What are the deep earthquakes?
How deep are earthquake foci?
What are the three types of seismic waves?
What waves travel as elastic motions at the highest speeds?
How many earthquakes occurred in Japan in 1965?
How many aftershocks are there in an earthquake?
What is the point at the surface immediately above the focus?
See 4 more
About this website

Is it worse if an earthquake is shallow or deep?
Shallow quakesShallow quakes generally tend to be more damaging than deeper quakes. Seismic waves from deep quakes have to travel farther to the surface, losing energy along the way.
What are shallow earthquakes called?
Shallow focus earthquakes are called crustal earthquakes as they exist in the earth's crustal layer. Deep focus earthquakes are known as intra plate earthquakes, as they are triggered off by collision between plates.
Are shallow earthquakes more destructive?
Most earthquakes occur at shallow depths, according to the U.S. Geological Survey, and they generally cause more damage than deeper earthquakes.
Where do shallow earthquakes occur?
(i) Shallow-focus earthquakes appear to be associated with mid-ocean ridges, with mountain ranges in the interior of the continents of Europe and Asia, and with the mountains and ocean trenches that surround the Pacific Ocean.
What causes shallow earthquakes?
Stresses associated with the collision of two plates cause deformation in the overriding plate, and thus shallow earthquakes. Shallow earthquakes also happen on the subducting slab when a locked zone (orange line, Figure 12.20) ruptures.
Does the depth of an earthquake matter?
The strength of shaking from an earthquake diminishes with increasing distance from the earthquake's source, so the strength of shaking at the surface from an earthquake that occurs at 500 km deep is considerably less than if the same earthquake had occurred at 20 km depth.
Which earthquakes cause the most damage?
What were the world's deadliest earthquakes?RankingLocationEstimated death toll1Shaanxi, China830,0002Port-au-Prince, Haiti316,0003Antakya, Turkey260,0004Antakya, Turkey250,0007 more rows•Oct 5, 2018
Where do the strongest earthquakes usually occur?
the Pacific OceanThe world's greatest earthquake belt, the circum-Pacific seismic belt, is found along the rim of the Pacific Ocean, where about 81 percent of our planet's largest earthquakes occur. It has earned the nickname "Ring of Fire".
Do earthquakes occur randomly?
Earthquakes are not randomly distributed around the earth, rather they are located in distinct zones which can be related to the margins of tectonic plates on the Earth's surface.
What plate boundary has shallow earthquakes?
divergent plate boundariesAt divergent plate boundaries, earthquakes tend to be weak and shallow.
What is the most common type of earthquake?
tectonic earthquakesThe most common are tectonic earthquakes. These occur when rocks in the earth's crust break due to geological forces created by movement of tectonic plates.
Where would you expect both shallow and deep earthquakes?
Shallow earthquakes are also common along transform faults, such as the San Andreas Fault. Along subduction zones, as we saw in Chapter 10, earthquakes are very abundant, and they are increasingly deep on the landward side of the subduction zone.
What are the 3 types of earthquake faults?
Earthquakes occur on faults - strike-slip earthquakes occur on strike-slip faults, normal earthquakes occur on normal faults, and thrust earthquakes occur on reverse or thrust faults.
What are the 3 types of earthquake waves?
There are three basic types of seismic waves – P-waves, S-waves and surface waves. P-waves and S-waves are sometimes collectively called body waves.
What are different types of earthquakes?
There are four different types of earthquakes: tectonic, volcanic, collapse and explosion. A tectonic earthquake is one that occurs when the earth's crust breaks due to geological forces on rocks and adjoining plates that cause physical and chemical changes.
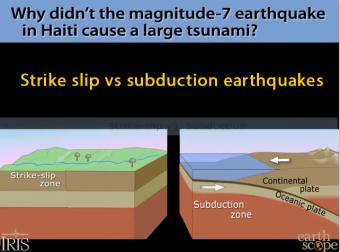
What is a subduction earthquake?
Where they collide and one plate is thrust beneath another (a subduction zone), the most powerful earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, and landslides occur.
Earthquakes - Shallow, Intermediate, and Deep Foci - VEDANTU
Earthquakes can take place anywhere between the Earth's surface and about 700 kilometres beneath the surface. With respect to scientific purposes, this earthquake depth range of 0 - 700 km is classified into 3 zones: shallow, deep and intermediate.
Shallow Focus and Deep Focus Earthquakes | Actforlibraries.org
The terms shallow focus and deep focus (and a third term: intermediate focus) earthquakes relates to the depth below the earth’s surface at which the earthquake occurs.
Difference between Shallow Focus and Deep Focus Earthquakes
Thus the difference between the two type of earthquakes lies in the depths where the focus point of the earthquake originates and the associated dynamics.
What are the deep earthquakes?
The deeper-focus earthquakes commonly occur in patterns called Benioff zones that dip into the Earth, indicating the presence of a subducting slab. Dip angles of these slabs average about 45°, with some shallower and others nearly vertical. Benioff zones coincide with tectonically active island arcs such as Japan, Vanuatu, Tonga, and the Aleutians, and they are normally but not always associated with deep ocean trenches such as those along the South American Andes. Exceptions to this rule include Romania and the Hindu Kush mountain system. In most Benioff zones, intermediate- and deep-earthquake foci lie in a narrow layer, although recent precise hypocentral locations in Japan and elsewhere show two distinct parallel bands of foci 20 km apart.
How deep are earthquake foci?
Shallow, intermediate, and deep foci. Most parts of the world experience at least occasional shallow earthquakes—those that originate within 60 km (40 miles) of the Earth’s outer surface. In fact, the great majority of earthquake foci are shallow. It should be noted, however, that the geographic distribution of smaller earthquakes is less ...
What are the three types of seismic waves?
Seismic waves generated by an earthquake source are commonly classified into three main types. The first two, the P (or primary) and S (or secondary) waves, propagate within the body of the Earth, while the third, consisting of Love and Rayleigh waves, propagates along its surface. The existence of these types of seismic waves was mathematically predicted during the 19th century, and modern comparisons show that there is a close correspondence between such theoretical calculations and actual measurements of the seismic waves.
What waves travel as elastic motions at the highest speeds?
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. The P seismic waves travel as elastic motions at the highest speeds. They are longitudinal waves that can be transmitted by both solid and liquid materials in the Earth’s interior.
How many earthquakes occurred in Japan in 1965?
In the Matsushiro region of Japan, for instance, there occurred between August 1965 and August 1967 a series of hundreds of thousands of earthquakes, some sufficiently strong (up to Richter magnitude 5) to cause property damage but no casualties. The maximum frequency was 6,780 small earthquakes on April 17, 1966.
How many aftershocks are there in an earthquake?
In some cases an earthquake may be followed by 1,000 or more aftershocks a day. Sometimes a large earthquake is followed by a similar one along the same fault source within an hour or perhaps a day. An extreme case of this is multiple earthquakes.
What is the point at the surface immediately above the focus?
The point at the surface immediately above the focus is known as the epicentre. Love and Rayleigh waves are guided by the free surface of the Earth. They follow along after the P and S waves have passed through the body of the planet.
Which is more damaging, a deep quake or a shallow quake?
Shallow quakes generally tend to be more damaging than deeper quakes. Seismic waves from deep quakes have to travel farther to the surface, losing energy along the way. Shaking is more intense from quakes that hit close to the surface like setting off "a bomb directly under a city," said Susan Hough, a USGS seismologist.
How deep are earthquakes?
A quake's destructive force depends not only on its strength, but also on location, distance from the epicenter and depth. Quakes can strike near the surface or deep within the Earth. Most quakes occur at shallow depths, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. Italy's quake was very shallow, originating between 2 1/2 miles (4 kilometers) and 6 miles (10 kilometers) underground, according to Italy's geological service and the USGS. The magnitude measurements also varied slightly—between magnitude 6 and 6.2. By contrast, the 6.8 quake in Myanmar was deeper—at 52 miles (84 kilometers), which is considered an intermediate depth.
What was the magnitude of the earthquake in Bagan?
A powerful earthquake measuring a magnitude 6.8 shook central Myanmar on Wednesday, damaging scores of ancient Buddhist pagodas in Bagan, a major tourist attraction, officials said. (Soe Thura Lwin via AP) Military personnel stand as they clear debris at a temple that was damaged by a strong earthquake in Bagan, Myanmar, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2016.
When was the earthquake in Bagan?
Military personnel clear debris at a temple that was damaged by a strong earthquake in Bagan, Myanmar, Thursday, Aug. 25, 2016. Using brooms and their hands soldiers and residents of the ancient Myanmar city famous for it's historic Buddhist pagodas, began cleaning up the debris from a powerful earthquake that shook the region ...
Why did Italy's earthquake do more damage than Myanmar?
Italy's earthquake was a lot weaker than the one in Myanmar, but it did far more damage because it happened at a shallower depth. The Associated Press explains the difference between shallow and deep earthquakes. ___. EARTHQUAKE MAGNITUDE IS MORE THAN JUST A NUMBER.
When did the 2016 earthquake hit Italy?
Rescuers search through debris of collapsed houses in Pescara del Tronto, Italy, Wednesday, Aug. 24, 2016. The magnitude 6 quake struck at 3:36 a.m. (0136 GMT) and was felt across a broad swath of central Italy, including Rome where residents of the capital felt a long swaying followed by aftershocks. (AP Photo/Sandro Perozzi)
What is a shallow focus earthquake?
SHALLOW FOCUS earthquakes are commonly occurring “crustal” earthquakes, caused by faults and movements of the continental plates. These are earthquakes with their focus nearer the surface of the earth. Shallow focus earthquakes are usually of large spread, causing greater damage at the surface or the earth’s crust.
Where do shallow focus earthquakes originate?
Shallow-focus and Deep-focus earthquakes are both “tectonic” earthquakes originating within the earth’s depths at various points. They start from the foci. A focal point is where the geological fault has begun to rupture. The focus of an earthquake however differs from its epicenter, the latter being the point on the ground’s surface directly above the focus.
What is the difference between shallow focus and deep focus earthquakes?
# Shallow focus earthquakes are of smaller magnitudes, of a range 1 to 5, while deep focus earthquakes are of higher magnitudes, 6 to 8 or more.
What scale is used to measure deep focus earthquakes?
However, deep focus earthquakes are best measured using the Moment Magnitude scale that has capacity to record earthquakes of magnitudes up to 10 on the scale. # Less energy is released during a shallow focus earthquakes, while tremendous energy accumulates during a deep focus earthquake.
How does an earthquake happen?
An earthquake occurs when energy stored inside the earth gets released with great pressure . When this happens, earthquake waves transfer the released energy to the surface of the earth. In the process, physical and chemical changes occur deep within the earth.
What is the name of the wave that radiates outwards?
Beginning at the focus of the earthquake, body waves called seismic waves radiate outwards along the rupturing fault. All of the rock in the path of the wave is compressed and expanded alternately, as the waves travel along the fault at great speeds.
Which is more damaging, a shallow earthquake or a deep earthquake?
Shallow quakes generally tend to be more damaging than deeper quakes. Seismic waves from deep quakes have to travel farther to the surface, losing energy along the way.
Where do earthquakes occur?
Quakes can strike near the surface or deep within the Earth. Most quakes occur at shallow depths, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. Italy’s quake was very shallow, originating between 2 1/2 miles (4 kilometers) and 6 miles (10 kilometers) underground, according to Italy’s geological service and the USGS.
How deep is the earthquake in Myanmar?
By contrast, the 6.8 quake in Myanmar was deeper — at 52 miles (84 kilometers), which is considered an intermediate depth. Shallow quakes generally tend to be more damaging than deeper quakes. Seismic waves from deep quakes have to travel farther to the surface, losing energy along the way.
How do seismic waves travel?
Seismic waves from deep quakes have to travel farther to the surface , losing energy along the way. Shaking is more intense from quakes that hit close to the surface like setting off “a bomb directly under a city,” said Susan Hough, a USGS seismologist.
Where was the most damage from the Myanmar earthquake?
While deep quakes may be less damaging, they’re usually more widely felt. Most of the destruction in the Myanmar quake was centered in the tourist town of Bagan where nearly 100 brick pagodas dating back centuries were damaged.
What are the deep earthquakes?
The deeper-focus earthquakes commonly occur in patterns called Benioff zones that dip into the Earth, indicating the presence of a subducting slab. Dip angles of these slabs average about 45°, with some shallower and others nearly vertical. Benioff zones coincide with tectonically active island arcs such as Japan, Vanuatu, Tonga, and the Aleutians, and they are normally but not always associated with deep ocean trenches such as those along the South American Andes. Exceptions to this rule include Romania and the Hindu Kush mountain system. In most Benioff zones, intermediate- and deep-earthquake foci lie in a narrow layer, although recent precise hypocentral locations in Japan and elsewhere show two distinct parallel bands of foci 20 km apart.
How deep are earthquake foci?
Shallow, intermediate, and deep foci. Most parts of the world experience at least occasional shallow earthquakes—those that originate within 60 km (40 miles) of the Earth’s outer surface. In fact, the great majority of earthquake foci are shallow. It should be noted, however, that the geographic distribution of smaller earthquakes is less ...
What are the three types of seismic waves?
Seismic waves generated by an earthquake source are commonly classified into three main types. The first two, the P (or primary) and S (or secondary) waves, propagate within the body of the Earth, while the third, consisting of Love and Rayleigh waves, propagates along its surface. The existence of these types of seismic waves was mathematically predicted during the 19th century, and modern comparisons show that there is a close correspondence between such theoretical calculations and actual measurements of the seismic waves.
What waves travel as elastic motions at the highest speeds?
Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. The P seismic waves travel as elastic motions at the highest speeds. They are longitudinal waves that can be transmitted by both solid and liquid materials in the Earth’s interior.
How many earthquakes occurred in Japan in 1965?
In the Matsushiro region of Japan, for instance, there occurred between August 1965 and August 1967 a series of hundreds of thousands of earthquakes, some sufficiently strong (up to Richter magnitude 5) to cause property damage but no casualties. The maximum frequency was 6,780 small earthquakes on April 17, 1966.
How many aftershocks are there in an earthquake?
In some cases an earthquake may be followed by 1,000 or more aftershocks a day. Sometimes a large earthquake is followed by a similar one along the same fault source within an hour or perhaps a day. An extreme case of this is multiple earthquakes.
What is the point at the surface immediately above the focus?
The point at the surface immediately above the focus is known as the epicentre. Love and Rayleigh waves are guided by the free surface of the Earth. They follow along after the P and S waves have passed through the body of the planet.
