
What is reinforced concrete wall?
Design of Reinforced Concrete Wall – Concept, Calculations Reading time: 3 minutes Reinforced concrete wall is designed as a compression member. Reinforced concrete wall is used in case where beam is not provided and load from the slab is heavy or when the masonry wall thickness is restricted.
When vertical reinforcement is placed in a wall?
Vertical reinforcement is placed after the wall has been stacked and completely erected. In case of a multistory wall then the vertical reinforcement is placed after the erection of each individual storey.
Can you have a window in a reinforced wall?
Reinforcement for Wall Openings Most walls will have window or door openings or both. Creating a wall opening in a reinforced concrete wall creates extra stress around that opening especially at the corners. Window and door headers also known as lintels can be subjected to significant bending moment and shear forces depending on several factors.
Where to place reinforcement steel in a wall?
The placement of reinforcing steel, especially the vertical ones should be clearly marked (i.e. off center or towards interior/exterior or centered in the wall). The designer should specify the lap splice type and lengths for every section of the wall where splicing is anticipated.
What are reinforced concrete walls?
Reinforced concrete (RC) structural walls (also known as shear walls) have commonly been used as lateral force-resisting elements in buildings in regions of moderate-to-high seismic hazard because they provide substantial lateral strength and stiffness to buildings when subjected to strong ground shaking.
What is a reinforced concrete retaining wall?
Retaining wall are generally used to retain earth or other material to maintain unequal levels on two faces. The material on the back face is called backfill. Retaining walls are used in the construction of basement below ground level, wing walls of bridge and to retain slopes in hilly terrain roads.
How do you reinforce a brick wall?
To reinforce your single brick wall, you may use reinforced concrete jackets and FRP structural repointing. If you don't know how the process of reinforced concrete jackets and FRP structural repointing is done, you may refer below.
What is reinforced soil retaining wall?
Reinforced soil retaining walls use a reinforced bank of earth as the retaining structure. The earth wall is then faced with 300mm concrete lego blocks. The bank is constructed in layers of earth with a geogrid laid between them. The geogrid reinforces the earth so it acts as a single mass.
What are the different types of retaining wall?
Types of retaining wallsGravity wall.Reinforced Retaining Wall.Concrete Cantilever retaining wall.Counter-fort / Buttressed retaining wall.Cantilevered wall.Reinforced Soil Retaining Wall.Soil nailed wall.Anchored wall.More items...•
What happens if the retaining wall fails?
What damages can be caused by the failure of a retaining wall? A failing retaining wall often causes the soil behind the wall to begin moving as the wall moves. Movement of the soil held back by the wall will cause damage to any structure supported by that soil.
How do you reinforce a wall?
0:148:28Tobermore's guide to constructing a reinforced retaining wall. - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAt length normally determined by the engineer the geogrid is placed in layers between the blocks andMoreAt length normally determined by the engineer the geogrid is placed in layers between the blocks and covered with backfill material which is then compacted.
Do brick walls need reinforcement?
Reinforcement is usually required in both load-bearing and nonload-bearing walls. The most common horizontal reinforcement for a masonry wall is a galvanized steel wire ladder or truss laid in the mortar between courses of brick or block.
What is reinforced brick wall?
Reinforced brick masonry is brickwork which is strengthened by using mild steel iron mesh or bars which are known as Reinforced brick masonry. The property of reinforced brick masonry is that it is capable of resisting compressive shear stress as well as tensile shear stress.
What are reinforced slopes?
Reinforced Soil Slopes (RSS) are compacted fill embankments that incorporate the use of horizontal placement of geosynthetic reinforcement to create a stable, oversteepened slope structure.
What are the benefits of reinforcing soil?
Some are the advantages why reinforced earth structures are an option preferred by civil engineering are mentioned as: Flexibility of the wall, very high resistance, ease installation, excellent appearance of the finished structure and considerable saving when comparing with conventional cast-in-place wall due to the ...
What is soil reinforcement?
Reinforced soil or mechanically stabilized soil consists of soil that is strengthened by tensile elements such as metal strips, geotextiles, or geogrids. The development of polymeric materials in the form of geosynthetics has brought major changes in geotechnical engineering.
Definition of Reinforced Concrete
Before explaining what is reinforced concrete, first know the definition of concrete. Concrete is a mixture of fine and coarse aggregate materials consisting of sand, gravel, crushed stone, or other similar materials which are mixed with cement and water to form a rock-like mass.
Types of Reinforced Concrete Building Structures
Installation of reinforced concrete structures is divided into 2 (two), namely precast (precast) and cast in place. If the installation of the building structure used is the casting method, then the reinforced concrete building structure is monolithic which can be useful in resisting earthquake loads.
What should be considered when designing a reinforced concrete shear wall?
While designing reinforced concrete curtains, some important details from architects to engineers should not be overlooked. One of them is that reinforced concrete curtain walls should be placed symmetrically in the building.
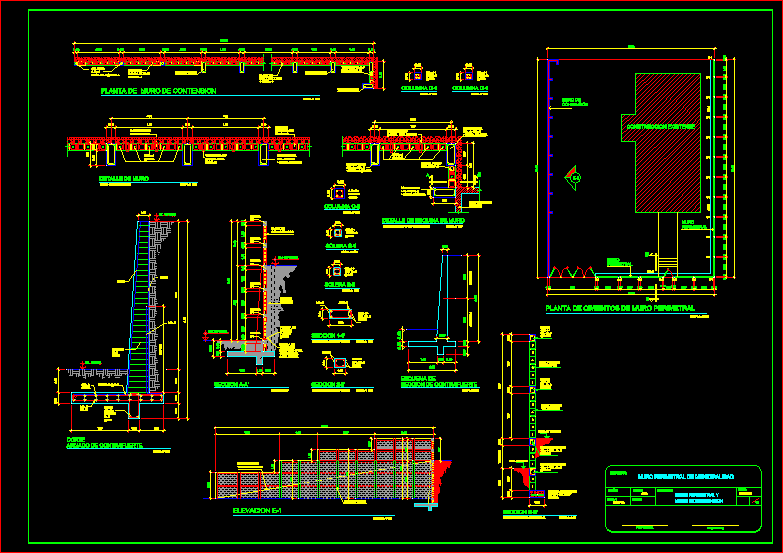
What is reinforced concrete wall?
Reinforced concrete wall is designed as a compression member. Reinforced concrete wall is used in case where beam is not provided and load from the slab is heavy or when the masonry wall thickness is restricted. Reinforced concrete wall is classified as:
What is a braced wall?
Braced: When cross walls are provided for the walls such that they can take lateral load and 2.5% of vertical load, then the wall is braced. Otherwise, the wall is known as unbraced wall.
What is a reinforced concrete retaining wall?
Types of reinforced concrete retaining walls are cantilever retaining walls and counterfort retaining walls. Functions and parts of these retaining walls are discussed. Retaining wall are generally used to retain earth or other material to maintain unequal levels on two faces. The material on the back face is called backfill.
What is retaining wall?
Retaining walls are used in the construction of basement below ground level, wing walls of bridge and to retain slopes in hilly terrain roads. Retaining wall can be constructed with masonry as well as reinforced concrete. In case of masonry retaining wall, the thickness of wall increases with height because masonry resists ...
What is a counterfort retaining wall?
Counterfort retaining wall consists of a stem, toe slab and heel slab as in case of cantilever retaining wall. But it also consists of counterforts are regular interval which divides the stem. The stem with combination of counterfort behaves like a tee-beam with varying width.
What are the parts of a cantilever retaining wall?
Parts of a cantilever retaining wall and its actions: 1. Vertical stem. Vertical stem in cantilever retaining wall resists earth pressure from backfill side and bends like a cantilever. The thickness of cantilever slab is larger at the base of stem and it decreases gradually upwards due to reduction of soil pressure with decrease in depth.
Why does the thickness of a masonry retaining wall increase with height?
In case of masonry retaining wall, the thickness of wall increases with height because masonry resists the lateral pressure by its weight. Thus it is also called gravity retaining wall. The reinforced concrete retaining wall resists the lateral pressure by structural action such as bending and results in thinner section.
What is a base slab?
The base slab form the foundation of the retaining wall. It consists of a heel slab and the toe slab. The heel slab acts as a horizontal cantilever under the combined action of the weight of the retaining earth from the top and the soil pressure acting from the soffit. The toe slab also acts as a cantilever under the action of the soil pressure acting upward. The stability of the wall is maintained by the weight of the earth fill and on the heel slab together with the self-weight of the structural elements of the retaining wall. Cantilever type retaining walls are suitable upto 5m depth of backfill.

Reinforced Soil Walls - Concept
Geogrids
- Geogrids are flexible, synthetic meshes which are manufactured specifically for slope stabilization and earth retention. These “grids” are available in a variety of materials, sizes and strengths. They can be made of high tensile strength plastics or woven polyester yarns and are typically packaged at the factory in rolls. The grids are rated by Long-Term Allowable Design Str…
Positive Interlock
- Allan Block’s gravel filled hollow core provides a multi-point interlock with the grid. As retaining wall heights increase, our exclusive “Rock-Lock” connection, combined with the weight of the wall blocks, provides the best block-to-grid interlock of any system on the market. See the tech sheets on connection testing or the Seismic Testing Executive Summary for testing results on the “Roc…
External Stability
- External stability exists when the entire wall system - the Allan Block facing units and the reinforced soil mass - act as a coherent structure to satisfy standard gravity wall analysis. Proper retaining wall designmust satisfy all four of the following considerations.
Internal Stability
- Internal stability is the ability of the reinforcement combined with the internal strength of the soil to hold the soil mass together and work as a single unit
Design Considerations
- Grid strengthSelect the right strength grid for the job. Choose LTADS grids from 500 lb/ft to 4000 lb/ft (7.3 kN/m to 58.4 kN/m).
- Embedment lengthGrid length must extend far enough behind the wall to create a sufficient reinforced gravity mass. Typically a minimum of 60% of total wall height.
- Number of layersInstall enough layers to adequately increase the internal strength of the soil …
- Grid strengthSelect the right strength grid for the job. Choose LTADS grids from 500 lb/ft to 4000 lb/ft (7.3 kN/m to 58.4 kN/m).
- Embedment lengthGrid length must extend far enough behind the wall to create a sufficient reinforced gravity mass. Typically a minimum of 60% of total wall height.
- Number of layersInstall enough layers to adequately increase the internal strength of the soil mass and handle all applied loads.
- Spacing between layersGrid layers must be correctly spaced to distribute internal forces. Typically spaced on 16 in. (405 mm) centers.