thermoregulatory machanism
- BY: TAHIR RAMZAN
- What is Thermoregulation The ability of an organism to keep its body temperature with in a certain range when temperature surrounding is extremely different.
- Homeostasis The human body has the ability to maintain a constant internal environment so that every organ and cell is provided the perfect conditions to perform its functions. ...
How does thermoregulation work in the body?
May 07, 2021 · Thermoregulation is a mechanism by which mammals maintain body temperature with tightly controlled self-regulation independent of external temperatures. Temperature regulation is a type of homeostasis and a means of preserving a stable internal temperature in order to survive.
What is the meaning of thermoregulatory?
Jun 06, 2017 · Thermoregulation is a process that allows your body to maintain its core internal temperature. All thermoregulation mechanisms are designed to return your body to homeostasis. This is a state of...
What are the three mechanisms of thermoregulation?
Thermoregulatory defense mechanisms Core body temperature is normally tightly regulated by an effective thermoregulatory system. Thermoregulatory control is sometimes impaired by serious illness, but more typically remains intact. The primary autonomic defenses against heat are sweating and active precapillary vasodilation; the primar …
What is the function of the thermoregulatory centre?
Thermoregulation is a process that allows your body to maintain its core internal temperature. All thermoregulation mechanisms are designed to return your body to homeostasis. Many factors can affect your body's temperature, such as spending time in cold or hot weather conditions.

What are the four mechanisms of thermoregulation?
The body uses four mechanism for temperature regulation: convection, radiation, conduction, evaporation.Dec 22, 2015
What are hypothalamic thermoregulatory mechanism?
Certain preoptic and rostral hypothalamic neurons are sensitive to changes in local preoptic temperature (Tpo). These neurons also receive much afferent input from peripheral thermoreceptors and control a variety of thermoregulatory responses.
What are the 3 types of thermoregulatory processes?
We will look at three broad categories of thermoregulatory mechanisms in this article: Changing behavior. Increasing metabolic heat production. Controlling the exchange of heat with the environment.
What does the term thermoregulation mean?
the maintenance or regulation of temperatureDefinition of thermoregulation : the maintenance or regulation of temperature specifically : the maintenance of a particular temperature of the living body. Other Words from thermoregulation Example Sentences Learn More About thermoregulation.Mar 4, 2022
How does the body Thermoregulate itself?
How does thermoregulation work? When your internal temperature changes, sensors in your central nervous system (CNS) send messages to your hypothalamus. In response, it sends signals to various organs and systems in your body.Jan 5, 2021
What organisms are Heterothermic?
Heterothermy or heterothermia (from Greek ἕτερος heteros "other" and θέρμη thermē "heat") is a physiological term for animals that vary between self-regulating their body temperature, and allowing the surrounding environment to affect it.
What is homeotherms in biology?
: having a relatively uniform body temperature maintained nearly independent of the environmental temperature : warm-blooded There are several mechanisms by which homeothermic animals increase their heat production, including shivering, sympathetic nervous system activation and stimulation of thyroid hormone secretion.
Are humans homeotherms?
Humans are homeotherms, i.e. they fix their temperature regardless of their environment. This is vital for normal cellular function and for metabolism to be independent of external temperature. The body has a warm 'core' and a cooler peripheral 'shell' whose role is to regulate heat transfer in and out of the core.
Why is thermoregulation important?
Thermoregulation is crucial to human life; without thermoregulation, the human body would cease to function. Thermoregulation also plays an adaptive role in the body's response to infectious pathogens. [1][2] Thermoregulation is a mechanism by which mammals maintain body temperature with tightly controlled self-regulation independent ...
What is the purpose of temperature regulation?
Temperature regulation is a type of homeostasis and a means of preserving a stable internal temperature in order to survive. Ectotherms are animals that depend on their external environment for body heat, while endotherms are animals that use thermoregulation to maintain a somewhat consistent internal body temperature even when their external ...
How does a thermoregulatory sweat test work?
To perform the thermoregulatory sweat test, the patient is placed in a chamber that slowly rises in temperature. Before the chamber is heated, the patient is coated with a special kind of indicator powder that will change in color when sweat is produced.
Is dantrolene safe for malignant hyperthermia?
The rapid treatment of malignant hyperthermia is paramount to prevent a fatality. Once malignant hyperthermia is suspected, dantrolene must be given intravenously as it is a ryanodine receptor antagonist. It is also important to rapidly cool the patient, give 100% oxygen, and regulate metabolic acidosis.
What is the temperature of a human body?
Humans and other mammals and birds are endotherms. Human beings have a normal core internal temperature of around 37 degrees Celsius (98.6 degrees Fahrenheit) measured most accurately via a rectal probe thermometer. This is the optimal temperature at which the human body’s systems function.
How does sweat work?
Sweat is produced by glands and through evaporation at the topmost skin layer (the epidermis) can release heat. This describes vaporization, one of the four mechanisms used to maintain core body temperature.
What causes a fever?
Cellular. Viral illness or another infectious disease can cause a person to develop a fever, raising the core temperature above 37 degrees Celsius. Fever is a result of the body releasing pyrogens such as cytokines, prostaglandins, and thromboxane.
How does the body release heat?
This increases blood flow to your skin where it is cooler — away from your warm inner body. This lets your body release heat through heat radiation. If your body needs to warm up, these mechanisms include: Vasoconstriction: The blood vessels under your skin become narrower.
What is the body's internal temperature?
Thermoregulation is a process that allows your body to maintain its core internal temperature. All thermoregulation mechanisms are designed to return your body to homeostasis. This is a state of equilibrium. A healthy internal body temperature falls within a narrow window. The average person has a baseline temperature between 98°F (37°C) ...
How does the body cool down?
If your body needs to cool down, these mechanisms include: 1 Sweating: Your sweat glands release sweat, which cools your skin as it evaporates. This helps lower your internal temperature. 2 Vasodilatation: The blood vessels under your skin get wider. This increases blood flow to your skin where it is cooler — away from your warm inner body. This lets your body release heat through heat radiation.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
metabolic conditions, such as an under-functioning thyroid gland. Your hypothalamus is a section of your brain that controls thermoregulation. When it senses your internal temperature becoming too low or high, it sends signals to your muscles, organs, glands, and nervous system.
What is the average temperature of a human body?
The average person has a baseline temperature between 98°F (37°C) and 100°F (37.8°C). Your body has some flexibility with temperature. However, if you get to the extremes of body temperature, it can affect your body’s ability to function.
What is physiological thermoregulation?
Physiological thermoregulation permits optimization of physiological processes over a relatively narrow range of temperature. No doubt fishes would enjoy the benefits of physiological thermoregulation to the same extent that birds and mammals do—if its costs were not so great for the water breathers.
Why is thermoregulation important?
Thermoregulation is indeed a unique homeostatic system because it relies on higher level central nervous system (CNS) processes for the conscious sensation and elicitation of corrective motor responses. There is little conscious awareness of most other homeostatic processes, such as those involved in the regulation of blood pressure, respiration, blood pH, and other systems, whereas we are almost always aware and keenly sensitive to changes in our external thermal environment. We continuously strive to maintain a comfortable thermal environment, primarily by using behavioral thermoregulation. Behavioral thermoregulatory mechanisms in humans, such as adding or removing clothing, adjusting a thermostat, or setting a forced convective environment with a fan, all involve high-level, cerebral processing. Other species of mammals and birds will also preferentially use behavioral rather than autonomic processes to thermoregulate. The regulation of body temperature via behavioral mechanisms involves little metabolic energy and is thus preferred over that of autonomic mechanisms. Most species of the reptile, amphibian, and fish phyla depend entirely on behavioral mechanisms to thermoregulate.
How is heat loss controlled?
Control of heat loss mechanisms are via biochemical, anatomical, physiological, and behavioral means. However, as in all levels of adaptation to the environment, systems cannot be considered or modeled in isolation.
What happens to the newborn during the period after birth?
In the period immediately after birth, the newborn has to adjust to an environment whose temperature may fluctuate widely and which is also usually lower than that of the uterus.
Examples of thermoregulatory in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web Biologically speaking it’s caused by a narrowing of the thermoregulatory zone. — Dr. Jennifer Gunter, Glamour, 19 Oct.
First Known Use of thermoregulatory
Our team at The Usage has selected the best smart thermostats of 2021.
Medical Definition of thermoregulatory
What made you want to look up thermoregulatory? Please tell us where you read or heard it (including the quote, if possible).
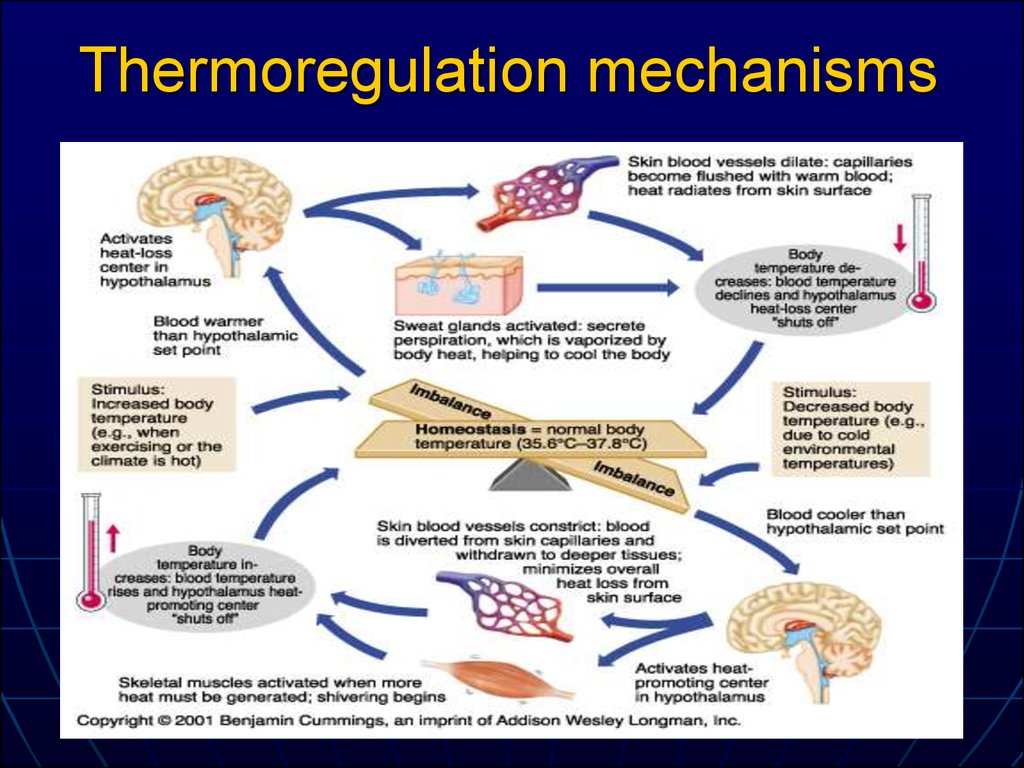
Thermoregulation
Mechanism of Thermoregulation
- The hypothalamus is a small section or a portion of a human brain, which is mainly involved in secretion or release of all hormones from their respective glands and controlling several body functions. The mechanisms of thermoregulation are also controlled by this Hypothalamus. When there is a small variation in the internal body temperature, the sensors in the central nervous sys…
Importance of Thermoregulation
- The mechanisms thermoregulation are all designed to return the body to homeostasis or a state of equilibrium. This process helps in controlling the loss or gain of heat and maintaining of an optimum temperature range by an organism. As mentioned earlier, average healthy body temperature falls within a 37°C to 37.8°C. However, if the body temperature falls from 37°C to 3…