14 Best Examples Of Operant Conditioning
- Walking Barefoot On Hot Pavement. Positive Punishment: Pain and thermal burns. ...
- Verbal Reprimand. Positive Punishment: Scolding and warning. ...
- Rewards In Video Games. ...
- Getting Fine For An Offense. ...
- Taking Away The Teenager’s Phone. ...
- Insulting Students For Misbehaviors. ...
- Parents Avoiding Childs Tantrums. ...
- Putting Headphones To Mask The Noise. ...
What are the 4 types of operant conditioning?
Understanding the Four Quadrants of Operant Conditioning
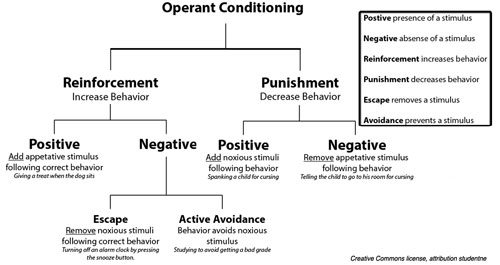
- Positive punishment (P+)
- Negative punishment (P-)-
- Positive reinforcement (R+)-
- Negative reinforcement (R-)-
Can You give Me a real life example of conditioned?
Examples of classical conditioning can be observed in the real world. One instance is various forms of drug addiction . If a drug is repeatedly taken in specific circumstances (say, a specific location), the user may become used to the substance in that context and require more of it to get the same effect, called tolerance.
What are some examples of classical conditioning in everyday life?
What are some examples of classical conditioning in everyday life?
- Smartphone Tones and Vibes. If you’ve ever been in a public area and heard a familiar notification chime, this classical conditioning example will certainly ring true for you.
- Celebrities in Advertising.
- Restaurant Aromas.
- Fear of Dogs.
- A Good Report Card.
- Experiences in Food Poisoning.
- Excited for Recess.
- Exam Anxiety.
What are the main ideas of operant conditioning model?
Operant conditioning is a theory of learning in behavioral psychology which emphasises the role of reinforcement in conditioning. It emphasises the effect that rewards and punishments for specific behaviors can have on a person’s future actions. The theory was developed by the American psychologist B. F. Skinner following experiments beginning in the 1930s, which involved the use of an ...
Which is the best example of operant conditioning?
Positive reinforcement describes the best known examples of operant conditioning: receiving a reward for acting in a certain way. Many people train their pets with positive reinforcement.
What are some examples of operant conditioning in the classroom?
Positive punishment This is a classic operant conditioning example in the classroom. Operant conditioning examples in the classroom also include a teacher scolding a student publicly for repeating mistakes. It's a positive punishment for coming late to class repeatedly or being too talkative.
What is an example of an operant?
Example 4. Apart from humans, Skinner's operant conditioning can also be used for pet behavioral modification. Most pet owners train their canine pals by offering them treats to encourage positive behavior. Doggie treats and toys are all excellent ways of enforcing positive behavior.
What is operant Behaviour example?
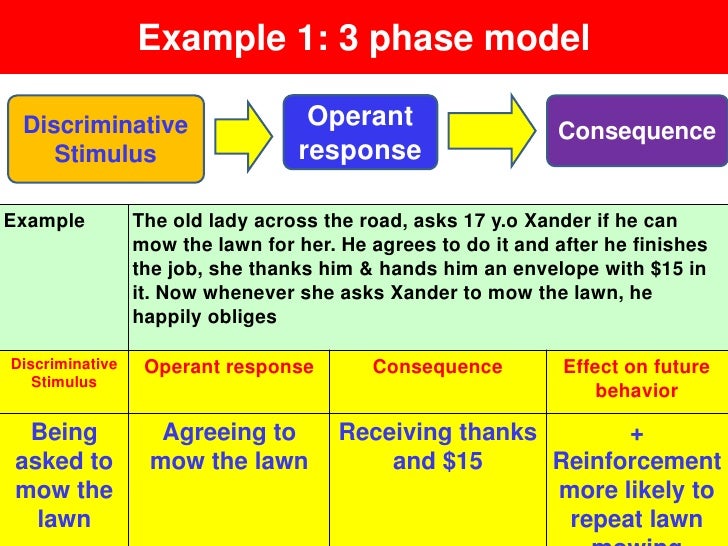
For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the sweets inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove; in operant terms, the box and the stove are "discriminative stimuli". Operant behavior is said to be "voluntary". The responses are under the control of the organism and are operants.
How operant conditioning is used in schools?
Using operant conditioning can give students immediate feedback about their behavior. When the teacher rewards positive behavior, other students are more likely to copy that behavior to earn the reward. The rewarded student is also more likely to repeat that behavior because of the positive feedback.
How is operant conditioning used by humans?
Operant conditioning (also known as instrumental conditioning) is a process by which humans and animals learn to behave in such a way as to obtain rewards and avoid punishments. It is also the name for the paradigm in experimental psychology by which such learning and action selection processes are studied.
What is an example of operant conditioning quizlet?
A lion in a circus learns to stand up on a chair and jump through a hoop to receive a food treat. This example is operant conditioning because attendance is a voluntary behavior. The exemption from the final exam is a negative reinforcement because something is taken away that increases the behavior (attendance).
What is operant conditioning?
In simpler words, operant conditioning allows humans to create an association between a behaviour and its consequence. Skinner believed that humans should look at observable, external causes behind human behaviour instead of only focusing on internal motivations.
What is classical conditioning?
This refers to a learning method that occurs via associations between a naturally occurring stimulus and environmental stimulus to generate a learned response.
How do teachers punish children?
Similarly, some teachers also punish children by giving them detention or extra homework. Doing so prevents the child from misbehaving in class for fear of being punished.
Which type of response neither increases or decreases the chances of behavior being repeated?
Neutral operant: This kind of response neither increases or decreases the chances of behavior being repeated. Punishers: This kind of response decreases the chances of behavior being repeated. This is why punishments are used to weaken behavior.
Do children need operant conditioning?
While most children are not eager to chores, giving them an incentive or allowance may encourage them to do so. Most parents unintentionally use operant conditioning while raising kids. After all, it’s one of the most foolproof ways to gain satisfactory results.
Real-Life Examples Of Operant Conditioning And Its Components
There are two main components in examples of operant conditioning —reinforcement and punishment. Let’s look at them in detail.
Join the Thrive Tribe
Stay ahead at work with smart stories, videos and podcasts delivered straight to your inbox.
What is Operant Conditioning?
Operant conditioning is a learning process whereby deliberate behaviors are reinforced through consequences. It differs from classical conditioning, also called respondent or Pavlovian conditioning, in which involuntary behaviors are triggered by external stimuli.
How do children condition their parents?
In a sense, young children condition their parents through negative reinforcement. Screaming, tantrums and other "acting out" behaviors are generally intended to draw a parent's attention. When the parent behaves as the child wants, the unpleasant condition - the screaming and crying - stops.
What is continuous reinforcement schedule?
A continuous reinforcement schedule (commonly abbreviated CRF) provides reinforcement for all noted behaviors. That is, every time the behavior occurs, reinforcement is provided. An intermittent reinforcement schedule (commonly abbreviated INT) reinforces some target behaviors but never all of them.
What is negative reinforcement?
Negative reinforcement is a different but equally straightforward form of operant conditioning. Negative reinforcement rewards a behavior by removing an unpleasant stimulus, rather than adding a pleasant one. An employer offering an employee a day off is an example of negative reinforcement. Rather than giving a tangible reward, they reduce ...
What is Skinner's theory of behavior?
Skinner's work took that first principle and applied it to human behavior, representing the school of psychology called behaviorism. Behaviorism defined much of psychology for the second half of the 20th century, but is currently being combined with other psychological perspectives. Operant Conditioning and You.
What is punishment in psychology?
Psychology defines punishment as something done after a given deliberate action that lowers the chance of that action taking place in the future. Whereas reinforcement is meant to encourage a certain behavior, punishment is meant to discourage a certain behavior. An employee who misses work may suffer a cut in wages.
What is a lab animal punished for?
Most often, a lab animal is punished for a given behavior with a mild electric shock. Just as there are examples of positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement, there are also examples of positive punishment (like the ones above) and negative punishment.
Who developed the theory of operant conditioning?
In the early 1900s, psychologist B.F. Skinner built on the concepts of reinforcer and punisher to create the theory of operant conditioning. Skinner believed that Pavlovian conditioning was far too simple to explain complex human behavior thoroughly.
What is Skinner's operant conditioning paradigm?
In Skinner’s operant conditioning paradigm, behavior can be manipulated when it is followed by reinforcement or punishment.
What are some examples of negative punishment?
Negative punishment removes a pleasant stimulus to stop undesired behavior. Examples: A parent takes away their child’s phone for refusing to do homework. Police issues the driver a speeding ticket for speeding. A worker loses their lunch break for getting to work late. The use of operant conditioning is widespread.
What is Pavlovian conditioning?
Pavlovian conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a leading field within the study of psychology at the time. Behaviorists believe that behavior is a response to external stimuli, and humans only learn by association, not by thoughts, feelings, or inner mental events.
What is instrumental conditioning?
Operant Conditioning in Psychology (With Examples) Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a learning process in which behavior is modified using rewards or punishments. By repeatedly pairing the desired behavior with a consequence, an association is formed to create new learning.
When did classical conditioning start?
2. Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov first experimented with classical conditioning in the late 1800s.
Who came up with the idea of instrumental conditioning?
Later, psychologist Edward Thorndike came up with the concept of instrumental conditioning when he observed the impact of reinforcement in puzzle box experiments with cats trying to escape. He called this process “trial-and-error” learning.
Classical Workout as the Foundation of Behaviorism
We tin can trace back the origin of operant conditioning to its predecessor, classical conditioning.
Constabulary of Effect & Operant Conditioning
Afterward, psychologist Edward Thorndike came upwardly with the concept of instrumental conditioning when he observed the bear on of reinforcement in puzzle box experiments with cats trying to escape. He called this process “trial-and-fault” learning.
Operant Workout
To study operant workout, BF Skinner made a bedroom, chosen the Skinner Box, and put a small animal inside. In the experiments, each time the animal pressed a lever or a bar, it received food or water as reinforcement 4 .
Schedules of Reinforcement Is a Cardinal Component
Behavior modification using reinforcers and punishers requires a continuous application to remain effective. Once the reinforcement or punishment stops, the learned beliefs gradually weakens and finally disappears in a process called extinction.
Final Thoughts on Operant Conditioning
Operant conditioning is something we often see around united states of america. Sometimes we exercise it intentionally just sometimes non. Recognizing the pros and cons of this type of behavior modification tin help us avoid pitfalls and reach the best results.
What is operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment. In operant conditioning, behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on the consequences of that behavior. Operant conditioning was defined and studied by behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner.
Why is operant conditioning considered incomplete?
First, operant conditioning is accused of being an incomplete explanation for learning because it neglects the role of biological and cognitive elements.
What is shaping in behavioral science?
Behavior Shaping. Operant conditioning can lead to increasingly complex behaviors through shaping, also referred to as the “method of approximations.”. Shaping happens in a step-by-step fashion as each part of a more intricate behavior is reinforced. Shaping starts by reinforcing the first part of the behavior.
Why are conditional reinforcers not innately desirable?
Conditioned reinforcers reinforce behavior not because they are innately desirable, but because we learn to associate them with primary reinforcers. For example, Paper money is not innately desirable, but it can be used to acquire innately desirable goods, such as food and shelter.
What happens when reinforcement is stopped?
Continuous reinforcement occurs when a particular response follows each and every performance of a given behavior. Learning happens rapidly with continuous reinforcement. However, if reinforcement is stopped, the behavior will quickly decline and ultimately stop altogether, which is referred to as extinction.
How did Skinner conduct his experiments?
To study operant conditioning, Skinner conducted experiments using a “Skinner Box,” a small box that had a lever at one end that would provide food or water when pressed. An animal, like a pigeon or rat, was placed in the box where it was free to move around. Eventually the animal would press the lever and be rewarded.
What are the two types of reinforcement?
There are two types of reinforcement: Positive reinforcement occurs when a behavior results in a favorable outcome, e.g. a dog receiving a treat after obeying a command, or a student receiving a compliment from the teacher after behaving well in class.
