
Full Answer
How to create a root?
Use the new SharePoint admin center
- In the upper right, make sure the All sites view is selected.
- In the URL column, select to sort A to Z so the current root site appears at the top of the list.
- Select the root site (https ://contoso. ...
- Select Replace site.
- In the URL of the site you want to use box, enter the full or relative URL of the site that you want to become the new root site.
What is the internal part of a root?
NPI Data:
- NPI Number: 1831167907
- Provider Enumeration Date: 03/14/2006
- Last Update Date: 04/17/2017
What are the three types of roots?
Types of Root Systems. Plants have three types of root systems: 1.) taproot, with a main taproot that is larger and grows faster than the branch roots; 2.) fibrous, with all roots about the same size; 3.) adventitious, roots that form on any plant part other than the roots. Fibrous systems are characteristic of grasses and are shallower than ...
What is the main purpose of a root?
Roots are important because they have four vital functions to the health and vigor of a tree, or any plant for that matter. Absorption. The root tips, and the root tips only, absorb water and minerals from the surrounding soil. Conduit. Those roots also conduct water and minerals up into the leaves and up into the trunk of the tree to feed the ...
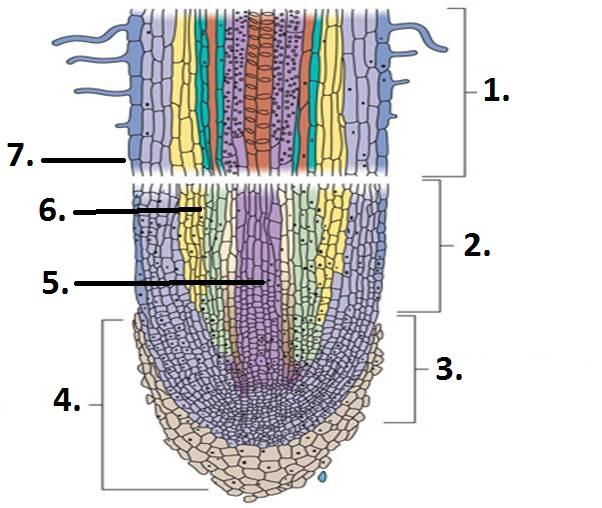
What is the structure of roots?
Typical roots contain three different sections, or zones: the meristematic zone, the zone of elongation, and the zone of differentiation. In the meristematic zone, named after the apical meristem, the plant cells undergo rapid mitotic division, creating new cells for root growth.
What is the structure and function of a root?
Roots absorb water and minerals and transport them to stems. They also anchor and support a plant, and store food. A root system consists of primary and secondary roots. Each root is made of dermal, ground, and vascular tissues.
What are the two types of root structures?
Taproots and fibrous roots are the two main types of root systems. In a taproot system, a main root grows vertically downward with a few lateral roots. Fibrous root systems arise at the base of the stem, where a cluster of roots forms a dense network that is shallower than a taproot.
What are the basic structures of a tree root?
Trees' root systems are made up of large, permanent roots (which mainly provide anchorage and transport), and many small, temporary feeder roots and root hairs. It is these small parts of the root system that are the primary water and nutrient absorbers.
What is structure of plant?
The main structures or 'organs' found in plants are the leaves, stems and roots. They are made up from groups of specialised tissues that have structures suited to the jobs they perform. The table below summarises the main features of these structures and their functions.
What's the structure of a root hair cell?
The root hair cell is roughly rectangular in shape with a cytoplasmic extension on its lateral end (the root hair). It has the following cellular components: A cell wall with intercellular spaces. A semi-permeable cell membrane.
What is the structure of a mature root?
The mature root tip can be divided into three main regions, the region of meristematic activity near the root cap, the region of elongation above that and the region of maturation.
What is the main root of a plant called?
taprootThe primary root, or radicle, is the first organ to appear when a seed germinates. It grows downward into the soil, anchoring the seedling. In gymnosperms and dicotyledons (angiosperms with two seed leaves), the radicle becomes a taproot.
What is root system in plants?
The root system is the descending (growing downwards) portion of the plant axis. When a seed germinates, radicle is the first organ to come out of it. It elongates to form primary or the tap root. It gives off lateral branches (secondary and tertiary roots) and thus forms the root system.
What is the structure of a tree?
As vascular plants, trees are organized into three major organs: the roots, the stems, and the leaves. The leaves are the principal photosynthetic organs of most higher vascular plants.
What are the three types of roots?
The different types of root systems are:Taproots.Fibrous roots.Adventitious roots.
What are the roots of a tree called?
Tree Roots Tap roots: Every tree starts with a tap root that provides stability and absorption. Over time, other roots outgrow the taproot. Most taproots don't continue to grow ever more deeply because deep soils lack the oxygen and nutrients that roots need to survive.
What is the structure of a root?
Structure of Root. The root is underground part of the plant. It anchors the plant in the soil. It is also used to absorb Water and minerals from the soil. .1 – he root structure is almost uniform throughout its length. It is without nodes and internodes.
What are the two types of roots?
There are two types of roots, tap root or primary root and adventitious rook. Tap root arise from the embryo. Adventitious root develops from other mature tissues of plant like stein etc. Root has three distinct tissue systems. These are epidermal. codex and vascular tissue systems.
What is the phloem composed of?
Phloem consists of sieve tube elements. parenchyma and few fibers. Cambium: A parenchymatous sheet of tissues separates the phloem strands from xylem. It becomes meristematic cambium at the start of secondary growth. Pith: In some plants a few parenchnyma cells are present in the centre of the xylem core to form pith.
What is the root primordium?
The pericyclic cells become meristematic in lateral root development in the specific region. These cells divide to form a small protuberance called root primordium. This protuberance pushes through the cortex by rupturing it.
Where do lateral roots come from?
Lateral roots arise from the deeper layers like pericycle. .16e origin of lateral roots has a specific position in different types of roots. In a diarch root the lateral roots arise between the phloem and xylem strands. In a triarch or tetrach root the lateral roots arise just opposite the protoxylem.
Which strands alternate with the ridge of the xylem?
Phloem: The phloem strands alternate with the ridge of the xylem and have the same number. In each phloem. the protophloem elemCnts are present towards the outside and metaphloem are present towards the inner side. Phloem consists of sieve tube elements. parenchyma and few fibers.
What is root hair?
Root hairs are tubular extensions of the outer walls of the epidermal cells. The root hairs bearing cells are smaller cells than other cells. A thin layer of cuticle is also present on some epidermal cells. Root hairs increase the absorptive surface, of the epidermal cells.
What are the characteristics of a root?
What are the main characteristics of Root? 1 It is descending part of the plant axis which lies inside the soil. 2 Chlorophyll is absent. The root is, therefore, non-green. 3 Roots are cylindrical structures. 4 There is no distinction of nodes and internodes. 5 Buds and leaves are usually absent. 6 Root cap is present over the apex. 7 The growing point is subterminal. 8 The branches of root arise from the inner region, thus are endogenous. 9 Root possesses root hairs which are always unicellular. 10 The roots are positively hydrotropic and geotropic but may be neutral or negatively phototropic.
What is the root system?
What is Root System? It is constituted of all the roots of the plant as well as its root hairs, which develops from the radicle of the embryo. It fixes the plant in the soil and absorbs water and minerals in the form of the soil solution.
What are the cells of the region of elongation?
The cells of the region of elongation can absorb water and minerals from the soil. They have central vacuoles and peripheral cytoplasm. Root Hair Zone- Root hair zone is 1-6 cm in length. Root hairs appear from outer cells of this zone in the form of tubular outgrowths.
What is the root cap?
Root Cap or Calyptra- It is a cap like parenchymatous multicellular structure which covers the tip of the root. It protects the root meristem from friction when it grows and pushes through the soil particles. The aquatic plants generally lack the root cap.
What is the region of cell elongation?
Region of Cell Elongation- It is situated behind the meristematic region. The region of cell elongation is 4-8 mm in length. It continuously receives new cells from the growing point. The cells elongate and bring about growth in the length of the root.
What is the meristematic region?
Meristematic Region or Region of Cell Division- It is a small region present behind the root cap (sub-terminal). It is about 1 mm long. It represents the growing point. Cells are thin, have a large nucleus and are non-vacuolated. It is made up of actively dividing meristematic cells.
What are some examples of plants that have roots?
Some roots are photosynthetic in their function as they possess chlorophyll. Example- Tinospora, Trapa, Podostemum and Taeniophyllum.
What are the layers of the root system?
The root is subdivided and extended through the soil particles, it is composed of a number of the layers which are the epidermis layer, the cortex layer, the xylem (wood) layer and the pith layer.
What is the structure of a plant?
The plant structure. The plant consists of the root system and the shoot system, The root system consists of the roots, The shoot system consists of the leaves and the stems, The plant takes the raw materials from the environment to make its food by the photosynthesis process.
Why is the root system important?
The root system is very important for the plant as it is branched and extended through the soil particles to fix the plant in the soil. The root system covers a large area of the soil to search for the water and the mineral salts that the plant needs, then absorbs them from the soil by the root hairs, and raises them to the other parts ...
How does the root system help plants survive?
The root system absorbs the water and the minerals from the environment, It anchors the plant in the ground, and it stores the food that has been made in the leaves by the photosynthesis process, So, the food can be used later by the plant to grow and survive.
What Does Root Mean?
A root is defined in the computer world as the top-level directory of a file system. Top-level directory means that all the other directories - including subdirectories and the files they contain - are included. The root directory is designated by a forward slash ("/") or backward slash ("\") depending on the system in question.
Techopedia Explains Root
The term "root" was adapted from a tree root because this data structure looks like an upside-down tree. The folders in the tree structure are the branches and the files themselves represent leaves.
What is the cortex of a root?
In a slightly old root a few layers of cortex next to epiblema undergo chemical changes —suberisation, and thus give rise to a zone meant for protecting the internal tissues. This band is known as exodermis.
Where does the root develop?
The root develops from the radicle of the embryo. Due to the fact that the extreme tip of the root remains covered by a cap, the apical meristem here is subterminal, as opposed to the terminal apical meristem of the stem. However, the primary body consists of three tissues systems; and, in fact, boundaries between the tissue systems are more ...
What is the bundle in the stem?
Thus, the bundle in the stem is the product of fusion of five strands and the number of bundles is half that of the phloem groups present in the root.
Which root group has many protoxylem groups?
According to the number of protoxylem groups roots may be monarch, as in Trapa natans, diarch, as in Lycopersicon, Nicotiana; triarch, as in Pisum; tetrach, as in Vicia, Cicer; pentarch, as in Ranunculus. Polyarch condition with many xylem groups is characters of monocotyledons.
Which layer of the cortex is made of parenchymatous cells?
It is made of mainly parenchymatous cells and is often massive for the purpose of storage. The endodermis, the last layer of cortex with characteristic Casparian thickenings, is of universal occurrence. Pericycle, normally uniseriate and rarely multiseriate, invariably occurs next to the endodermis.
Do phloem strands join up with xylem strands?
The phloem branches remain in same position, whereas the branches of xylem strands swing laterally, as in the first type, and ultimately join up with the phloem strands. Thus the number of bundles in the stem is twice that of phloem groups present in the root.
Why is the vascular skeleton of a plant formed?
It has been stated that the vascular skeleton in a plant is formed due to continuity of root-stem axis and the lateral appendages. The epidermal tissues and ground tissues are directly continuous in the two organs, stem and root.
What is root system?
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras.
Who invented the root system?
The concept of a root system was originally introduced by Wilhelm Killing around 1889 (in German, Wurzelsystem ). He used them in his attempt to classify all simple Lie algebras over the field of complex numbers. Killing originally made a mistake in the classification, listing two exceptional rank 4 root systems, when in fact there is only one, now known as F 4. Cartan later corrected this mistake, by showing Killing's two root systems were isomorphic.
Is a root system an integer?
is an integer. Some authors only include conditions 1–3 in the definition of a root system. In this context, a root system that also satisfies the integrality condition is known as a crystallographic root system. Other authors omit condition 2; then they call root systems satisfying condition 2 reduced.
Can a Dynkin diagram have more than one simple root?
Although a given root system has more than one possible set of simple roots, the Weyl group acts transitively on such choices. Consequently, the Dynkin diagram is independent of the choice of simple roots; it is determined by the root system itself. Conversely, given two root systems with the same Dynkin diagram, one can match up roots, starting with the roots in the base, and show that the systems are in fact the same.

Characteristics of The Root
- The characteristics of the root are mentioned below: 1. The root is the underground descending portion of the plant axis. 2. The roots are non-green due to the absence of chlorophyll pigments. The roots of Trapa and Tinosporashow photosynthesis. 3. The root generally develops from the …
Types of Roots
- The roots are divided into three types which are: 1. Taproot 2. Fibrous root 3. Adventitious root 1. Taproot:The seed’s radicle elongates and grows to form the primary root. The lateral branches of the primary root are called secondary roots. The secondary roots, in turn, branch to form tertiary roots, e.g., dicotyledonous roots. The primary root, with its lateral branches, forms the taproot sy…
Regions of The Root
- A root is differentiated into four regions: 1. Root cap: 1. i. A thickened, protective cap-like structure is present at the root apex. 2. ii. The root cap cells secrete mucilage (mucus), which lubricates the passage of the root through the hard soil. 3. iii. In some aquatic plants, the root pockets are present. 2. Meristematic region: 1. i. It is situated behind the root cap. 2. ii. This region is made u…
Modifications of Roots
- Roots may be modified to perform special functions like storage of food, support, and respiration apart from the normal functions. These modifications are found both in tap and adventitious roots. (i) Taproot: (a) Conical Root:When the root is swollen at the base and gradually tapers towards the apex, it is said to be conical. Example: Carrot (Daucus carota). (b) Fusiform Root:Th…
Functions of Roots
- The Primary and Secondary functions of roots are as follows: A. Primary functions: (i) Roots help in the fixation and absorption of water and minerals from the soil. (ii) Roots help in the upward movement of the absorbed water and minerals into the stem. (iii) Roots penetrate the soil and provide support to plants. B. Secondary functions: (i) Roots of many plants store food. (ii) Some …
FAQs
- Q.1. What are roots? Ans: The roots are the underground organ found in vascular plants that helps to absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil. Q.2. Where are root hairs present in the root? Ans:The root bears unicellular root hairs in the zone of maturation. Q.3. Mention the types of roots. Ans:The main types of roots are taproot, fibrous root, and adventitious root. Q.4. Write th…