What is Substitution Reaction
- Electrophilic Substitution. Electrophilic substitution is the replacement of an atom or a functional group by an electrophile. ...
- Nucleophilic Substitution. Nucleophilic substitution is the replacement of an atom or a functional group by a Nucleophile. ...
- Radical Substitution. Radical substitution includes the reactions of radicals with substrates. ...
What is an example of substitution reaction?
Substitution Reaction
- 1. Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction: (a) What are nucleophiles? ...
- SN2 Reaction – Mechanism of SN2 Reaction. In this reaction, the elimination of the leaving group and the addition of the nucleophile occur simultaneously.
- SN1 Reaction – Mechanism of SN1 Reaction. ...
- 2. ...
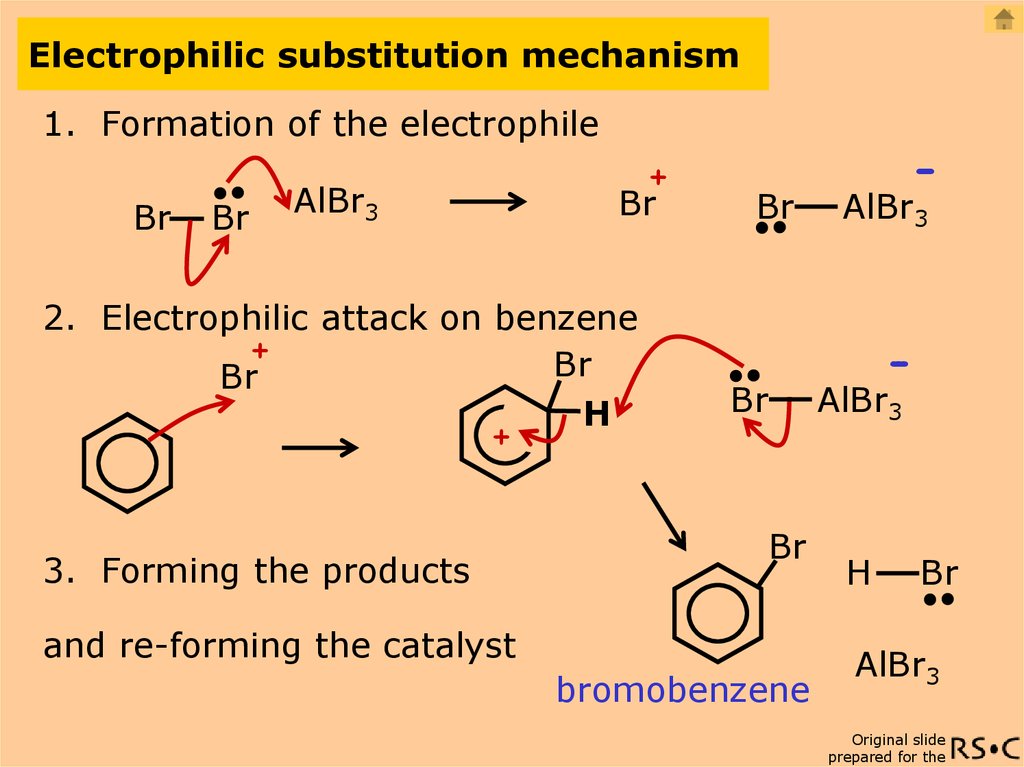
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. ...
- Electrophilic Aliphatic Substitution. ...
How to solve organic reaction mechanisms?
Product details
- Publisher : Wiley; 1st edition (March 30, 2015)
- Language : English
- Paperback : 248 pages
- ISBN-10 : 111840159X
- ISBN-13 : 978-1118401590
- Item Weight : 1.31 pounds
- Dimensions : 8.3 x 0.5 x 10.9 inches
What are synthesis reactions in organic chemistry?
The use of NHCs in organic synthesis has led to substantial advances in transition-metal catalysis and organocatalysis over the past decade. Chiral NHCs can not only serve as a substrate for organic reactions.
What are the mechanisms of a chemical reaction?
- measurement of the effect of temperature ( Arrhenius equation) to determine the activation energy
- spectroscopic observation of reaction intermediates
- determination of the stereochemistry of products, for example in nucleophilic substitution reactions
- measurement of the effect of isotopic substitution on the reaction rate

What is substitution reaction explain with example?
A substitution reaction is also called a single displacement reaction, single replacement reaction, or single substitution reaction. Examples: CH3Cl reacted with a hydroxy ion (OH-) will produce CH3OH and chlorine. This substitution reaction replaces the chlorine atom on the original molecule with the hydroxy ion.
Why is a substitution reaction?
In a substitution reaction, one atom is swapped with another atom. These are very useful reactions in the chemical industry because they allow chemists to change one compound into something more useful, building up designer molecules like drugs.
What is meant by a substitution reaction give an example with equation of the substitution reaction of an alkane?
Substitution reaction is a reaction in which hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon are replaced by other atoms. It is a characteristic of saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes). For example: Methane (alkane) reacts with chlorine, in the presence of sunlight, to form chloromethane and hydrochloric acid.
What do you mean by substitution?
Definition of substitution 1a : the act, process, or result of substituting one thing for another. b : replacement of one mathematical entity by another of equal value. 2 : one that is substituted for another.
What is a Nucleophile substitution reaction?
Nucleophilic substitution is a fundamental class of reactions in organic and inorganic chemistry in which an electron-rich nucleophile selectively...
What occurs in a substitution reaction?
Substitution reaction is also known as single displacement reaction or single replacement reaction is a chemical reaction during which one function...
What are the substitution reactions used for?
One of the most important reactions in synthetic organic chemistry is an electrophilic aromatic substitution. These reactions are used to synthesiz...
Is hydrolysis a substitution reaction?
Hydrolysis is just a heat substitute. This can be achieved by sn2 displacement of a primary halogen by water, by the reaction of a water-stabilized...
What is the difference between substitution and elimination reactions?
The obvious difference between replacement and elimination reactions is that replacement reactions substitute one replacement with another when eli...
1. What are the different types of substitution reaction?
Broadly substitution reactions are classified as nucleophilic reactions and electrophilic reactions. When the atoms involved in the substitution re...
2. What is a chemical formula?
Chemists have designated all identified elements found on earth with a particular symbol for easy representation and understanding. Students can fi...
3. What are chemical equations?
During the process of chemical reactions all the molecules of any compound or substances undergoing the process of chemical change also change. So...
4. Which are the other types of chemical reactions that we learn in Chemistry?
There are four basic types of chemical reactions that we study in the introductory chapters of Chemistry. First is the synthesis type of reaction i...
5. Where can I find all the materials to learn more about chemical reactions?
Chemical reactions are an indispensable part of the study of chemistry. Every chapter and topic is explained by mentioning the examples of any such...
6. Is hydrolysis given as a substitution reaction?
Hydrolysis is simply a heat substitute. This is achieved by the displacement of sn2 of a primary halogen by water, by the water-stabilized trapped...
7. What takes place in a substitution reaction?
Substitution reaction is otherwise called a single replacement reaction or single displacement reaction, which is a chemical reaction during which...
8. Explain about Nucleophile substitution reaction.
Nucleophilic substitution is defined as a fundamental class of reactions in both organic and inorganic chemistry, where an electron-rich nucleophil...
9. Explain what the substitution reactions used for.
The most important reactions of synthetic organic chemistry can be given as an electrophilic aromatic substitution. These reactions can be used to...
What is substitution reaction?
A substitution reaction is a reaction between molecules where an atom or a group of atoms replaces a current atom in the original molecule. For example, a hydrogen atom might get kicked off so that a different atom can be put on. There are two types of substitution reactions: nucleophilic and electrophilic.
What is the leaving group of a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
Nucleophilic substitution reactions can occur with any carbon chain that has a good leaving group. Often this leaving group is a halide, usually bromine or chlorine, but oxygen groups, typically in the form of water, can be the leaving group as well. The less basic a leaving group is, the more its to leave increases.
How does substitution occur in acyl chloride?
Lesson Summary. Substitution reactions occur by replacing a current atom on a molecule with a new atom. This can occur through nucleophilic substitution, such as in the reaction that makes sodium nitrite a cancer causing substance.
What is the simplest form of an aromatic compound?
These aromatic compounds have excess electrons that are shared through the entire system. The simplest form of these aromatic compounds is benzene. Normally when there is a double bond in the system, an additional reaction will occur. The double bond will break and the new atom will be put on in place of the double bond.
How are nucleophiles and bases similar?
A nucleophile is similar to a base in that they both have a lone pair, or a pie bond. They differ only in which atom they attack. Nucleophiles attack the atom that is deficient in electrons, usually the carbon atom, while bases attack protons. A stronger base will be a strong nucleophile.
What is substitution reaction?
Substitution reaction is otherwise called a single replacement reaction or single displacement reaction, which is a chemical reaction during which one functional group can be replaced by the other functional group in a chemical compound. For this, halogenation is a good example.
What is a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
In organic chemistry, a Nucleophilic substitution reaction can be defined as a type of reaction, where a nucleophile gets attached either to the positive charged molecules or atoms of the other substance. The Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Mechanism.
What is SN1 reaction?
SN1 reactions are defined by the bulky groups which are attached to the carbocations. The tertiary carbocation reaction is faster to that of the secondary carbocation, which is faster than the primary carbocation. In the rate-determining step, the nucleophile is not needed.
What type of substitution is an atom attached to the aromatic ring?
In this electrophilic substitution type, an atom which is attached to the aromatic ring, mostly hydrogen is substituted by an electrophile. The reactions that take place are said as aromatic halogenation, aromatic acylation and sulfonation, and aromatic nitration. Also, it is further composed of alkylation and acylation.
What are some examples of nucleophilic substitution?
One of the good examples of a nucleophilic substitution reaction is given as the hydrolysis of alkyl bromide (R-Br), under the basic conditions. Whereas, the nucleophile the base OH−, and the leaving group is the Br−. The reaction for this can be given as follows:
What type of reaction is CH3Cl?
These types of reactions are referred to the nucleophilic and possess major importance in the field of organic chemistry. Let us say, for example, when the CH3Cl compound is reacted with the hydroxyl ion (OH-), it leads to the formation of the original molecule, which is called methanol with that hydroxyl ion.
What are the most important reactions in organic chemistry?
The most important reactions of synthetic organic chemistry can be given as an electrophilic aromatic substitution. These reactions can be used to synthesize the important intermediates, used as precursors for agrochemical, pharmaceutical, and industrial products manufacturing.
What is the Sn2 mechanism?
We will be studying this; this mechanism is called the Sn2 mechanism–a simultaneous concerted single step mechanism.
What is the mechanism in which the nucleophile attacks the carbon?
There is really two reasonable possibilities; one possibility would be a simultaneous mechanism. Or in other words, a concerted mechanism in which the nucleophile attacks the carbon, starts to form a bond with the carbon group, at the same time as the leaving group leaves.
Substitution Reactions in Organic Chemistry
Substitution reactions are an important reaction in organic chemistry. But what is substitution reaction? A substitution reaction is any chemical reaction in which an atom, ion, or group in a molecule is replaced by another.
Types of Substitution Reactions
As mentioned, there are two distinct types of substitution reactions. These are nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions. In nucleophilic substitution reactions, a nucleophile replaces a functional group in a compound. In electrophilic substitution reaction, the functional group is replaced by an electrophile.
Substitution Reaction Examples
There are many uses for substitution reactions. Two examples that have already been mentioned are the formation of methanol from chloromethane and hydroxide, as well as the formation of ethylbenzene from benzene and an ethyl group. Some other substitution reaction examples are:
Free radical reaction
In this tutorial, Sal introduces free radical reactions by showing the reaction of methane with chlorine.
Nucleophilicity and basicity
In this tutorial, Sal discusses the difference between nucleophilicity and basicity.
Elimination reactions
In this tutorial, Sal explains the difference between an E1 and an E2 elimination reaction.
Sn1 and Sn2
In this tutorial, Jay covers the definitions of nucleophile/electrophile, The Schwartz Rules (may the Schwartz be with you!), and the differences between SN1 and SN2 reactions.
E1 and E2 reactions
In this tutorial, Jay covers the E1 elimination mechanism, carbocation rearrangements, and the details of the E2 elimination reaction.
