What causes chromosomal abnormalities?
This can happen with or without loss of genetic material.
- Deletions: A portion of the chromosome is missing or deleted.
- Duplications: A portion of the chromosome is duplicated, resulting in extra genetic material.
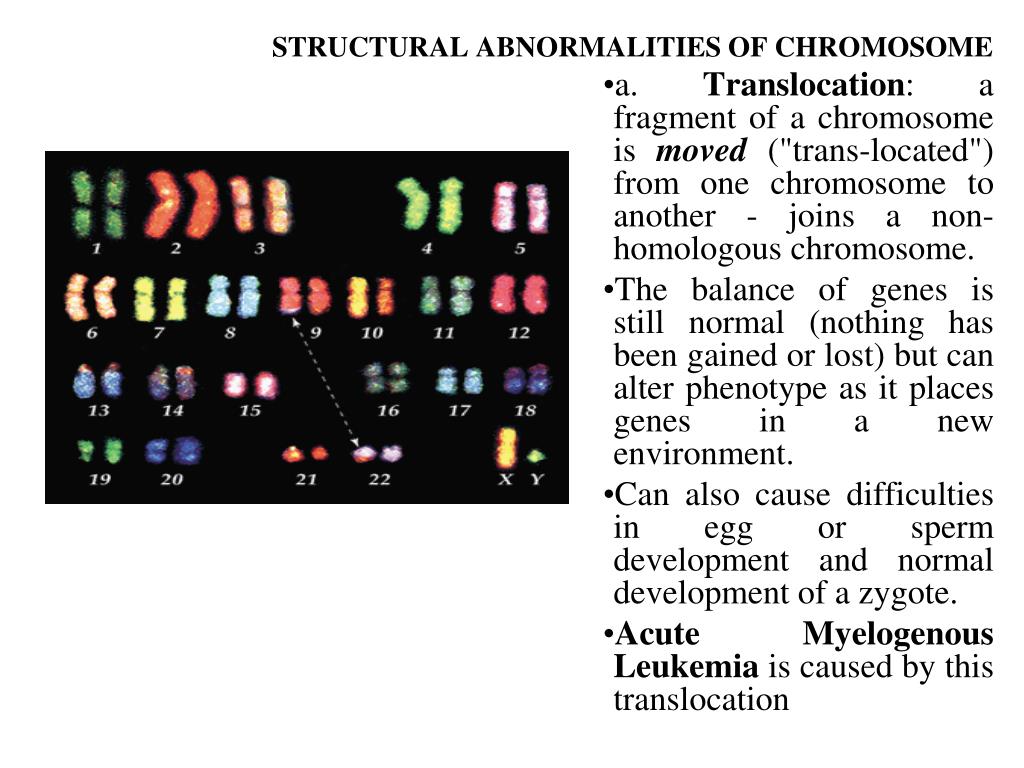
- Translocations: A portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome. ...
- Inversions: A portion of the chromosome has broken off, turned upside down, and reattached. ...
What are chromosome abnormalities?
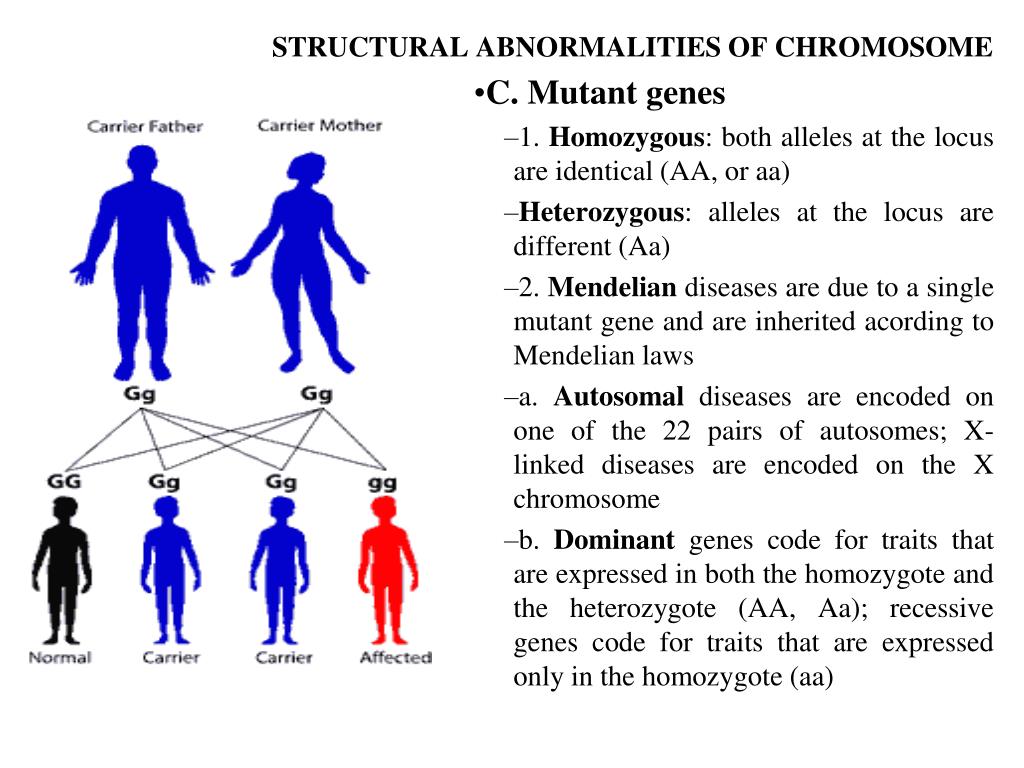
Chromosome abnormalities can be numerical or structural. A numerical abnormality mean an individual is either missing one of the chromosomes from a pair or has more than two chromosomes instead of a pair. A structural abnormality means the chromosome's structure has been altered in one of several ways.
What are the types of chromosomal defects?
Types of chromosomal abnormalities. These are mainly divided into two types also known as numeric abnormalities: Polyploidy; Aneuploidy; Polyploidy. This mainly occurs in plants in which the count of chromosomes entirely increases due to the failure of cytokinesis in cell division.
What is a normal karyotype?
Normal karyotype refers to a karyotype of a normal individual in a particular population. It is the most common karyotype among the individuals of that species as well. The number of chromosomes in a somatic cell of a particular species is called the somatic number, which is designated as 2n. In humans, this 2n is equal to 46.
What are examples of structural abnormalities?
Examples of Structural AbnormalitiesAmino acid substitution: a2 B26glu-val (Sickle Cell hemoglobin)Amino acid deletion: a2 B26glu deleted (Hb Leiden)Amino acid addition: a2141-172B2 (Hb Constant Spring)Chain fusion: a2 delta-B2 (Hb Lepore)
What is the most common structural chromosomal abnormality?
The most common type of chromosomal abnormality is known as aneuploidy, an abnormal chromosome number due to an extra or missing chromosome. Most aneuploid patients have trisomy (three copies of a chromosome) instead of monosomy (single copy of a chromosome).
What is an example of a chromosomal abnormality?
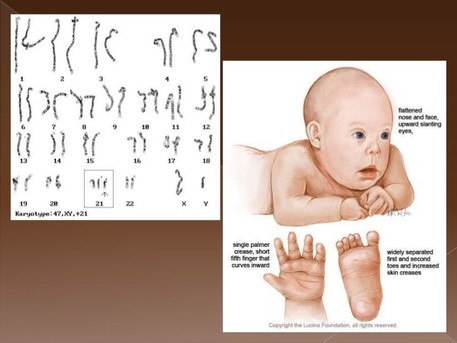
Some chromosomal abnormalities occur when there is an extra chromosome, while others occur when a section of a chromosome is deleted or duplicated. Examples of chromosomal abnormalities include Down syndrome, Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13, Klinefelter syndrome, XYY syndrome, Turner syndrome and triple X syndrome.
What is a chromosomal abnormality?
A chromosomal abnormality, or chromosomal aberration, is a disorder characterized by a morphological or numerical alteration in single or multiple chromosomes, affecting autosomes, sex chromosomes, or both.
What are the 3 most common chromosomal abnormalities?
Some of the most common chromosomal abnormalities include: Down's syndrome or trisomy 21. Edward's syndrome or trisomy 18. Patau syndrome or trisomy 13.
What are the 4 types of chromosomal abnormalities?
The most common types of aneuploidy are monosomies, when only one chromosome of a pair is present, and trisomies, when there are three copies of a chromosome instead of a pair. The four main types of structural chromosomal aberrations are deletion, duplication, inversion, and translocation.
What is the main cause of chromosomal abnormalities?
Chromosome abnormalities often happen due to one or more of these: Errors during dividing of sex cells (meiosis) Errors during dividing of other cells (mitosis) Exposure to substances that cause birth defects (teratogens)
How do you treat chromosomal abnormalities?
Key Points to Remember In many cases, there is no treatment or cure for chromosomal abnormalities. However, genetic counseling, occupational therapy, physical therapy and medicines may be recommended.
How do you know if your baby has a chromosomal abnormality?
The earliest you can have tests for chromosomal anomalies is about 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. These different kinds of tests can be screening tests or diagnostic tests. Antenatal screening tests work out the chance or risk of your baby having certain chromosomal anomalies or other conditions that can cause disability.
How common are chromosome abnormalities?
Each person has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all. For each pair, you get one chromosome from your mother and one chromosome from your father. About 1 in 150 babies is born with a chromosomal condition.
How chromosomal abnormalities can be diagnosed?
Chromosomal disorders can be diagnosed before birth using prenatal tests such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis or after birth using a blood test. Cells obtained from these tests are grown in the laboratory, and then the chromosomes are examined under a microscope.
Can you prevent chromosomal abnormalities?
The risk can be lowered by: Seeking medical care three months before becoming pregnant to discuss health problems and medicine use. Taking a daily prenatal vitamin that contains 400 micrograms of folic acid for three months before becoming pregnant.
What is the most common cause of abnormal chromosome number?
Abnormal chromosomes most often happen as a result of an error during cell division. Chromosome abnormalities often happen due to one or more of these: Errors during dividing of sex cells (meiosis) Errors during dividing of other cells (mitosis)
What is the most common trisomy?
The most common is Standard Trisomy 21, in which the father's sperm or the mother's egg cell contains the extra chromosome. In Mosaic Down syndrome, the extra chromosome spontaneously appears as the embryo develops.
What is aneuploidy XXY?
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY aneuploidy) is the most common human sex chromosome disorder. Approximately 1 in 500-600 males is born with an extra X chromosome. The prevalence rate is 5-20 times higher in males who are mentally challenged than in the general male population.
What is another name for trisomy 13?
Patau's syndrome is a serious rare genetic disorder caused by having an additional copy of chromosome 13 in some or all of the body's cells. It's also called trisomy 13. Each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, which carry the genes you inherit from your parents.
What are structural chromosome abnormalities?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when there is a change in the structure or parts of a chromosome. The total number of chromosomes is typically 46 total per cell. Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when part of a chromosome is missing, a part of a chromosome is extra, or a part has switched places with another part. Ultimately, this leads to having too much or too little genetic material. This is a cause of some birth defects.
What is structural abnormality?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when part of a chromosome is missing, a part of a chromosome is extra, or a part has switched places with another part. Ultimately, this leads to having too much or too little genetic material. This is a cause of some birth defects. Each chromosome has many segments.
What are structural chromosome abnormalities?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when there is a change in the structure or parts of a chromosome. The total number of chromosomes is typically 46 total per cell. Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when part of a chromosome is missing, a part of a chromosome is extra, or a part has switched places with another part. Ultimately, this leads to having too much or too little genetic material. This is a cause of some birth defects.
What is structural abnormality?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when part of a chromosome is missing, a part of a chromosome is extra, or a part has switched places with another part. Ultimately, this leads to having too much or too little genetic material. This is a cause of some birth defects. Each chromosome has many segments.
What is the short arm of a chromosome called?
The short arm, which is the upper half of the chromosome, is known as the "p arm.". The long arm, which is the lower half of the chromosome, is the "q arm.". The centromere is the center part of a chromosome that appears "pinched" between the p and q arms.
When a chromosome has additional material attached to it, the origin of this material might not be identifiable with?
When a chromosome has additional material attached to it, the origin of this material might not be identifiable with conventional banding methods. This is especially likely if the abnormality is subtle and originated de novo or is acquired. The abbreviation "add" (from the Latin additio) is used.
Where is the long arm segment of chromosome 4?
The long-arm segment between bands 9q12 and 9q13 has been inserted, in its original orientation, into the long arm of chromosome 4 at band q31 .
What is a derivative chromosome?
A structurally rearranged chromosome generated by events involving two or more chromosomes or the result of multiple events within a single chromosome is a derivative chromosome. Thus, each unbalanced product of a translocation event is a derivative chromosome. The identity of a derivative chromosome is determined by its centromere. Examples are as follows:
How many copies of the same centromere are in an isodicentric chromosome?
Unlike isochromosomes, isodicentric chromosomes contain two copies of the same centromere. One of the two centromeres might be inactive, in which case the chromosome is pseudodicentric (psu dic). The breakpoints in isodicentric chromosomes are usually on the band adjacent to the centromere on the opposite arm:
How many copies of the short arm of chromosome 18 are there?
Here, we have an isodicentric chromosome comprised of two copies of the entire short arm of chromosome 18, two copies of the centromere, and two copies of the small portion of the long arm between the centromere and band qll.2.
What is the colon in a karyotype?
This karyotype describes a terminal deletion involving the long arm of chromosome 1. The colon present in the long form indicates a break at band 1q32 and deletion of the region distal to it. The rest of the chromosome, from 1pter to 1q32, is present.
Which chromosomes are translocated in a male karyotype?
This describes a male karyotype with a translocation involving chromosomes 5 and 12 , an extra chromosome 21, and a marker chromosome.
What are structural chromosome abnormalities?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when there is a change in the structure or components of a chromosome. The total number of chromosomes is usually normal (46 total per cell). Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when part of a chromosome is missing, a part of a chromosome is extra, or a part has switched places with another part. Ultimately, this leads to having too much or too little genetic material. This is a cause of some birth defects.
What is structural abnormality?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when part of a chromosome is missing, a part of a chromosome is extra, or a part has switched places with another part. Ultimately, this leads to having too much or too little genetic material. This is a cause of some birth defects.
What is the short arm of a chromosome called?
The short arm, which is the upper half of the chromosome, is known as the "p arm.". The long arm, which is the lower half of the chromosome, is the "q arm.". The centromere is the center part of a chromosome that appears "pinched" between the p and q arms.
What does deletion mean in genetics?
The term "deletion" simply means that a part of a chromosome is missing or "deleted.". A very small piece of a chromosome can contain many different genes. When genes are missing, there may be errors in the development of a baby, since some of the "instructions" are missing. One example of a genetic syndrome caused by a deletion is called "Cri du ...
What is structural chromosomal abnormality?
Structural chromosomal abnormalities are those alterations in which, due to different genetic reasons or protein expression (due to a previous genetic mutation in the nucleotide sequence of a given gene), the structure of a chromosome is damaged. The integrity of the chromosome is lost and, depending on which (and how many) genes are involved, the consequences will be more or less serious. Many of these anomalies end in spontaneous abortions, as a functional organism cannot develop. Let’s see what types exist.
What are chromosomal abnormalities?
Chromosomal abnormalities are alterations that can occur by chance when the egg or sperm is formed or when the fetus is beginning to develop. However, certain factors (advanced age of the mother or certain environmental influences) can increase the risk that these genetic accidents in the structure or number of chromosomes occur.
What is the name of the abnormality that occurs when one chromosome loses one arm and the other has?
Isochromosomes are abnormalities that consist of one chromosome has lost one of the arms and the other has doubled. This happens when the division of the centromere (the structure that joins the sister chromatids) occurs in a transverse plane rather than vertical.
What is the anomaly of having two chromosomes from the same parent?
Uniparental dysomias are abnormalities that consist of both chromosomes of the same pair come from the same parent. For example, chromosome 15 from the mother is duplicated and chromosome 15 from the father is absent. It is not a numerical anomaly since the total number of chromosomes is still 46, what happens is that in a given pair, the two chromosomes come from a parent. Prader-Willi Syndrome is an example of this anomaly and follows the same pattern that we have taught, being a maternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 15.
What is a balanced chromosome translocation?
Balanced chromosomal translocations are abnormalities that consist of a genetic segment of a chromosome moves and inserts into another chromosome without there being a loss or gain of total DNA. In the end, the genetic functionality is maintained, the genes are simply on another chromosome.
What is chromosomal inversion?
Chromosomal inversions are abnormalities consisting of a change in direction of a genetic segment within a chromosome. The chromosome “breaks” in two places and the resulting DNA segment is reinserted but in the reverse direction, altering the way genes are transcribed into proteins.
What is a deletion of a chromosome?
Chromosomal deletions are abnormalities that consist of a more or less large part of a chromosome is lost. These deletions or losses of chromosomal portions can occur anywhere on any chromosome and, depending on how much (and which) genes are lost, the effects will be more or less severe. An example of this type of chromosome abnormality is Cri du Chat syndrome, a rare disease that develops from the partial deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5.
What causes chromosome abnormalities?
The most common cause of chromosome abnormalities is an error in cell division. Cell division occurs in two distinct ways:
What are structural abnormalities?
Structural chromosome abnormalities occur when the shape of a chromosome is altered. There are several types of structural abnormalities, including: 1 Deletions. Deletions occur due to a loss of genetic material and vary in severity. Some involve a single missing base pair; others involve a missing piece of the chromosome itself. 2 Inversions. Inversions occur when a particular segment of a chromosome breaks, turns around, and reattaches to itself. There are two types of inversions: pericentric and paracentric. Parents can pass on inversions to their offspring, but they don’t always result in birth defects. 3 Rings. Rings occur when both ends of a chromosome bend and fuse together, forming a circle. Sometimes rings result in a loss of genetic material, in other instances they do not. Parents can pass on rings to their offspring, but they may or may not cause health problems.
How many chromosomes are there in a human body?
Your genes are located on chromosomes which are long DNA molecules that contain genetic material. Normal human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes in all. If one or several pairs of chromosomes have an abnormality, it can increase your risk of having a child with a birth defect or congenital condition.
What is it called when you have more than two chromosomes?
If you have more than two chromosomes, it’s called trisomy . Some of the most common numerical chromosome abnormalities include Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) and Trisomy 18 (Edward’s syndrome).
Can inversions cause birth defects?
Parents can pass on inversions to their offspring, but they don’t always result in birth defects. Rings. Rings occur when both ends of a chromosome bend and fuse together, forming a circle. Sometimes rings result in a loss of genetic material, in other instances they do not.
Fragile Sites
Insertion Within A Chromosome
Insertion Between Two Chromosomes
Reciprocal Translocations
Whole-Arm Translocations
- Whole-arm translocationsare a type of reciprocal translocation in which the entire arms of two nonacrocentric chromosomes are interchanged. Such rearrangements are described by assigning the breakpoints to the arbitrary centromeric regions designated as p10 or q10, as the actual ultimate composition of the centromeres is not known. If both chromoso...
Robertsonian Translocations