What are the major stages of the sintering process?
Sintering Process The aim of the MEBIOS process is the formation of a ventilation route in the sintering bed by creating a low-density area around the large pellets arising from a kind of wall effect and suppression of sinter bed shrinkage due to support of the load by the dense large pellets in the upper part of the sinter bed.
What is the difference between sintering and annealing?
Sintering, by definition, is a process used in manufacturing to compact solid materials. The resulting product is a harder, stronger, more durable mass due to the high heat and pressure applied forcing the atoms of the material into tighter bonds with each other.
What is the method sintering used for?
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. The word "sinter" comes from the Middle High German sinter, a cognate of English "cinder". Click to see full answer.
Why do we do a sintering process in iron making?
Sintering is the process of forming and compacting a material by pressure and heat. Sintering is a major step in powder metallurgy and ceramics processing. The driving force for sintering is the reduction in total particle surface area. Surface energies are larger in magnitude than grain boundary energies.

What is the purpose of sintering process?
The purpose of sintering is to impart strength and integrity to the material. During the sintering process the temperature must be kept below the melting point of the constituent materials.Sep 12, 2019
What is sintering process in metallurgy?
sintering, the welding together of small particles of metal by applying heat below the melting point. The process may be used in steel manufacturing—to form complex shapes, to produce alloys, or to work in metals with very high melting points.Feb 25, 2022
What are the types of sintering process?
Basically, sintering processes can be divided into three types: solid state sintering, liquid phase sintering and viscous sintering, which are all widely used in the industry. The driving force of sintering is the reduction in the total interfacial energy, which occurs via densification and grain growth.
What materials can be sintered?
Sintering is the process of fusing particles together into one solid mass by using a combination of pressure and heat without melting the materials. Common particles that are sintered together include metal, ceramic, plastic, and other various materials.
How many stages are there in sintering?
The microstructural evolution during the sintering process has generally been divided into three stages. The initial stage can be defined as the interval between the beginning of the heat treatment and the point at which necks between particles impinge upon each other.
What is sintering with regards to a ceramic?
Sintering (Firing) of ceramic materials is the method involving consolidation of ceramic powder particles by heating the “green” compact part to a high temperature below the melting point, when the material of the separate particles difuse to the neghbouring powder particles.Nov 22, 2014
How does SPS work?
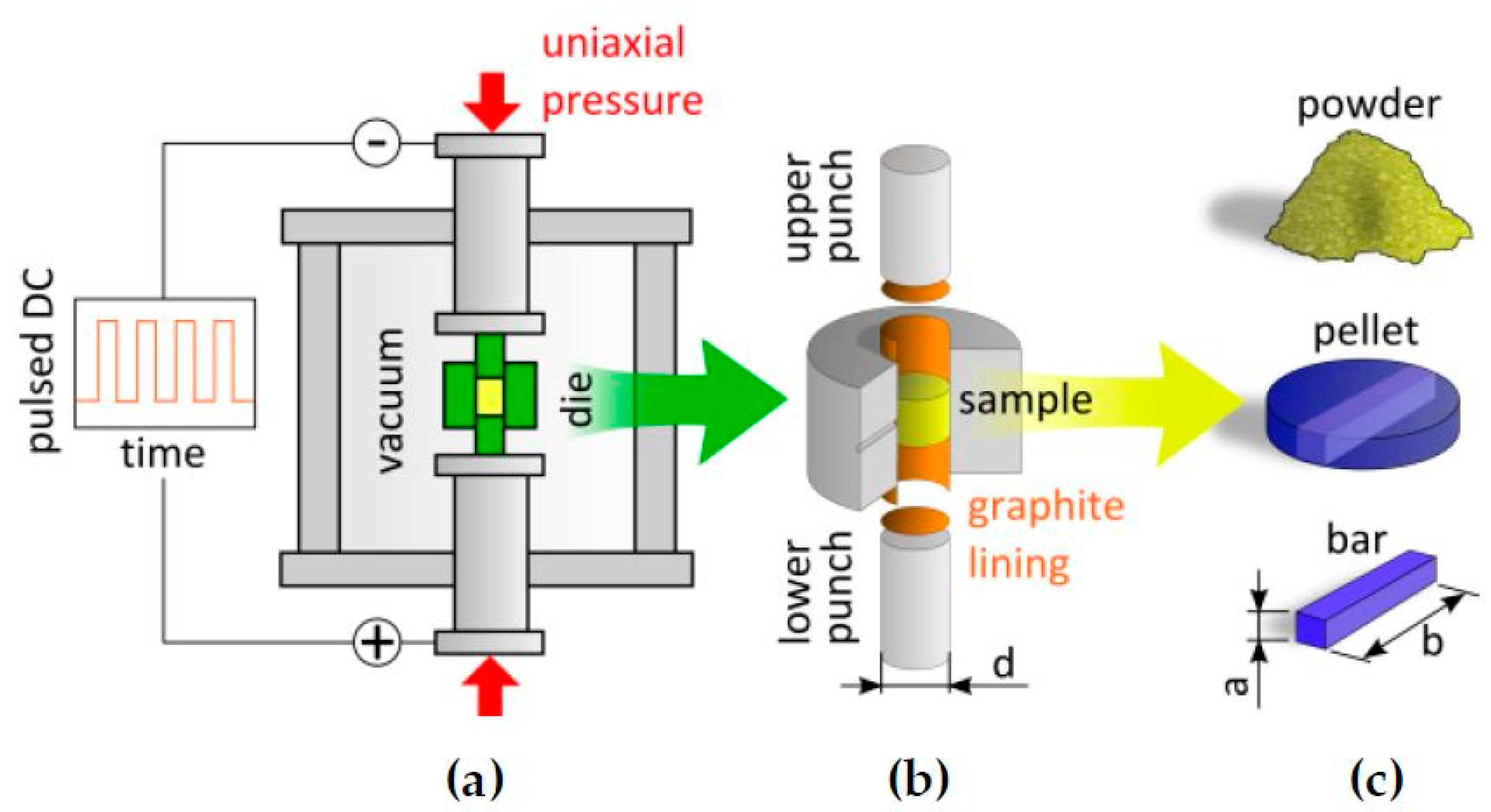
SPS process has been a major success in developing bulk ceramic nanomaterials in various research laboratories by restricting grain growth during densification as SPS processing involves high heating rate, lower sintering temperatures and short holding times . Despite last two decades of research, to date, SPS processing of nanoceramics has been confined to laboratory scale development. The bottleneck for the use of SPS in industrial scale production of ceramic components has been due to two factors: (1) only regular geometric shape, like square, disc, rectangular or cylindrical shaped components can be made via SPS and (2) only one sample can be reliably sintered in one heating cycle. Although multiple die cavities within a large diameter graphite die can be used to make a number of small samples in a single heating cycle, often the difference in powder size uniformity or impurity can cause differences in shrinkage behavior, leading to difference in density among simultaneously sintered components. Also, the lab-scale SPS machine can make 10-20 mm diameter samples and the size of the samples also is determined by the final sintering temperature. In particular, if the powder compact requires high sintering temperature of more than 1500 °C, then normal lab-scale SPS machine cannot be used to sinter larger diameter samples of more than 20 mm diameter. Some of the large capacity commercial machines can be used to densify samples of 50 mm diameter with 4-5 mm thickness even for difficult-to-sinter ceramics, like TiB 2, ZrB 2 and HfB 2, etc. This aspect needs to be considered while using SPS for commercial scale production, otherwise it is a great and fast processing tool to make nanomaterials.
What is the process of sintering hollow fibres?
The sintering process of the ‘green’ hollow fibres is similar to the sintering processes utilised in the manufacture of porous ceramic membranes via other techniques. The major concern during sintering of the hollow fibres is the removal of the binder and subsequent sintering without collapsing the hollow fibre shape.
Why is sintering used in wastewater?
Sintering process prevents the leaching of harmful substance from the sludge to the environment, giving way to use sintered sludge as a cost effective adsorbent to adsorb the heavy metals from wastewater.
What are the two types of sintering?
1.2 CATEGORIES OF SINTERING. Basically, sintering processes can be divided into two types: solid state sintering and liquid phase sintering. Solid state sintering occurs when the powder compact is densified wholly in a solid state at the sintering temperature, while liquid phase sintering occurs when a liquid phase is present in ...
How many stages are there in sintering?
The microstructural evolution during the sintering process has generally been divided into three stages.
What is sinter made of?
The sinter product is made up of oxides, sulfates, sulfides, some metallic lead together with ferrites and silicates. A typical sinter contains 40–52% Pb and 1–2% sulfur. The sinter product must exhibit enough permeability and strength to perform well in the lead blast furnace.
What is liquid phase sintering?
In general, compared with solid state sintering, liquid phase sintering allows easy control of microstructure and reduction in processing cost, but degrades some important properties, for example, mechanical properties.
Why is sintering used in metallurgy?
Because the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy.
What is sintering in ceramics?
Ceramic sintering. Sintering is part of the firing process used in the manufacture of pottery and other ceramic objects. These objects are made from substances such as glass, alumina, zirconia, silica, magnesia, lime, beryllium oxide, and ferric oxide.
Why is sintering important?
Sintering is an important cause for loss of catalyst activity, especially on supported metal catalysts. It decreases the surface area of the catalyst and changes the surface structure. For a porous catalytic surface, the pores may collapse due to sintering, resulting in loss of surface area.
How does sintering occur?
This diffusion is caused by a gradient of chemical potential – atoms move from an area of higher chemical potential to an area of lower chemical potential. The different paths the atoms take to get from one spot to another are the sintering mechanisms. The six common mechanisms are:
What is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat or pressure without melting it to
Sintering . Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction . Sintering happens naturally in mineral deposits or as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials.
What happens to the density of a collection of grains during sintering?
In most cases, the density of a collection of grains increases as material flows into voids, causing a decrease in overall volume. Mass movements that occur during sintering consist of the reduction of total porosity by repacking, followed by material transport due to evaporation and condensation from diffusion.
What is liquid phase sintering?
Liquid phase sintering is the process of adding an additive to the powder which will melt before the matrix phase.
What is sintering in metallurgy?
What is Sintering – Definition. Sintering is the process of forming and compacting a material by pressure and heat. Sintering is a major step in powder metallurgy and ceramics processing. Sintering is the process of forming and compacting a material by pressure and heat.
What is sintering in mining?
Sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points such as tungsten, molybdenum or uranium dioxide ceramics. For example, tungsten carbide (WC), which is used extensively in mining in top hammer rock drill bits, downhole hammers, and many more applications, is made by powder metallurgy, ...
How are compacted metals bonded?
During sintering, compacted metal powders are bonded or sintered by heating in a furnace to a temperature that is usually below the melting point of the major constituent. Sintering of powder metals is a process in which particles under pressure chemically bond to themselves in order to form a coherent shape when exposed to a high temperature.
What is solid state sintering?
This process is known as solid-state sintering. If the temperature is above the melting point of a component in the powder metal part, the liquid of the melted particles fills the pores. This type of sintering is known as liquid-state sintering.
What is the driving force of sintering?
The driving force for sintering is the reduction in total particle surface area. Surface energies are larger in magnitude than grain boundary energies. Sintering is usually carried out below the melting temperature, so that a liquid phase is normally not present. Sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high ...
What are the characteristics of an elemental powder?
During this process, a number of characteristics are increased including the strength, ductility, toughness, and electrical and thermal conductivity of the material . If different elemental powders are compact and sintered, the material would form into alloys and intermetallic phases.
Is uranium dioxide a high melting point?
On the other hand the uranium dioxide has very high melting point and has well known behavior. The UO 2 is fed into dies and pressed biaxially into cylindrical pellet form using a load of several hundred MPa – this is done in pressing machines operating at high speed.
What happens to the porous spaces between the material's particles during the sintering process?
The porous spaces between the material's particles are minimized during the sintering process as the material is squeezed together under high temperature and pressure. This increases some of the material's properties, including:
What are the properties of sintering?
The porous spaces between the material's particles are minimized during the sintering process as the material is squeezed together under high temperature and pressure. This increases some of the material's properties, including: 1 Thermal and electrical conductivity 2 Material strength 3 Translucency
What is liquid phase sintering?
In liquid phase sintering, the liquid phase is present in the compact (or particles melting occurs) during sintering. When compared to solid-state sintering, the liquid phase sintering allows easy control over the microstructure of grains, and hence processing cost is low. Liquid phase also enhances mass transport.
What is solid sintering?
Sintering is mainly classified into solid-state sintering and liquid phase sintering. When powder compact is densified wholly in the solid state at the sintering temperature, then it is known as solid sintering. In liquid phase sintering, the liquid phase is present in the compact (or particles melting occurs) during sintering.
What is sintering in chemistry?
Sintering is a thermal treatment technique of compacting and forming of solid material using heat and pressure without melting the main constituent (or without heating it to its liquefaction temperature). It is basically atomic diffusion. It will happen in any material at any temperature above absolute zero, but it is faster in higher temperature.
Why is sintering faster in small particles than large particles?
In thermodynamic understating, it is a surface energy reduction process by reducing surface area. Since small particles have more surface energy , the sintering is faster in small particles than in large particles.
Why is sintering used?
Sintering is used to make strong, reliable and high-performance shapes, such as ceramic, medical implants etc. Sintering happens when atoms of material at boundaries of particles diffuse and form one single solid particle. It is helpful to reduce or eliminate porosity, increase conductivity, etc.
What is it called when atoms go into solution?
In areas where capillary pressures are high, atoms will preferentially go into solution and then precipitate in areas of lower chemical potential where particles are not close or in contact. This is called contact flattening and densifies the system in a way similar to grain boundary diffusion in solid state sintering.
What is sintering furnace?
Sintering furnaces are available that can apply accelerated cooling rates in the cooling zone and material grades have been developed that can transform to martensitic microstructures at these cooling rates. This process, together with a subsequent tempering treatment, is known as sintering hardening, a process that has emerged, in recent years, has a leading means of enhancing sintered strength.
What happens to copper when sintering?
At sintering temperature, the copper melts and then diffuses into the iron powder particles creating swelling. By careful selection of copper content, it is possible to balance this swelling against the natural shrinkage of the iron powder skeleton and provide a material that does not change in dimensions at all during sintering.
What is sintering powder?
Sintering is a heat treatment applied to a powder compact in order to impart strength and integrity. The temperature used for sintering is below the melting point of the major constituent of the Powder Metallurgy material. After compaction, neighbouring powder particles are held together by cold welds, which give the compact sufficient “green ...
What is liquid phase sintering?
Permanent liquid phase sintering. For certain materials, such as cemented carbides or hardmetals, a sintering mechanism involving the generation of a permanent liquid phase is applied. This type of liquid phase sintering involves the use of an additive to the powder, which will melt before the matrix phase and which will often create ...
What are the stages of liquid chemistry?
The process has three stages: Rearrangement. As the liquid melts, capillary action will pull the liquid into pores and also cause grains to rearrange into a more favourable packing arrangement. Solution-precipitation.
Does sintering a compact cause shrinkage?
In a compact that contains only iron powder particles, the solid state sintering process would generate some shrinkage of the compact as the sintering necks grow. However, a common practice with ferrous PM materials is to make an addition of fine copper powder to create a transient liquid phase during sintering.

How Does It Work?
- Just as a material has a melting point, it will also have a desirable sintering point, at which the heat and pressure are enough to reduce the porous spaces between the material’s particles and squeeze loose material together into a solid lump. This use of pressure and heat takes place na…
Types
- There are several types of sintering, depending on the material being joined or the specific sintering process, as follows:
Advantages
- While the different methods and materials offer a range of benefits, there are a number of general advantages associated with sintering: 1. Purity: Sintering offers high levels of purity and uniformity in the starting materials, which can be maintained due to the simple fabrication process 2. Repeatable: Controlling the grain size during input allows for highly repeatable operat…
Where Is It used?
- Because sintering can enhance material properties such as electrical and thermal conductivity, strength, and translucency, it has uses in a range of industries and applications. The process of creating metal parts by pressing powders dates back many centuries and has been used to make items from almost every type of ceramic or metal. Modern uses include the creation of structura…
FAQs
- What is the Meaning of Sintered?
The word ‘sinter’ came to the English language from German in the late 18thCentury and has comparisons to the English word ‘cinder.’ Sintering is a heat treatment process that involves subjecting aggregate material to temperature and pressure in order to compact the loose materi… - Why is Sintering done and Why is it Important?
Sintering is done to impart strength and integrity to a material as well as reducing porosity and enhancing electrical conductivity, translucency and thermal conductivity. This is important to deliver desirable properties to products and also allows items to be created from metals with hi…
Conclusion
- Sintering works through the diffusion of atoms across particle boundaries before fusing together into one piece under the influence of pressure and/or heat. While this process can occur naturally for mineral deposits, it is also widely used by a range of industries to manufacture items from materials including ceramics, metals and plastics. Sintering occurs at heats below the melting p…
Overview
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms in the materials diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creati…
General sintering
Sintering is effective when the process reduces porosity and enhances properties such as strength, electrical conductivity, translucency and thermal conductivity; yet, in other cases, it may be useful to increase its strength but keep its gas absorbency constant as in filters or catalysts. During the firing process, atomic diffusion drives powder surface elimination in different stages, starting from the formation of necks between powders to final elimination of small pores at the …
Ceramic sintering
Sintering is part of the firing process used in the manufacture of pottery and other ceramic objects. These objects are made from substances such as glass, alumina, zirconia, silica, magnesia, lime, beryllium oxide, and ferric oxide. Some ceramic raw materials have a lower affinity for water and a lower plasticity index than clay, requiring organic additives in the stages before sintering. The general procedure of creating ceramic objects via sintering of powders includes:
Sintering of metallic powders
Most, if not all, metals can be sintered. This applies especially to pure metals produced in vacuum which suffer no surface contamination. Sintering under atmospheric pressure requires the use of a protective gas, quite often endothermic gas. Sintering, with subsequent reworking, can produce a great range of material properties. Changes in density, alloying, and heat treatments …
Plastics sintering
Plastic materials are formed by sintering for applications that require materials of specific porosity. Sintered plastic porous components are used in filtration and to control fluid and gas flows. Sintered plastics are used in applications requiring caustic fluid separation processes such as the nibs in whiteboard markers, inhaler filters, and vents for caps and liners on packaging materials. Sintered ultra high molecular weight polyethylenematerials are used as ski and snowb…
Liquid phase sintering
For materials that are difficult to sinter, a process called liquid phase sintering is commonly used. Materials for which liquid phase sintering is common are Si3N4, WC, SiC, and more. Liquid phase sintering is the process of adding an additive to the powder which will melt before the matrix phase. The process of liquid phase sintering has three stages:
• rearrangement – As the liquid melts capillary action will pull the liquid into pores and also caus…
Electric current assisted sintering
These techniques employ electric currents to drive or enhance sintering. English engineer A. G. Bloxam registered in 1906 the first patent on sintering powders using direct current in vacuum. The primary purpose of his inventions was the industrial scale production of filaments for incandescent lamps by compacting tungsten or molybdenum particles. The applied current was particularly effective in reducing surface oxides that increased the emissivity of the filaments.
Pressureless sintering
Pressureless sintering is the sintering of a powder compact (sometimes at very high temperatures, depending on the powder) without applied pressure. This avoids density variations in the final component, which occurs with more traditional hot pressing methods.
The powder compact (if a ceramic) can be created by slip casting, injection moulding, and cold isostatic pressing. After presintering, the final green compact can be machined to its final shap…