterior translation of the tibia on the femur. A soft endpoint is regarded as a forward translation of the tibia without a distinct, firm, clear endpoint. [5]
Which is better, Lachman's or pivot shift?
The anterior drawer test has a sensitivity of 48% and a specificity of 93%. The pivot shift test has a sensitivity of 61% and a specificity of 97% and has the highest positive predictive value of the 3 tests.[5] Results have suggested that the pivot shift test has a lower sensitivity than the Lachman test because it is generally a harder test to perform in the acute setting due to patient guarding. [9]
What does a positive Lachman Test mean?
The Lachman Test is positive if there is excessive anterior translation of the proximal tibia greater than the uninjured side and also a lack of a firm endpoint indicating an anterior cruciate ligament injury.
What does a hard end point mean in a cruciate ligament?
The motion must have a soft end point. Any hard end point suggests a certain stability of the anterior cruciate. Where this occurs within 3 mm , it suggests complete stability; where it only occurs after 5 mm , it suggests relative stability with previous elongation of the anterior cruciate.
What is the insufficiency of the anterior cruciate ligament?
Insufficiency of the anterior cruciate ligament is therefore particularly evident in this position of the joint as it approaches extension due to the occurrence of lateral subluxation of the proximal tibia (pivoting).
What is the Lachman test?
Lachman Test (or Noulis Test) is used to assess the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) of the knee. It’s certain proof of anterior cruciate ligament insufficiency.
How to exclude posterior cruciate lesion?
Where the end point is hard, a posterior cruciate lesion must be excluded by testing the spontaneous posterior drawer and applying the active tests.
How does a supine patient extend their leg?
The examiner asks the supine patient to extend the leg in such a way as to lift the foot o the examining table. During this maneuver, the examiner keeps his or her eyes on the knee the better to discern the contours of the tibial tuberosity and patellar ligament. The examiner achieves slight passive flexion in the knee by passing one hand beneath the thigh of the patient’s affected leg and resting it on the contralateral knee. The effect of the quadriceps is increased by immobilizing the foot on the examining table.
Which ligament is more or less taut?
First, all parts of the anterior cruciate ligament are more or less equally taut.
What is the purpose of the Lachman test?
The test is designed to assess single and sagittal plane instability.
How accurate is the Lachman test?
Katz and Fingeroth reported that the Lachman test has a diagnostic accuracy of acute ACL ruptures (within 2 weeks of examination) of 77.7% sensitivity and > 95% specificity. This study reported the diagnostic accuracy of subacute/chronic ACL ruptures (more than 2 weeks before examination) as having an 84.6% sensitivity and >95% specificity. It is important to note that in this study all examinations were performed under anesthesia, and therefore the diagnostic accuracy in physiotherapy clinical practice may be less.
How to perform a stable Lachman test?
The Stable Lachman test is recommended for examiners with small hands. The patient lies supine with the knee resting on the examiner’s knee. One of the examiner’s hands stabilizes the femur against the examiner’s thigh, and the other hand applies anterior stress. Adler and associates described a modification of this method, which they called the “drop leg Lachman test.” The patient lies supine. The test leg is abducted off the side of the examining table, and the knee is flexed to 25°. One of the examiner’s hands stabilizes the femur against the table while the patient’s foot is held between the examiner’s knees. The examiner’s other hand then is free to apply the anterior translation force. These researchers found that greater anterior laxity was demonstrated by this version of the test than by the classic version. The two legs are compared.
What test is used to diagnose ACL rupture?
Other special tests with the purpose of diagnosing ruptures of the ACL by testing its integrity include the knee anterior drawer test and the pivot shift test.
Where should the examiner place his hand?
The examiner should place one hand behind the tibia and the other on the patient's thigh. It is important that the examiner's thumb be on the tibial tuberosity. On pulling the tibia anteriorly, an intact ACL should prevent forward translational movement of the tibia on the femur ("firm end-feel").
Which aspect of the tibia should be applied to achieve the best results?
Frank reported that to achieve the best results, the tibia should be slightly laterally rotated and the anterior tibial translation force should be applied from the posteromedial aspect. The hand on the tibia should apply the translation force.
When to assess laxity of joint?
The best time to assess joint laxity is immediately after the injury, before swelling occurs, or in the chronic state. The examiner may need to allow time for swelling to reduce before true joint mobility can be assessed.
What is a positive Lachman’s test?
A positive Lachman test indicates a torn ACL.
What is Lachman Test?
The Lachman test is used to check for an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear or injury in the knee joint. It is considered the most sensitive and specific test for diagnosing acute ACL injuries.
What is the knee flexed to in a Lachman test?
In Lachman test only the knee joint is involved as the knee is bent into 20 to 30 degrees of flexion. In anterior drawer test both the knee and hip joint are involved. As the hip is flexed to 45° and the knee is flexed to 90°. The examiner grasps the patient’s lower thigh (femur) with one hand to stabilize the femur.
Which is better, Lachman or anterior drawer?
Jonsson et al. concluded that in analyzing an acutely injured knee in an individual without anaesthesia, the Lachman test was superior to the anterior drawer test. However, in chronic conditions, both the evaluations had higher diagnostic accuracy.
Can a Lachman test be performed on an ACL tear?
But both the Lachman and anterior drawer test are performed one by one, as this will help confirm the diagnosis of an ACL tear.
Is the Lachman test as reliable as the knee anterior drawer test?
There are also many other special tests like the knee anterior drawer test and pivot shift test. They are also used to diagnose ACL injury or tear, but they are not as reliable as the Lachman test. Hence, it is considered superior to both the anterior drawer test and pivot shift test.
When to do a false positive test?
This can give you a false positive test in the end. The best time to conduct the test is immediately after the injury before swelling occurs or in the chronic state. If the swelling has occurred, the examiner should wait for the swelling to go down and then conduct the test.
What is the Lachman Test of the Knee?
The Lachman Test is commonly used in orthopedic examinations to test for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) integrity. The test primarily targets the posterolateral bundle of the ligament. It tests one-plane anterior stability and is one of the most well known and most used special tests.
What does it mean when the ACL is soft?
A soft end feel / endpoint is indicative of secondary structures stopping the continued anterior translation of the tibia. Excessive anterior translation may also be noted. A hard/firm end feel will be felt when the ACL is intact and abruptly halts continued anterior translation.
How many degrees should a knee be flexed?
The knee to be tested should be flexed to about 20 degrees. One of the examiners hands holds and stabilizes the distal femur of the leg to be tested. The examiners other hand firmly grasps the proximal tibia of the same leg.
Is the Lachman test accurate?
The Lachman Test is quite accurate but should not be used as the only criterion for ruling in or out AC L integrity . Of the ACL integrity tests, it is widely considered to be the most sensitive.
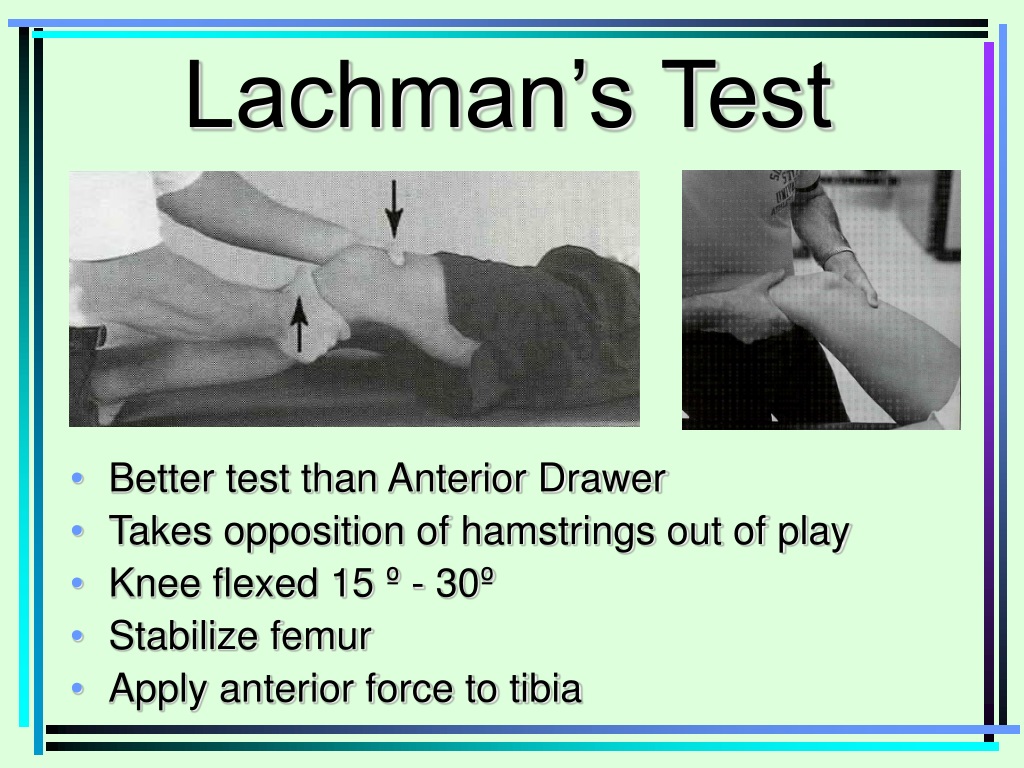
How Do You Perform The Lachman’s Test?
What Does A Positive Lachman Test Mean?
- The Lachman Test is positive if there is excessive anterior translation of the proximal tibia greater than the uninjured side and also a lack of a firm endpoint indicating an anterior cruciate ligament injury. The end point of motion must be soft and gradual without a hard stop; any hard stop suggests a degree of stability of the anterior cruciate ...
Lachman Test Modifications
- 1. Prone Lachman Test:
Prone Lachman Test is another special test for ACL injury. The patient is prone. The examiner grasps the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia and immobilizes the patient’s leg in his or her own axilla. With the other hand, the examiner grasps the distal femur immediately proximal to the pat… - 2. Stable Lachman Test:
The patient is supine. The examiner places the patient’s thigh over his or her ow n thigh. This holds the patient’s leg in constant flexion that the patient cannot change. With the distal hand, the examiner pulls the tibia anteriorly while the other hand immobilizes the patient’s thigh on the exa…
Notes
- A false-negative Lachman test may occur in these situations: 1. The femur is not properly stabilized. 2. Meniscus lesion or degenerative changes such as osteophytes on the intercondylar eminence block translation. 3. The tibia is medially rotated. 4. A significant hemarthrosis. 5. Protective hamstring spasm. 6. Tear of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. In a concurre…
Accuracy
- The accuracy and reliability of the anterior cruciate ligament test appears to vary. Katz et al. found that in the hands of an experienced clinician, accuracy of this test was 1: 1. Sensitivity: 81.8 % 2. Specificity: 96.8 % The sensitivity and specificity of the Lachman test knee increases to 100% if the patient was anesthetized 2.
Reference
- Katz JW, Fingeroth RJ. The diagnostic accuracy of ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament comparing the Lachman test, the anterior drawer sign, and the pivot shift test in acute and chronic knee...
- DeHaven KE. Arthroscopy in the diagnosis and management of the anterior cruciate ligament deficient knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983 Jan-Feb;(172):52-6. PMID: 6822005.
- Katz JW, Fingeroth RJ. The diagnostic accuracy of ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament comparing the Lachman test, the anterior drawer sign, and the pivot shift test in acute and chronic knee...
- DeHaven KE. Arthroscopy in the diagnosis and management of the anterior cruciate ligament deficient knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983 Jan-Feb;(172):52-6. PMID: 6822005.
- Jonsson T, Althoff B, Peterson L, Renström P. Clinical diagnosis of ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament: a comparative study of the Lachman test and the anterior drawer sign. Am J Sports Med...
- Larson RL. Physical examination in the diagnosis of rotatory instability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983 Jan-Feb;(172):38-44. PMID: 6822003.
Purpose
Technique
- Lie the patient supine on the bed. Place the patient's knee in about 20-30 degrees flexion. According to Bates' Guide to Physical Examination, the leg should also be externally rotated slightly. The examiner should place one hand behind the tibia and the other on the patient's thigh. It is important that the examiner's thumb be on the tibial tuberosity. On pulling the tibia anteriorly…
Technique Modification
- The Stable Lachman test is recommended for examiners with small hands. The patient lies supine with the knee resting on the examiner’s knee. One of the examiner’s hands stabilizes the femur against the examiner’s thigh, and the other hand applies anteriorstress.Adler and associates described a modification of this method, which they called the “drop leg Lachman test.” The pati…
Evidence
- Katz and Fingeroth reported that the Lachman test has a diagnostic accuracy of acute ACL ruptures (within 2 weeks of examination) of 77.7% sensitivity and >95% specificity. This study reported the diagnostic accuracy of subacute/chronic ACL ruptures (more than 2 weeks before examination) as having an 84.6% sensitivity and >95% specificity. It is important to note that in t…
Clinical Notes
- Frank reported that to achieve the best results, the tibia should be slightly laterally rotated and the anterior tibial translation force should be applied from the posteromedial aspect. The hand on the tibia should apply the translation force. With acute trauma, swelling prevents the examiner from getting a true indication of the joint’s mobility. The best time to assess joint laxity is immediatel…