The Replication Experiment
- Purpose. A replication experiment is performed to estimate the imprecision or random error of the analytical method.
- Factors to consider. ...
- Time period of experiment. ...
- Matrix of sample. ...
- Number of materials and concentrations to be tested. ...
- Number of test samples. ...
- Data calculations. ...
- Criteria for acceptable performance. ...
- Recommended minimum studies. ...
What does it mean to replicate an experiment?
Replication is the act of reproducing or copying something, or is a copy of something. When an experiment is repeated and the results from the original are reproduced, this is an example of a replication of the original study. A copy of a Monet painting is an example of a replication.
What is the purpose of replicating an experiment?
- The original results were a false positive.
- The replicated results were a false negative.
- Both studies were correct but differed due to unknown differences in experimental conditions or methodologies.
How many replicates in an experiment?
You can determine the number of experiments you would do by multiplying 3X4X n, where n is the number of replications. Please note that replications should be at least 2. The more you do replications, the more precise results you get. Best of luck!
What is each time you repeat an experiment called?
- Iterative design focuses on incremental or cyclical improvement. ...
- The user feedback you gather in the iterative design process can help you identify usability problems. ...
- Some aspects of product design, such as color, form, typography, and wording create an emotional connection with users. ...
What is replication in an experiment example?
1:145:41How To Think About Replication (LE: Module 2, Part 6) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo there are a number of samples in each group. Which could be an experiment or a control an exampleMoreSo there are a number of samples in each group. Which could be an experiment or a control an example of biological replicates are distinct plates of cells that are treated in the same way.
What is an example of a replication?
Replication is the act of reproducing or copying something, or is a copy of something. When an experiment is repeated and the results from the original are reproduced, this is an example of a replication of the original study. A copy of a Monet painting is an example of a replication.
What does replication mean in a science experiment?
In engineering, science, and statistics, replication is the repetition of an experimental condition so that the variability associated with the phenomenon can be estimated. ASTM, in standard E1847, defines replication as "the repetition of the set of all the treatment combinations to be compared in an experiment.
What is a replication in an experiment quizlet?
Replication. Occurs when each treatment is applied to more than one experimental unit; ensures the effect of a treatment is not due to some characteristic of a single experimental unit. Completely randomized design. One in which each experimental unit is randomly assigned to a treatment.
What is replication in chemistry?
Replication occurs by means of partial unwinding of the two strands accompanied by synthesis of a new strand complementary to each of the originals. A rather complex mechanism exists for DNA replication, involving many different enzymes and protein factors.
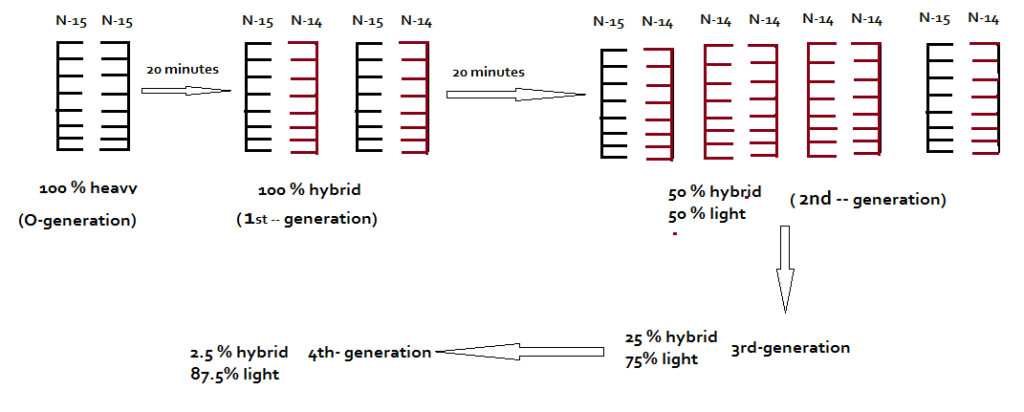
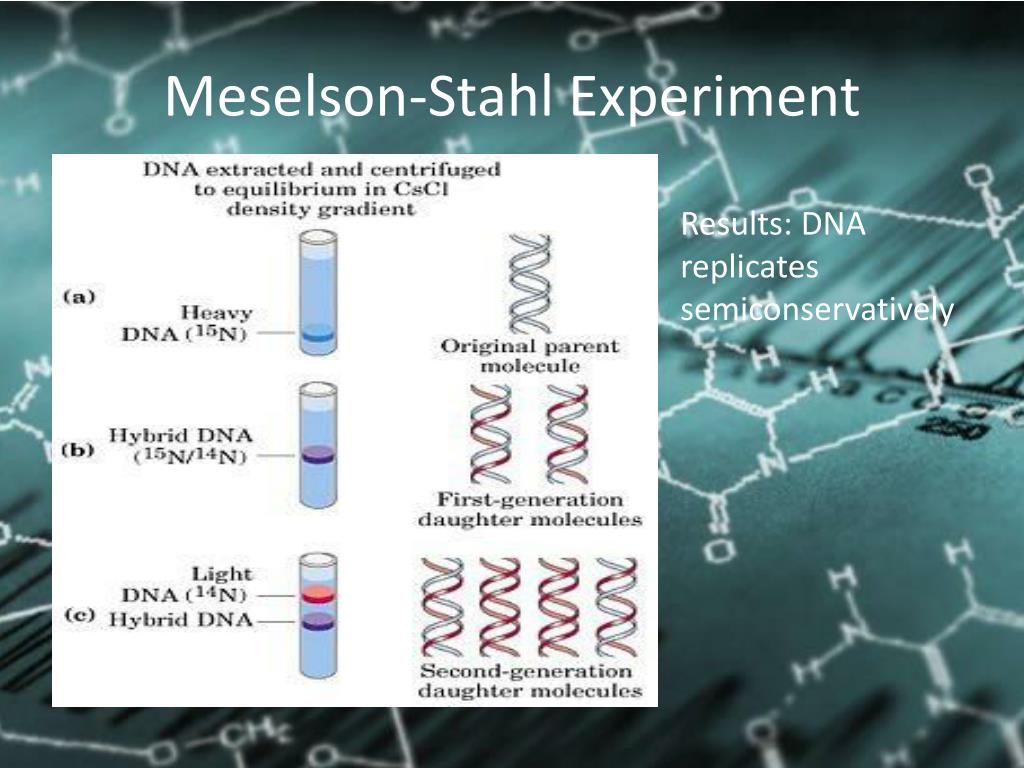
What does replication mean in biology?
DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell.
What is the purpose of replication?
The purpose of DNA replication is to produce two identical copies of a DNA molecule. This is essential for cell division during growth or repair of damaged tissues. DNA replication ensures that each new cell receives its own copy of the DNA.
What is scientific replication?
(Really a subdivision of 2) Researchers will use the conclusion of the experiment to enact other experiments, or in practical uses for the science. For example, based on the experiment, doctors start prescribing penicillin.
What does it mean to replicate an expirement?
Replication in an expirement means the results an expirement found could be repeated, usually by someone else, and usually that someone else is independent and not connected to the original expirementers. However, within one study, replication is still important. Usually one part of an expirement or even the whole thing will be done multiple times ...
Why is DNA linked to the origin of replication?
Thus, an alien DNA is linked with the origin of replication, so that, this alien piece of DNA can replicate and multiply itself in the host organism. It is because of the requirement of the origin of replication that a piece of DNA if needed to be propagated during recombinant DNA procedures, requires a vector.
What happens if an observation can't be repeated?
If an observation can’t be repeated by other people - If you’ve provided the coordinates for the galaxy and described it, but nobody else can find it there - then it is not an objective reality. It is not a scientific finding, so it is not useful to others in the field.
What was the sequence hypothesis?
[2] He thought that it was not the chemical composition of the bases ACGT which caused this or that activity to take place in the cell, but rather their order alone.
What is the act of copying a transaction called?
That act of copying your transaction is called replication.
What is the second meaning of replication?
That can be called replication. The second meaning is more specific to microbiology and genetics. It refers to increase in a number of genetically identical biological specimens, whether bacteria (generally cell culture) or genetically identical test subjects like mice, Continue Reading.
What is the purpose of replication?
In engineering, science, and statistics, replication is the repetition of an experimental condition so that the variability associated with the phenomenon can be estimated . ASTM, in standard E1847, defines replication as "the repetition of the set of all the treatment combinations to be compared in an experiment. Each of the repetitions is called a replicate ."
Does evaluation allow for item to item variation?
Evaluation or testing of a single item does not allow for item-to-item variation and may not represent the batch or process. Replication is needed to account for this variation among items and treatments.
What does it mean when a researcher can replicate a study?
If a researcher can replicate a study’s results, it means that it is more likely that those results can be generalized to the larger population.
What does it mean when a researcher replicates earlier research?
1 If the researcher obtains the same or similar results in follow-up experiments, it means that the original results are less likely to be a fluke.
Why do scientists want to replicate a study?
In other cases, scientists may want to replicate the experiment to further demonstrate the results.
How can replication be strengthened?
The Nobel Prize-winning psychologist Daniel Kahneman has suggested that because published studies are often too vague in describing methods used, replications should involve the authors of the original studies in order to more carefully mirror the methods and procedures used in the original research.
Why do scientists need to replicate experiments?
Finally, the researcher can draw conclusions about an experimental. Scientists must replicate experiments to ensure validity and account for error.
Why is replication important in science?
Common choices that can affect the reliability of results by being made after the experiment has started include when to stop the experiment, how to analyse the data, and which subgroup comparisons to carry out. The replication reduces variability in experimental results.
What is a well replicated experiment?
A well-replicated experiment ensures that the effect of one thing (the independent variable) on the other (the dependent variable) is real, true, reliable, valid. It accounts for the variation we expect to exist in nature.
