
Tolerance curves are often used to describe fitness components across environmental gradients. Such curves can be obtained by assessing performance in a range of constant environmental conditions.
What does a tolerance curve indicate about an organism?
What is a tolerance curve in ecology? Tolerance. An organism's capacity to survive variation in environmental conditions. An organisms tolerance to a given factor will influence its distribution. This graph shows the average distribution of flies according to temperature. We would expect to find most flies between 15-24°C. Click to see full answer.
What is the definition of range of tolerance?
Tolerance range refers to the range of conditions of the external environment an organism is able to withstand. The population size of a certain species can be lowered if conditions are outside optimum range. The population is lowered because the organisms cannot survive if there is too much or too little of a factor.
What is a normal glucose tolerance test?
- Fasting glucose level less than 90 mg/dL
- One-hour glucose level less than 130 to 140 mg/dL
- Two-hour glucose level less than 120 mg/dL
What exactly is tolerance?
Tolerance is a fair and objective attitude towards others whose beliefs and lifestyles are different than yours Subjects that may require tolerance include religion, politics, and education
What is tolerance range?
Why is the range of tolerance different for a generalist plant versus a specialist plant?
What is a shiner compared to a topminnow?
What is the bell curve in biology?
What happens when you move from the middle part of the curve to the lower part?
Do different organisms have different tolerance ranges?
Can a species survive if there is too much or too little of the factor?
See 4 more
About this website
What is the purpose of a tolerance curve graph?
The graph below, called a tolerance curve, summarizes the responses of organisms to different levels of physical environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, pH, altitude, etc. The x-axis (along the bottom) represents the range of the environmental factor.
What is ecological tolerance in biology?
An organism's capacity to survive variation in environmental conditions.
What does a tolerance curve indicate about an organism?
A tolerance curve indicates how an organism can survive and function in conditions outside the organism's optimal range, however its performance is reduced greatly.
What is ecological tolerance example?
Organisms have specific requirements for successful growth, development and reproduction. Example: There may be a coldest temperature and hottest temperature an animal can survive in their environment. That is their range of tolerance.
Why is ecological tolerance important?
These studies have shown that tolerance can provide a potent mechanism against natural enemies and that it plays a significant role in the ecology and evolution of plants. The rich literature on plant tolerance also provides clear guidelines on how to best measure tolerance in animals.
What affects ecological tolerance?
Many different physical, abiotic (non- living) factors influence where species live, including temperature, humidity, soil chemistry, pH, salinity and oxygen levels. Just as species have geographic ranges, they also have tolerance ranges for the abiotic environmental conditions.
How does tolerance affect the distribution of a species?
Tolerance ranges are the ranges in abiotic factors in which a species can survive. The wider a species's tolerance range, the wider the distribution of that species. The lower and upper limits of the tolerance range induce stress on the species, which lowers its growth and reproductive rates.
What are the three zones of ecological tolerance?
Ecological tolerance is the range of tolerance that an organism can endure before injury or death, Identify the three zones of ecological tolerance. Optimal range, zones of physiological stress, and zone of intolerance.
What are the 3 types of tolerance?
These are grouped into form tolerance, orientation tolerance, location tolerance, and run-out tolerance, which can be used to indicate all shapes.
What is limits of tolerance in ecology?
limits of tolerance The upper and lower limits to the range of particular environmental factors (e.g. light, temperature, availability of water) within which an organism can survive.
What is ecological tolerance quizlet?
Ecological Tolerance. the range of abiotic conditions in which a species can survive. Range. The range of environmental conditions that are tolerable for survival in a species. Too little or too much of a specific environmental condition may result in death.
Why are limiting factors and tolerance important in ecology?
Limiting factors and tolerance range are factors that determine the survival of organisms. With the more and more human impact on nature, we might approach tolerance limits of species which may result in their extinction. These factors also help to analyze the distributions and migration of organisms.
What does ecological mean in biology?
Ecology is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment; it seeks to understand the vital connections between plants and animals and the world around them.
What is ecological tolerance quizlet?
Ecological Tolerance. the range of abiotic conditions in which a species can survive. Range. The range of environmental conditions that are tolerable for survival in a species. Too little or too much of a specific environmental condition may result in death.
What is ecological process in biology?
Ecological processes such as primary production, respiration, energy, carbon and nutrient flow through food webs, reproduction, and decomposition are represented as rates of change, which requires repeated measurement over time.
What are the three zones of ecological tolerance?
Ecological tolerance is the range of tolerance that an organism can endure before injury or death, Identify the three zones of ecological tolerance. Optimal range, zones of physiological stress, and zone of intolerance.
Range of Tolerance and Niche Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Shelford's Law of Tolerance, For each behavioral or physiological requirement, organisms may exhibit either:, Range of Tolerance and more.
Chapter 11 Flashcards | Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. When Aldo Leopold said, "The first rule to intelligent tinkering is to save all the pieces." In terms of biodiversity he meant that we should A. Save records of all species that have disappeared B. Not interfere with the disappearance of species C. Not cause species to disappear D. Not interfere with nature E. Aldo Leopold did ...
What is the difference between tolerance range and optimal range ...
What is the difference between tolerance range and preference range for environmental conditions? preference range is the one which need operation of things healthy,reliable & trouble free etc ...
Range of Tolerance Overview and Examples - Study.com
Range of Tolerance: Definition. Every society is different, but in mainstream America, there are some common taboos: exposed tattoos (although tolerance appears to be increasing for this one ...
What is tolerance in biology? - Quora
Answer (1 of 8): Earth's ecosystems are affected by both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors, and are regulated by the law of tolerance. The law of tolerance states that the existence, abundance and distribution of species depends on the tolerance level of each species to physical an...
What is tolerance in biology?
Tolerance. An organism’s capacity to survive variation in environmental conditions. An organisms tolerance to a given factor will influence its distribution. This graph shows the average distribution of flies according to temperature.
Can a tolerance change?
Acclimation: Sometimes it is possible for the tolerance of an organism to change slightly if conditions are changed slowly.
What is the ability to use genomics and other omics approaches on non-model species?
Also the ability to use genomic and other omics approaches on non-model species is developing rapidly ( Shafer et al., 2015 ). This provides a range of opportunities to pinpoint genes and mechanism responsible for fitness and plastic responses in the field on a wide range of species. This does not leave laboratory experiments out-of-date but do provide additional opportunities that should be exploited.
Why do populations adapt differently?
Theories emphasize that populations can adapt differently depending on the type of environmental fluctuations (see above). The experimental evolution setup in which rapidly reproducing species are let to evolve multiple generations in different kinds of environments is capable of resolving whether evolutionary responses to constant and fluctuating environments are similar and whether adaptations are specific to particular kinds of fluctuations. For example if experimental bacterial strains can be identified from each other ( Bennett and Lenski, 1993; Ashrafi et al., 2017 ), it allows comparing fitness of the strains in competition.
Is tolerance curve good predictor of fitness?
Empirical and theoretical evidence suggests that many tolerance curves presented in the literature are not good predictors of fitness in fluctuating environments. However, very few studies have properly tested the extent of the problem. Lack of this knowledge is problematic in the broad context of understanding evolutionary processes in natural systems and the genetic background for adaptation to environmental fluctuations. One reason why it is of outmost important to obtain a better understanding of tolerance curves is that they are often being used to predict future distributions of species (e.g., Chevin et al., 2010; Huey et al., 2012; Valladares et al., 2014 ). Further, experimental molecular work that aims at elucidating the genetic architecture of fitness components is typically performed on populations held in constant environments and therefore may not detect adaptive genetic variation of relevance for populations in their natural habitat. Failure to recognize by which means the genotype, population or species is adapted to environmental fluctuations will make it hard to predict how e.g. climate change induced alternations in fluctuations affect biota, and extinction risks ( Botero et al., 2015 ). Here we present avenues for how studies can test the value of tolerance curves and suggest ways that can provide data suitable for predicting performance in fluctuating environments, and distribution and abundance of biota in rapidly increasing stressful and fluctuating environments.
Is tolerance curves a predictor of performance?
In addition to empirical evidence, theoretical work suggests that tolerance curves are poor predictors of performance in fluctuating environments ( Levins, 1968; DeWitt and Langerhans, 2004; Botero et al., 2015 ). For example, evolutionary theories predict that responses to fluctuating and constant environmental conditions will favor genetically determined broad and narrow tolerance curves, respectively ( Slatkin and Lande, 1976; Lynch and Gabriel, 1987; Gomulkiewicz and Kirkpatrick, 1992; Gilchrist, 1995 ). However, the main message from models that take into account inducible and reversible plastic responses to environmental fluctuations, in addition to genetically determined tolerance curves, suggests that inducible plasticity is superior to genetically fixed strategies (broad or narrow tolerance curves) under nearly all conditions ( Levins, 1968; DeWitt and Langerhans, 2004 ), and especially in frequently fluctuating environments ( Padilla and Adolph, 1996 ). However, if environmental cues for predicting future environmental conditions are unreliable inducible plasticity also becomes a burden ( Reed et al., 2010) and risk spreading strategies, such as bet-hedging are expected to evolve ( Levins, 1968; DeWitt and Langerhans, 2004 ). Thus, when populations are exposed to environments with different predictabilities, amplitudes, and frequencies of fluctuations, different adaptation mechanisms are expected to operate ( Botero et al., 2015 ).
Is plastic inducible morphologies always adaptive?
Padilla, D. K., and Adolph, S. C. (1996). Plastic inducible morphologies are not always adaptive: the importance of time delays in a stochastic environment. Evol. Ecol. 10, 105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01239351
Does evolution affect tolerance curves?
Interestingly, when we look back at earlier literature on experimental evolution in fluctuating environments, the results indicate that different fluctuations might lead to separate adaptations that are not visible in traditional tolerance curves obtained across constant temperatures. For example a study with ciliates showed no adaptation to fluctuating environments when measured at constant temperatures, but strains adapted to rapidly fluctuating thermal environments had increased expression of the heat shock protein Hsp90, indicating evolution of tolerance to cope with acute stress ( Ketola et al., 2004 ). From studies that have tested the effect of evolution in fluctuating environments on tolerance curves and performance also in fluctuating environments ( Bennett and Lenski, 1993; Leroi et al., 1994; Kassen and Bell, 1998; Hughes et al., 2007; Ketola and Saarinen, 2015 ), only one study shows a positive link between tolerance curve parameters obtained across constant environments and the performance in fluctuating environments ( Hughes et al., 2007) and one suggests a strong negative link ( Ketola and Saarinen, 2015 ).
What is the theory of tolerance?
Good restated the theory of tolerance as: Each and every species is able to exist and reproduce successfully only within a definite range of environmental conditions.
Who developed the law of tolerance?
Shelford's law of tolerance is a principle developed by American zoologist Victor Ernest Shelford in 1911. It states that an organism 's success is based on a complex set of conditions and that each organism has a certain minimum, maximum, and optimum environmental factor or combination of factors that determine success.
Why does sugar maple tolerate less precipitation?
Because temperature and rainfall interact to determine the availability of water, sugar maple tolerates lower annual precipitation at the edge of its northern range (by about 50 cm). Good restated the theory of tolerance as: Each and every species is able to exist and reproduce successfully only within a definite range of environmental conditions.
Is tolerance fixed or variable?
Tolerance ranges are not necessarily fixed. They can change as: Seasons change. Environmental conditions change. Life stage of the organism changes. Example – blue crabs. The eggs and larvae require higher salinity than adults. The range of the optimum may differ for different processes within the same organism.
What is tolerance range?
Tolerance ranges of species. Abiotic (non-living) factors that influence where a species can live. Life is found almost everywhere on Earth, but it is not distributed evenly around the planet. Different species are found in different areas; some species have overlapping ranges, others do not. Each species has a set of environmental conditions ...
Why is the range of tolerance different for a generalist plant versus a specialist plant?
The range of tolerance is different for a generalist plant versus a specialist plant because generalist plants' tolerance curve would have been wider representing that it can support different conditions and specialist plants' tolerance graph would have been narrower meaning that it would support limited conditions.
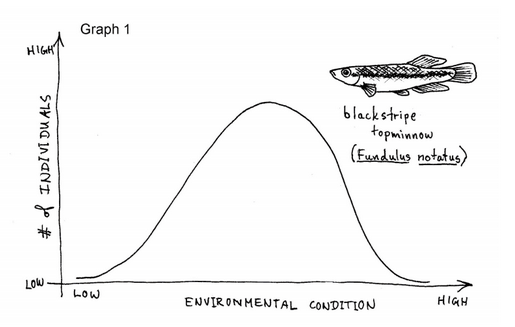
What is a shiner compared to a topminnow?
What is Graph 2 telling us about shiners compared to the topminnows? Shiners have a much narrower tolerance range for oxygen than topminnows do. The shiner can only survive and thrive in a narrow band of oxygen levels, so you would expect that its geographical range would be more restricted; it would not be distributed as widely as the topminnow since it wouldn’t do well in stagnant ponds with lower oxygen levels, for example. If you look closely, you’ll also notice that the peak of the curve for the shiner is a little bit to the right of the peak of the curve for the topminnow. This tells us that compared to topminnows, shiners do best in water that is slightly more oxygenated.
What is the bell curve in biology?
If you draw a graph of how many individuals in a population live under which part of the range of any given factor, you almost always get a bell-shaped curve.
What happens when you move from the middle part of the curve to the lower part?
As you move from the middle part to lower oxygen levels (to the left) or to higher oxygen levels (to the right), the curve is not as high – there are fewer individuals that live in lakes that have the lower or higher amounts of oxygen.
Do different organisms have different tolerance ranges?
This example points out an important aspect of tolerance ranges – different types of organisms have different tolerance ranges for the same factor. And in fact, the tolerance range of a single individual may change over time; individuals of a certain species of salmon, for example, start life in a freshwater stream, migrate out to the open ocean, ...
Can a species survive if there is too much or too little of the factor?
In other words, they can tolerate (or survive within) a certain range of a particular factor, but cannot survive if there is too much or too little of the factor. Take temperature, for example.
