What is meant by pressure gradient?
Definition of pressure gradient : the space rate of variation of pressure in a given direction specifically : such rate of variation in a direction normal to an isobar.
What is pressure gradient in anatomy and physiology?
In order for blood to flow through a vessel or across a heart valve, there must be a force propelling the blood. This force is the difference in blood pressure (i.e., pressure gradient) across the vessel length or across the valve (P1-P2 in the figure to the right).
What is a pressure gradient in the heart?
The valve gradient is the difference in pressure on each side of the valve. When a valve is narrowed (a condition called stenosis), the pressure on the front of the valve builds up as blood is forced through the narrow opening. This causes a larger pressure difference between the front and back of the valve.
What is meant by steep pressure gradient?
A steep pressure gradient is when the pressure changes very rapidly and significantly between two areas. For example, if a low-pressure front is moving in, the area right at the edge of the low-pressure front is likely to have a steep pressure gradient because the pressure is dropping quickly as the front moves in.
How does pressure gradient affect blood flow?
Like all fluids, blood flows from a high pressure area to a region with lower pressure. Blood flows in the same direction as the decreasing pressure gradient: arteries to capillaries to veins. The rate, or velocity, of blood flow varies inversely with the total cross-sectional area of the blood vessels.
Where does a pressure gradient occur?
The pressure gradient force is the force produced when air with different pressures are placed next to each other. Pressure differences occur in the atmosphere due to differences in the density of air. Warm air is less dense than cold air. The height of the atmosphere (thickness) is higher when the air is warm.
What is pressure gradient in mitral valve?
The normal area of the mitral valve orifice is about 4–6 cm2 when the mitral valve area goes below 2 cm2, the valve causes an impediment to the flow of blood into the left ventricle, creating a pressure gradient across the mitral valve. This gradient may increase by the rise in heart rate or cardiac output.
What is the relationship between blood flow and a pressure gradient quizlet?
Blood flow is directly proportional to the pressure gradient. Blood flow is inversely proportional to resistance. Increase in cross-sectional area causes the velocity of blood flow to to decrease.
How does a pressure gradient force work?
The change in pressure measured across a given distance is called a "pressure gradient". The pressure gradient results in a net force that is directed from high to low pressure and this force is called the "pressure gradient force". The pressure gradient force is responsible for triggering the initial movement of air.
What is a pressure gradient quizlet?
pressure gradient. the difference between high and low pressure areas. strongest winds. in areas where the pressure gradient is the greatest.
What is the gradient in simple terms?
b : a part sloping upward or downward. 2 : change in the value of a quantity (such as temperature, pressure, or concentration) with change in a given variable and especially per unit distance in a specified direction.
How do you find the pressure gradient?
The pressure gradient can be determined mathematically by taking the difference in pressure between two locations (in Pascals) and dividing it by the distance between the two locations (in meters).
What is a pressure gradient quizlet?
pressure gradient. the difference between high and low pressure areas. strongest winds. in areas where the pressure gradient is the greatest.
What causes pressure gradient?
Warm air is less dense and has a lower barometric pressure than the cold air at high latitudes. These differences in barometric pressure are what create the pressure gradient force and wind as air constantly moves between areas of high and low pressure.
What is pressure gradient in mitral valve?
The normal area of the mitral valve orifice is about 4–6 cm2 when the mitral valve area goes below 2 cm2, the valve causes an impediment to the flow of blood into the left ventricle, creating a pressure gradient across the mitral valve. This gradient may increase by the rise in heart rate or cardiac output.
How is pressure gradient formed?
Pressure gradient force, is the force produced by differences in barometric pressure between two regions and is responsible for the flow of air from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure.
What is an example of a pressure gradient?
The most consistent pressure gradient in Earth's atmosphere is the decrease in air pressure that occurs as altitude increases. This pressure gradie...
What causes pressure gradient?
Pressure gradients have many causes. But within Earth's atmosphere, most pressure gradients are caused by uneven heating of Earth's surface.
What is the pressure gradient formula?
The most common form of the pressure gradient formula is PG = PD/D. In this formula, the variable PG stands for pressure gradient, PD stands for pr...
What Is a Pressure Gradient?
The pressure gradient is a way to describe the difference in atmospheric pressure from one location to another. You can think of this as how much the air pressure (at a particular height, or level, in the atmosphere) changes as you travel from one specific location to another. The greater the difference in pressure between the two locations, the greater the pressure gradient.
How to tell the position of a pressure gradient?
Because of this, you can often tell the position of the pressure gradient simply by considering the current wind direction. Wind is created by the movement of air parcels from regions of high pressure to regions of low pressure.
Why is the pressure gradient always positive?
Because the pressure gradient flow is always from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, the resulting pressure gradient is always said to be positive, since a larger number minus a smaller number would not produce a negative number (and distance, in the denominator, is never negative). Lesson Summary.
What does a gradient mean in art?
Gradients. Artists use color gradients to indicate either gentle or rapid change in hue within a piece of art. The atmospheric pressure gradient can be thought of in much the same way. You can have steep pressure gradients (with rapid changes over a given distance), or gentle pressure gradients (with less substantial changes over a given distance). ...
What unit is used to measure pressure?
Regardless of the device being used, the pressure is typically measured using the official SI unit of pressure, Pascals (Pa). Your local television weather forecast may use millibars, but the scientific community generally uses Pascals for discussing pressure. The Formula.
What is pressure measured with?
Pressure is measured with a device called a barometer that's either located at surface level or sent aloft using a radiosonde. Radiosondes are collections of meteorological instruments sent aloft in weather balloons to collect scientific data.
Which pressure gradient is more substantial?
Vertical pressure gradients are considered more substantial in terms of atmospheric lifting and instability. Surface-level winds and large, regional-scale airflow are more often analyzed in a horizontal sense.
Where is the interstitial pressure gradient measured?
Interstitial liquid pressure gradients have been measured from the alveolar wall to the lung hilum194-196 ( Fig. 6-11 ), and these pressure gradients from the alveoli to hilar interstitial space form the basis for interstitial drainage of the liquid filtered across the microvessels. The filtered fluid moves along the interstitial fluid pressure gradient into the connective tissue surrounding the pulmonary artery, airways, and veins. 176 When fluid filtration exceeds the pumping capacity of the lymphatic system, fluid first accumulates in the hilar regions and in sheaths around the large pulmonary vessels, 201 where pressure is lowest and interstitial compliance is highest. This accounts for the “cuffs” of fluid typically observed around vessels in edematous lungs and that are often visible near the hila in chest radiographs.
Why are pressure gradients fallacious?
However, interpretation of pressure gradients may be fallacious because of high variability in healthy subjects; variation with position, hydration, degree of collateralization, and overlap in values between normal and symptomatic patients .
What are the factors that determine the subdiaphragmatic venous return?
The pressure gradients of the trunk (Fig. 2.21) are fundamental factors in subdiaphragmatic venous return. Whereas the veins of the lower extremities are endowed with valves, vessels above the inguinal ligament, such as the iliac vessels and the inferior vena cava are no longer equipped with these devices.
What causes a pressure gradient in the superior sagittal sinus?
A pressure gradient between the superior sagittal sinus and the internal jugular vein was first noted in 1995 raising the possibility that IIH is caused by venous hypertension secondary to compression of the transverse sinus. This theory is consistent with the observation that stenosis of the transverse sinus can be seen in up to 90% patients with IIH. Support also comes from those patients who are cured by the insertion of a stent into the venous sinus (see below). It may be that venous sinus stenosis perpetuates IIH once it has been triggered by another mechanism.
What is the normal pressure gradient for a venogram?
A venous pressure gradient of 2 to 14 mm Hg between the hilar LRV and the IVC during venography has been considered the gold standard for diagnosis, the normal being 0 to 1 mm Hg. Venography also demonstrates narrowing, collaterals, and the nature of venous reflux in the left gonadal vein, as well as direction of flow across the narrowed segment of LRV (Fig. 22.5 ). However, interpretation of pressure gradients may be fallacious because of high variability in healthy subjects; variation with position, hydration, degree of collateralization, and overlap in values between normal and symptomatic patients. Conversely, postoperative symptom resolution has been reported with no change in pressure gradients. 12 Thus radiographic evidence alone is not sufficient to prompt invasive treatment because imaging criteria do not necessarily correlate with symptomatology. 12
What is the oesophageal pressure used to indicate?
Otherwise, the oesophageal pressure may be used to indicate the pleural pressure , but there are conceptual and technical difficulties.
What is the pressure gradient created by the RPF and resistance in the vessel?
A pressure gradient created by the RPF and resistance in the vessel drives filtration from the vascular space into the renal tubules.
Where is the pressure gradient in vacuum?
There is a pressure gradient between the bottom and the top of the log during the vacuum state.
Why does extracranial blood leak back to the epidural space?
proposed another theory that it may be due to an increased epicranial subgaleal interstitial pressure after injury, in which extracranial blood could leak to epidural space through a fracture due to a pressure gradient. When interstitial subgaleal pressure decreased, blood leaks back.
Is interpolation for maximum mean pressure mixed?
Although the effects are mixed, with less extreme effects of linear interpolation for maximum and mean pressure and more extreme effects of linear interpolation for pressure gradient (hypothesis 3), in all cases, the relative effect was small.
Does exercise hemodynamics show a lower mean pressure gradient?
The exercise hemodynamics in our patients showed a lower mean pressure gradient by labeled valve size than patients with bioprosthetic valves in other studies.
What is the pressure gradient?
In atmospheric science, the pressure gradient (typically of air but more generally of any fluid) is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure increases the most rapidly around a particular location. The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pascals per metre (Pa/m).
What is the horizontal pressure gradient?
The horizontal pressure gradient is a two-dimensional vector resulting from the projection of the pressure gradient onto a local horizontal plane. Near the Earth's surface, this horizontal pressure gradient ...
What is the pressure gradient in the troposphere?
Within planetary atmospheres (including the Earth's ), the pressure gradient is a vector pointing roughly downwards , because the pressure changes most rapidly vertically, increasing downwards (see vertical pressure variation ). The value of the strength (or norm) of the pressure gradient in the troposphere is typically of the order of 9 Pa/m ...
What is the main force acting on the air to make it move as wind?
As indicated above, the pressure gradient constitutes one of the main forces acting on the air to make it move as wind. Note that the pressure gradient force points from high towards low pressure zones. It is thus oriented in the opposite direction from the pressure gradient itself.
How much pressure does a gradient of 0.425 psi/ft at 2000 ft.?
From the previous example, a gradient of 0.425 psi/ft at 2000 ft. resulted in 850 psi pressure.
How to find pressure at a given depth?
To find a pressure at a given depth, simply multiply the VERTICAL depth by the given fluid gradient.
What happens when fluid doesn't reach surface?
If the fluid doesn’t reach the surface, then there is some ‘fluid level’, or depth, where the pressure is zero and then the pressure increases according to the gradient.
What is the density of pure water?
The density of pure water is 1000 kg/m3. To convert to gradient:
Can we calculate the equivalent fluid column if we know the pressure and the gradient?
Similarly, if we know the pressure and the gradient, we can calculate the equivalent fluid column resulting from that pressure.
The Bernoulli principle and pressure gradients using Doppler measurements
Continuous wave Doppler and pulsed wave Doppler can measure the velocity of erythrocytes as they travel through the heart and vessels. The velocity of erythrocytes ( i.e blood) can be used to estimate pressure gradients (pressure differences) between the atria, ventricles, and connecting vessels.
Disadvantages of the Bernoulli equation
The Bernoulli equation is highly dependent on the precision of the Doppler measurement. The Doppler beam must be parallel to the direction of the blood flow (refer to The Doppler Equation ). Any angle error between the Doppler beam and the blood flow will result in an underestimation of the velocity.
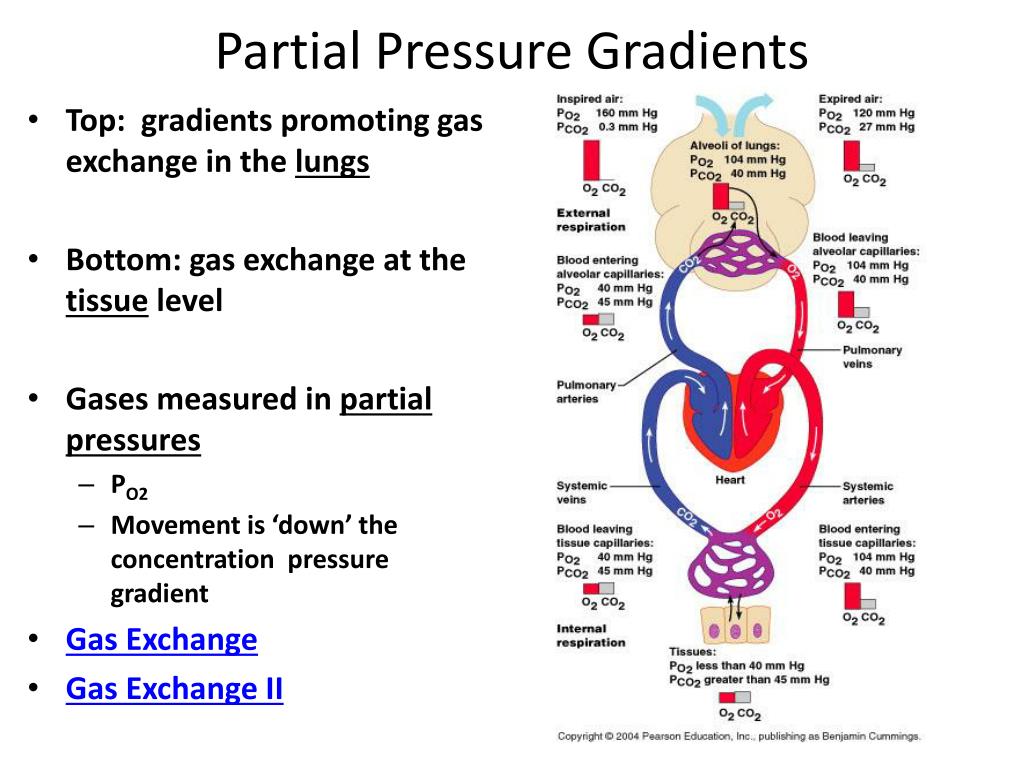
partial pressure gradient Definition
The difference in the concentration of a gas in the mixture of gases, in which the gas has higher pressure in one site and lower pressure in another site is termed as partial pressure gradient.
Overview of Partial Pressure Gradient
The relative proportion of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases do not differ from their proportion at the sea level and high altitude. The molecules of gases are in continuous random motion and exert pressure. The pressure of a gas depends on the temperature and the concentration of gases.
The Partial pressure of gases
Dalton’s Law states that the pressure exerted by each gas in the mixture is independent of the pressure exerted by the other gases in the mixture of gases. The total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of all individual pressures in a mixture of gases, also termed as partial pressures.
External Respiration
The two gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide are most important physiologically. They are important in both inhalation and exhalation. The partial pressure allows the processes of external and internal respiration and enables them to diffuse independently of one another.
Internal Respiration
The exchange of gases between capillaries in the body and blood cells is called internal respiration. The internal respiration includes the movement of oxygen to the interstitial fluid and on to cells from the capillaries and diffusion of carbon dioxide from the cells into the interstitial fluid and onward into the capillaries.