Where is the sagittal sinus located?
falx cerebriThe superior sagittal sinus (SSS), which is the longest dural sinus, lies along the superior edge of the falx cerebri, which is attached to the crista galli at the interhemispheric space just underneath the cranial vault.
What happens when the superior sagittal sinus is blocked?
The superior sagittal sinus (SSS) and transverse sinus are the major dural sinuses that receive a considerable amount of venous drainage. The occlusion of them has been suggested to cause intracranial hypertension, hemorrhage, and lead to potentially fatal consequences.
What does the superior sagittal sinus collect?
The superior sagittal sinus is midsagittal and superior to the falx cerebri. It collects blood from cerebral and cerebelli veins going to the confluence of sinuses (torcular herophili).
What is the purpose of inferior sagittal sinus?
The inferior sagittal sinus is a dural venous sinus found within the inferior, free margin of the falx cerebri (a fold of dura mater). This sinus collects the blood from the falx and often from the medial surfaces of the brain hemispheres.
What fluid is in the sagittal sinus?
Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to venous circulation.
Why is the superior sagittal sinus important?
The purpose of the superior sagittal sinus is to carry waste and fluids away from the brain as veins do throughout the rest of the body.
Is superior sagittal sinus thrombosis a stroke?
Superior sagittal sinus (SSS) thrombosis is an uncommon cause of stroke. Presenting symptoms of raised intracranial pressure may be followed by focal neurological deficits. The presence of headache, hemiparesis, and focal epilepsy in a relatively young patient is indicative of SSS thrombosis.
Can sagittal sinus cause hydrocephalus?
Many of these patients have increased intracranial pressure, but hydrocephalus occurred only in 2/55 patients with thrombosis of the superior sagittal sinus in our cohort.
What is sagittal sinus meningioma?
Introduction. Parasagittal sinus meningiomas are a common intracranial tumor in the elderly, with a relatively rare occurrence in young adults [1], [2]. These tumors arise from the meninge which is the membrane that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
What drains the inferior sagittal sinus?
The inferior sagittal sinus courses along the inferior border of the falx cerebri, superior to the corpus callosum. It receives blood from the deep and medial aspects of the cerebral hemispheres and drains into the straight sinus.
What is clinical importance of negative pressure in sagittal sinus?
In the sitting position, the sagittal sinus has a negative pressure that can result in (potentially fatal) air embolism if opened. When supine, bleeding from the sinuses can be torrential. Likewise, when upright, human internal jugular veins tend to collapse under negative pressure, but engorge on lying.
Where does the inferior sagittal sinus receive blood from?
falx cerebriIt receives blood from the falx, corpus callosum, cingulum, and medial cerebral hemispheres. The occlusion of this sinus is rarely clinically significant. The straight sinus is situated at the line of the junction of the falx cerebri with the tentorium cerebelli.
Can blocked sinuses affect the brain?
The millions of people who have chronic sinusitis deal not only with stuffy noses and headaches, they also commonly struggle to focus, and experience depression and other symptoms that implicate the brain's involvement in their illness.
Does the superior sagittal sinus drain blood?
The superior sagittal sinus drains blood from cortical veins of the cerebral hemispheres, veins of the falx cerebri and meninges, diploic veins of the skull and emissary veins from the scalp. It empties into the confluence of sinuses in the occipital region.
What happens if the coronary sinus is blocked?
Acute coronary sinus occlusion causes abrupt elevation of the transcapillary pressure which, in turn, causes increased myocardial perfusion pressure even in the presence of normal healthy coronary arteries. In addition, the venous and capillary engorgement may directly result in direct myocardial injury.
Is sinus blockage serious?
Most sinus infections last from a couple of days to a few weeks and are not a serious medical concern, but if left untreated, sinusitis can lead to further complications. These include nasal polyps, a deviated septum and serious allergies.
What is the superior sagittal sinus?
The superior sagittal sinus is one of several endothelial-lined spaces in the brain known collectively as the dural venous sinuses. It lies within the superior convex margin of the falx cerebri which attaches to the internal surface of the calvaria ( in the midline ). The superior sagittal sinus drains blood from cortical veins ...
What drains blood from the cerebral hemisphere?
The superior sagittal sinus drains blood from cortical veins of the cerebral hemispheres, veins of the falx cerebri and meninges, diploic veins of the skull and emissary veins from the scalp. It empties into the confluence of sinuses in the occipital region. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the superior sagittal sinus.
How many lacunae are there on each side?
There are typically two or three of them on each side; a small frontal, a large parietal and an intermediate occipital lacunae. The lacunae communicate with the sagittal sinus through small slit-like openings and often become confluent (single large lacuna) in the elderly.
Where does the superior sagittal sinus originate?
The superior sagittal sinus begins anteriorly close to the crista galli of the ethmoid bone where it occasionally receives an emissary vein from the nasal cavity through the foramen cecum of the frontal bone. It then courses through the root of the falx cerebri, between the periosteal and meningeal layers of this dural infolding.
Which sinus is narrow and wide?
In cross-section, the superior sagitt al sinus appears triangular with its apex pointing inferiorly and continuing downward as the falx cerebri. The sinus is narrow anteriorly and widens as it runs posteriorly.
Which veins drain into the posterior end of the sinus?
Additionally, emissary veins from the pericranium drain into the posterior end of the sinus through ...
Can sinus occlusion cause seizures?
In the chronic setting, however, gradual occlusion of the sinus allows for the development of collateral drainage vessels.
How long does it take for the cerebral venous system to form?
The formation of the whole venous system begins during the 3 and 4 weeks of gestation, eventually forming from the aortic arch. The development of the cerebral venous system closely follows that of the neural tube in a caudal to rostral manner. The superior sagittal sinus has been theorized to originate from a plexiform of vessels and eventually combining to form a single vascular channel. Also, its position within the cranial vault is dependent on embryological signals from the falx cerebri. These positional signals may explain the reason for the preferential laterality of the position of the superior sagittal sinus relative to the sagittal suture. [1][3]
What is the superior sagittal sinus?
The superior sagittal sinus is the major component of the superficial cerebral venous system and knowledge of this structure , and its variations are of practical clinical importance to neurosurgeons, neurologists, and radiologists in the treatment of a number of conditions.
Why is the superior sagittal sinus important?
In addition to direct thrombosis of the vessel, the superior sagittal sinus is often implicated in the development of meningiomas due to its intimate proximity to the falx cerebri. When surgical intervention is necessary for these situations, the clinician must account for a tumor that may involve the superior sagittal sinus as this often time complicates gross resection resulting in suboptimal tumor resection with increased rates of recurrence. When intracranial pressure increases, there is increased reverse flow of venous blood through the emissary and diploic veins of the scalp and cranium, leading to increased rates of scalp, skull, and intracranial hemorrhage during craniotomies. In addition to being aware of the increased rate of hemorrhage, the surgeons must also know the location of the superior sagittal sinus relative to the sagittal suture and take extreme caution to avoid injuring the sinus while creating burr holes. [5]
What is the clinical significance of the superior sagittal sinus?
Clinical Significance. Due to its multiple connections including its significant role in draining the cerebral hemispheres as well as receiving blood from the diploic, meningeal and emissary veins from the scalp, there are multiple complications and pathological processes that can affect the superior sagittal sinus.
How many draining vessels are there in the sagittal sinus?
Regarding the draining vessels of the superior sagittal sinus, there are numerous normal variants and the average number of draining vessels ranges from 13 to 19 vessels for each hemisphere of the cortex. This number is generally equal on each side for any given individual. The most significant draining vessel of the superior sagittal sinus is ...
What is the sinus prone to?
This section will briefly discuss some of the more common pathologies affecting the sinus. First and foremost, the superior sagittal sinus is prone to thrombosis, presenting with various features from headaches, hemiparesis, sixth nerve palsy, papilledema, nausea, and seizures.
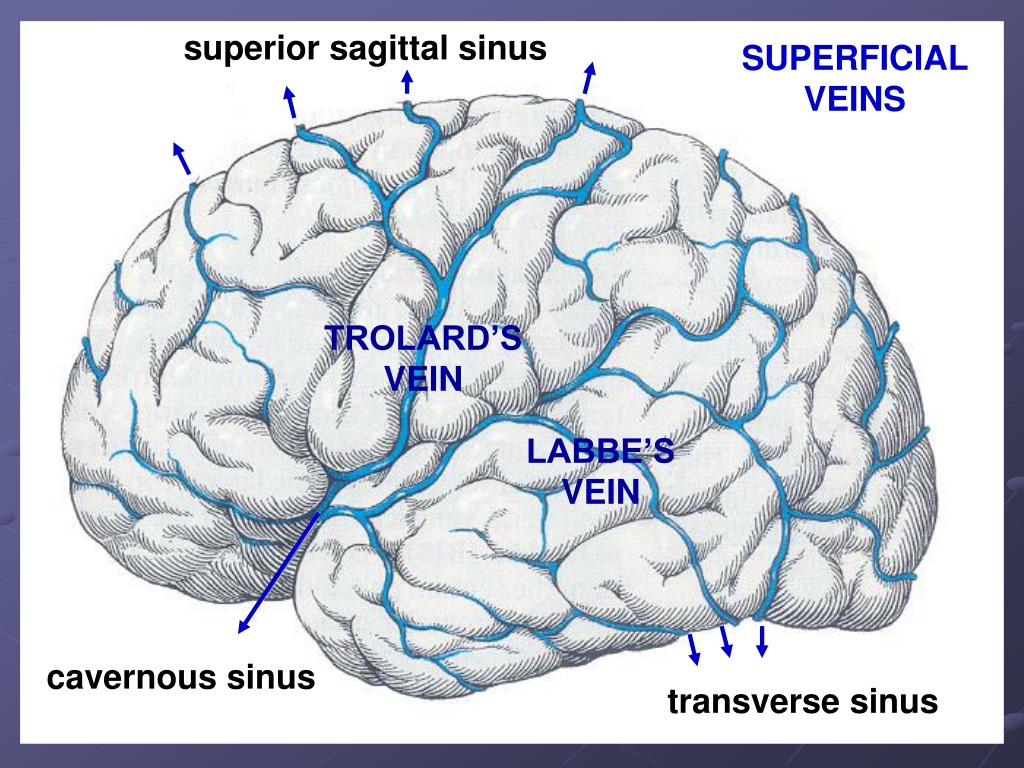
Which vein drains the superior sagittal sinus?
The most significant draining vessel of the superior sagittal sinus is the vein of Trolard which connects the superficial middle cerebral vein and the superior sagittal sinus. The Rolandic vein, which drains the primary motor and somesthetic sensory cortices of the brain, is another significant tributary of the superior sagittal sinus.[5]