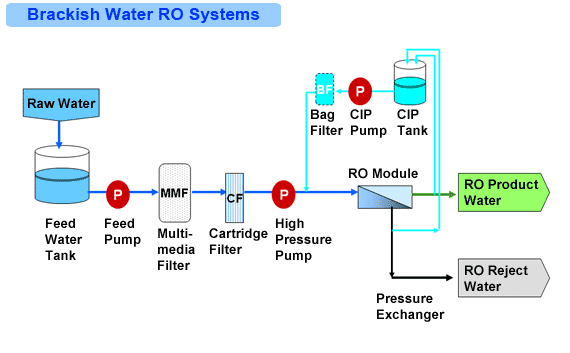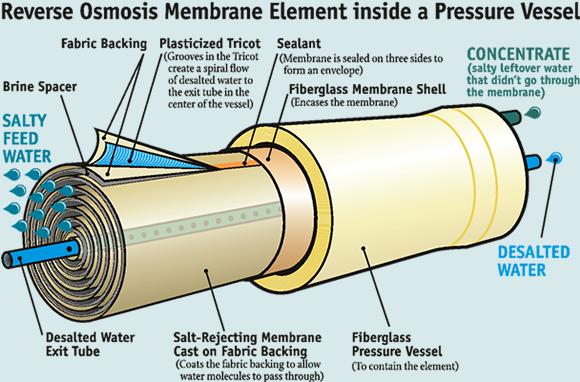
Do you need to replace reverse osmosis membrane?
The reverse osmosis membrane on average should be replaced every 3-5 years, if it is still producing good quality water you may be able to keep it longer than five years.
What is reverse osmosis in simple words?
Definition of reverse osmosis : the movement of fresh water through a semipermeable membrane when pressure is applied to a solution (such as seawater) on one side of it.
What is purpose of reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane (synthetic lining) to filter out unwanted molecules and large particles such as contaminants and sediments like chlorine, salt, and dirt from drinking water.
Where is the reverse osmosis membrane?
0:534:56How to Identify Your Reverse Osmosis Membrane - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI've only found one in my numerous years of experience that didn't have some kind of identifyingMoreI've only found one in my numerous years of experience that didn't have some kind of identifying mark on it. So you need to shut off the water supply to your system you're going to go to the valve.
Can you drink reverse osmosis water?
The short answer to the question, “is reverse osmosis water safe?” is that reverse osmosis water is safe to drink. Though reverse osmosis removes hard minerals from water, it also removes a wide range of other contaminants which can have a negative health impact.
Is reverse osmosis water good for you?
Reverse osmosis systems produce cleaner water, save you money, and are better for the environment. The only downsides are minor; reverse osmosis systems will reduce some good minerals from your water along with the contaminants. However, you'll have no problem replacing these minerals with a healthy diet.
What does reverse osmosis not remove from water?
Reverse osmosis units do not effectively remove most organic compounds, bacterial microorganisms, chlorine by-products, or dissolved gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and radon.
Which is better reverse osmosis or filtration?
Carbon filtration excels at removing chlorine taste and odor. It also does a great job of capturing large particulates. Reverse Osmosis, on the other hand, will remove almost anything from your water, but it works better if the large particles are removed ahead of it to prevent premature fouling of the membrane.
How long do reverse osmosis filters last?
every 12 monthsRO filters replacement should ideally be done every 12 months. This is to ensure optimal effectiveness of your whole reverse osmosis system. Failure to do this would result to contaminants being still present in your drinking water.
What does an RO membrane look like?
0:033:05How Ro Membranes Work - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWithin this membrane and fill the membrane up are all RO systems are going to drain water to theMoreWithin this membrane and fill the membrane up are all RO systems are going to drain water to the drain as they run that is the water passing through the membrane.
What is the cost of RO membrane?
Filmtec Dow 75 GPD membrane with Housing for RO service Solid Fil... KONVIO 80 GPD RO High 3000 TDS Membrane for All Type of RO Water ......Vontron 75 GPD membrane for RO service Solid Filter Cartridge (0.0001, Pack of 4)BrandVontronApplicationReverse OsmosisSuitable ForWater Purifier6 more rows
What is difference between membrane and filter?
The Differences Between Membrane and Media Filtration Both processes filter our pollutants. Both processes have two common methods for filtering. Membrane filtration sets itself apart in that it doesn't use a chemical process to filter water.
What are the advantages of reverse osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis systems can remove pollutants from water including lead, pesticides, fluoride, pharmaceuticals, arsenic and much more. And with a carbon filter, an RO system can also remove chlorine to improve the taste, odor and appearance of your water.
How does reverse osmosis purify water?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water treatment process that removes contaminants from water by using pressure to force water molecules through a semipermeable membrane. During this process, the contaminants are filtered out and flushed away, leaving clean, delicious drinking water.
What's the difference between reverse osmosis water and distilled water?
Reverse osmosis performs water filtration by passing it through multiple stages of filtration stripping off all the minerals. In the final filtration stage, it adds healthy minerals back into the water. Distillation, on the other hand, also purifies water but doesn't add healthy minerals to the water.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse Osmosis works by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water across the semipermeabl...
What is an example of the use of reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a means of pulling clean water out of polluted water or saltwater by pushing water through a membrane under pressure. An example...
What are the disadvantages of reverse osmosis?
The drawback of RO water is that it can significantly reduce these good minerals which can help in overall health of the heart and muscles. Those w...
What is osmosis and reverse osmosis?
Osmosis is a process in which liquid water flows through a semipermeable membrane from a diluted solution into a more concentrated solution. This i...
What is the principle of reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis ( RO) is a water purification process that removes ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water using a partia...
What Is Reverse Osmosis Membrane Made of?
Reverse osmosis membranes are made from a variety of materials, but the most common is synthetic polymers . The polarity of these membranes is perfect for the job because they will only allow water molecules to pass through them, while other dissolved solids are left out.
What Is Reverse Osmosis in Simple Terms?
Reverse osmosis is a process that forces water through a membrane, creating two separate streams of water.
How Much Does RO Membrane Cost?
Reverse osmosis membranes are priced based on their quality, size, and the company that manufactures the membrane.
How is reverse osmosis different from simple membrane filtration?
However, reverse osmosis is different from simple membrane filtration because it involves diffusion and is affected by flow rate and pressure.
What is reverse osmosis used for?
Reverse osmosis can be used to purify water. WLADIMIR BULGAR / Getty Images
What happens when water is moved across the membrane?
Reverse osmosis occurs when the water is moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient, from lower concentration to higher concentration. To illustrate, imagine a semipermeable membrane with fresh water on one side and a concentrated aqueous solution on the other side. If normal osmosis takes place, the fresh water will cross the membrane to dilute the concentrated solution. In reverse osmosis , pressure is exerted on the side with the concentrated solution to force the water molecules through the membrane to the freshwater side.
How to understand reverse osmosis?
In order to understand reverse osmosis, it helps to first understand how mass is transported via diffusion and regular osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Osmosis is a special case of diffusion in which the molecules are water and the concentration gradient occurs ...
Is osmosis thermodynamically favorable?
Diffusion and osmosis are thermodynamically favorable and will continue until equilibrium is reached. Os mosis can be slowed, stopped, or even reversed if sufficient pressure is applied to the membrane from the 'concentrated' side of the membrane. Reverse osmosis occurs when the water is moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient, ...
Can a solute cross a membrane?
Large molecules (solute) can't cross the membrane, so they remain on one side. Water (solvent) can cross the membrane. The result is that solute molecules become more concentrated on one side of the membrane, while the opposite side becomes more dilute.
Is reverse osmosis a new purification technique?
Reverse osmosis is not a new purification technique. The first examples of osmosis through semipermeable membranes was described by Jean-Antoine Nollet in 1748. While the process was known in laboratories, it wasn't used for desalination of seawater until 1950 at the University of California in Los Angeles. Multiple researchers refined methods of using reverse osmosis to purify water, but the process was so slow that it wasn't practical on a commercial scale. New polymers allowed for the production of more efficient membranes. By the beginning of the 21st century, desalination plants became capable of desalinating water at the rate of 15 million gallons per day, with around 15,000 plants in operation or planned.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis which is also commonly referred to as RO is a type of filtration method used for the removal of molecules and ions from a certain solution.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse Osmosis works by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water across the semipermeable RO membrane, leaving almost all (around 95 to 99 per cent) dissolved salts in the reject stream behind .
What is reverse osmosis in water purification?
In water purification, the reverse osmosis process is very important. Many water purifiers used today use reverse osmosis in the purification process as one of the steps.
How to reverse osmosis with aqueous solution?
The solutions should be kept on opposite sides with a semipermeable membrane placed in between to separate the two solutions. Pressure should be applied on the side with the concentrated solution. Now this will result in water molecules moving through the membrane to the freshwater side. This basically sums up the process of reverse osmosis.
What is the osmotic pressure of a solution?
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure required to stop solvent flow through the semipermeable membrane. Therefore, when the solution side (the side where the solute concentration is high) is subjected to a pressure greater than the osmotic pressure, the solvent particles on the solution side move through the semipermeable membrane to the region where the solute concentration is low. Such inverse solvent movement through the semipermeable membrane is called reverse osmosis.#N#It is important to note that the pressure applied to the solution side must be higher than the osmotic pressure for the reverse osmosis process to proceed. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, which depends on the concentration of the solution. In water purification, the reverse osmosis process is very important. Many water purifiers used today use reverse osmosis in the purification process as one of the steps.
What are the disadvantages of reverse osmosis?
Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis 1 Cellulose acetate membranes have limited pH tolerance. They degrade at temperatures greater than 35oC. They are vulnerable to bacteria. They eventually hydrolyze. 2 Polyamide membranes are intolerant of temperature greater than 35oC. They have poor tolerance for free chlorine. 3 Thin-film composites are intolerant of chlorine. High flux polysulfones require softening or deionization of feed water to function properly.
Why do solutes not cross the membrane?
To break down the process further, due to the presence of membrane , large molecules of the solute are not able to cross through it and they remain on the pressurized side. The pure solvent, on the other hand, is allowed to pass through the membrane. When this happens the molecules of the solute start becoming concentrated on one side while the other side of the membrane becomes dilute. Furthermore, the levels of solutions also change to some degree.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) has been known for more than a century, but it did not become a commercial process until the early sixties when a special membrane was developed (1,2,3,4). Because RO operates at a comparatively low temperature and is relatively energy efficient, it is employed in various applications, e.g., desalination, treatment of waste water, reclamation of minerals, concentration of whey and other food products, and purification of water (5,6). In recent years, RO has been used increasingly in making processed water for dialysis in hospitals and for certain cosmetics and drugs by pharmaceutical manufacturers (7,8). In addition to these applications, RO is capable of producing water of sufficient purity to be used as Water For Injection (WFI) and for the preparation of parenteral solutions (9,10,11,12). This ITG will focus on the chemical and microbiological quality of water produced by reverse osmosis.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse osmosis is a process which uses a membrane under pressure to separate relatively pure water (or other solvent) from a less pure solution. When two aqueous solutions of different concentrations are separated by a semi-permeable membrane, water passes through the membrane in the direction of the more concentrated solution as a result of osmotic pressure (Figure 1). If enough counter pressure is applied to the concentrated solution to overcome the osmotic pressure, the flow of water will be reversed (Figure 2).
What molecules enter the membrane by hydrogen bonding?
The water mole cules that enter the membrane by hydrogen bonding can be pushed through under pressure. Most organic substances with a molecular weight over 100 are sieved out, i.e., oils, pyrogens and particulates including bacteria and viruses (13).
What is fouling in RO systems?
A major problem in operating RO systems is concentration polarization or fouling which is the gradual build up of rejected solute on the feed side, immediately adjacent to the membrane. A flush cycle is often used to reduce build up. The spiral wound construction is less susceptible to fouling than that of the hollow fiber unit. A membrane module lasts two to three years on the average. The shut down procedure for non-working hours should assure that minimum flow and operating pressures are continued with a timed internal flush cycle.
What is the active barrier in RO?
The skin is the active barrier and primarily allows water to pass through. Two types of RO construction are commonly used: 1. spiral wound ---sheets of membrane sandwiched with mesh spacers are connected and wound around a permeate tube; and 2. hollow fiber. Either of these modules is assembled into a pressure housing.
What is RO made of?
The majority of the commercially manufactured RO membranes are made from cellulose acetate, polysulfonate, and polyamide. Many other kinds of membrane made of a single polymer or a copolymer are also available for specific purposes. The membrane consists of a skin about 0.25 microns and a support layer about 100 microns. The skin is the active barrier and primarily allows water to pass through.
How are salt ions rejected?
Salt ions, on the other hand, are rejected by a mechanism related to the valence of the ion. Ions are repelled by dielectric interactions; ions with higher charges are repelled to a greater distance from the membrane surface. Monovalent ions such as chloride ions will not be rejected as efficiently as, for example, divalent sulfate ions. The nominal rejection ratio of common ionic salts is 85 - 98%.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis ( RO) is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to separate ions, unwanted molecules and larger particles from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome osmotic pressure, a colligative property that is driven by chemical potential differences of the solvent, ...
Why is pretreatment important in reverse osmosis?
Pretreatment is important when working with reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes due to the nature of their spiral-wound design. The material is engineered in such a fashion as to allow only one-way flow through the system. As such, the spiral-wound design does not allow for backpulsing with water or air agitation to scour its surface and remove solids. Since accumulated material cannot be removed from the membrane surface systems, they are highly susceptible to fouling (loss of production capacity). Therefore, pretreatment is a necessity for any reverse osmosis or nanofiltration system. Pretreatment in sea water reverse osmosis systems has four major components:
How does osmosis work?
In the normal osmosis process, the solvent naturally moves from an area of low solute concentration (high water potential ), through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration (low water potential). The driving force for the movement of the solvent is the reduction in the Gibbs free energy of the system when the difference in solvent concentration on either side of a membrane is reduced, generating osmotic pressure due to the solvent moving into the more concentrated solution. Applying an external pressure to reverse the natural flow of pure solvent, thus, is reverse osmosis. The process is similar to other membrane technology applications.
How does solar desalination work?
A solar-powered desalination unit produces potable water from saline water by using a photovoltaic system that converts solar power into the required energy for reverse osmosis. Due to the extensive availability of sunlight across different geographies, solar-powered reverse osmosis lends itself well to drinking water purification in remote settings lacking an electricity grid. Moreover, solar energy overcomes the usually high-energy operating costs as well as greenhouse emissions of conventional reverse osmosis systems, making it a sustainable freshwater solution compatible to developing contexts. For example, a solar-powered desalination unit designed for remote communities has been successfully tested in the Northern Territory of Australia.
What is the difference between a TFC and a cellulose membrane?
The cellulose triacetate membrane is prone to rotting unless protected by chlorinated water, while the thin-film composite membrane is prone to breaking down under the influence of chlorine. A thin-film composite (TFC) membrane is made of synthetic material, and requires chlorine to be removed before the water enters the membrane. To protect the TFC membrane elements from chlorine damage, carbon filters are used as pre-treatment in all residential reverse osmosis systems. TFC membranes have a higher rejection rate of 95–98% and a longer life than CTA membranes.
When was osmosis first discovered?
A process of osmosis through semipermeable membranes was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. For the following 200 years, osmosis was only a phenomenon observed in the laboratory. In 1950, the University of California at Los Angeles first investigated desalination of seawater using semipermeable membranes. Researchers from both University of California at Los Angeles and the University of Florida successfully produced fresh water from seawater in the mid-1950s, but the flux was too low to be commercially viable until the discovery at University of California at Los Angeles by Sidney Loeb and Srinivasa Sourirajan at the National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, of techniques for making asymmetric membranes characterized by an effectively thin "skin" layer supported atop a highly porous and much thicker substrate region of the membrane. John Cadotte, of FilmTec Corporation, discovered that membranes with particularly high flux and low salt passage could be made by interfacial polymerization of m -phenylene diamine and trimesoyl chloride. Cadotte's patent on this process was the subject of litigation and has since expired. Almost all commercial reverse-osmosis membrane is now made by this method. By 2019, there were approximately 16,000 desalination plants operating around the world, producing around 95 million cubic metres per day (25 billion US gallons per day) of desalinated water for human use. Around half of this capacity was in the Middle East and North Africa region.
What is a second sediment filter?
optionally, a second sediment filter with smaller pores. an activated carbon filter to trap organic chemicals and chlorine, which will attack and degrade certain types of thin-film composite membrane. a reverse osmosis filter, which is a thin-film composite membrane.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is essentially a pressure-driven membrane diffusion process. In practice, RO membranes retain 95–99% of the dissolved solutes (organic and inorganic) from the feed stream into the concentrate, while the permeate can be considered as high-quality water. Therefore, RO is classified as a concentration process. RO has several advantages compared to other concentration technologies. RO is an energy-saving process as removal of the solvent does not require change in phases. Compared to other competing processes, RO is more economic in concentrating diluted solutions and for medium concentrations. Also, RO concentrated fluids are not subjected to any heat damage or losses in aroma compounds, as has occurred in other concentration processes. This is of utmost importance in concentrating liquid foods. Like other membrane processes, RO offers flexibility in different applications and scales, RO concentration is best explained as the mechanism of preferential sorption capillary flow. According to this mechanism, permeation occurs due to the preferential sorption of constituents from fluid mixture and their permeation through the porous membrane. For RO to take place, it is essential that a membrane has the right chemical nature (polar and nonpolar effects) and that its pores are of appropriate size and number (steric effect).
What is reverse osmosis in water treatment?
Desalination by reverse osmosis (RO) is by far the most widespread application for membrane in water treatment. It is capable of removing nearly all colloidal and dissolved matter from an aqueous solution, producing a brine concentrate and an almost pure water permeate.
How does osmosis work?
In water purification systems, the osmotic pressure is overcome using hydraulic pressure, which is applied using a pump to the concentrated side . Pure water is then driven from the concentrated solution and collected downstream of the membrane.
How does reverse osmosis work?
Reverse osmosis is a very efficient process, allowing for the simultaneous concentration, fractionation, and purification of the product and the accomplishment of multiple tasks in a single unit operation. It does not impart pH or chemical changes in the product and, since no significant heating is required, there is no heat degradation of the product. Thus, reverse osmosis has a minimal effect on the quality characteristics and nutritional value of the finished product, especially when compared to evaporative concentration where inevitably there is heat degradation, as well as flavor and nutritional losses.
Which requires less energy: evaporative or reverse osmosis?
Overall, reverse osmosis systems require less energy than evaporative systems per unit of water removed from the product. Reverse osmosis systems require almost exclusively electric energy for pumping and recirculating, whereas evaporative systems require steam in addition to electric energy for pumping.
How can energy be recovered from a desalination plant?
In large desalination plants, energy can be recovered from the rejected brine by running it through turbines to generate electricity that can be used in the plant. Such a recovery system can lead to energy savings of up to 30%.
What is RO technology?
RO has several advantages compared to other concentration technologies. RO is an energy-saving process as removal of the solvent does not require change in phases. Compared to other competing processes, RO is more economic in concentrating diluted solutions and for medium concentrations.
What is the role of the membrane in reverse osmosis?
In this stage the reverse osmosis takes place. The role of the membrane is to filter out organic and inorganic compounds such as fluoride. In this stage, impurities are known as Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) like sodium, calcium, magnesium will be reduced.
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is among the many different methods of water filtration and water purification. Here we will be discussing everything there is to know about these systems, how it works, and the function of a semi-permeable membrane. The reverse osmosis membrane is an important component used in water filtration.
What Is The Membrane?
The heart of every apparatus is its osmosis membrane. The membrane is usually crafted from a very thin-film composite (TFC) which is a semipermeable membran e. This very important yet flimsy material is prone to corrosion by chlorine.
How Effective Is a Membrane?
The efficiency of the use of a membrane to produce clean water is shown below:
How does a filtered water membrane work?
The membrane will magnify an effect to have a reduced TDS count in the water down to 1/10,000 (0.0001) of a micron. The resulting water would have been clean and considered pure by water standards. This filtered water is now available drinking water and for some, this ends the 3-stage cycle.
What happens when water passes through a membrane?
When water passes through the layers of fibers in the membrane, the holes become smaller, this way the contaminants in the water are hindered by the membrane and at the same time are flushed out by the water that continually flows through the membrane and into the drain.
Why is a semi-permeable membrane necessary?
The presence of a semi-permeable membrane makes it so that the contaminants in the water cannot pass through. This membrane has to be semi-permeable so that it will allow the water molecules to go through but not the contaminants.
What is the membrane used in reverse osmosis?
The semi-permeable membrane used in reverse osmosis allows water to pass through, trapping back the undesired particles. This brings the impurity levels in the water down to 0.0009 microns, making the purified water safe to drink or use for other purposes.
What does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
With a pore size of around 0.0001 microns , an RO’s system membrane is quite efficient. So, when you use reverse osmosis, what does it remove?
Why is reverse osmosis better than tap water?
This is mainly because tap water contains traces of lead, nitrates, sulfur, and many other compounds, giving it a different taste. Therefore, reverse osmosis helps to provide people with clean, fresh, and tastier water. No Added Chemicals.
How does RO work?
Through the RO process, applied pressure helps overcome the osmotic pressure, forcing a more concentrated liquid through a semi-permeable membrane to a lesser concentrated one. In essence, it’s osmosis taking place backward, hence, reverse osmosis. Instead of water moving towards a concentrated solute, it moves to a lower solute concentration ...
What percentage of Americans use reverse osmosis?
With over 40 percent of Americans using reverse osmosis purified water, it’s only fair to answer this crucial question in detail; what does reverse osmosis remove from tap water?
What are the pros and cons of reverse osmosis?
Pros of Reverse Osmosis. Clean water with Fewer Contaminants. As the process removes up to 99% of contaminants in tap water, it means that this water is suitable for drinking. Fewer contaminants mean fewer diseases and health issues.
What bacteria can be removed from water by reverse osmosis?
Bacteria – reverse osmosis system can also sieve off bacteria, such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter, leaving the water clean and potable.