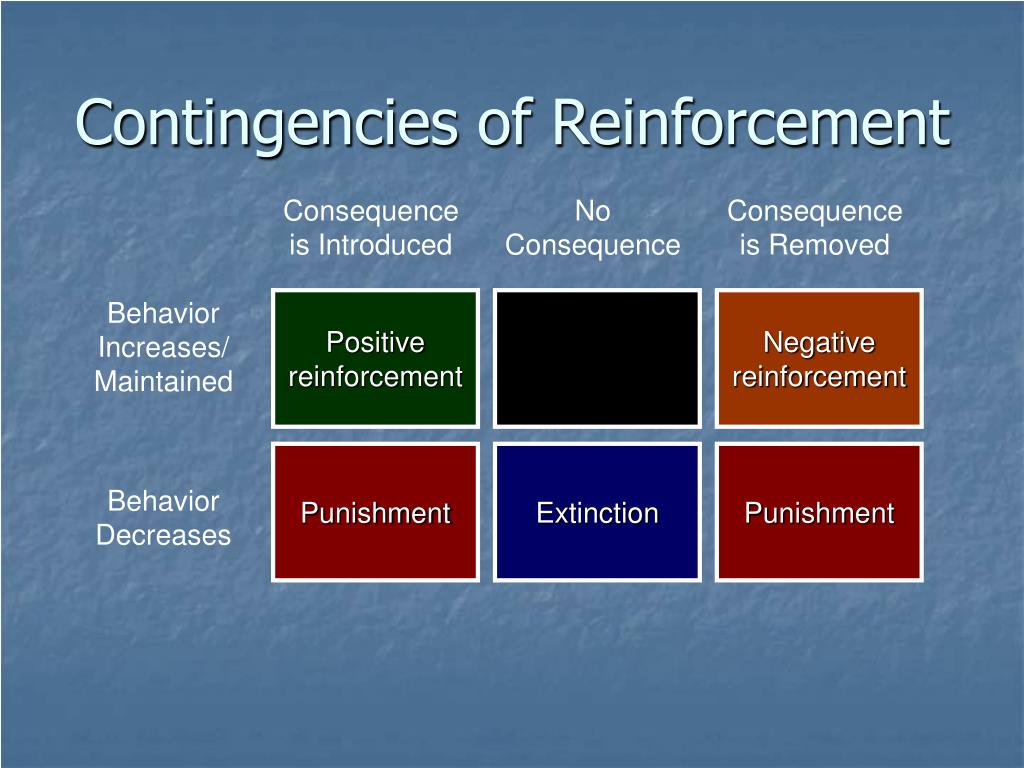
Four contingencies of reinforcement?
- Positive Reinforcement. Positive reinforcement is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of improving the probability of that conduct happening again – by giving a positive ...
- Negative reinforcement. ...
- Extinction. ...
- Punishment. ...
Full Answer
What are the four contingencies of reinforcement?
… Disrupting memory reconsolidation provides an opportunity to abruptly reduce the behavioural expression of fear memories with long-lasting effects. The success of a reconsolidation intervention is, however, not guaranteed as it strongly depends on the destabilization of the memory.
What are contingencies of reinforcement?
- Positive Reinforcement. Positive reinforcement is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of improving the probability of that conduct happening again – by giving a positive ...
- Negative reinforcement.
- Extinction.
- Punishment.
What is contingent reinforcement?
with regard to behavior therapy, a method wherein strengthening, or advantage is rendered every time the wanted behavior is carried out- that being, the advantage is dependent upon the behavior. CONTINGENCY REINFORCEMENT: "Contingency reinforcement is a major part of Pavlovian conditioning ."
What are examples of contingencies?
- The risk of loss or damage to property by fire, explosion, or other hazards;
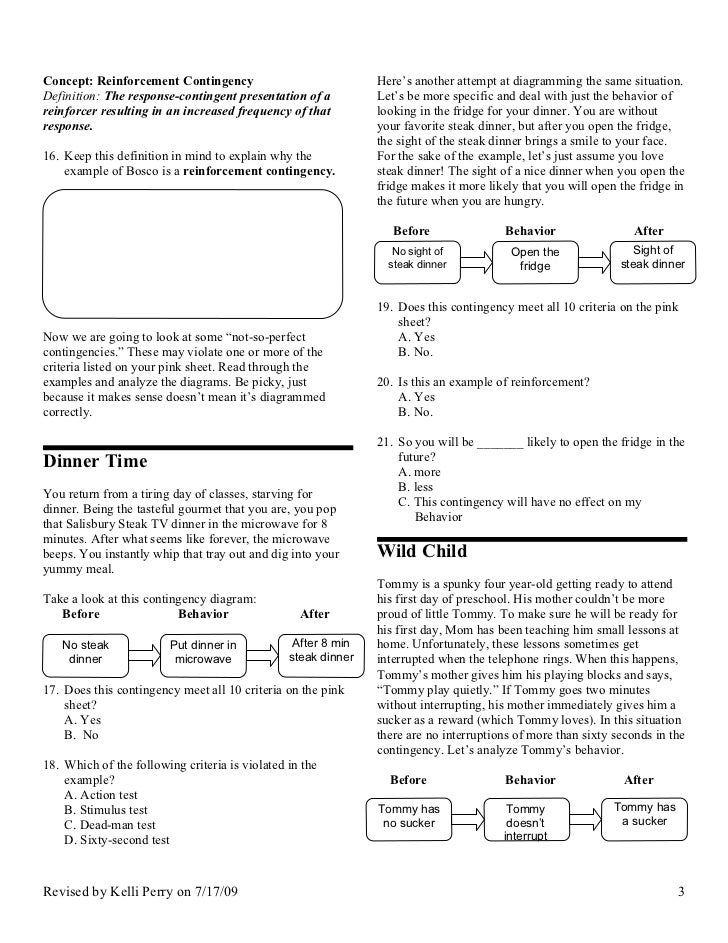
- The threat of expropriation of assets;
- Actual or possible claims and assessments.
- Pending or threatened litigation.
- Obligation related to product warranties and product defects;
What is reinforcement contingency example?
Parents use contingent reinforcement to control their children's behavior. For example, if a mother wants a child to share toys with a sibling, she may offer praise when sharing occurs. The child likes the praise so continues to share in order to gain more praise.
What is a contingent reinforcer?
the process or circumstances in which the delivery of positive stimulus events (e.g., material goods, verbal praise) and, more rarely, the elimination of negative stimulus events (e.g., penalties) depend on the performance of desired behavior.
What is reinforcement contingency psychology?
the contingency (relationship) between a response and a reinforcer. The contingency may be positive (if the occurrence of the reinforcer is more probable after the response) or negative (if it is less probable after the response).
What are the four kinds of reinforcement contingencies?
The four kinds of reinforcement contingencies are positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment, and extinction.
What defines a contingency of reinforcement quizlet?
Contingencies of reinforcement. relationships between a r response and the changes in stimulation that follow the response. ex: when college report cards deliver more than once a year it encourages study habits. continous reinforcement. a type of reinforcement schedule by which all correct responses are reinforced.
What does contingent feedback mean?
Contingency means that the feedback strongly corresponds with task. behaviour that can be controlled by the students. Elementary school. students (N=296) received individualized feedback about their. performance during a series offive lessons.
What is an example of contingency in psychology?
A naturally existing contingency, in layman's terms, “natural consequence” happens without the manipulation of the behavioral analysts. Such an example would be, hitting the snooze button makes you late for work which causes you to leave your house without the opportunity for breakfast.
What contingency means?
Definition of contingency 1 : a contingent event or condition: such as. a : an event (such as an emergency) that may but is not certain to occur trying to provide for every contingency. b : something liable to happen as an adjunct to or result of something else the contingencies of war.
What does contingent mean in psychology?
adj. dependent on circumstances, events, or conditions.
What is the four term contingency in ABA?
A four-term contingency is something that is very important when understanding behavior and the “why” that Grafton tries to identify within its philosophy. Motivation>Antecedent>Behavior>Consequence.
What are the examples of reinforcement?
Reinforcement can include anything that strengthens or increases a behavior. 3 In a classroom setting, for example, types of reinforcement might include giving praise, letting students out of unwanted work, or providing token rewards, candy, extra playtime, or fun activities.
What are the four basic contingencies psychology?
The four contingencies are positive and negative reinforcement, punishment, and extinction. Positive reinforcement occurs when the desired behavior... See full answer below.
What does contingent mean in psychology?
adj. dependent on circumstances, events, or conditions.
What is the difference between a contingent and Noncontingent pairing?
Pairings of a neutral stimulus and primary reinforcer were delivered either contingent upon a participant response or noncontingently (i.e., independent of a participant response).
What is contingent behavior?
contingent behavior actions that are dependent upon a specific stimulus. behavior disorder a general concept referring to any type of behavioral abnormality that is functional in origin.
What is non contingent reinforcement?
Noncontingent reinforcement (NCR) is a powerful method to reduce problematic behavior. NCR involves giving the student access to a reinforcer frequently enough that they are no longer motivated to exhibit disruptive behavior to obtain that same reinforcer.
What is positive reinforcement?
Positive reinforcement is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of improving the probability of that conduct happening again – by giving a positive ordeal as a result. Examples:Giving a child food or a toy for a job well done (assuming that the food or toy is desirable in that context).
What is the reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of diminishing the probability of that conduct?
Punishment . Punishment is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of diminishing the probability of that conduct by giving an undesirable affair as a result. Examples:A convicted thief is imprisoned for robbery (Learn Net).
What is the term for when a conduct is trailed by no reaction?
Extinction. Extinction happens when a conduct is trailed by no reaction, which diminishes the probability of the conduct happening once more. Examples:John is disruptive in class and is placed in a time-out room where he cannot be rewarded for disruption.
How to Help a Meth Addict
Methamphetamine (meth) is a substance that has very limited medical use. The substance is only available legally under the name Desoxyn , which is a medication with limited indications for the treatment of obesity and ADHD. As a substance of abuse , ...
Meth and Pregnancy
One study of meth-related emergency room visits found that more than 400,000 reproductive-aged women reported using meth in the prior month. As methamphetamine use continues to rise, so do treatment and hospital admissions. In 2012, meth ranked ...
Meth Overdose
Methamphetamine, most commonly known as “meth,” “crystal,” “speed,” and “ice,” is an addictive stimulant that causes users to experience an intense euphoric rush 1 . Meth can be smoked, snorted, injected, or consumed orally by users. ...
Methamphetamine Detox and Withdrawal
Methamphetamine (meth) is a powerful central nervous system stimulant with highly addictive properties. It can be smoked, nasally inhaled, injected and even eaten. No matter how it is used, the effects have a rapid onset followed by a high that can ...
Meth Abuse
Summary Methamphetamine is a psychostimulant often abused for the euphoric “high” it provides. Some signs of abuse include frequent paranoia, agitation, sweating, insomnia, skin changes, weight loss, and more. Abusing this powerfully addictive ...
Contingency Management
What Is Contingency Management? Contingency management (CM) , often called motivational incentives , is a type of behavioral therapy rooted in the basis of operant conditioning . This type of treatment provides rewards for the desired behaviors such ...
Therapy for Addiction Treatment and Recovery
How Can Therapy Help Me? The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) outlines several principles of addiction treatment based on data the organization has collected for the past 40 years. 1 These principles aim to improve the odds of success in ...
What is contingent reinforcement?
It’s a technique that might be seen as the core technology behind applied behavioral analysis, since it allows a therapist, parent, or caregiver to exercise discretion and guidance in reinforcing a certain beneficial behavior—and to avoid providing reinforcement for undesirable behaviors.
When does reinforcement occur?
A reinforcement can occur immediately after the behavior or with some delay. Although an immediate reinforcement can provide an instantaneous and clear connection between the behavior and the reward, in some cases delaying the reward may be achieving exactly the behavior that is desired.
What is differential reinforcement?
Differential Reinforcement. Another aspect of reinforcement is when it is used to teach preferable behaviors over existing behaviors. It’s relatively easy to reinforce an existing behavior; teaching a new behavior requires a differential approach, prompting the patient to adopt new responses to an existing stimulus.
What are the three terms of contingency?
This is a basic application of logic to the central three-term contingency, or the so-called ABCs of ABA: 1 Antecedent – the prompts leading to the behavior. 2 Behavior – the actions performed as a result of the antecedent. 3 Consequence – the outcome of those actions as they affect the person acting.
What is a positive reinforcer?
The terms have slightly different meanings than what you may be used to in this context—a positive reinforcer is one that is added as the consequence; a negative reinforcer is one that is removed as a consequence.
Is candy a positive or negative reinforcer?
For example, offering a child candy for cleaning his or her room is a positive reinforcer. Keeping them grounded until they clean it is a negative reinforcer. Both can work, but negative reinforcement is often associated with aversive therapies—punishment—which are increasingly frowned upon in most ABA circles.
Can you use immediate reinforcement immediately?
A reinforcement can occur immediately after the behavior or with some delay. Although an immediate reinforcement can provide an instantaneous and clear connection between the behavior and the reward, in some cases delaying the reward may be achieving exactly the behavior that is desired. Teaching patience is one of the primary examples of using delayed rewards.
What is contingent reinforcement?
Contingent reinforcement is used to enforce the notion that there is some type of consequence for both good and bad behaviors. The consequence is dependent on whether the person providing the reinforcement wants the behavior to stop or to continue.
Is negative reinforcement the same as punishment?
Despite the connotations in its name, negative reinforcement is not the same as punishment. It is more of a reward, because something negative is removed when a desired behavior occurs. Punishment is a negative consequence meted out in response to an undesired behavior in the hopes that the behavior will not occur again.

Positive Reinforcement
- Positive reinforcement is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of improving the probability of that conduct happening again – by giving a positive ordeal as a result. Examples:Giving a child food or a toy for a job well done (assuming that the food or toy is desirable in that context).
Negative Reinforcement
- Negative reinforcement is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of improving the probability of that conduct happening again – by evacuating a negative boost. Examples:A student receives help when he requests help after struggling with a problem.
Extinction
- Extinction happens when a conduct is trailed by no reaction, which diminishes the probability of the conduct happening once more. Examples:John is disruptive in class and is placed in a time-out room where he cannot be rewarded for disruption.
Punishment
- Punishment is a reaction that takes after a conduct and has the impact of diminishing the probability of that conduct by giving an undesirable affair as a result. Examples:A convicted thief is imprisoned for robbery (Learn Net).