
What are the 12 leads of an ECG?
The 12 Lead Groups
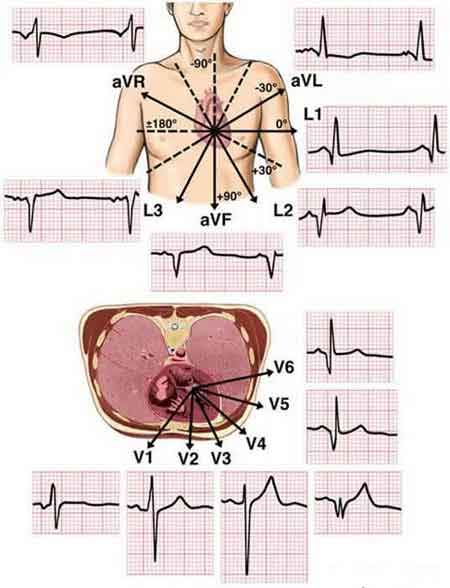
- Vertical plane (Frontal Leads): Leads I, II, and III require a negative and positive electrode (bipolarity) for monitoring. ...
- Einthoven's Triangle. ...
- Horizontal Plane (Transverse Leads) By using 6 chest electrodes, you get 6 transverse leads that provide information about the heart's horizontal plane: V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6.
How many leads are used in a twelve lead EKG?
The standard ECG – which is referred to as a 12-lead ECG since it includes 12 leads – is obtained using 10 electrodes. These 12 leads consists of two sets of ECG leads: limb leads and chest leads. The chest leads may also be referred to as precordial leads.
What is a 3 lead EKG?
What does a 3-lead ECG show? 3-lead ECGs are used most often for recording a 24-hour reading. A 24-hour reading is a frequently used tool for the diagnosis of heart problems and is reimbursed as a long-term reading. How do you perform a 3-lead ECG?
How to put on EKG leads?
- Although the ECG test is referred to as a 12-electrode test, there are only 10 leads. 2 of the leads contain 2 electrodes each. ...
- Use a new ECG test kit on every patient. ...
- When you’re putting the chest leads on either men or women, do not use the nipples as a reference point. ...
How do you perform a 3-lead ECG?
Position the 3 leads on your patient's chest as follows, taking care to avoid areas where muscle movement could interfere with transmission:WHITE.RA (right arm), just below the right clavicle.BLACK.LA (left arm), just below the left clavicle.RED.LL (left leg), on the lower chest, just above and left of the umbilicus.
What is the difference between 3-lead and 12 lead ECG?
The new TeleECG monitors all the heart's walls in greater detail, as it is able to record 12 leads for 24/48 hours. Unlike the standard 3-lead ECG, this new device is provided with more electrodes and allows to “spy” and observe the heart in more detail and at a regional and anatomical level from several points.
What is the difference between 3-lead and 5 lead ECG?
3-lead is usually used on transport monitors, and monitors two different areas of the heart (one lateral, two inferior). 5-lead is preferred in an ICU, to monitor the third (anterior) area.
Is 3-lead ECG accurate?
We also found excellent agreement on the interpretation of the 3-lead tele-ECGs compared to the gold standard: 98% (kappa = 0.96, P < 0.001) and for the 12-lead tele-ECG compared to the gold standard: 98% (kappa = 0.96, P < 0.001).
Which ECG lead is most important?
The most useful lead is V4R, which is obtained by placing the V4 electrode in the 5th right intercostal space in the mid-clavicular line.
What does lead 3 assess?
Lead III records electrical difference between the left leg and the left arm electrodes. The above illustration shows Leads I, II, and III, their placement and the electrical potential on these three leads. Records electrical differences between the left and right arm electrodes.
Which ECG lead is best at diagnosing arrhythmias?
If arrhythmia diagnosis is the goal of monitoring, lead V1 is the best lead; lead V6 is the next best lead. If ST segment monitoring for ischemia or reocclusion following percutaneous coronary interventions is the goal, the best lead depends on the coronary artery involved.
What are the 3 types of ECG?
There are 3 main types of ECG: a resting ECG – carried out while you're lying down in a comfortable position. a stress or exercise ECG – carried out while you're using an exercise bike or treadmill.
What is 5 lead ECG used for?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive method of monitoring the electrophysiology of the heart. Electrodes are placed on the patient's torso, and the electrical activity of the heart is measured from several leads (voltage difference between electrodes).
What is an abnormal ECG lead?
Defects or abnormalities in the heart's shape and size: An abnormal ECG can signal that one or more aspects of the heart's walls are larger than another meaning that the heart is working harder than normal to pump blood.
Is lead 3 positive or negative?
Lead III has the positive electrode on the left leg and the negative electrode on the left arm. These three bipolar limb leads roughly form an equilateral triangle (with the heart at the center) that is called Einthoven's triangle in honor of Willem Einthoven who developed the electrocardiogram in the early 1900s.
Where do 3 lead ECG electrodes go?
0:055:33How to place 3 lead EKG - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo that you can read your own heart rhythm. So you have three leads in your kit. They should be redMoreSo that you can read your own heart rhythm. So you have three leads in your kit. They should be red yellow and green if they're not red yellow and green maybe they have writing on them and in in this
What is the main purpose of a 12 lead ECG?
This can help your physician to determine if you have had a “heart attack”, or a new arrhythmia. The 12-lead EKG provides more information on the diagnosis of your cardiac arrhythmia than an outpatient Holter or Event monitor, as it represents information recorded from a larger surface area surrounding the heart.
What is the difference between ECG and 12 lead ECG?
ECG stands for electrocardiogram, and EKG is the German spelling for elektrokardiographie, which is the word electrocardiogram translated into the German language. An ECG (EKG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. An ECG may also be called a 12-lead ECG or a 12-lead EKG.
What does a 12 lead ECG mean?
What Is a 12 Lead ECG? A 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is a medical test that is recorded using leads, or nodes, attached to the body. Electrocardiograms, sometimes referred to as ECGs, capture the electrical activity of the heart and transfer it to graphed paper.
What can a 12 lead ECG detect?
The 12-lead ECG is widely used to diagnose cardiovascular disease, particularly acute myocardial infarction, in clinics and hospital-based practice.
What is the purpose of an ECG electrode?
ECG Electrodes are small sensor pads (self adhesive,disposable, pre gelled) applied on the skin to enable detection of the electrical activity of the heart, ...
Where is the red electrode in the rib cage?
RA: placed the red electrode within the frame of rib cage,right under the clavicle near shoulder ( see chart in follow picture) LA: the yellow electrode is placed below left clavicle, which is in the same level of the Red electrode.
Can you use alcohol pads on skin?
If alcohol pad is used to cleanse skin, allow to site to dry, before electrode placement. ECG Electrodes are small sensor pads (self adhesive,disposable, pre gelled) applied on the skin to enable detection of the electrical activity of the heart, which is transmitted to the monitor, amplified and displayed as the ECG trace.
How does an electrocardiograph generate an ECG lead?
Figure 16. The electrocardiograph generates an ECG lead by comparing the electrical potential difference in two points in space. In the simplest leads these two points are two electrodes (illustrated in this figure). One electrode serves as exploring electrode (positive) and the other as the reference electrode. The electrocardiograph is constructed such that an electrical current traveling towards the exploring electrode yields a positive deflection, and vice versa.
What is Mason Likar's lead system?
Mason-Likar’s lead system simply implies that the limb electrodes have been relocated to the trunk. This is used in all types of ECG monitoring (arrhythmias, ischemia etc). It is also used for exercise stress testing (as it avoids muscle disturbances from the limbs).
What is an ECG lead?
An ECG lead is a graphical description of the electrical activity of the heart and it is created by analysing several electrodes.
What is the order of the leads in the Cabrera system?
In the Cabrera system, the leads are placed in their anatomical order. The inferior limb leads (II, aVF and III) are juxtaposed, and the same goes for the lateral limb leads and the chest leads. As mentioned earlier, inverting lead aVR into –aVR improves diagnostics additionally.
What is the lateral limb lead?
Lead aVL, I and –aVR are called lateral limb leads, because they primarily observe the lateral wall of the left ventricle. Note that lead aVR differs from lead –aVR (discussed below). All six limb leads are presented in a coordinate system, which the right hand side of Figure 18 (panel A) shows.
Where are the limb leads placed?
Leads I, II, III, aVF, aVL and aVR are all derived using three electrodes, which are placed on the right arm, the left arm and the left leg. Given the electrode placements, in relation to the heart, these leads primarily detect electrical activity in the frontal plane.
What is the difference in electrical potential?
Electric potential difference is defined as a difference in electric potential between two measurement points. In electrocardiology these measurement points are the skin electrodes. Thus, the electrical potential difference is the difference in the electrical potential detected by two (or more) electrodes.
How is depolarization transmitted?
Depolarization is distributed from cell to cell, producing a wave of depolarization that can be transmitted across the entire heart. This wave represents a flow of electricity and it can be detected by electrodes placed on the surface of the body.
What is an ICG?
ICG: Impedance Cardiography/Cardiac Output - Record cardiac output, thoracic impedance changes, or any kind of bioimpedance signal. Use Acq Knowledge for a fully automated ICG analysis and dZ/dt waveform classifier.
What is the ECG of the heart?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic recording of the changes occurring in the electrical potentials between different sites on the skin (leads) as a result of cardiac activity. Depolarization of the cardiac cells is the central electrical event of the heart. This occurs when the cardiac cells, which are electrically polarized, lose their internal negativity. Depolarization is distributed from cell to cell, producing a wave of depolarization that can be transmitted across the entire heart. This wave represents a flow of electricity and it can be detected by electrodes placed on the surface of the body. Once depolarization is complete, the cardiac cells are able to restore their resting polarity through a process called repolarization. This flow of electricity can also be sensed by recording electrodes.
How many channels are there in sleep studies?
Sleep Studies - Long term recordings with up to 16 channels of data. Record EEG, EOG, EMG, respiration, temp., sound, limb position and more. Filter out EEG frequencies to score sleep stages.
What does each apex of the triangle represent?
Each apex of the triangle represents where the body’s composition, around the heart, connects electrically with the limbs. Einthoven’s law states that if the values for any two points of the triangle are known, the third can be computed. This Application Note details 1-lead ECG, 3-lead ECG, 6-lead ECG, and 12-lead ECG.
What is second degree heart block?
The presence of second-degree AV block is diagnosed when one or more (but not all) of the atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles due to impaired conduction. Second degree type II heart block is characterized on a surface ECG by intermittently nonconducted P waves not preceded by PR prolongation and not followed by PR shortening. There is usually a fixed number of non-conducted P waves for every successfully conducted QRS complex, and this ratio is often specified in describing these blocks.
What is the pacemaker of the heart?
Normally, the pacemaker of the heart that is responsible for triggering each heart beat is the SA node. However, if the ventricle does not receive triggering signals at a rate high enough from either the SA node or the AV node, the ventricular myocardium itself becomes the pacemaker (escape rhythm). This is called Idioventricular Rhythm. Ventricular signals are transmitted cell-to-cell between cardiomyocytes and not by the conduction system, creating wide sometimes bizarre QRS complexes (> 0.12 sec). The rate is usually 20-40 bpm. If the rate is >40 bpm, it is called accelerated idioventricular rhythm. The rate of 20-40 is the "intrinsic automaticity" of the ventricular myocardium. It can be regarded as a "backup plan" or "redundancy" built into the body.
What is AV block?
In first-degree AV block, every atrial impulse is transmitted to the ventricles, resulting in a regular ventricular rate.
What is the atrioventricular node?
Describes an abnormal heart rhythm resulting from impulses coming from the atrioventricular node, the "junction" between atria and ventricles. In junctional rhythms, the sinoatrial node does not control the heart's rhythm, this can happen in the case of a block in conduction somewhere along the pathway. When this happens, the heart's AV node takes over as the pacemaker, the atria will still contract before the ventricles; however, this does not happen by the normal pathway of activation and instead is due to a backwards or retrograde conduction (conduction comes from the AV node into and through the atria)
What is the rate of action potentials in the atrium?
Occurs when action potentials fire very rapidly within the atrium in a chaotic manner. The result is a very fast atrial rate (about 400-600 beats per minute). The atrial action potentials all attempt to conduct through the AV node, however the AV node will only allow a certain number of atrial action potentials to reach the ventricles. This is why the ventricular rate is not also 400-600, but rather around 100-200 beats per minute.
What is the condition where the heart muscle is uncoordinated?
Ventricular fibrillation is a condition in which there is uncoordinated contraction of the cardiac muscle of the ventricles in the heart, making them quiver rather than contract properly. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients.
Why does my heart beat so fast?
Ventricular tachycardia is a type of arrhythmia in which the lower chambers of your heart (ventricles) beat very quickly because of a problem in your heart's electrical system. In ventricular tachycardia, your heart may not be able to pump enough blood to your body and lungs because the chambers are beating so fast that they don't have time to properly fill with blood before each contraction.
