What is the function of spongy bone?
Spongy bone provides balance to the dense and heavy compact bone by making bones lighter so that muscles can move them more easily. In addition, the spaces in some spongy bones contain red bone marrow, protected by the trabeculae, where hematopoiesis occurs.
What are the examples of spongy bone?
Spongy bone is specifically found within the ends of long bones, pelvic bones, ribs, skull bones, and vertebrae in the spine. Thus, it is found in both flat and long bones of the body.
Where are spongy bone located?
Spongy bone is found mostly at the ends of bones and contains red marrow. Bone marrow is found in the center of most bones and has many blood vessels. There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow.
What is spongy and compact bone?
Compact bones are the present in the outer layer of long bones, while spongy bones are present in the middle of the long bones. The main difference between spongy and compact bones is their structure and function.
What are 3 differences between compact and spongy bones?
The main difference between compact and spongy bone is that compact bone is the hard outer layers of the bone whereas spongy is the more porous, inner layers of the bone. Compact bones lack spaces between lamellae whereas spongy bones consist of spaces between lamellae. Compact bones are called cortical bones.
Is the skull spongy bone?
Flat bones are made up of a layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. They have a flat shape, not rounded. Examples include the skull and rib bones.
How is spongy bone formed?
Osteoblasts penetrate the disintegrating cartilage and replace it with spongy bone. This forms a primary ossification center. Ossification continues from this center toward the ends of the bones. After spongy bone is formed in the diaphysis, osteoclasts break down the newly formed bone to open up the medullary cavity.
Is spongy bone soft?
Though spongy bone may remind you of a kitchen sponge, this bone is quite solid and hard, and is not squishy at all. The inside of your bones are filled with a soft tissue called marrow. There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow.
Do all bones have spongy bone?
Spongy Bone Tissue Whereas compact bone tissue forms the outer layer of all bones, spongy bone or cancellous bone forms the inner layer of all bones.
What is spongy bone structure?
1:083:22COMPACT BONE VS SPONGY BONE - EASY FAST REVIEW!! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis porous nature makes spongy bone less dense compared to compact bone. And in fact spongy bone isMoreThis porous nature makes spongy bone less dense compared to compact bone. And in fact spongy bone is more vascular. And it contains the red bone marrow where red blood cells are made because of its
What is the major difference between compact and spongy bone quizlet?
Compact bone has more bone matrix and less space due to osteons. Spongy bones have less bone matrix and more space due to trabeculae.
What do compact and spongy bone have in common?
Compact and spongy bone may differ in some ways, nevertheless, these bones do share several similarities. Both are made of osteocytes, bone cells, and a mineral matrix that holds the osteocytes in place. Both types of bone are also living tissues containing bone, blood vessels, and nerves.
What are the 2 other terms for spongy bone?
cancellous bone, also called trabecular bone or spongy bone, light, porous bone enclosing numerous large spaces that give a honeycombed or spongy appearance.
What's another name for spongy bone?
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone.
What is an example of compact bone?
Sesamoid bones develop in areas where there is a lot of movement, and therefore friction, such as the kneecaps, or patellae, and in hands and feet. All of these types are compact bones because they are covered with compact tissue for protection. The femur is an example of a long, compact bone.
What is spongy bone structure?
1:083:22COMPACT BONE VS SPONGY BONE - EASY FAST REVIEW!! - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThis porous nature makes spongy bone less dense compared to compact bone. And in fact spongy bone isMoreThis porous nature makes spongy bone less dense compared to compact bone. And in fact spongy bone is more vascular. And it contains the red bone marrow where red blood cells are made because of its
What is a spongy bone?
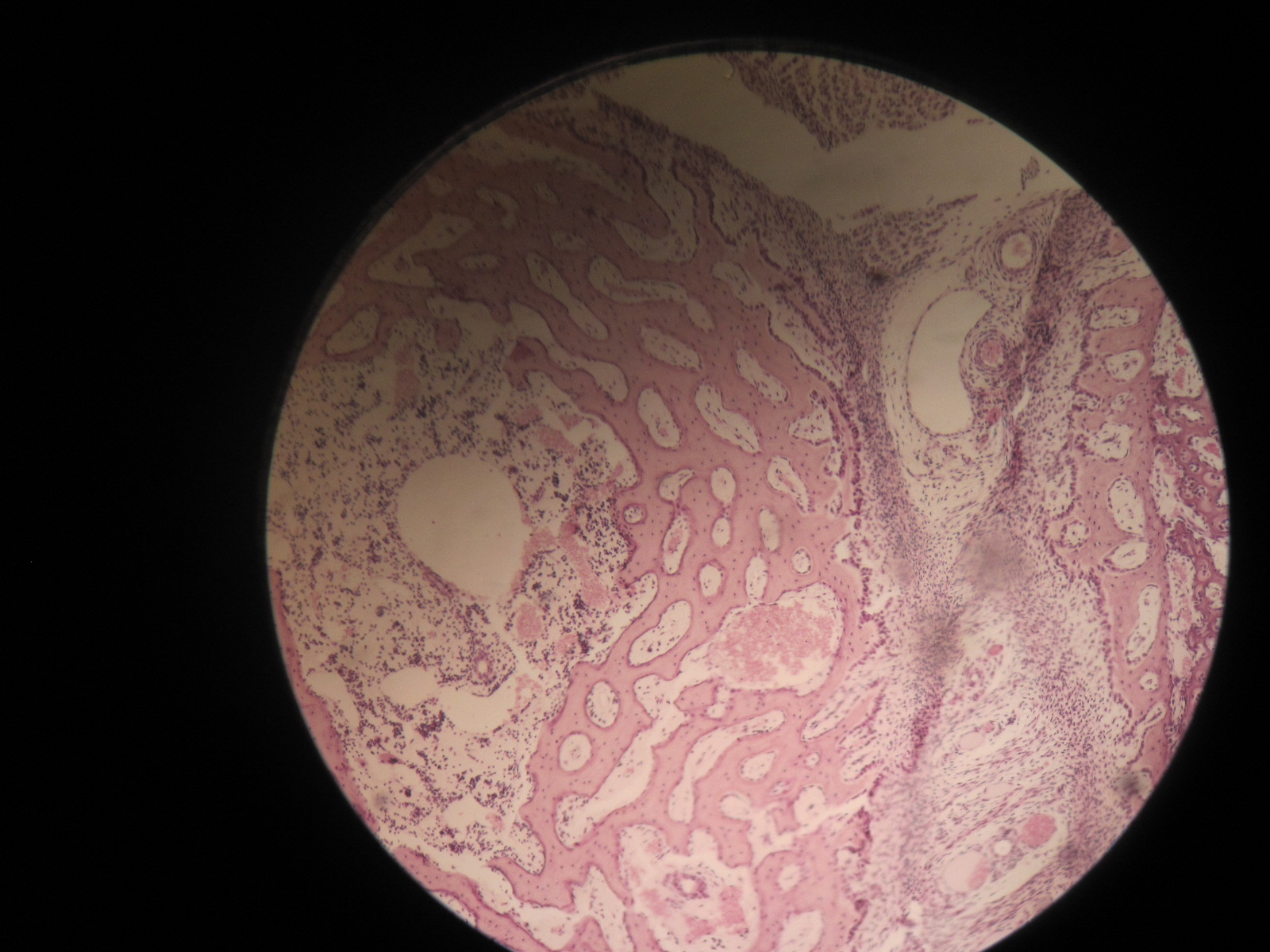
The spongy bone is a much porous kind of bone which is found in the animals. The spongy bones are also called Cancellous bones or the Trabecular bones. This bone is highly vascularized and consists of red bone marrow. Usually, spongy bone is situated at the end of long bones, with the surrounding of harder compact bone. This bone also presents in the ribs, inside the vertebrae, in the joint bones, and in the skull. Spongy bones are weaker and softer as compared compact bone, but it is much flexible too. It is referred by a lattice-like a matrix network, known as trabeculae which give it spongy shape.
Where is spongy bone located?
Usually, spongy bone is situated at the end of long bones, with the surrounding of harder compact bone. This bone also presents in the ribs, inside the vertebrae, in the joint bones, and in the skull. Spongy bones are weaker and softer as compared compact bone, but it is much flexible too.
How does spongy bone reduce the weight of the skeleton?
Reduces the Weight of the Skeleton: The low density and low weight of spongy bone balance out the heavier and denser compact bone in order to reduce the overall weight of the skeleton. This act makes it easier for the movement of muscle to the limbs.
What is the function of spongy bone?
The trabeculae of the spongy bone work to form along with lines of stress, which gives the bone strength and the flexibility in this area. Spongy bone also lies in joints and work as a shock absorber when we jump, walk, or run.
What is the hardest part of the skeleton?
It is referred by a lattice-like a matrix network, known as trabeculae which give it spongy shape. What is Bone:� Bone is basically one of the hardest parts of the skeleton within the Vertebrate. We can also say that skeleton is a collection of numerous rigid animal substances or structures like baleen or ivory.
Where are lacunae and osteocytes found?
The lacunae and their osteocytes are present in trabeculae matrix on the bone with the bone marrow. Blood vessels travel from the harder compact bone toward the spongy bone, by supply the materials which are necessary for the production of blood cells.
Which bone is denser, spongy or compact?
The compact bone is denser with having few open spaces, the spongy bone is good for form and stores bone marrow across the lattice-like trabeculae network. Compact bone is made up of primarily of fat in its medullar cavity, and it stores yellow bone marrow. The spongy bone has red bone marrow which is used in erythropoiesis.
What is bone in anatomy?
bone. [ bōn] 1. the hard, rigid form of connective tissue constituting most of the skeleton of vertebrates, composed chiefly of calcium salts. 2. any distinct piece of the skeleton of the body. See anatomic Table of Bones in the Appendices for regional and alphabetical listings of bones, and see color plates 1 and 2.
Which bone contains air filled spaces?
pneumatic bone bone that contains air-filled spaces. premaxillary bone premaxilla. pterygoid bone pterygoid process. rider's bone localized ossification sometimes seen on the inner aspect of the lower end of the tendon of the adductor muscle of the thigh in horseback riders.
What happens when cartilage breaks loose?
Some of the cartilage cells break loose, so that channels develop in the bone shaft. Blood vessels enter the channels, bearing with them small cells of connective tissue, some of which become osteoblasts, cells that form true bone. The osteoblasts enter the hardened cartilage, forming layers of hard, firm bone.
Which bone forms the roof of the nasal fossa?
ethmoid bone the sievelike bone that forms a roof for the nasal fossae and part of the floor of the anterior cranial fossa. See anatomic Table of Bones in the Appendices. facial b's the bones that form the skeleton of the face, including the hyoid, palatine, and zygomatic bones, the mandible, and the maxilla.
What is the outermost layer of bone?
Bone is not uniform in structure but is composed of several layers of different materials. The outermost layer, the periosteum, is a thin, tough membrane of fibrous tissue. It gives support to the tendons that secure the muscle to the bone and also serves as a protective sheath.
Why is bone replaced with fibrous tissue?
In osteitis fibrosa cystica, bone is replaced by fibrous tissue because of abnormal calcium metabolism. The condition usually is due to overactivity of the parathyroid glands. osteoma refers to abnormal new growth, either benign or malignant, of the tissue of the bones.
What chemical is found in bones?
Bone tissue also contains a large number of nerves. The basic chemical in bone, which gives bone its hardness and strength, is calcium phosphate. Development. Cartilage forms the major part of bone in the very young; this accounts for the great flexibility and resiliency of the infant skeleton.
Where is spongy bone found?
It is found in the long bones and it is surrounded by compact bone. The term spongy comes from the fact that it is a highly vascularized and porous tissue. Trabeculae are spaces created in the tissue by thin areas of osteoblast cells. As a result, trabecular bone has about 10 times the surface area of compact bone.
What is the difference between spongy and compact bone?
Compact Bone. Compact bone, also called cortical bone, surrounds spongy bone and makes up the other 80% of the bone in a human skeleton. It is smooth, hard and heavy compared to spongy bone and it is also white in appearance, in contrast to spongy bone which has a pink color.
What is compact bone made of?
Compact bone is made up of units called lamellae which are sheets of collagen aligned in a parallel pattern that gives the bone strength. Blood vessels supply compact bone with oxygen and nutrients through structures called Haversian canals or osteons. The image above shows the relationship between spongy bone and hard (compact) bone.
What are the long bones of the human body?
Reviewed by: BD Editors. Last Updated: April 24, 2019. Spongy bone and compact bone make up the long bones of the human skeleton. Long bones are longer than they are wide, like the tibia and the femur.
What is the difference between spongy and compact bones?
The main difference between spongy and compact bones is their structure and function. Visit BYJU’S to learn more differences.
What are compact bones made of?
Compact bones are also called cortical bones. They light, spongy and soft in nature. They are heavy, tough and compact in nature. They are made up of trabeculae. They are made up of osteons. They fill the inner layer of most bones. They fill the outer layer of most bones. Bone-marrow cavity absent.
What is the primary skeletal structure that supports muscles and gives shape to the body?
Bones are the primary skeletal structure that supports muscles and gives shape to the body. Spongy and compact bones are two basic structural bone types. They make up the long bones in the body. Long bones are dense hard bones that provide strength, structure and mobility.