A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known fo…
What are retroviruses biological definition?
Retroviruses are viruses with RNA as genetic material. They belong to the family Retroviridae of Retroviruses. Once it has infected a cell, it converts its RNA into DNA by reverse transcription. This viral DNA is then inserted into the DNA of the host cell where it starts replicating.
What does retrovirus mean?
A retrovirus is a virus that works by converting its own RNA into DNA once it is in a host cell. It then integrates this DNA into the DNA of the host cell, allowing the virus to replicate. Three retroviruses can cause illness in humans, and each one has different symptoms. One of these retroviruses is Human Immunodeficiency Virus, or HIV.
What is the difference between RNA virus and retrovirus?
• Virus contains genetic material as DNA or RNA but retrovirus contains only RNA. • If the virus has DNA, it inserts DNA into the host cell, and it is integrated directly into the host genome at the lytic phase, whereas retrovirus has RNA as its genetic material and needs to convert RNA to DNA before insert it into the host genome.
How is retrovirus different from DNA virus?
• Virus contains genetic material as DNA or RNA but retrovirus contains only RNA. • If the virus has DNA, it inserts DNA into the host cell, and it is integrated directly into the host genome at the lytic phase, whereas retrovirus has RNA as its genetic material and needs to convert RNA to DNA before insert it into the host genome.
What are two examples of a retrovirus?
Besides human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes AIDS, there a two other retroviruses that can cause human illness. One is called human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and the other is called human T-lymphotropic virus type 2 (HTLV-II).
What is the primary difference between a virus and a retrovirus?
Retroviruses differ from other viruses in that each virion contains two complete copies of the single-stranded RNA genome.
Is retrovirus A virus?
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell.
Why is the virus called as retrovirus?
Retroviruses are "retro" because they reverse the direction of the normal gene copying process. Usually, cells convert DNA into RNA so that it can be made into proteins. But with retroviruses, the process has to start by going backward.
How does a retrovirus infect a cell?
Upon infection with a retrovirus, a cell converts the retroviral RNA into DNA, which in turn is inserted into the DNA of the host cell. The cell then produces more retroviruses, which infect other cells. Many retroviruses are associated with diseases, including AIDS and some forms of cancer.
What type of virus is Covid 19?
COVID-19 is caused by a virus called SARS-CoV-2. It is part of the coronavirus family, which include common viruses that cause a variety of diseases from head or chest colds to more severe (but more rare) diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).
Are retroviruses contagious?
This retrovirus is one of thousands that became a part of the human genome after infecting our ancestors long ago. Nowadays, these retroviruses are no longer contagious, but are instead passed along through inheritance in part of the genome that scientists consider "junk" DNA.
Can retroviruses be cured?
One of the most well known retroviruses is HIV. AIDS can now be treated, but there is still no cure.
Where do retroviruses hide?
Retroviruses enter the host cell through the attachment of their surface glycoproteins to specific plasma membrane receptors, which leads to fusion of virus and cell membranes (Fig.
What is the difference between RNA viruses and retroviruses quizlet?
How are retroviruses different from other types of viruses? - Retrovirus RNA is incorporated into the host cell's DNA in order to be translated. - Retroviruses use the enzyme reverse transcriptase to transcribe a copy of DNA from their own RNA.
Are virus and retrovirus the same?
Retroviruses are a type of virus that use a special enzyme called reverse transcriptase to translate its genetic information into DNA. That DNA can then integrate into the host cell's DNA. Once integrated, the virus can use the host cell's components to make additional viral particles.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA retroviruses viruses?
The viruses that contain DNA as their genetic material are called the DNA viruses. RNA viruses, on the other hand, contain RNA as their genetic material. DNA viruses are mostly double-stranded while RNA viruses are single-stranded. RNA mutation rate is higher than the DNA mutation rate.
What differentiates a virus from a bacteria?
On a biological level, the main difference is that bacteria are free-living cells that can live inside or outside a body, while viruses are a non-living collection of molecules that need a host to survive.
What are retroviruses?
Retroviruses are viruses that contain RNA as genetic material. They contain the enzyme reverse transcriptase which has the ability to transcribe RN...
Name a retrovirus in humans?
HTLV-1 is a retrovirus found in humans. This retrovirus causes cancer in humans. Another retrovirus known as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) cau...
How does a retrovirus work?
The retrovirus infects the host cell and uses the enzyme reverse transcriptase to convert RNA into DNA. This viral DNA is then integrated into the...
How can a retrovirus be treated?
Antiretroviral drugs are used to treat infections caused by retroviruses, especially HIV.
What is a retrovirus?
Retrovirus. Retrovirus. =. A retrovirus is a virus that uses RNA as its genetic material. When a retrovirus infects a cell, it makes a DNA copy of its genome that is inserted into the DNA of the host cell.
How does a retrovirus behave?
The term "retrovirus" means it behaves backwards from the original way that we all think about genetics, which is that DNA makes RNA, and RNA makes protein. So retroviruses have an RNA genome, and when they get into cells that RNA is reverse-transcribed into DNA, so it goes backwards.
Which virus causes AIDS?
Now, the most famous one right at the moment is the human immunodeficiency virus which causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS. But there are many different kinds of retroviruses that are associated with diseases, including cancer, leukemia, and AIDS, obviously.
What is the RNA that goes into the packaging materials?
Some of that RNA is translated into proteins, which are needed to package the retrovirus. And another of those RNAs is the RNA genome that goes into those packaging materials and is excreted from the cell and goes on to infect other cells. So there are many different kinds of retroviruses.
What are retroviruses?
Human retroviruses. Treatment. Takeaway. Viruses are tiny microbes that can infect cells. Once in a cell, they use cellular components to replicate. They can be classified according to several factors, including: the type of genetic material they use (DNA or RNA) the method they use to replicate within the cell. their shape or structural features.
What is the difference between a virus and a retrovirus?
There are many technical differences between viruses and retroviruses. But generally, the main difference between the two is how they replicate within a host cell.
How do retroviruses replicate?
Here’s a look at the steps of the life cycle of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) to help illustrate how retroviruses replicate: 1 Attachment. The virus binds to a receptor on the surface of the host cell. In the case of HIV, this receptor is found on the surface of immune cells called CD4 T cells. 2 Entry. The envelope surrounding the HIV particle fuses with the membrane of the host cell, allowing the virus to enter the cell. 3 Reverse transcription. HIV uses its reverse transcriptase enzyme to turn its RNA genetic material into DNA. This makes it compatible with the host cell’s genetic material, which is vital for the next step of the life cycle. 4 Genome integration. The newly synthesized viral DNA travels to the cell’s control center, the nucleus. Here, a special viral enzyme called integrase is used to insert the viral DNA into the host cell’s DNA. 5 Replication. Once its DNA has been inserted to the host cell’s genome, the virus uses the host cell’s machinery to produce new viral components, such as viral RNA and viral proteins. 6 Assembly. The newly made viral components combine close to the cell surface and begin to form new HIV particles. 7 Release. The new HIV particles push out from the surface of the host cell, forming a mature HIV particle with the help of another viral enzyme called protease. Once outside the host cell, these new HIV particles can go on to infect other CD4 T cells.
How does HIV work?
HIV uses its reverse transcriptase enzyme to turn its RNA genetic material into DNA. This makes it compatible with the host cell’s genetic material, which is vital for the next step of the life cycle. Genome integration. The newly synthesized viral DNA travels to the cell’s control center, the nucleus.
How does a virus use the host cell's machinery?
Once its DNA has been inserted to the host cell’s genome, the virus uses the host cell’s machinery to produce new viral components, such as viral RNA and viral proteins. Assembly. The newly made viral components combine close to the cell surface and begin to form new HIV particles. Release.
What is the name of the genetic material used to replicate within a cell?
the type of genetic material they use (DNA or RNA) the method they use to replicate within the cell. their shape or structural features. Retroviruses are a type of virus in the viral family called Retroviridae.
What is the best treatment for retrovirus?
A combination of the drugs interferon and zidovudine may also be used. Both of these drugs help to prevent retroviruses from attacking new cells and replication.
What are the virions of retroviruses?
Virions of retroviruses consist of enveloped particles about 100 nm in diameter. The outer lipid envelope consists of glycoprotein. The virions also contain two identical single-stranded RNA molecules 7–10 kilobases in length. The two molecules are present as a dimer, formed by base pairing between complementary sequences. Interaction sites between the two RNA molecules have been identified as a " kissing stem-loop ". Although virions of different retroviruses do not have the same morphology or biology, all the virion components are very similar.
How does a retrovirus work?
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thu s changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards).
How are gammaretroviral vectors used in gene therapy?
Gammaretroviral and lentiviral vectors for gene therapy have been developed that mediate stable genetic modification of treated cells by chromosomal integration of the transferred vector genomes. This technology is of use, not only for research purposes, but also for clinical gene therapy aiming at the long-term correction of genetic defects, e.g., in stem and progenitor cells. Retroviral vector particles with tropism for various target cells have been designed. Gammaretroviral and lentiviral vectors have so far been used in more than 300 clinical trials, addressing treatment options for various diseases. Retroviral mutations can be developed to make transgenic mouse models to study various cancers and their metastatic models .
What happens if a virus is integrated into a host chromosome?
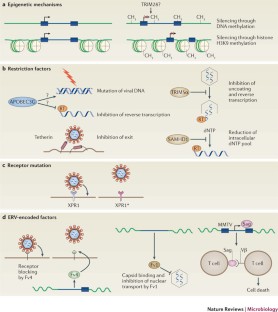
If viral DNA is integrated into host chromosomes, it can lead to permanent infections. It is therefore important to discover the body's response to retroviruses. Especially exogenous retroviruses are associated with pathogenic diseases. For example, mice have mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV), which is a retrovirus.
What is the name of the strand of DNA that is replicated by reverse transcriptase?
Within the cell, reverse transcriptase creates a complementary strand of DNA from the retrovirus RNA and the RNA is degraded; this strand of DNA is known as cDNA (4). The cDNA is then replicated, and the two strands form a weak bond and enter the nucleus (5).
What are the enzymes that are involved in retrovirus replication?
There are two strands of RNA within the cell that have three enzymes: protease, reverse transcriptase, and integrase (1).
What is the pol region in retrovirus?
Retroviruses (and orterviruses in general) follow a layout of 5'– gag – pro – pol – env –3' in the RNA genome. gag and pol encode polyproteins, each managing the capsid and replication. The pol region encodes enzymes necessary for viral replication, such as reverse transcriptase, protease and integrase.
What is retrovirus vector?
Retroviral vectors are genetically engineered retroviruses. They have been used for the transfer of genes into the mammalian host cells for over 20 years. The retroviral vectors derived from the Moloney murine leukaemia virus are the most common retrovirus.
What is the structure of a retrovirus?
Retrovirus Structure. It consists of two concentric outer circles of the lipid bilayer that contains the envelope protein complex embedded in it. The capsid proteins are hexagonal. The copies of the RNA genome are in the form of a loop bound by nucleoproteins. The main virion components are:
What is the name of the virus that turns RNA into DNA?
Once it has infected a cell, it converts its RNA into DNA by reverse transcription. This viral DNA is then inserted into the DNA of the host cell where it starts replicating. For eg., Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
How are HTLV I and II related?
The type I and II are closely related to each other. A person infected with HTLV I virus develops acute T-cell leukaemia. It affects the spinal cord and causes a neurological disorder. It was the first human retrovirus to be discovered and can be transmitted through blood transfusion, needle sharing, breastmilk, or sexual contact. HTLV II is also associated with neurological disorders and some types of blood cancers. However, very less is known about this type of virus.
What are the limitations of retroviral vectors?
One of the limitations of using retroviral vectors in gene therapy is that the integrase enzyme can insert the genetic material in the middle of the original genes of the host cell. This causes the disruption of the gene.
How many types of retrovirus are there?
There are three types of retrovirus affecting humans:
What is the function of RNA?
It has non-coding regions at the terminal which help in replication, whereas, the internal regions encode virion proteins for gene expression.
What are the components of a retrovirus?
Retrovirus virions consist of the outer lipid envelope of glycoprotein. The virions contain two identical single-stranded RNA molecules that are present as a dimer. Although the virions do not have the same biology or morphology, their components are very similar. Some of the main virion components are: Envelope.
How does a retrovirus work?
Similar to other viruses, retrovirus uses the cellular machinery of the organism they infect to make copies of themselves. Getting affected by a retrovirus requires an additional step. The genome needs to be reversed-transcribed into DNA before it is copied in a usual way. 2.
How does a retrovirus replicate?
The copy of the DNA genome gets into the host genome inside the nucleus via an enzyme called integrase. As a result, the retroviral genome is transcribed into RNA whenever the host genome transcribes, allowing retrovirus to replicate.
What is the name of the gene that carries the genetic blueprint?
Retrovirus is a virus that belongs to the family of Retroviridae. It characteristically carries the genetic blueprint in the form of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Retrovirus is named after an enzyme known as reverse transcriptase. The reverse transcriptase transcribes the RNA into DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). It is a process that constitutes a reversal of the actual direction of cellular transcription from DNA into RNA. The reverse action makes the genetic material from a retrovirus to permanently incorporate into the DNA genome of the infected cell. The enzyme is popularly used in biological sciences to synthesize genes. The best example of a retrovirus is Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
What is the function of the Env gene?
Env proteins are responsible for the entry of virions into the host cell. Due to the functional copy of env gene retroviruses are distinct from retroelements.
What is reverse transcriptase?
It is a process that constitutes a reversal of the actual direction of cellular transcription from DNA into RNA. The reverse action makes the genetic material from a retrovirus to permanently incorporate into the DNA genome of the infected cell.
What type of virus undergoes reverse transcription to convert the RNA into DNA?
Retrovirus – retrovirus undergoes reverse transcription to convert the RNA into DNA.
Why is it called a retrovirus?
It is called a retrovirus because it has the ability to go' 'transcribe in reverse' ' from RNA to DNA with the help of the enzyme Reverse Transcriptase.
What is the difference between a virus and a retrovirus?
Retroviruses are viruses whose genetic material is composed specifically of RNA, and they can integrate their genetic information into the host's genome after infection. Interestingly, some microscopic agents have a life cycle that seems to be "in reverse" or seems to go "in opposite direction" to the life cycle that common viruses undergo. This is because they can go against one of the central dogmas of biology by doing reverse transcription that allows them to transcript from RNA back to DNA, which is the opposite of what other viruses do to generate viral materials within the host.
How do retroviruses work?
They are capable of breaking one of the central dogmas in biology by performing a reverse transcription from RNA into DNA, modifying the genome of their hosts permanently . These characteristics and the fact that these viruses attack the cells of the immune system make them harder to treat. There is no cure for the diseases caused by retroviruses, but there are some treatments available to minimize their effects on human health.
What type of virus causes lymphocytes to change?
Other human retroviruses are the Human T-cell Lymphotropic Viruses type 1 or HTLV-1 and type 2 HTLV-2. These viruses are also capable of causing changes in lymphocytes. Sometimes these changes in the blood cells can lead to the development of inflammation and a very rare type of blood cancer. The HTLV-1 was the first oncogenic human retrovirus to be discovered in 1977.
How are retroviruses different from other viruses?
What makes retroviruses different from other viruses is that they can insert their genetic information into the host's genome while other viruses generate copies of themselves in the cytoplasm that cannot change the genetic information of the host. This special characteristic of retroviruses has amazed scientists for years.
Why are retroviruses so hard to treat?
Retroviruses are hard to treat because they can modify the host's DNA by introducing their genome, and attack cells that are involved in the immune response like T-lymphocytes. As the virus attacks the immune system itself, a person infected won't have enough resources to recover from almost any disease or condition. The changes in the DNA of the host cells are permanent and cannot be reversed. Also, retroviral infections remain dormant for a while, making it even harder to determine if a person has the virus or not, and also, reducing the efficacy of the retroviral medications that cannot affect the dormant viruses "hiding" in their hosts.
What type of virus causes AIDS?
Some human retroviruses are the Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 or HIV, which causes AIDS, and human T-lymphotropic viruses type 1 and 2, which cause cancer and inflammatory disease.
Why are retroviruses called retroviruses?
Retroviruses are "retro" because they reverse the direction of the normal gene copying process. Usually, cells convert DNA into RNA so that it can be made into proteins. But with retroviruses, the process has to start by going backward. First, the viral RNA is transformed into DNA. Then the cell can copy the DNA.
How does a retrovirus work?
A retrovirus is a virus whose genes are encoded in RNA, and, using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase, replicates itself by first reverse-coding ...
What is the enzyme that replicates itself?
Latesha Elopre, MD, MSPH. on July 24, 2020. A retrovirus is a virus whose genes are encoded in RNA, and, using an enzyme called reverse transcriptase, replicates itself by first reverse-coding its genes into the DNA of the cells it infects. Like other viruses, retroviruses need to use the cellular machinery of the organisms they infect ...
Why are retroviruses used in gene therapy?
4 This is because these viruses are both easy to modify and easily integrated into the host genome. This means that, in theory, they can be used to cause the cellular machinery to make proteins in an ongoing way.
What enzyme is used to turn RNA into double stranded DNA?
The enzyme that does this backward transcription is known as reverse transcriptase. 1 . Retroviruses use reverse transcriptase to transform their single-stranded RNA into double-stranded DNA. It is DNA that stores the genome of human cells and cells from other higher life forms. Once transformed from RNA to DNA, ...
What is the most common retrovirus?
The most well-known retrovirus that infects humans is HIV. 1 However, there are several other human retroviruses. These include the human T-cell lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1). HTLV-1 is associated with certain T-cell leukemias and lymphomas. There are many additional retroviruses which have been identified as infecting other species. 2
Why is reverse transcriptase inhibitor important?
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors prevent HIV from becoming integrated into the genome of the host cell.

Overview
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards). The new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell ge…
Structure
Virions, viruses in the form of independent particles of retroviruses, consist of enveloped particles about 100 nm in diameter. The outer lipid envelope consists of glycoprotein. The virions also contain two identical single-stranded RNA molecules 7–10 kilobases in length. The two molecules are present as a dimer, formed by base pairing between complementary sequences. Interaction sites …
Multiplication
When retroviruses have integrated their own genome into the germ line, their genome is passed on to a following generation. These endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), contrasted with exogenous ones, now make up 5–8% of the human genome. Most insertions have no known function and are often referred to as "junk DNA". However, many endogenous retroviruses play important roles in ho…
Transmission
• Cell-to-cell
• Fluids
• Airborne, like the Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus.
Provirus
The DNA formed after reverse transcription (the provirus) is longer than the RNA genome because each of the terminals have the U3 - R - U5 sequences called long terminal repeat (LTR). Thus, 5' terminal has the extra U3 sequence, while the other terminal has the U5 sequence. LTRs are able to send signals for vital tasks to be carried out such as initiation of RNA production or management of the rate of transcription. This way, LTRs can control replication, hence, the entir…
Early evolution
Studies of retroviruses led to the first demonstrated synthesis of DNA from RNA templates, a fundamental mode for transferring genetic material that occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. It has been speculated that the RNA to DNA transcription processes used by retroviruses may have first caused DNA to be used as genetic material. In this model, the RNA world hypothesis, cellular organisms adopted the more chemically stable DNA when retroviruses evolved to create
Gene therapy
Gammaretroviral and lentiviral vectors for gene therapy have been developed that mediate stable genetic modification of treated cells by chromosomal integration of the transferred vector genomes. This technology is of use, not only for research purposes, but also for clinical gene therapy aiming at the long-term correction of genetic defects, e.g., in stem and progenitor cells. Retroviral vector particles with tropism for various target cells have been designed. Gammaretro…
Cancer
Retroviruses that cause tumor growth include Rous sarcoma virus and mouse mammary tumor virus. Cancer can be triggered by proto-oncogenes that were mistakenly incorporated into proviral DNA or by the disruption of cellular proto-oncogenes. Rous sarcoma virus contains the src gene that triggers tumor formation. Later it was found that a similar gene in cells is involved in cell signaling, which was most likely excised with the proviral DNA. Nontransforming viruses can ran…