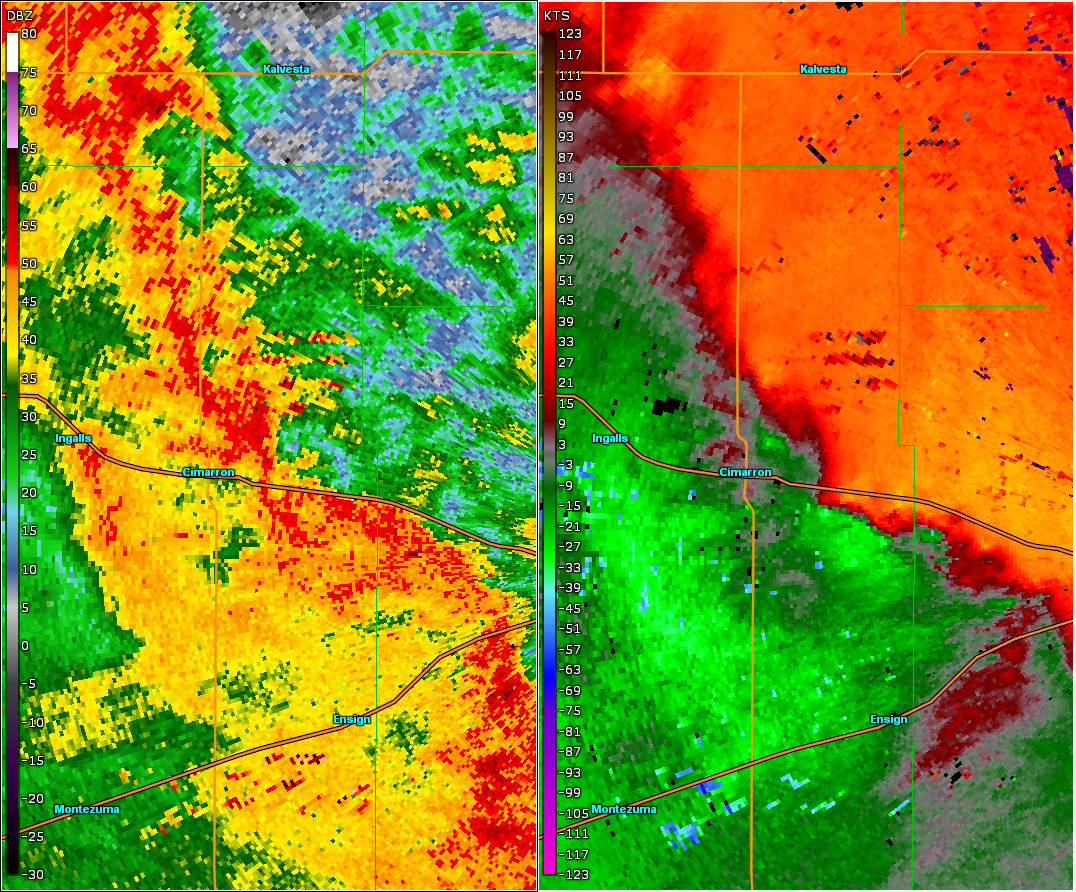
Can QLCS produce tornadoes?
Any QLCS can produce damaging winds, large hail, dangerous lightning, heavy rain and even tornadoes. Here's a look at the futurecast at 2pm tomorrow & the significant tornado parameter. This is a QLCS, fancy name for squiggly line of storms. This is mostly a straight line wind threat but with embedded tornadoes possible.
What is a quasi-linear convective system tornado?
These are technically called "Quasi-Linear Convective System" (QLCS) tornadoes. For simplicity, I call them "squall line tornadoes." These tornadoes are not landspouts (a third form of tornado) in spite of what some in the media have reported.
What is a QLCS storm?
This is a QLCS, fancy name for squiggly line of storms. This is mostly a straight line wind threat but with embedded tornadoes possible. Tornado threat increases as it moves east from here. #ncwx pic.twitter.com/9YpLWii3s0
What is a QLCS?
A QLCS is an abbreviation for a Quasi-Linear Convective System. Sounds complicated, right? This can be simply defined as a strong line of thunderstorms that is 'not' perfectly straight. This is a type of squall line.
Are QLCS tornadoes strong?
Although QLCS tornadoes are short-lived – often lasting only a few minutes – and generally weaker, they can still cause significant damage. Even if a tornado doesn't form, widespread wind damage is common with these systems.
What is a QLCS weather?
A QLCS is an abbreviation for a Quasi-Linear Convective System. Sounds complicated, right? This can be simply defined as a strong line of thunderstorms that is 'not' perfectly straight. This is a type of squall line. A typical squall line will develop ahead of a cold front here in the Carolinas.
How does a QLCS tornado form?
The development of the QLCS is dependent on the storm produced cold pool and the environmental shear. Once these two components can find a balance then the QLCS becomes a machine that can go great distances, producing severe weather including even tornadoes.
What are the 3 types of tornadoes?
Various types of tornadoes include the multiple vortex tornado, landspout, and waterspout. Waterspouts are characterized by a spiraling funnel-shaped wind current, connecting to a large cumulus or cumulonimbus cloud.
What is the shortest tornado?
Rope tornadoes can be as narrow as 2-3 feet wide. One such tornado was reported to have a damage path only 7 feet long.
Do tornadoes last longer than hurricanes?
A tornado might only last a few minutes, while hurricanes can persist for weeks. A hurricane can strengthen and weaken multiple times throughout its life cycle.
What does it mean when you see a shelf cloud?
Shelf clouds are harmless themselves but typically indicate strong storms. Shelf clouds form at the leading edge of a thunderstorm. Shelf clouds can even form before a derecho strikes. If you see a shelf cloud coming your way, it probably means you are about to get hit by a strong thunderstorm.
What is a line of thunderstorms called?
Multi-cell Line (Squall Line) Sometimes thunderstorms will form in a line which can extend laterally for hundreds of miles. These "squall lines" can persist for many hours and produce damaging winds and hail.
Do wall clouds produce tornadoes?
A rotating wall cloud is the area of the thunderstorm that is most likely to produce tornadoes, and the vast majority of intense tornadoes. Tornadogenesis is most likely when the wall cloud is persistent with rapid ascent and rotation.
What was the worst tornado in history?
the Tri-State TornadoThe deadliest tornado of all time in the United States was the Tri-State Tornado on March 18, 1925 in Missouri, Illinois and Indiana. It killed 695 people and injured over 2,000.
What is the biggest tornado ever?
the El RenoOfficially, the widest tornado on record is the El Reno, Oklahoma tornado of May 31, 2013 with a width of 2.6 miles (4.2 km) at its peak.
How rare is a fire tornado?
Fire tornadoes are rare but are being recorded more often in recent years. In 2018, a fire tornado was captured on video along the Colorado River near the Arizona-California state line. In 2020, at least three huge wildfires in California spawned them.
Is a QLCS a squall line?
The term QLCS stands for 'Quasi-Linear Convective System' These are tornadoes that form very quickly with little warning. They 'spin up' with a line of storms often called a squall line.
What causes a mesocyclone?
Mesocyclones are believed to form when strong changes of wind speed and/or direction with height ('wind shear') sets parts of the lower atmosphere spinning in invisible tube-like rolls.
What does it mean when you see a shelf cloud?
Shelf clouds are harmless themselves but typically indicate strong storms. Shelf clouds form at the leading edge of a thunderstorm. Shelf clouds can even form before a derecho strikes. If you see a shelf cloud coming your way, it probably means you are about to get hit by a strong thunderstorm.
What is a eyewall Mesovortices?
Eyewall mesovortices are small scale rotational features found in the eyewalls of intense tropical cyclones. In these vortices, wind speed can be up to 10% higher than in the rest of the eyewall. Eyewall mesovortices are a significant factor in the formation of tornadoes after tropical cyclone landfall.
What is a QLCS storm?
A QLCS is an abbreviation for a Quasi-Linear Convective System. Sounds complicated, right? This can be simply defined as a strong line of thunderstorms that is 'not' perfectly straight. This is a type of squall line. A typical squall line will develop ahead of a cold front here in the Carolinas.
What is QLCs in weather?
Weather. What is a 'QLCS'? The common cause for most of the tornadoes in the Carolinas. A line of thunderstorms does not always form a straight line. When there are 'kinks' in the lines then a tornado can quickly spin up. This is not rare. Author: Chris Mulcahy. Published: 3:08 PM EDT April 29, 2021.
How long do tornadoes last?
They are better known and referenced as spin-up tornadoes. They do not last long. Usually only up to about a minute. An estimated 90% of the tornadoes we get here in the Carolinas are these QLCS tornadoes.
How fast do squall lines move?
These can also form along an MCS, which is like a mini cold front. These lines move fast, sometimes moving at 45 to 60 mph. This is because the winds within the storms, are driving it faster.
When do tornadoes happen?
They can happen anytime of day or night, but the afternoon and evening hours are most common (since that is when the atmosphere tends to be most unstable). Tornadoes form in these breaks between the bows, where you can get inflow notches into the storm. This is where the spin-up occurs. Credit: WCNC.
Can QLCs cause tornadoes?
Any QLCS can produce damaging winds, large hail, dangerous lightning, heavy rain and even tornadoes. Here's a look at the futurecast at 2pm tomorrow & the significant tornado parameter. This is a QLCS, fancy name for squiggly line of storms. This is mostly a straight line wind threat but with embedded tornadoes possible.
What type of tornado is in Nebraska?
When we talk about the vicious twin tornadoes in northeast Nebraska last week, those are "supercell" type tornadoes. Supercell refers to the parent storm.
Is a tornado a landspout?
These tornadoes are not landspouts (a third form of tornado) in spite of what some in the media have reported. In general, this is the hierarchy of tornadoes: Supercell tornadoes. Squall line tornadoes. Landspout tornado.
What is a QLCS tornado?
QLCS tornadoes are associated with lines of strong thunderstorms, and frequently occur during late night and early morning hours.
When do QLCs tornadoes occur?
QLCS tornadoes frequently occur during the late night and early morning hours. These tornadoes, however, tend to be weaker and shorter-lived on average than those associated with supercell thunderstorms. NSSL researchers are looking for ways to detect QLCS tornadoes more effectively.
What is the most dangerous tornado?
Supercell Tornadoes. Tornadoes that come from a supercell thunderstorm are the most common, and often the most dangerous. A rotating updraft is a key to the development of a supercell, and eventually a tornado. There are many ideas about how this rotation begins.
What type of tornado is a non supercell tornado?
Another type of non-supercell tornado is a landspout. A landspout is a tornado with a narrow, rope-like condensation funnel that forms while the thunderstorm cloud is still growing and there is no rotating updraft - the spinning motion originates near the ground.
How does an air tube form a tornado?
Once the updraft is rotating and being fed by warm, moist air flowing in at ground level , a tornado can form.
How fast does wind shear cause tornadoes?
An example of wind shear that can eventually create a tornado is when winds at ground level, often slowed down by friction with the earth's surface, come from the southwest at 5 mph. But higher up, at 5000 feet above the same location, the winds are blowing from the southeast at 25 mph! An invisible “tube” of air begins to rotate horizontally. Rising air within the thunderstorm tilts the rotating air from horizontal to vertical – now the area of rotation extends through much of the storm.
How do tornadoes form?
Once the updraft is rotating and being fed by warm, moist air flowing in at ground level, a tornado can form. There are many ideas about this too. Scientists still have many questions. As few as 20 percent of all supercell thunderstorms actually produce tornadoes.
What is a QLCS tornado?
A landspout is a tornado with a narrow, rope-like condensation funnel that forms while the thunderstorm cloud is still growing and there is no rotating updraft - the spinning motion originates near the ground. Landspout tornadoes and tornadoes both fit this description but tornadoes form from rotating supercell thunderstorms while landspout tornadoes form from a ground circulation getting sucked up into a storm. Landspout tornadoes are short-lived and generally weak but can still hold winds of up to 100 mph. Landspouts are commonly weak; however, in rare occasions, a landspout can be as strong as an EF3 tornado.
How does a QLCS tornado form?
The whole process is very complex and only partially understood. The cold front lifts the warm air ahead of it forcibly forming the rain line. The rain cools the air causing the air to sink, called a cold pool, which produces strong winds.
What does QLCS mean?
First of all, what does “QLCS” stand for? The term QLCS stands for 'Quasi-Linear Convective System'. These are tornadoes that form very quickly with little warning. They 'spin up' with a line of storms often called a squall line. O.K. Could you please enlighten on its formation? Why Not? Let’s see hereinfor.
What scale is used to categorize tornadoes?
Tornadoes are catagorized using the EF Scale (NOT THE F SCALE THEY CHANGED) which is based off of damage assessment and (if measured) wind speed.
Is there such a thing as a weak tornado?
I know from these sights and experiences that in truth there is no such thing as a “weak tornado”. They are all strong. They are all dangerous. They all have the ability to kill. And they are utterly unpredictable.
Is a tornado dangerous?
All tornadoes, no matter how weak or strong, are dangerous. All of them.
Can tornadoes destroy anything?
Tornadoes are a concentrated force of nature that can destroy most anything in their path. And nobody can predict where that meteorological buzzsaw will touch down or travel.