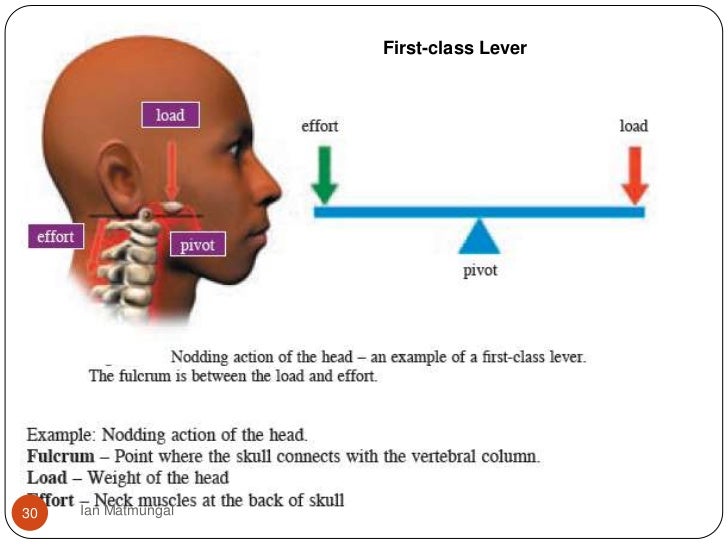
- First class lever – the fulcrum is in the middle of the effort and the load. ...
- Second class lever – the load is in the middle between the fulcrum and the effort. Second class lever This type of lever is found in the ankle area. ...
- Third class lever – the effort is in the middle between the fulcrum and the load.
What are some examples of a third class lever?
‰ÛÜWhat Are Some Examples of Third-Class Levers?
- An Elbow Lifting a Bowling Ball. Taking part in bowling is always fun. ...
- Snow Shovel. When there is a heavy snowstorm, snow paths must be shoveled so that maneuvering around through the snow is possible.
- Baseball Bat. ...
- Canoe Oars. ...
Why is the elbow considered a third class lever?
Third-class levers are plentiful in human anatomy. One of the most commonly used examples is found in the arm. The elbow (fulcrum) and the biceps brachii (effort) work together to move loads held with the hand, with the forearm acting as the beam.
What are the three classes of levers?
- The 1st part is The Fulcrum, known as the pivot point, axis, or balance point,
- The 2nd part is the Resistance or load
- The 3rd part is the Effort Force
- The 4th part is the Lever Arm, which can be divided into 2 seperate parts, The Force Arm and The Resistance arm.
Is the first class lever the most common in the body?
Answer. The first class lever is the most common lever in the human body. This statement is false. In a third-class lever, the most common in the human body, force is applied between the resistance (weight) and the axis (fulcrum).

What are the 3 classes of levers in the human body?
There are three types of lever.First class lever – the fulcrum is in the middle of the effort and the load.Second class lever – the load is in the middle between the fulcrum and the effort.Third class lever – the effort is in the middle between the fulcrum and the load.
Why are 3rd class levers the most common in the human body?
So why does the human body rely so much upon 3rd class levers to initiate movement? The answer is simple convenience.
Why is your arm a third class lever?
There are three classes of levers , and all three classes are present in the body. For example, the forearm is a 3rd class lever because the biceps pulls on the forearm between the joint (fulcrum) and the ball (load).
What is a 3nd class lever?
Third Class Levers In a third class lever, the effort is located between the load and the fulcrum. In a third class lever, the effort is located between the load and the fulcrum. If the fulcrum is closer to the load, then less effort is needed to move the load (©2020 Let's Talk Science).
What is a class 3 lever examples?
In a Class Three Lever, the Force is between the Load and the Fulcrum. If the Force is closer to the Load, it would be easier to lift and a mechanical advantage. Examples are shovels, fishing rods, human arms and legs, tweezers, and ice tongs. A fishing rod is an example of a Class Three Lever.
What kind of lever is your arm?
Class 3 leverClass 3 lever – bend your arm The pivot is at the elbow and the forearm acts as the lever arm. The biceps muscle provides the effort (force) and bends the forearm against the weight of the forearm and any weight that the hand might be holding.
What type of lever is hip?
third class leverThe hip joint is a third class lever. It cannot produce the same load force to effort ratio as a second class lever. However, this doesn't mean that it is not good at what it does. Third class levers can take a small movement near the fulcrum and make a large movement where the load is.
What type of lever is walking?
third-class leversIn the human body, third-class levers have the pivot point at one end. The muscles apply force to the lever near the pivot. This causes the levers (your bones) to move.
What type of lever is the knee?
Third class lever system There are many examples of third class lever systems, including both flexion and extension at the knee joint. These movements are involved in running, jumping and kicking.
What class of lever is most common in the human body?
In a third-class lever, the most common in the human body, force is applied between the resistance (weight) and the axis (fulcrum) (figure 1.23a).
What class of lever is most common in the human body?
Third-class leversThird-class levers are plentiful in human anatomy. One of the most commonly used examples is found in the arm. The elbow (fulcrum) and the biceps brachii (effort) work together to move loads held with the hand, with the forearm acting as the beam.
What is the most common type of lever found in the human body?
third-class leverIn a third-class lever, the most common in the human body, force is applied between the resistance (weight) and the axis (fulcrum) (figure 1.23a).
Which class of lever is most commonly found in the human body and why do you think this is the case?
Elbow Joint as a Third Class Lever Examples of the third class lever system are abundant in the human body. In our case of a weighted bicep curl and a calf raise, the lever system involved in a bicep curl is mechanically less efficient than the lever system involved in a calf raise.
How to make a 3rd class lever?
Now, you'll make a model of your forearm as third-class lever. Measure the length of your upper arm and forearm and outline your model on the cardboard. Keep the upper arm and forearm pieces separate, and at the end of the forearm, trace your hand. Cut out your model arm from the cardboard.
What is the output force of a second class lever?
In a second-class lever, the output force is in between the fulcrum and the input force. An example of a second class lever is a wheelbarrow. The fulcrum is the wheel, the load of stuff in the wheel barrow requires the output force to be lifted, and the person at the handle supplies the input force. In a third-class lever, the input force is in ...
What is a lever in a machine?
A lever is a type of simple machine where a rigid arm is arranged around a fixed point or fulcrum. Input, the force you put in, directed into an output force. The classic example of a lever is a seesaw. The fulcrum is in the middle, and when you push down on your side of the seesaw (input), it makes the person on the other side of the seesaw go up ...
What does the paperclip on your arm mean?
The two paperclips on your upper arm represent the bicep muscle on your arm, the paper clip on the forearm represents where the muscle attaches. The distance between the three paperclips represents the length of the input effort arm of your lever. Tie one end of your string to the thumb of your cardboard hand.
What are some examples of third class levers?
The elbow joint is an example of a third class lever, operating with the effort between the load and fulcrum.
Which lever is the most mechanically advantageous?
A second class lever is the only lever that can promise that the effort arm will always be greater than the load arm. This arrangement results in a bigger effort arm to load arm ratio, making the second class lever the most mechanically advantageous.
How to make cinder block easier to lift?
To make it even easier, you could move the cinder block closer to the rock, moving the fulcrum closer to the load. This decreases the load arm and increases the effort arm, making the lever more efficient and allowing you to lift the rock while applying less force.
Why does the effort arm work harder when you curl the weight?
When you try to curl the weight, your bicep has to work harder because it is at a mechanical disadvantage.
What is the LA in a muscle?
The load arm (LA) is the distance between the fulcrum and the load; in the body, this is the distance between the joint and the loaded body part. The greater the ratio of the effort arm to the load arm, the more efficient the lever system is (i.e. the easier it is to move the load). Therefore, if the distance between a muscle’s insertion site ...
Which joint is the fulcrum?
The fulcrum is made up of the metacarpophalengeal joint. In this arrangement, the load is in the middle, and the effort is farthest from the fulcrum. Therefore, the act of plantarflexion can move much more weight than elbow flexion, even if your bicep is just as strong as your calf. The calf as a second class lever.
What are the parts of a lever?
Parts of a Lever. Synovial joints are moveable joints; a few examples of these are the shoulder, spine, knee, elbow, and ankle. To understand why some synovial joints have more efficient lever systems, we must first understand the relationships between the three lever parts: an effort or force applied to the lever, a fulcrum, and a load. ...
What are the first, second, and third class levers?
First, second and third class levers in the body. Levers in our body are formed from bones, joints and muscles. A lever consists of: a rigid structure (bone) a force acting upon it (muscle) to produce a turning movement (angular motion) a fulcrum which is a fixed point (joint)
Where is the second class lever?
Second class lever. This type of lever is found in the ankle area. When standing on tiptoe, the ball of the foot acts as the fulcrum, the weight of the body acts as the load and the effort comes from the contraction of the gastrocnemius muscle.
What is a fulcrum in physics?
a fulcrum which is a fixed point (joint) a load or resistance that is placed on the rigid structure (weight of body part being moved and anything that it is carrying) A typical lever . There are three types of lever. 1. First class lever – the fulcrum is in the middle of the effort and the load. First class lever.
When a lever's effort arm is longer than its load arm, it is said to have a high mechanical?
When a lever's effort arm is longer than its load arm, it is said to have high mechanical advantage . Levers with high mechanical advantage can move large loads with a relatively small amount of effort. Second class levers always have high mechanical advantage . First class levers can have high mechanical advantage, if the fulcrum is close to the load.
How to recall the order of the levers?
To recall the order of the levers use the term 'FLE' - this will help you to remember which part of the lever is in the middle.
What is the fulcrum of a bicep curl?
During a biceps curl, the fulcrum is the elbow joint, the effort comes from the biceps contracting and the resistance is the weight of the forearm and any weight that it may be holding.
How Does a 3rd Class Lever Work?
In 3rd class levers, the fulcrum is at one end of the lever, the load at the other end, and you apply force in between in this case the force is the muscle. Although the force is applied in the middle, the muscle attachments are usually close to the joint.
Why are 3rd class levers the most common?
3rd class levers are the most common levers, why? Although we use 3rd class levers more than any others in the human body, they in fact offer no mechanical advantage thus, regardless of where you apply the force , the force you apply must always be greater than the force of the load. So why does the human body rely so much ...
What happens to the speed of a lever as the length of the lever increases?
According to the laws of physics, as the length of the lever increases, the possible speed increases but so does the force required to produce it.
What is the lever in the human body?
Levers in The Human Body. Lets talk about the levers in the human body. A 1st class lever would be the Human head sitting on the spine. The fulcrum would be in the middle “The Spine”. The neck muscles would be the effort force. And the weight of the head would be the resistance. The function is to change direction.
What is a lever?
Levers are one of the simplest forms of a machine. A lever is a simple machine that allows you to gain a mechanical advantage in moving an object or in applying a force to an object. A lever is a simple machine that consists of 4 parts. The 1st part is The Fulcrum, known as the pivot point, axis, or balance point,
How to find equilibrium of a force arm?
And equilibrium is achieved by the Effort x Force Arm = Resistance x Resistance arm
Why is the mechanical advantage always greater than >1?
The mechanical advantage is always greater than >1 because the Force arm is always going to be longer than the resistance arm.
Where is the fulcrum in a lever?
1st we will look at The first Class lever. It’s set up with the Fulcrum in the middle with the Effort and Resistance on the sides.
Where is the effort force in the brachialis muscle?
This is the 3rd class lever, so we know the Effort force is in the middle, this is where the brachialis muscle inserts.
Where is the resistance set up in the effort force?
It is set up with the resistance in the middle of the effort force and the fulcrum.
