What is the reason for renal ultrasound?
Your physician might order a kidney ultrasound if he or she thinks you’re suffering from:
- Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones)
- An infection
- Blockage
- Cysts
- A tumor
- An abscess
- Fluid collection.
What is a renal ultrasound used for?
Renal ultrasound is used to evaluate any abnormalities in retroperitoneal anatomical structures, but for the functional status of the urinary system it gives only limited clues. Usually when there is any concern related to the kidney or bladder, doctors may recommend a renal ultrasound. For a renal ultrasound the patient should have a full bladder.
What to expect at a kidney ultrasound?
What to Expect
- You'll probably lie on your stomach throughout the procedure.
- The technician will apply gel to your skin.
- Then they'll run the transducer over your skin to view and photograph the kidneys.
- You should feel pressure but not pain.
- You may be asked to hold still for a few moments or adjust your position.
What can a renal ultrasound show?
Renal Ultrasound is also known as a kidney ultrasound. It is a diagnostic exam that produces real-time images of the size, shape, and location of the kidney as well as the ureters (thin tubes that carry urine from the kidney to the bladder) and bladder.

How long does a renal Doppler take?
How Long Does a Renal Doppler Ultrasound Take? The renal artery ultrasound is a painless, safe procedure that generally takes one hour to complete.
What does a Doppler ultrasound of the kidney show?
A renal ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys and its surrounding blood vessels. This test is used to detect kidney abnormalities and to assess blood flow to the kidneys.
Why would a cardiologist order a renal ultrasound?
Patients with unexplained kidney problems, or who have high blood pressure that seems resistant to medication and lifestyle changes may be asked to undergo a renal artery ultrasound. If a patient with hypertension suddenly finds it difficult to control her blood pressure, this could be a warning sign.
How do you do a renal Doppler test?
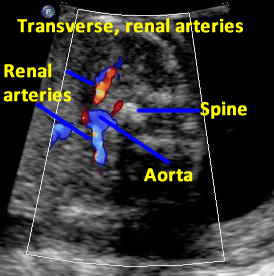
The procedure begins with the patient in the supine position and the head of the bed elevated about 30 degrees. A low-frequency scanhead (2.5–5.0 MHz) is used to depict the abdominal aorta and renal arteries (RAs). The two main approaches for imaging the RAs are through the anterior abdominal wall and the flank.
What is most common indication for renal ultrasound?
Indications for renal ultrasonography include the following :Evaluation of cystic kidney disease.Diagnosis of hydronephrosis.Measurement of kidney size and echogenicity as part of an evaluation of chronic kidney disease.Detection of renal artery occlusive disease via Doppler images.More items...•
Can you see kidney failure on an ultrasound?
Sonography is indicated in most cases of acute renal failure because of the single functioning kidney and the frequency of urologic complications. The routine perioperative use of ureteral stents has reduced ureteral obstruction, but bladder dysfunction remains common.
Is there any prep for a renal ultrasound?
How do I prepare for a kidney ultrasound? EAT/DRINK: Drink a minimum of 24 ounces of clear fluid at least one hour before your appointment. Do not empty your bladder prior to the procedure. Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting or sedation, is required.
What are the symptoms of a blocked renal artery?
SymptomsHigh blood pressure that's hard to control.A whooshing sound as blood flows through a narrowed vessel (bruit), which your doctor hears through a stethoscope placed over your kidneys.Elevated protein levels in the urine or other signs of a problem with kidney function.More items...•
What happens if the renal artery is blocked?
The kidneys need a good blood supply. The main artery to the kidney is called the renal artery. Reduced blood flow through the renal artery can hurt kidney function. A complete blockage of blood flow to the kidney can often result in permanent kidney failure.
Why is renal artery doppler done?
Imaging tests commonly done to diagnose renal artery stenosis include: Doppler ultrasound. High-frequency sound waves help your doctor see the arteries and kidneys and check their function. This procedure also helps your doctor find blockages in the blood vessels and measure their severity.
What is the most common cause of renal artery stenosis?
More than 90% of the time, renal artery stenosis is caused by atherosclerosis, a process in which plaque made up of fats, cholesterol, and other materials builds up on the walls of the blood vessels, including those leading to the kidneys.
Is renal hypertension curable?
Because your kidneys are not getting enough blood, they react by making a hormone that makes your blood pressure rise. This condition is a treatable form of high blood pressure when properly diagnosed.
What can be seen on a kidney ultrasound?
A kidney ultrasound may be used to assess the size, location, and shape of the kidneys and related structures, such as the ureters and bladder. Ultrasound can detect cysts, tumors, abscesses, obstructions, fluid collection, and infection within or around the kidneys.
Why is renal artery doppler done?
Imaging tests commonly done to diagnose renal artery stenosis include: Doppler ultrasound. High-frequency sound waves help your doctor see the arteries and kidneys and check their function. This procedure also helps your doctor find blockages in the blood vessels and measure their severity.
What does a dark spot on a kidney ultrasound mean?
Benign cysts in the kidneys tend to appear as black spots on an ultrasound because the waves pass through them and don't bounce back. Your doctor can explain the potential implications of any light or dark spots revealed by an imaging scan.
What are symptoms of renal artery stenosis?
SymptomsHigh blood pressure that's hard to control.A whooshing sound as blood flows through a narrowed vessel (bruit), which your doctor hears through a stethoscope placed over your kidneys.Elevated protein levels in the urine or other signs of a problem with kidney function.More items...•
Why do we use a renal doppler ultrasound?
Renal Doppler ultrasound is routinely performed because it is a useful technique for evaluating a wide range of various renal pathologic conditions. An understanding of normal anatomy, as well as important anatomic variants, as well as basic physical concepts, are necessary for correct interpretation. This activity outlines the vascular anatomy, imaging indications, and technique and briefly reviews some of the common pathologies where it may be used by an interprofessional team.
What are the indications for Doppler US of transplant renal arteries?
Indications for Doppler US of transplant renal arteries include screening to determine baseline values of hemodynamic parameters, abnormalities such as tenderness, rising creatinine, oliguria/anuria, hematuria, or ureteral dilatation, evaluation of vascular patency, evaluation for iatrogenic complications post-biopsy, and assessment for lymphoproliferative disease. [6]
How long do you have to be NPO before a renal doppler?
Before a renal Doppler US, patients should remain NPO for eight hours. This includes tobacco products or chewing gums as this promotes the ingestion of air which subsequently limits the examination due to artifacts. However, for renal transplant examinations, patients do not need to be NPO. If patients need to take necessary medications before their exam, this can be achieved with a small glass of water. Simethicone is a well-known emulsifying agent, and prior research has shown its ability to break down large pockets of gas. Hence, Simethicone can be administered to improve sonographic visualization, especially in patients with obesity; however, the cost-effectiveness of the routine use of Simethicone is questionable, and hence this is currently not standard in daily clinical practice. [9]
What is the role of Doppler US?
Doppler US examination of the renal vasculature plays a critical role in the evaluation of native as well as transplanted kidneys.
Why is Power Doppler important?
Power Doppler has certain benefits due to its greater sensitivity to flow and reduced angle dependence. This is especially helpful when assessing global renal perfusion and the parenchymal microvasculature to evaluate for cortical perfusion defects. [11]
What is the difference between left and right renal veins?
The renal veins generally lie anterior to the renal arteries at the renal hilum. The left renal vein measures 6 to 10 cm in length and is significantly longer than the right renal vein , which measures 2 to 4 cm. The left renal vein passes between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery before entering the IVC medially. During its course, the left renal vein receives almost always blood from the left adrenal and gonadal veins and, in the majority of patients, from the lumbar veins. The most common congenital anomaly of the left renal venous system is the circumaortic left renal vein (consisting of anterior and posterior limbs that encircle the abdominal aorta) seen in up to 17 % of the population. The shorter right renal vein empties into the IVC laterally, noting that, when compared to the left, the right gonadal and adrenal veins drain into the right renal vein more infrequently in only 7 % and 31 % of cases, respectively. [3][4][5]
What are the segments of the renal artery?
Before entering the renal hilum and parenchyma, the main renal artery divides into five segmental branches, including apical, superior, middle, inferior, and posterior segmental arteries. The segmental arteries supply end arteries to the renal parenchyma and divide further into lobar, interlobar, arcuate, and interlobular arteries. The interlobular arteries supply the afferent glomerular arterioles, which, in turn, feed into the glomeruli.
What Is a Renal Artery Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic tool that is used to assess the structural and functional characteristics of the main artery supplying the kidney. Renal artery disease correlates with the degree of kidney dysfunction. As the end-organ, the kidney depends on a normal flow through its artery to supply oxygen and nutrients to is cells, as well as to serve as the source of waste products and electrolytes for active and passive filtration, elimination, or re-absorption.
What is the use of Doppler duplex ultrasound?
Renal artery Doppler duplex ultrasound uses the combined approach of B mode ultrasound, which renders an image based on the differences of reflected sound waves from differing tissue densities; and Doppler technology that uses to advantage reflections from red blood cells that render actual flow imagery.
Why is a negative renal ultrasound not reassuring?
Because renal artery ultrasound is not as sensitive as confirmatory imaging methods, such as CT and MRI, a negative result is not necessarily reassuring, but indicative of the necessity for the more involved imaging that uses contrast.
What is renal resistive index?
Computations of renal “resistive index”: A pre-operative measurement comparing systolic blood flow velocity with end-diastolic velocity, which correlates well with a predicted benefit of planned revascularization surgery.
What is the purpose of duplex ultrasonography?
Duplex Doppler ultrasonography can assess function via information gleaned from the renal arteries; is also can provide information on the structure and anatomy. B-mode imaging combined with Doppler measurements can identify both stenotic lesions and arterial flow, and make comparisons to the blood flow of the aorta.
What is the function of the kidneys?
The kidneys not only eliminate waste, but are integral to electrolyte balance, homeostatic hydration, and blood pressure control. Renal artery ultrasound is indicated in
Is renal artery ultrasound accurate?
While renal artery ultrasound is useful as a screen or for initial investigation into renal artery disease, from atherosclerotic obstructions to renal artery hypertension, confirmation is via more invasive methods. CT Arteriography: Invasive due to its intravenous contrast is highly accurate for and confirmatory of atherosclerotic renovascular ...
What is a Doppler ultrasound?
A Doppler ultrasound is a noninvasive test that can be used to estimate the blood flow through your blood vessels by bouncing high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) off circulating red blood cells.
How does a Doppler ultrasound determine how fast blood flows?
Narrowing of an artery, such as in your neck (carotid artery stenosis) A Doppler ultrasound can estimate how fast blood flows by measuring the rate of change in its pitch (frequency).
Can a Doppler ultrasound show blood flow?
A regular ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images, but can't show blood flow. A Doppler ultrasound may help diagnose many conditions, including: Blood clots. Poorly functioning valves in your leg veins, which can cause blood or other fluids to pool in your legs (venous insufficiency)
Why do you need a kidney ultrasound?
blockage. buildup. cyst. infection. kidney stone. tumor. Other reasons you might need a kidney ultrasound include: guiding your doctor to insert a needle for a tissue biopsy of your kidney. draining fluid from a kidney abscess or cyst.
What is ultrasound in medical terms?
What is an ultrasound? Ultrasound, or sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves sent out by a transducer pressed against your skin. The sound waves move through your body, bouncing off organs back to the transducer.
Can you make an ultrasound appointment at the same time?
Once the procedure is done, the technician will forward the results to your doctor. They’ll review them with you during an appointment that you can make the same time you make the ultrasound appointment.
What is kidney ultrasound?
A kidney ultrasound (renal ultrasound) is an imaging test that allows your healthcare provider to look at your right and left kidney, as well as your bladder. The kidneys are the filtration system of your body. They filter the waste products out of your blood. The waste products then leave your body as urine.
How long does it take to get a kidney ultrasound?
This gel won’t harm your skin or stain your clothes. A probe is then gently applied against your skin. You may be asked to hold your breath several times or roll on your side during the test. Typically, the ultrasound will take about 20 to 30 minutes to complete.
How to prepare for an ultrasound?
The preparation for this test will depend on the type of ultrasound procedure your healthcare provider has ordered. Some things you might need to do to get ready for your ultrasound could include: 1 Drinking a quart of water before the test to obtain better images. 2 Eating a fat-free dinner the night before the test. 3 Fasting (limiting or avoiding food for a period of time).
What is ultrasound for pregnancy?
Ultrasound is an imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to see inside your body. This diagnostic test sends these sound waves — inaudible to the human ear — through your body tissues. The echoes are recorded and transformed into video or photographic images of the internal structures of the body. You might also hear this test call sonography or ultrasonography. Many people associate this test with pregnancy because it’s often used to look at a baby while it’s developing within the mother’s uterus. However, an ultrasound can be used for many reasons and it’s a useful diagnostic tool.
How long does it take for an ultrasound to show results?
In most cases, the results of your ultrasound are available within 24 hours after the test, Monday through Friday. The healthcare provider who ordered the test will usually discuss the test results with you.
Why do people use ultrasounds during pregnancy?
You might also hear this test call sonography or ultrasonography. Many people associate this test with pregnancy because it’s often used to look at a baby while it’s developing within the mother’s uterus. However, an ultrasound can be used for many reasons and it’s a useful diagnostic tool.
How to get better images of ultrasound?
Drinking a quart of water before the test to obtain better images. Eating a fat-free dinner the night before the test. Fasting (limiting or avoiding food for a period of time). In some cases, you may not need to do anything before your ultrasound.
