Key Terms
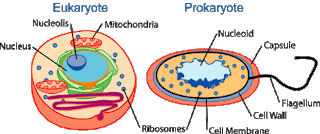
- eukaryotic: Having complex cells in which the genetic material is organized into membrane-bound nuclei.
- prokaryotic: Of cells, lacking a nucleus.
- nucleoid: the irregularly-shaped region within a prokaryote cell where the genetic material is localized
Full Answer
What is the comparison between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Aug 16, 2017 · In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent, moreover, membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells. Other major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are that prokaryotic cells are exclusively unicellular, while the same does not apply to eukaryotic cells.
What types of organisms have prokaryotic cells?
Mar 29, 2022 · Prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelle. Eukaryotic Cell vs. Prokaryotic Cell. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell …
What are five characteristics of prokaryotes?
Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and organelles bound by plasma membranes. Fungi, plants, and animals are made of eukaryotic cells (eukaryotes). Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus or organelles. All bacteria and members of Archaea are made of prokaryotic cells (prokaryotes). Table of Contents
What structures are found within prokaryotic cells?
A eukaryotic cell is a cell that has membrane bound organelles and a nucleus which houses the genetic material. A prokaryotic cell is a cell that does not possess any membrane bound organelles and its genetic material is found floating freely within its cell wall. Also Read: Eukaryotic Cells- Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples

What is a Prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a primitive type of cell that is characterized by the absence of a nucleus. Furthermore, prokaryotes do not possess membrane-...
What is a Eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells are cells that possess a true nucleus along with membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can either be unicellular or multicellular.
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell?
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucle...
Define Cell?
The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of life. Cell plays a vital role in all biological activities and include membrane-bound organ...
What is Ribosome?
The ribosome is a multi-component cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein. Therefore, it is called the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes ar...
List out the unique features of Animal and Plant Cells.
Both animal and plant cells have several unique features. Listed below are some important features: In structure, both animal and plant cells are q...
List out the functions of Chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are the plastids found in all plant cells. These cell organelles comprise the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll and are involv...
Who discovered Cell and Cell Theory?
The cell was first discovered in the year 1665 by an English natural philosopher Robert Hooke. The Cell Theory was explained by Theodor Schwann and...
What is the nucleus of an eukaryotic cell?
The word eukaryote comes from two Greek roots, eu (good, well), and karyon (nut, kernel), so a eukaryote has a well-defined or “good” nucleus (kernel) in its cells.
Why do all living things use cellular organization?
All living organisms use cellular organization to create structures to conduct life processes. Cells organize into tissues, which organize into organs, which organize into amazing life forms like plants, fungi, dogs, ducks, and people.
What are fungi made of?
Fungi, plants, and animals are made of eukaryotic cells (eukaryotes). Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus or organelles. All bacteria and members of Archaea are made of prokaryotic cells (prokaryotes).
How big are eukaryotic cells?
One eukaryotic cell could be double to 1,000 times the size of a prokaryotic cell. Eukaryotic cells measure between 10 µm and 100 µ m, which means you could barely see them with a standard school light microscope.
Which organisms have no nuclear membrane?
Archaea – Single-cell organisms. They have no nuclear membrane and share some qualities with bacteria (rDNA, circular chromosomes, asexual reproduction), but are set apart from bacteria by their unique rDNA and ether-linked lipids in their cell membranes. Only the domain, Eukaryota, has eukaryotic cells.
Where is DNA stored in eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells store chromatin (DNA and proteins) in a gel-like fluid called the nucleoplasm, inside the nucleus. Mitochondria, found only in eukaryotic cells, have their own DNA chromosome, which may indicate they were once freely existing, independent prokaryotic cells “captured” by eukaryotic cells.
Do prokaryotic cells have mitochondria?
Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria; nearly every eukaryotic cell has mitochondria. Prokaryotic cells have no organelles enclosed in plasma membranes; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus and organelles, each enclosed in plasma membranes. Prokaryotic cells have circular strands of DNA; eukaryotic cells have multiple molecules of double-stranded, ...