
The reticular interstitial pattern refers to a complex network of curvilinear opacities that usually involved the lung diffusely. They can be subdivided by their size (fine, medium or coarse). The subdivision refers to the size of the lucent spaces created by the intersection of lines:
What are the patterns of reticulation in HRCT?
Why is the interlobular septal thickening?
What is the HRCT of a definite usual interstitial pneumonia pattern in a patient with id?
What is thickening of the interlobular septum?
How long is an interlobular septa?
How big is a cyst?
Is thickening of the interlobular septa a diagnosis?
See 2 more
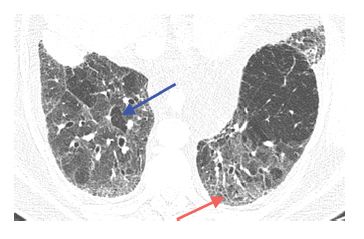
What do reticular opacities mean?
Reticular opacities seen on HRCT in patients with diffuse lung disease can indicate lung infiltration with interstitial thickening or fibrosis. Three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation.
What does reticulation in lungs mean?
Reticulation results from thickening of the interlobular or intralobular septa and appears as several linear opacities that resemble a mesh or a net on HRCT scans. 7. The presence of reticulation is indicative of interstitial lung disease.
What causes opacities in the lungs?
The causes of ground-glass opacities can be divided into acute and chronic. Among the acute causes are infections (atypical bacterial and viral infections), alveolar hemorrhage, pulmonary edema, diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary embolism, and some neoplasms.
What does reticular mean in radiology?
The reticular appearance refers to a collection of innumerable small linear opacities that together produce an appearance resembling a “net”. The pattern can be fine, medium or coarse. Fine and medium patterns are shown here. Reticular patterns represent interstitial lung disease.
What is the survival rate for interstitial lung disease?
The median survival for patients with ILD was 21.6 months (8.3–34.9). The ability to perform spirometry was associated with better survival (3-year survival rate 67.8%, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 63.3–72.3) [Figure 3]....Table 1.CharacteristicsPatients died (n=199)Patients survived (n=399)Mediastinal LAD3810319 more rows•Dec 31, 2020
What is the best treatment for interstitial lung disease?
Many people diagnosed with interstitial lung diseases are initially treated with a corticosteroid (prednisone), sometimes in combination with other drugs that suppress the immune system. Depending on the cause of the interstitial lung disease, this combination may slow or even stabilize disease progression.
Is opacity in the lung serious?
Lung opacities can indicate many conditions besides cancer. Many times they are benign (noncancerous). They may be due to infections, hemorrhages, a history of smoking, and even COVID-19. Lung opacities are common, 2021 research suggests.
How do you treat lung opacity?
The current main treatment methods for pulmonary multifocal GGO are forming a troika including the following: surgery, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), and thermal tumor ablation (including radiofrequency ablation, microwave ablation, and cryoablation).
Are lung opacities cancerous?
Yes, a lung nodule can be cancerous. But most lung nodules aren't cancerous. Lung nodules are small clumps of cells in the lungs. They're very common.
What are reticular opacities on CT?
In chest radiology, reticular and linear opacification refers to a broad subgroup of pulmonary opacification caused by a decrease in the gas to soft tissue ratio due to a pathological process centered in or around the pulmonary interstitium.
What does reticular mean in medical terms?
(reh-TIH-kyoo-ler DER-mis) The thick bottom layer of the dermis (the inner layer of the skin). The reticular dermis has blood vessels and connective tissue that supports the skin. Hair follicles, oil and sweat glands, and other structures are also found in the reticular dermis.
What causes reticular?
Reticular veins are very common, affecting about 80% of adults and can be caused by hormone imbalances, weak veins, and as a result of genetic factors. Age, weight, UV damage to the skin, and occupations which require a lot of time spent sitting or standing can be contributing factors.
Is interstitial lung disease serious?
Interstitial lung disease can lead to a series of life-threatening complications, including: High blood pressure in your lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Unlike systemic high blood pressure, this condition affects only the arteries in your lungs.
Is interstitial lung disease a terminal illness?
The life expectancy for interstitial lung disease depends on the cause and severity. Some people with mild ILD can live normal lives without treatment or with minimal treatment. Your outlook (prognosis) is better if your disease isn't getting worse (it's stable).
What do you mean by reticulation?
Reticulation is a net-like pattern, arrangement, or structure. Reticulation or Reticulated may refer to: Reticulation (single-access key), a structure of an identification tree, where there are several possible routes to a correct identification. A coloration pattern of some animals (e.g. the reticulated giraffe)
What is reticulation medical term?
re·tic·u·la·tion The presence or formation of a reticulum or network, such as that observed in the red blood cells during active regeneration of blood. Also used to describe a chest radiographic pattern. See: reticulonodular pattern.
What is reticular opacification?
In chest radiology, reticular and linear opacification refers to a broad subgroup of pulmonary opacification caused by a decrease in the gas to soft tissue ratio due to a pathological process centered in or around the pulmonary interstitium. This includes thickening of any of the interstitial compartments by blood, water, tumor, cells, fibrous disease or any combination thereof. The thickening of the interstitium can be reticular, reticulonodular, or linear where the predominant pattern is a result of the underlying pathological process.
What is the reticular interstitial pattern?
The reticular interstitial pattern refers to a complex network of curvilinear opacities that usually involved the lung diffusely. They can be subdivided by their size (fine, medium or coarse). The subdivision refers to the size of the lucent spaces created by the intersection of lines:
Is the thickening of the interstitium linear or reticular?
On this page: Article: Reticular. Reticulonodular. Linear.
What are fine reticular opacities?
Fine reticular opacities are reliable evidence of interstitial lung disease that requires consideration of a variety of acute and chronic diseases. Acute interstitial disease is most often the result of interstitial edema or pneumonia. Both may spread through the bronchovascular and septal interstitium. Involvement of the interlobular septa in the periphery of the lung are described as Kerley B lines. Kerley B lines are a common finding in patients with interstitial edema, but when they are more chronic they are a clue to suspect lymphangitic spread of a tumor. The collagen vascular and idiopathic interstitial lung diseases cause interstitial scarring that is more disorganized and does not spare the normal interstitial septa. Fine reticular opacities may be evidence of an early stage of these diseases.
What is diffuse reticular pattern?
The diffuse, fine reticular pattern (see Fig. 18.1 ) is one of the most reliable patterns for identifying diffuse interstitial disease. Because this pattern is linear, the lines must be distinguished from the normal pattern of blood vessels. In the early stages of an interstitial disease, this may be impossible by chest radiography, and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) may be required to confirm minimal interstitial disease. Interstitial diseases may spread throughout the bronchovascular or the septal interstitium while fibrotic diseases destroy the normal lung tissues, but both processes cause fine reticular opacities.
What are Kerley lines?
Kerley lines are the most reliable radiologic observation for making the distinction of bronchovascular versus septal interstitial disease. 150 , 175 , 235 Kerley B lines are short lines that are perpendicular to the pleura and continuous with it. The latter feature distinguishes the Kerley B lines from small vessels. Kerley B lines are usually observed in the costophrenic angles on the posteroanterior view and, occasionally, on the lateral view in the retrosternal clear space. They were first thought to represent only enlarged lymphatics but, based on pathologic correlations, these lines represent more generalized, enlarged interlobular septa. (Answer to question 1 is a .) Although it is true that the engorgement of septal lymphatic vessels would contribute to Kerley B lines, this has probably been overemphasized. In lymphangitic carcinomatosis, metastatic tumor spreads through dilated lymphatics in the interlobular septa and causes fine reticular opacities. In the other entities listed in Chart 18.1 , dilation of lymphatics is not a sufficient explanation for the presence of Kerley B lines. Furthermore, in congestive heart failure, edema of the loose connective tissue of the interlobular septa accounts for Kerley lines, rather than engorged lymphatics.
What is bibasilar linear opacity in chest x-ray indicates?
Scar vs. Atelectasis: "bibasilar linear opacity" is a term used by radiologists to describe thin lines seen in the bases of both lungs. The typical cause for this are benig... Read More
Chest x ray. small opacity left base believed to be a confluence of shadows. what does confluence of shadows mean in radiology?
One possibility: You may have a virtual consult on HT and upload the image/report. In general it means that there are several areas which come together to create one a... Read More
Implications of circular opacity in the left mid zone, vascular, as reported in the chest x-ray report.?
Need more info: First step would be to compare to an old cxr. If no previous cxr for comparison then consider f/u in 6 weeks or ct scan of chest if the patient has r... Read More
Chest x ray:no acute pulmonary disease.small opacity at left base believed to be confluence of shadows.follow up should be obtained if there is continued concern for pulmonary pathology.is this something that is concerning, what does it mean? thanks?
Need more info: All imging results need to be interpreted in the clinical context and the doctor who ordered the tests is usually in the best position to do that. Tal... Read More
I did chest x-ray for short breath as advised by doctor. result is a 0.7 cm nodular opacity in the left upper zone is new. anything to worry?
Yes: All results need to be interpreted in the clinical context and the doctor who ordered the tests is usually in the best position to do that. Talk to th... Read More
Can linear atelectasis left base been seen on chest x ray as faint opacity left lung base can they look the same on chest radiograph?
Yes: If there is any uncertainty about the xray findings, your physician should review them with the radiologist and determine whether further studies such... Read More
Had chest ct scan done due to abnormal chest x-ray the ct scan says small pluralparenchymal opacity in left lung base adjacent several cysts what does it mean?
Mgt: There may be several possible conditions associated with these findings. Infections may cause cysts. I would suggest a TB test and uploading the scan ... Read More
Overview
Interstitial (in-tur-STISH-ul) lung disease describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream.
Causes
In your lungs, the main airways (bronchi) branch off into smaller and smaller passageways — the smallest, called bronchioles, lead to tiny air sacs (alveoli).
Risk factors
Factors that may make you more susceptible to interstitial lung disease include:
Complications
Interstitial lung disease can lead to a series of life-threatening complications, including:
What are the patterns of reticulation in HRCT?
Three principal patterns of reticulation may be seen. These are interlobular septal thickening, honeycombing, and irregular reticulation.
Why is the interlobular septal thickening?
Irregular interlobular septal thickening usually reflects lung fibrosis and is similar in significance to irregular reticulation, which is described later. The architectural distortion associated with fibrosis causes the septa to become jagged or angulated in appearance (Fig. 2.4C, Table 2.1). Irregular septal thickening may be seen with any cause of fibrotic lung disease, and other findings, such as honeycombing and traction bronchiectasis, are more helpful in the formulation of a differential diagnosis.
What is the HRCT of a definite usual interstitial pneumonia pattern in a patient with id?
HRCT of a definite usual interstitial pneumonia pattern in a patient with idiopathic pulmonaryfibrosis. HRCT through the upper lungs (A)and mid-lung (B)shows irregular reticulation as the predominant abnormality. Scan through the lung bases (C)shows subpleural and basilar fibrosis with significant honeycombing. The abnormalities predominate at the lung bases. D. Sagittal reformation shows predominance of abnormalities at the bases and in the posterior lung, including the costophrenic angles.
What is thickening of the interlobular septum?
2.2). Intralobular interstitial thickeningresults in an irregular reticular pattern smaller in scale than the reticular pattern of interlobular septal thickening.
How long is an interlobular septa?
They comprise connective tissue and contain pulmonary veins and lymphatics. Interlobular septa are approximately 1 to 2 cm in length and 1/10th of a millimeter in thickness. Only a few interlobular septa are seen on HRCT in normal patients.
How big is a cyst?
2. Most cysts are 3 to 10 mm in diameter. Some may be larger or smaller.
Is thickening of the interlobular septa a diagnosis?
The presence of a few thickened interlobular septa can be seen in a wide variety of diffuse lung diseases and is, in general, a nonspecific finding. For the purposes of differential diagnosis, thickened septa should be ignored unless they represent a predominant abnormality (Fig. 2.3A, B).
