
What is the difference between first-generation and second-generation rodenticides?
According to the CDC, first-generation anticoagulants (FGARs) are those that were developed before 1970. first-generation anticoagulants become more toxic with each successive feeding. They rarely kill rodents after a single feeding. As a result, they tend to be less successful than second-generation rodenticides.
What is a 2nd generation anticoagulant?
Second-Generation Anticoagulants. The second-generation anticoagulant rodenticides (SGARs) are substantially more potent than the first-generation compounds, and a lethal dose can be ingested in a single feeding. Included in this class of rodenticides are the compounds difenacoum, brodifacoum, bromadiolone and difethialone.
What is the difference between anticoagulant rodenticides and other rodenticides?
Anticoagulant rodenticides that are in wide use today are members of a more potent class of anticoagulants known as second-generation rodenticides. The following section provides a more detailed comparison between first and second generation rodenticides. Other rodenticides are non-anticoagulants and work in different ways.
What are rodenticides?
Rodenticides are poisons that are used to kill rodents. In the state of California, rodenticides must be placed in tamper-proof bait stations. Rodenticides may be classified as anticoagulants (those that cause internal bleeding) or non-anticoagulants. Let’s go over the basic types of rodenticides.

What does second generation rodenticide mean?
The second-generation anticoagulant rodenticides (SGARs) are substantially more potent than the first-generation compounds, and a lethal dose can be ingested in a single feeding. Included in this class of rodenticides are the compounds difenacoum, brodifacoum, bromadiolone and difethialone.
What's the difference between first generation and second generation rat poison?
The second-generation anticoagulants are more acutely toxic than first-generation anticoagulant rodenticides. Their superior potency is related to their greater affinity for vitamin K-epoxide reductase. Bromadiolone and difenacoum were the first compounds of the second generation introduced to the market.
What are the categories of rodenticide?
There are a number of rodenticides that work differently than anticoagulants. These are currently used within the United States: bromethalin, cholecalciferol, zinc phosphide, and strychnine. Each of these pesticides works in a different way.
What is the most commonly used rodenticides?
They include brodifacoum, difenacoum, bromadiolone, and flocoumafen. Of these, brodifacoum is the most common active ingredient in commercially available rodenticides in the United States and is usually found in a 0.005% concentration.
What kind of rat poison do exterminators use?
Bromadiolone is a rodenticide meant to kill rats and mice. Anticoagulants like bromadiolone work by preventing the blood from clotting. Unlike some other rat poisons, which require multiple days of feeding by an animal, bromadiolone can be lethal from one day's feeding.
What is the safest mouse poison?
This non-toxic poison is made of 100% natural products and is safe around your pets and children.Neogen RODENTICIDE 45-Pack Ramik Rat and Mouse Bait Pail, Green, 4.2 LB, (04285) ... Farnam Just One Bite II Bait Chunks, 8lbs (64, 2 oz chuncks)More items...
Is bromethalin second generation?
Second-generation anticoagulants registered in the United States include brodifacoum, bromadiolone, difenacoum, and difethialone. Other rodenticides that currently are registered to control mice include bromethalin, cholecalciferol and zinc phosphide. These compounds are not anticoagulants. Each is toxic in other ways.
What is the best rat poison?
The best rat poison to buy in 2022Pest Expert Formula B+ Advanced: Best rapid-acting rat killer. ... Roshield Wax Block Bait Rat & Mouse Killer: Best wax bait rat poison. ... The Big Cheese All Weather Block Bait: Best cheap rat poison. ... Ratkil Rat & Mouse Killer – Single Feed: Best cheap Brodifacoum-based rat killer.More items...•
Is a rodenticide a pesticide?
Rodenticides are pesticides that kill rodents, including mice and rats. They are often formulated as baits with attractive substances like peanut butter or molasses.
Is Ratsak first generation?
If you must use baits, choose first generation rodenticides such as Ratsak Double Strength and Racumin.
What kills rats instantly?
For best results, consider using snap traps, which are a fast method to kill rats instantly. To prevent other animals from getting into the traps, place them inside a box or under a milk crate. Bait the traps with peanut butter, which is cheap and attractive to rats.
Are there any safe rodenticides?
Safe alternatives include single- and multiple-entrance snap traps, electrocuting traps, glue traps (provided you use them only indoors and frequently dispatch stuck rodents), and even first-generation baits with these active ingredients: chlorophacinone, diphacinone, diphacinone sodium salt, war-farin, and warfarin ...
What is the best rat poison?
The best rat poison to buy in 2022Pest Expert Formula B+ Advanced: Best rapid-acting rat killer. ... Roshield Wax Block Bait Rat & Mouse Killer: Best wax bait rat poison. ... The Big Cheese All Weather Block Bait: Best cheap rat poison. ... Ratkil Rat & Mouse Killer – Single Feed: Best cheap Brodifacoum-based rat killer.More items...•
What is the difference between brodifacoum and bromadiolone?
Both brodifacoum and bromadiolone are toxic substances that can act as pesticides. Brodifacoum is a lethal poison known as 4-hydroxycoumarin vitamin K antagonist anticoagulant while bromadiolone is a potent anticoagulant rodenticide.
Which is better brodifacoum or difenacoum?
Sinusoids in the livers of rodenticide-treated rats contained an accumulation of dense material, lipid droplets, cells with pycnotic nuclei and hemolysed erythrocytes. Overall, our results show that brodifacoum causes more severe effects in liver cells than difenacoum.
What is the difference between diphacinone and bromethalin?
The key difference between bromethalin and diphacinone is that bromethalin is not an anticoagulant, whereas diphacinone is a non-anticoagulant substance. Bromethalin and Diphacinone are two types of rodenticides. This means these are poisonous substances that can kill rodents.
What are rodenticides?
Rodenticides are pesticides that kill rodents. Rodents include not only rats and mice, but also squirrels, woodchucks, chipmunks, porcupines, nutria, and beavers. Although rodents play important roles in nature, they may sometimes require control. They can damage crops, violate housing codes, transmit disease, and in some cases cause ecological damage. 1
What are the active ingredients in rodenticides?
Many rodenticides stop normal blood clotting; these are called anticoagulants. Bromadiolone, chlorophacinone, difethialone, brodifacoum, and warfarin are all anticoagulants. ...
What are signs of rodenticide poisoning?
Always follow label instructions and take steps to minimize exposure. If any exposure occurs, be sure to follow the First Aid instructions on the product label carefully. For additional treatment advice, contact the Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222. If you wish to discuss an incident with the National Pesticide Information Center, please call 1-800-858-7378.
How toxic are rodenticides?
All rodenticides can be toxic when eaten. 3,4,5,6 Most rodenticides are also toxic when inhaled and when they come into contact with skin. The exceptions include warfarin, which is low in toxicity when inhaled or if skin contact occurs. 6 Strychnine, cholecalciferol, and zinc phosphide are relatively low in toxicity upon skin contact. 3,5,7 Bromethalin is moderately toxic for dermal exposure. 4 See Table 1.
What if pets and wildlife eat rodents that have been poisoned?
Rodenticide baits are made to attract animals. Pets and wildlife may take the bait if they find it. When an animal eats the bait directly, it is called primary poisoning. Secondary poisoning is caused by eating poisoned prey. It may also be called relay toxicosis. See the fact sheet on Ecotoxicology. For ways to prevent exposures, see the information below about what you can do to reduce risks.
What was the first anticoagulant?
ACUTE TOXICITY CLASSIFICATION - RODENTICIDES. Warfarin was the first anticoagulant rodenticide. 1 It was registered for use in 1950. 4 Warfarin was discovered in moldy sweet clover that had made a herd of cattle sick.
When was zinc phosphide first used?
Zinc phosphide was first registered in 1947. 1 It changes into phosphine gas in the presence of water and acid. The phosphine gas is very toxic; it blocks the body's cells from making energy, and the cells die. 15 Phosphine exposure is particularly damaging to the heart, brain, kidney, and liver. 15
What is the second generation of rodenticide?
The second-generation anticoagulant rodenticides (SGARs) are substantially more potent than the first-generation compounds, and a lethal dose can be ingested in a single feeding. Included in this class of rodenticides are the compounds difenacoum, brodifacoum, bromadiolone and difethialone.
How long does it take for a rodenticide to be excreted?
The first-generation compounds are excreted fairly rapidly by mammals, usually within a week. However, the use of any rodenticides pose a poisoning risk to children, pets and wildlife. First-Generation Rodenticides. Types.
What is the second generation of anticoagulant?
Anticoagulant rodenticides that are in wide use today are members of a more potent class of anticoagulants known as second-generation rodenticides. The following section provides a more detailed comparison between first and second generation rodenticides. Other rodenticides are non-anticoagulants and work in different ways.
What is non-anticoagulant rodenticide?
Non-anticoagulant rodenticides, including bromethalin, cholecalciferol, and zinc phosphide, are US EPA-registered and frequently used in controlling pest rodent populations. The potency of these rodenticides is highly variable, with rodent mortalities typically occurring on the order of several hours to days following ingestion of a lethal dose. These rodenticides belong to three different chemical classes that differ from one another as well as the anticoagulants in their mode of action, or anatomical change leading to rodent death.
What are some rodent control measures?
Poisons have been used as rodent-control measures for many years. Before the 1940s, rodenticides contained heavy metals such as arsenic and thallium or poisons such as strychnine and red squill. Most of these chemicals are no longer used as rodenticdes with the exception of strychnine, which is currently registered for use only below-ground as a bait application to control pocket gophers. For more details, see US EPA’s RED Facts on Strychnine.
What is the first line of defense against rodents?
Rodent Control. The first line of defense against rodents should be exclusion and trapping. These methods do not pose a poisoning risk to children, pets and wildlife. If you plan to use rodenticides, be sure to follow all label directions.
How to keep rodents out of your home?
To permanently keep rats and mice out of your home or business, you will need to prevent access by sealing all possible entry points. It is equally as important to eliminate rodent attractions such as food and water by keeping food in tightly sealed glass or plastic containers and repairing leaky pipes.
When did the DPR reevaluation of SGARs begin?
DPR accepted comments on the proposed decision until January 16, 2019. On March 12, 2019 , DPR issued a notice of its final decision to begin reevaluation of SGARs along with response and summary of the received 17,000 comments. The reevaluation is based on DPR’s investigations of reported non-target wildlife exposure to SGARs.
What is the active ingredient in SGAR?
On November 16, 2018, after investigating reported non-target wildlife exposure, the Department of Pesticide Regulation (DPR) issued a notice of proposed decision to begin reevaluation of pesticide products containing the second-generation anticoagulant rodenticide (SGAR) active ingredients brodifacoum, bromadiolone, difenacoum, and difethialone. DPR accepted comments on the proposed decision until January 16, 2019. On March 12, 2019, DPR issued a notice of its final decision to begin reevaluation of SGARs along with response and summary of the received 17,000 comments. The reevaluation is based on DPR’s investigations of reported non-target wildlife exposure to SGARs.
How to contact DPR about AB1788?
For any questions regarding AB1788, please contact DPR’s Executive Office at (916) 445-4000.
Does AB 1788 change SGAR registration?
AB 1788 does not change the registration status of SGAR products, requirements for SGAR registrants or the annual registration renewal of SGAR products. Per California Notice 2018-01, while SGARs are under reevaluation, DPR will not approve any labels that expand their use through label amendments or new registrations.
What is rodenticide in California?
Rodenticides are poisons that are used to kill rodents. In the state of California, rodenticides must be placed in tamper-proof bait stations. Rodenticides may be classified as anticoagulants (those that cause internal bleeding) or non-anticoagulants.
Why do you use rodenticide?
With all that said, it is understandable that you might consider using rodenticides to avoid the devastating health and safety consequences that stem from a full-blown rodent infestation. Backed with an in-depth knowledge of first-generation, second-generation, and other rodenticides, you can make an informed and responsible decision about using bait boxes.
What is difethialone?
Difethialone: Difethialone is a second-generation anticoagulant rodenticide with a high secondary poisoning risk.
What is a toxic rodenticide?
Toxic rodenticide products, including anticoagulants and non-anticoagulant, are used in both consumer-and professional-grade bait stations. These substances are designed to kill rats, mice, gophers, squirrels, chipmunks, and other rodents.
When were SGARs developed?
Second-generation anticoagulant rodenticides (SGARs) were developed after the 1970s. Second-generation anticoagulants are not dependent on multiple successive feedings. These rodenticides are very likely to kill rodents after a single feeding.
How many cases of rodent poisoning in California?
Since 1994, there have been over 400 confirmed cases of wildlife poisoning from anticoagulant rodent baits in the state of California alone. The list of animals that have been harmed is lengthy; it includes birds of prey, scavenging animals, and predatory mammals.
What is the best toxin for rodents?
Zinc phosphate: Zinc phosphate is an acute toxin that is capable of killing a rodent within hours of a single feeding. It is challenging to find zinc phosphate in the consumer market. However, some consumers prefer to use it because it has a low secondary kill risk.
How long does it take to treat a second generation rodenticide?
Because the second generation anticoagulant rodenticides can be very long acting, treatment may be required for weeks to months.
What are the symptoms of a rodenticide?
Specific clinical signs can include widespread bruising, bleeding into body cavities, and blood in the urine or feces; if the bleeding is sudden and significant, then cardiovascular shock and death can result. Bleeding can occur internally or externally and can affect any part of the body. Non-anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity symptoms are more ...
What is the cause of rodenticide toxicity?
Rodenticide Toxicity. Rodenticide toxicity can be caused by any of several types of rodent poisons that fall into two general categories, anticoagulants, and non-anticoagulants. Anticoagulant rodenticides work by interfering with the activation of Vitamin K, a critical component in the production of blood clotting factors in the liver.
How long does it take for a rodent to bleed?
Because animals maintain body stores of blood clotting factors, there is typically a delay of 3-5 days between ingestion of the anticoagulant rodenticides and the onset of bleeding. In many cases of secondary poisoning (ingestion of poisoned rodents), smaller, non-lethal doses are consumed repeatedly.
What is the diagnosis of non-anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity?
Diagnosis of non-anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity is based on detection of the chemical in the digestive system or tissues of the animal.
How many cases of rodenticide poisoning in New York?
Over 40 cases of rodenticide poisonings in wildlife were identified by the New York State Wildlife Health Program between 2012 and 2014. Animals affected included several species of birds that prey on rodents, including red-tailed hawks and owls. In addition, squirrels, skunks, raccoons, and woodchucks died from rodenticide poisoning.
Does rodenticide cause seizures?
Clinical Signs By Rodenticide. Bromethalin can cause rapid onset of seizures when high doses are consumed along with clinical signs such as muscular hyperexcitability, muscle tremors, increased reflexes in the hind limbs, and hyperthermia (elevated body temperature).
More Information
We started out with Generation probably 18 or 19 years ago, and it did what we needed it to do a lot quicker than anything else.
Stewarding Resources for the Future
As part of our commitment to environmental stewardship, Liphatech is a proud member of the Ag Container Recycling Council. The ACRC collects and safely recycles the HDPE plastic jugs and pails from our ag, animal health and structural pest control products.
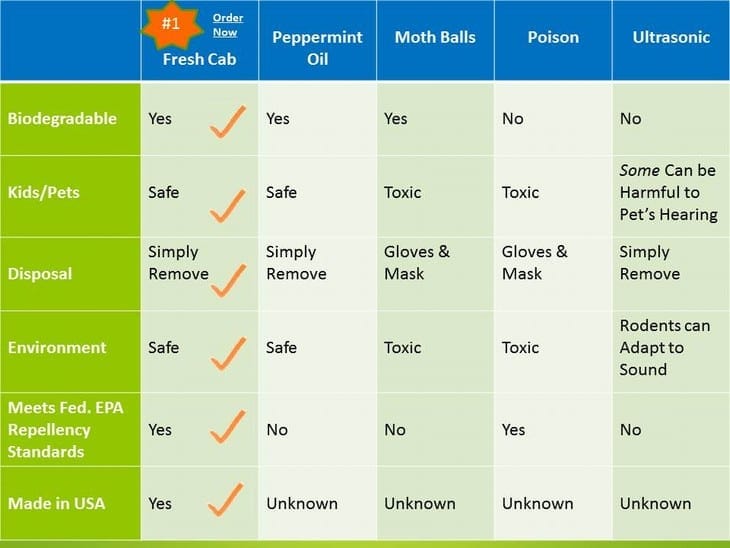
Overview
Classes of rodenticides
Anticoagulants are defined as chronic (death occurs one to two weeks after ingestion of the lethal dose, rarely sooner), single-dose (second generation) or multiple-dose (first generation) rodenticides, acting by effective blocking of the vitamin K cycle, resulting in inability to produce essential blood-clotting factors—mainly coagulation factors II (prothrombin) and VII (proconvertin).
Low-toxicity/Eco-friendly rodenticides
Powdered corn cob or corn meal gluten, have been developed as rodenticides and were approved in the EU and patented in the US in 2013. These preparations rely on electrolyte imbalance to cause death.
Inert gas killing of burrowing pest animals is another method with no impact on scavenging wildlife, one such method has been commercialized and sold under the brand name Rat Ice.
Non-target issues
One of the potential problems when using rodenticides is that dead or weakened rodents may be eaten by other wildlife, either predators or scavengers. Members of the public deploying rodenticides may not be aware of this or may not follow the product's instructions closely enough.
The faster a rodenticide acts, the more critical this problem may be. For the fa…
Notable rat eradications
The entire rat populations of several islands have been eradicated, most notably Campbell Island, New Zealand, Hawadax Island, Alaska (formerly known as Rat Island), Macquarie Island and Canna, Scotland (declared rat-free in 2008). According to the Friends of South Georgia Island (www.fosgi.org), all of the rats have been eliminated from South Georgia Island (which is about the size of Long Island, New York).
See also
• Poison shyness
• Pesticide
• Thallium poisoning
Further reading
• Plunkett, Signe J. (2001). Emergency Procedures for the Small Animal Veterinarian. Harcourt Publishers. pp. 289–292. ISBN 0-7020-2487-2.
• Gfeller, Roger W.; Shawn P. Messonnier (2004). Small Animal Toxicology and Poisonings. Mosby. pp. 321–326. ISBN 0-323-01246-9.
• Endepols, Stefan; Buckle, Alan; Eason, Charlie; Pelz, Hans-Joachim; Meyer, Adrian; Berny, Philippe; Baert, Kristof; Prescott, Colin (September 2015). "RRAC guidelines on Anticoagul…
• Plunkett, Signe J. (2001). Emergency Procedures for the Small Animal Veterinarian. Harcourt Publishers. pp. 289–292. ISBN 0-7020-2487-2.
• Gfeller, Roger W.; Shawn P. Messonnier (2004). Small Animal Toxicology and Poisonings. Mosby. pp. 321–326. ISBN 0-323-01246-9.
• Endepols, Stefan; Buckle, Alan; Eason, Charlie; Pelz, Hans-Joachim; Meyer, Adrian; Berny, Philippe; Baert, Kristof; Prescott, Colin (September 2015). "RRAC guidelines on Anticoagulant Rodenticide Resist…
External links
• National Pesticide Information Center
• Fact Sheet on EPA's Proposed Risk Mitigation Decision for Nine Rodenticides
• EPA Rodenticide Cluster Reregistration Eligibility Decision Fact Sheet
Overview
Chemistry
Toxicity
Safety
Prevention
Symptoms
Risks
Other animals
- The rodenticides with high secondary poisoning risks to birds such as hawks and owls include difethialone, brodifacoum, and possibly bromadiolone (see Table 3).23 The rodenticides that pose the greatest secondary poisoning risks for wild mammals, dogs and cats include chlorophacinone, diphacinone, bromadiolone, and brodifacoum. Bromethalin and chol...
Management