
APA Dictionary of Psychology sensory neuron a neuron that receives information from the environment, via specialized receptor cells, and transmits this information—in the form of nerve impulses—through synapses with other neurons to the central nervous system.
What are the functions of a sensory neuron?
Types of Sensory Neurons
- Olfactory sensory neurons are bipolar neurons located in the nasal cavity. ...
- Gustatory receptors, or taste receptors, detect the chemicals found in food to give us a sense of taste.
- Photoreceptors are a special type of neuroepithelial cell that converts light into electrical signals. ...
Why is a neuron called a sensory neuron?
The neurons that gets activated by a sensory input is called sensory neurons. Motor neurons are the neurons that are attached to muscles and other organs throughout the body. Sensory neurons are also called the afferent neurons while motor neurons are also called as the efferent neurons.
What is the difference between the sensory and motor neurons?
There are three main types of neurons:
- Motor neurons make the connection between the brain and muscles throughout the body. ...
- Sensory neurons are neurons that let us feel sensation. ...
- Interneurons are the nerve cells that connect motor neurons to other motor neurons and sensory neurons to other sensory neurons.
Which best describes sensory and motor neurons?
Sensory neurons carry stimuli information to the brain; motor neurons carry processed information to muscles and glands Sensory neurons carry stimuli information to the brain; motor neurons carry processed information to muscles and glands sympathetic nervous system

Why are sensory neurons important in psychology?
To accurately respond to stimuli, the brain relies on information communicated by sensory neurons. Sensory neurons detect inputs from the environment, convert them into signals (electrical impulses), and pass the information on to the brain and spinal cord, where a response can be generated.
Where are the sensory neurons?
Unipolar cell bodies of sensory neurons are located within sensory ganglia which may be in the dorsal root of the spinal cord or along cranial nerves. The receptive field of the neurons limits the ability of the sensory system to relay environmental information.
What are the types of neurons in psychology?
There are three main types of neurons, including: sensory, relay and motor. Each of these neurons has a different function, depending on its location in the body and its role within the nervous system.
What are sensory neurons quizlet?
Sensory Neuron. Neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord.
What are sensory neurons also known as?
Afferent neurons, also called sensory neurons, are the nerve fibers responsible for bringing sensory information from the outside world into the brain. Sensory information may involve special senses, such as vision, hearing, smell, or taste, as well as the sense of touch, pain, and temperature.
What is the function of sensory neurons quizlet?
Sensory neurons are nerve cells within the nervous system responsible for converting external stimuli from the organism's environment into internal electrical impulses.
What is the difference between sensory and motor neurons?
A sensory neuron transmits impulses from a receptor, such as those in the eye or ear, to a more central location in the nervous system, such as the spinal cord or brain. A motor neuron transmits impulses from a central area of the nervous system to…
What are the 3 types of neurons and their functions?
In terms of function, scientists classify neurons into three broad types: sensory, motor, and interneurons.Sensory neurons. Sensory neurons help you: ... Motor neurons. Motor neurons play a role in movement, including voluntary and involuntary movements. ... Interneurons.
Are bipolar neurons sensory or motor?
sensory neuronsBipolar neurons are relatively rare. They are sensory neurons found in olfactory epithelium, the retina of the eye, and ganglia of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
What is the difference between sensory and motor neurons quizlet?
Sensory neurons carry signals from the outer parts of your body (periphery) into the central nervous system. Motor neurons (motoneurons) carry signals from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body.
What is the main function of sensory receptors?
A sensory receptor is a structure that reacts to a physical stimulus in the environment, whether internal or external. It is a sensory nerve ending that receives information and conducts a process of generating nerve impulses to be transmitted to the brain for interpretation and perception.
Which cell is a sensory cell quizlet?
Sensory epithelial cells that contain ciliated mechanoreceptors are often called hair cells. the inner ear of mammals is used for hearing (auditory sense), balance (equilibrium) and sensing acceleration. Acceleration in three dimensions is detected by hair cells with cupulae in the semicircular canals.
Are sensory neurons in the CNS or PNS?
The human nervous system The peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS.
What are the 5 sensory neurons?
It is common to group them into 5 classes: mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, nociceptors, electromagnetic receptors and chemoreceptors.
Where are sensory receptors located?
Sensory receptors occur in specialized organs such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth, as well as internal organs. Each receptor type conveys a distinct sensory modality to integrate into a single perceptual frame eventually.
Are sensory neurons in the CNS?
Information coming from the sensory neurons in the head enters the central nervous system (CNS) through cranial nerves. Information from the sensory neurons below the head enters the spinal cord and passes towards the brain through the 31 spinal nerves.
What is sensory neuron?
A sensory neuron (sometimes referred to as an afferent neuron) is a nerve cell that detects and responds to external signals. Sensory neurons receive information via their receptors, which are part of the peripheral nervous system, and convert this information into electrical impulses. These impulses act as signals and are passed on to ...
What is the structure of a sensory neuron?
Structure of Sensory Neurons. A typical neuron is comprised of dendrites, an axon, and a cell body, and the sensory neurons are no exception. Most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar, which means they have a single axon extending from the cell body that forms two extensions: the dendrites and the axon. The sensory neuron “begins” with the dendrites, ...
What is the stimulus that triggers the sensory neuron to send a signal?
The stimulus triggers the sensory neuron to send a signal then carries information towards the central nervous system. Specifically, depolarization is initiated at the sensory receptors and transmitted along the dendrites to the cell body and then to the axon. At the axon terminal, the signal initiates the release of chemicals into the synapse.
What are the three types of neurons?
There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, relay neurons, and motor neurons.
Where does the transduction of sensory signals take place?
The transduction of the signal takes place in the sensory receptor at the dendritic end of the neuron.
Which part of the brain receives sensory information?
The spinal cord and brain then receive and respond to this information. There are various types of sensory neurons that differ in their structure, location, and stimuli to which they respond. Morphology of a typical sensory neuron.
Where are sensory and motor neurons generated?
Whereas in motor neurons, the new nerve impulse is generated in the neuron of the motor cortex of the brain, in the sensory neurons, the new signal is generated in the peripheral nervous system.
What is the cell body of a neuron?
The soma (cell body) is the central and largest part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and, for this reason, it is the place where most of the protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 μm in diameter. The cell body receives the signals from other neurons through the dendrites.
What are the parts of a neuron?
Typically, neurons are composed of three main parts: cell body (soma), dendrites and an axon. The cell body stores the genetic information, cell nucleus and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA); the axon is the structure that searches for other neurons to create the interconnections.
How does summation work in neuron?
Summation of the many signals received from the synaptic inputs is performed in the postsynaptic neuron. The amplitude of the summed signal depends on the total number of input signals and how closely these signals occur in time; the amplitude decreases when the signals become increasingly dispersed in time. The amplitude of the summed signal must exceed a certain threshold in order to make the neuron fire an action potential. Not all neurons contribute, however, to the excitation of the postsynaptic neuron; inhibitory effects can also take place due to a particular chemical structure associated with certain neurons. A postsynaptic neuron thus receives signals which are both excitatory and inhibitory, and its output depends on how the input signals are summed together. This input/output operation is said to represent one neural computation and is performed repeatedly in billions of neurons.
Where does the transmission of information from one neuron to another take place?
The transmission of information from one neuron to another takes place at the synapse, a junction where the terminal part of the axon contacts another neuron. The signal, initiated in the soma, propagates through the axon encoded as a short, pulse-shaped waveform, i.e., the action potential. Although this signal is initially electrical, it is converted in the presynaptic neuron to a chemical signal (“neurotransmitter”) which diffuses across the synaptic gap and is subsequently reconverted to an electrical signal in the postsynaptic neuron, see Figure 2.1. (b).
Which neuron transmits the signal toward a synapse?
Figure 2.1. (a) An archetypal neuron and (b) three interconnected neurons. A presynaptic neuron transmits the signal toward a synapse, whereas a postsynaptic neuron transmits the signal away from the synapse.
How do you get the data about the electrical and chemical properties of an axon?
Most of the data about the electrical and chemical properties of the axon is obtained by inserting small needlelike probes into the axon.
How big is a neuron?
For instance, in terms of size, a neuron can vary from 4 to 100 μ in diameter, and the nucleus varies from 3 to 18 μ [ WIK 14 ]. Neurons send signals to other cells as electrochemical waves traveling along the axons (from the Greek άξων, (axon), meaning “axis”).
Neurons & Neurotransmission: AQA A Level Psychology Assessment Mat
Digital textbook replacements for key GCSE, A Level and IB subjects and specifications.
Biopsychology: Exam Buster Revision Guide for AQA A Level Psychology
Printed workbooks designed to support students throughout their course. Ideal for independent learning, remote learning and exam revision.
AQA A-Level Psychology Biopsychology Knowledge Book
Collections of editable PowerPoints covering the key specification and unit content.
Biopsychology Full Topic PowerPoints for AQA A Level Psychology
Individual teaching resources for delivering specific topics, including teaching instructions.
Build a Neuron
Short exam-style and exam-standard assessment papers (with mark schemes) to help test specific units or key topics in the relevant specification.
What is the function of a neuron?
The function of a neuron is to transmit nerve impulses along the length of an individual neuron and across the synapse into the next neuron. The central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which consists of sensory and motor nerve cells all contain these information processing neurons.
What is the structure of a neuron?
Anatomy of a Neuron. The neuron contains the soma (cell body) from which extend the axon (a nerve fiber conducting electrical impulses away from the soma) and dendrites (tree-like structures that receive signals from other neurons). The myelin sheath is an insulating layer that forms around the axon and allows nerve impulses to transmit more ...
What is the layer of the axon that allows nerve impulses to travel faster?
The myelin sheath is an insulating layer that forms around the axon and allows nerve impulses to transmit more rapidly along the axon. Neurons do not touch each other, and there is a gap, called the synapse, between the axon of one neuron the dendrite of the next.
How many axons does a neuron have?
Most neurons just have one axon which can range in size from 0.1 millimeters to over 3 feet (Miller & Zachary, 2017). Some axons are covered in a fatty substance called myelin which insulates the axon and aids in transmitting signals quicker.
What is the purpose of the myelin sheath?
Its purpose is to insulate one nerve cell from another and so to prevent the impulse from one neuron from interfering with the impulse from another.
What is the function of the terminal buttons in the axon?
Located at the end of the neuron, the axon terminals (terminal buttons) are responsible for transmitting signals to other neurons . At the end of the terminal button is a gap, which is known as a synapse. Terminal buttons hold vessels which contain neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are released from the terminal buttons into ...
What is the function of dendrites in the nervous system?
Dendrites are covered in synapses, which allows them to receive signals from other neurons. Some neurons have short dendrites, whilst others have longer ones. In the central nervous system, neurons are long and have complex branches that can allow them to receive signals from many other neurons.
Where are sensory neurons found?
Sensory neurons are found in receptors such as the eyes, ears, tongue and skin , and carry nerve impulses to the spinal cord and brain.
What are the three main types of neurons?
Board: There are three main types of neurons, including: sensory, relay and motor . Each of these neurons has a different function, depending on its location in the body and its role within the nervous system.
What is the process of connecting an axon to another neuron?
The axon terminal connects the neuron to other neurons (or directly to organs), using a process called synaptic transmission.
What happens when motor neurons are stimulated?
When motor neurons are stimulated they release neurotransmitters that bind to the receptors on muscles to trigger a response, which lead to movement. As you can see from the diagrams above, all three neurons consist of similar parts. The dendrites receive signals from other neurons or from sensory receptor cells.
Where do dendrites receive signals?
The dendrites receive signals from other neurons or from sensory receptor cells. The dendrites are typically connected to the cell body, which is often referred to as the ‘control centre’ of the neuron, as it’s contains the nucleus.
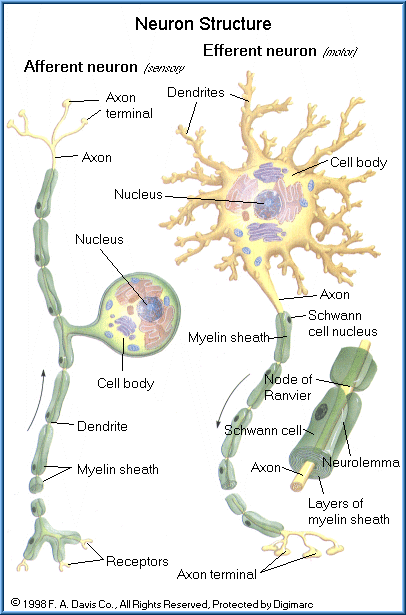
Definition
Overview of Neurons
- Neurons are cells of the nervous systemthat can transmit electrical impulses to facilitate communications between the brain and the rest of the body. There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, relay neurons, and motor neurons. Motor neurons control movement, sensory neurons allow us to feel sensations, and relay neurons allow motor neurons and sensor…
Structure of Sensory Neurons
- A typical neuron is comprised of dendrites, an axon, and a cell body, and the sensory neurons are no exception. Most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar, which means they have a single axon extending from the cellbody that forms two extensions: the dendrites and the axon. The sensory neuron “begins” with the dendrites, as this is where the signal is received from the external envir…
Location of Sensory Neurons
- The cell bodies of sensory neurons cluster together at regions called the dorsal ganglia of the spinal cord, sometimes called the dorsal root ganglia. Note that the term ganglia simply means a collection of cell bodies. Sensory neurons begin in the periphery. For example, in the skin, we can perceive tactile stimuli that detect touch, pain, and cold because of the sensory neurons located …
Function of Sensory Neurons
- Sensory neurons make up all the senses in the body, even those of which you are not consciously aware! The function of sensory neurons is to detect and transmit signals from a peripheral region to a more central location in the central nervous system, i.e., the spinal cord or the brain. The transduction of the signal takes place in the sensory receptorat the dendritic end of the neuron. …
Sensory Neurons vs. Motor Neurons
- To put it simply, sensory neurons are for “feeling,” and motor neurons are for “doing.” Motor neurons are efferent (meaning they carry information out towards the periphery from the central nervous system). In contrast, sensory neurons are efferent (they carry information in towards the central nervous system from the periphery). Motor neurons tend to have a multipolar morpholog…
Types of Sensory Neurons
- Sensory neurons can be classified in various ways, including by their morphology, location, and the stimulus they are responsible for detecting. Below are some examples of sensory neurons classified by the type of stimulus to which they respond. 1. Olfactory sensory neurons are bipolar neurons located in the nasal cavity. They are activated by odor molecules in the air and give us o…