
Full Answer
What is a CT scan and what does it show?
Your doctor may recommend a CT scan to help:
- Diagnose muscle and bone disorders, such as bone tumors and fractures
- Pinpoint the location of a tumor, infection or blood clot
- Guide procedures such as surgery, biopsy and radiation therapy
- Detect and monitor diseases and conditions such as cancer, heart disease, lung nodules and liver masses
What are the most common reasons for a CT scan?
Reasons You May Need a CT Scan
- Car Accident or Trauma. ...
- To Guide Procedures. ...
- Detect the Location of a Problem. ...
- Check Areas of the Body with Small Bones. ...
- An Injury or Issue with the Brain or Head. ...
- Spinal Issues and Chronic Pain. ...
- Abdominal Issues. ...
- Cancer Treatments. ...
What is the difference between mammography and tomography?
Regular mammography obtain standard 2D images, while tomosynthesis utilize movement to gain 3D pictures, in a similar way as a CT scanner. However, tomosynthesis models can also aquire 2D images. Breast imaging is performed while the system compresses the breast between the clear plastic paddle and the imaging detector.
What is the difference between a MRI and a CAT scan?
A CAT scan, or a computed tomography scan, uses radiation to evaluate spinal abnormalities. For instance, a CT scan can be used to evaluate spinal fractures, disc herniation, and spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal. CT scanning is more rapid than an MRI, and provides better detail of the bones of your spine.
What can a tomography detect?
Why it's doneDiagnose muscle and bone disorders, such as bone tumors and fractures.Pinpoint the location of a tumor, infection or blood clot.Guide procedures such as surgery, biopsy and radiation therapy.Detect and monitor diseases and conditions such as cancer, heart disease, lung nodules and liver masses.More items...•
What is the difference between CT scan and tomography?
A computerized tomography (CT) scan is usually a series of X-rays taken from different angles and then assembled into a three-dimensional model by a computer. Tomography means a picture of a slice.
What is a tomography procedure?
A computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan allows doctors to see inside your body. It uses a combination of X-rays and a computer to create pictures of your organs, bones, and other tissues. It shows more detail than a regular X-ray. You can get a CT scan on any part of your body.
How long does a tomography take?
You can expect your CT scan appointment to last approximately 15 minutes start to finish. If you are having a CT scan with oral contrast, it could take as long as an hour and 15 minutes. Once the CT scan is complete, a radiologist will study the images and share the results with your doctor.
What should you not do before a CT scan?
Before Your CT ScanDo not eat or drink for 4 hours before your CT scan.Arrive 2 hours before your scheduled CT scan to drink a special liquid that will help the technologist see your stomach and bowels.Have blood tests performed several days before your CT scan, if your physician requires them.More items...
How long does radiation stay in your body after a CT scan?
Head: 2 mSv, equal to about 8 months of background radiation. Spine: 6 mSv, equal to about 2 years of background radiation. Chest: 7 mSv, equal to about 2 years of background radiation.
Why do you have to drink water before a CT scan?
Preparing for a CT scan The water hydrates you prior to having contrast media for the CT. In the waiting area you will be asked to drink another 500ml of water which outlines the stomach and bowel clearly on the scans. The water also helps fill your bladder so that it shows on the scan.
What are the types of tomography?
There are 2 basic types of tomography: linear and nonlinear. In both techniques, the tube moves in one direction while the film cassette moves in the opposite direction, with both motions centered around a fulcrum.
Will a radiographer tell you if something is wrong?
“Plenty of patients ask, but techs should not give information and should not even react to what they're seeing on the image,” Edwards said. “They aren't doctors, and while they do know how to get around your anatomy, they aren't qualified to diagnose you.”
What does tomography mean in medical terms?
Definition of tomography : a method of producing a three-dimensional image of the internal structures of a solid object (such as the human body or the earth) by the observation and recording of the differences in the effects on the passage of waves of energy impinging on those structures — compare computed tomography.
Why can't you have caffeine after a CT scan?
If you received IV contrast for your particular test then you need to drink at least 8, 500 ml glasses of water or juice each day for the following two days and avoid alcohol and caffeine the day of your exam. This will prevent dehydration and allow your kidneys to filter the contrast out of your body.
Is tomography an MRI?
MRI. CT scans and MRIs are both used to capture images within your body. The biggest difference is that MRIs (magnetic resonance imaging) use radio waves and CT (computed tomography) scans use X-rays.
What are the types of tomography?
There are 2 basic types of tomography: linear and nonlinear. In both techniques, the tube moves in one direction while the film cassette moves in the opposite direction, with both motions centered around a fulcrum.
What can a CT scan show that an MRI Cannot?
People with metal implants, pacemakers or other implanted devices shouldn't have an MRI due to the powerful magnet inside the machine. CT scans create images of bones and soft tissues. However, they aren't as effective as MRIs at exposing subtle differences between types of tissue.
Which is better a CT scan or MRI?
Advantages of MRIs Magnetic resonance imaging produces clearer images compared to a CT scan. In instances when doctors need a view of soft tissues, an MRI is a better option than x-rays or CTs. MRIs can create better pictures of organs and soft tissues, such as torn ligaments and herniated discs, compared to CT images.
Why would a doctor order an MRI after a CT scan?
MRI instead of CT scans In some situations, your doctor may suggest MRI if a CT scan hasn't been able to give all the information they need. In some cancers, such as cervix or bladder cancer, MRI is better than CT at showing how deeply the tumour has grown into body tissues.
What is computed tomography?
Computed tomography ( CT ) is an imaging procedure that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed pictures, or scans, of areas inside t...
What can a person expect during a CT procedure?
During a CT procedure, the person lies very still on a table, and the table passes slowly through the center of a large donut-shaped x-ray machine....
How is CT used in cancer?
CT is used in cancer in many different ways: To screen for cancer To help diagnose the presence of a tumor To provide information about the stage...
How is CT used in cancer screening?
Studies have shown that CT can be effective in both colorectal cancer screening (including screening for large polyps ) and lung cancer screenin...
What is total, or whole-body, CT?
Total, or whole-body, CT creates pictures of nearly every area of the body—from the chin to below the hips. This procedure, which is used routinely...
What is combined PET/CT?
Combined PET/CT uses two imaging methods, CT and positron emission tomography (PET), in one procedure. CT is done first to create anatomic pict...
Is the radiation from CT harmful?
Some people may be concerned about the amount of radiation they receive during CT. CT imaging involves the use of x-rays , which are a form of...
What are the risks of CT scans for children?
Radiation exposure from CT scans affects adults and children differently. Children are considerably more sensitive to radiation than adults because...
What is being done to reduce the level of radiation exposure from CT?
In response to concerns about the increased risk of cancer associated with CT and other imaging procedures that use ionizing radiation , sever...
What is a CT scan?
Computed tomography is commonly referred to as a CT scan. A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce images of the inside of the body. It shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, organs and blood vessels.
Why do we need a CT scan?
CT scans may be performed to help diagnose tumors, investigate internal bleeding, or check for other internal injuries or damage. CT can also be used for a tissue or fluid biopsy.
Why are CT scans sometimes ordered with contrast?
CT scans may be done with or without contrast. Contrast refers to a substance taken by mouth or injected into an IV line that causes the particular organ or tissue under study to be seen more clearly. Contrast examinations may require you to fast for a certain period of time before the procedure. Your doctor will notify you of this prior to the procedure.
How do I prepare for a CT scan?
If you are having a computed tomography angiography (CTA) or a virtual colonoscopy, you will be given specific instructions when you make your appointment .
What are the risks of a CT scan?
If you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant, you should notify your health care provider.
Why do you have a call button on a scanner?
You may have a call button so that you can let the technologist know if you have any problems during the procedure. The technologist will be watching you at all times and will be in constant communication.
How long after a CT scan can you take medication?
Depending on your oral medication for diabetes, you may be asked to discontinue use of the medication for 48 hours after the CT examination.
What is computed tomography?
Computed tomography ( CT) is an imaging procedure that uses special x-ray equipment to create detailed pictures, or scans, of areas inside the body. It is sometimes called computerized tomography or computerized axial tomography (CAT).
How is CT used in cancer screening?
Studies have shown that CT can be effective in both colorectal cancer screening (including screening for large polyps) and lung cancer screening.
What is combined PET/CT?
Combined PET/CT uses two imaging methods, CT and positron emission tomography ( PET), in one procedure. CT is done first to create anatomic pictures of the organs and structures in the body, and then PET is done to create pictures that provide functional data about the metabolic pathways (chemical reactions that take place in a cell to create and use energy) that are active in tissues or cells. Cancer cells often use different metabolic pathways than normal cells.
What are the risks of CT scans for children?
Radiation exposure from CT scans affects adults and children differently. Children are considerably more sensitive to radiation than adults because of their growing bodies and the rapid pace at which the cells in their bodies divide. In addition, children have a longer life expectancy than adults, providing a larger window of opportunity for radiation-related cancers to develop ( 5 ).
What is being done to reduce the level of radiation exposure from CT?
In response to concerns about the increased risk of cancer associated with CT and other imaging procedures that use ionizing radiation, several organizations and government agencies have developed guidelines and recommendations regarding the appropriate use of these procedures.
What is NCI doing to improve CT imaging?
Researchers funded by NCI are studying ways to improve the use of CT in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment. NCI also conducts and sponsors clinical trials that are testing ways to improve CT or new uses of CT imaging technology. Some of these clinical trials are run by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group
Where can people get more information about CT?
Additional information about CT imaging is available from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the federal agency that regulates food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics, biologics, and radiation-emitting products.
What is Tomography?
Think of the last time you or a family member was injured. You likely went to the hospital, and they may have checked the area of injury with an imaging procedure. Maybe it was an X-ray machine, which delivers a beam of light into the body, allowing for visualization of organs that are not able to be seen by the naked eye (that is, without cutting into the body and opening up the skin). About 40 years ago, technology advanced beyond the single plane images displayed on a piece of film and is now able to produce a cross-sectional image of your organs, bones and tissues.
How does tomography help doctors?
Even more informative is the ability of tomography to generate images of multiple slices of the tissue, from one end to the other. Think again of the bread example. Say you turn the loaf of bread vertically and begin slicing it from the top down to the bottom. Each slice may be a little different. Perhaps one of the slices reveals a hole in the bread or another contains a green mold. The capability of imaging serial slices allows the doctor to see through the whole tissue, one slice at a time, in an effort to not miss anything that may indicate injury or disease.
What is a CT scan?
Many different procedures utilize the process. Two of the more common techniques are CT scans and MRIs. A CT scan, or computed tomography scan , is a computerized X-ray technique used to generate the serial sections. CT scans can provide visualization of almost every part of the body and are most often used to detect injury or disease, such as internal bleeding or tumor growth.
What is the process of examining tissue?
Tomography is a visualization process that produces an image of what's inside a tissue. Imagine a loaf of bread. When you cut into the loaf, you are then able to view what was once hidden by an outer layer of crust -- the slice, or cross-section, gives you the ability to see both sides of the piece of bread. The same idea applies for tomography. Although the image generated is still two-dimensional, doctors are now able to see into tissues.
When was X-ray technology invented?
Although the existence of X-ray technology stems from the late 19th/early 20th century, tomography was merely a theoretical proposal until the 1970's. Godfrey Hounsfield invented the CT scanner in 1972. The first machines only visualized the head and were slow to produce serial sections. Fast forward 40 years, and the tomography equipment available now can generate sections of nearly any organ in about 10 seconds. This rapidity not only allows for quicker patient visits, but also reduces the risk of inaccurate results due to breathing or other uncontrollable bodily functions. The field continues to advance, with the ultimate goal of accurate and less invasive patient diagnostics.
Why do MRIs not use X-rays?
In contrast, MRIs do not use X-rays, but instead magnetic fields to produce serial images of the body's internal organs. Like CT scans, they are often used to help diagnose injury and disease (i.e. detecting a joint injury or uterine cyst), but because an MRI does not use X-rays, there is a reduced risk of exposure to the patient. Determining which type of tomography procedure you should undergo depends mainly on the area of the body affected and what the reason is for the test. For example, CT scans are best for detecting lung cancer, whereas MRIs are better for diagnosing spinal cord injuries.
Where did the word "tomography" come from?
The origin of the word "tomography" is from the Greek word "tomos" meaning "slice" or "section" and "graphe" meaning "drawing.". A CT imaging system produces cross-sectional images or "slices" of anatomy, like the slices in a loaf of bread.
What is CT imaging?
Although also based on the variable absorption of x rays by different tissues, computed tomography (CT) imaging, also known as "CAT scanning" (Computerized Axial Tomography), provides a different form of imaging known as cross-sectional imaging. The origin of the word "tomography" is from the Greek word "tomos" meaning "slice" or "section" ...
How does a CT work?
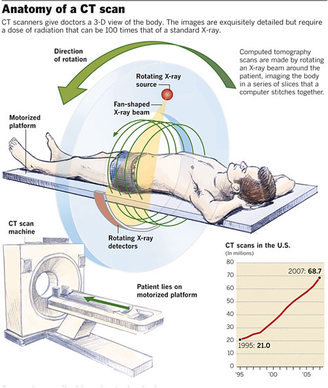
How a CT system works 1 A motorized table moves the patient (Figure 3) through a circular opening in the CT imaging system. 2 As the patient passes through the CT imaging system, a source of x rays rotates around the inside of the circular opening. A single rotation takes about 1 second. The x-ray source produces a narrow, fan-shaped beam of x rays used to irradiate a section of the patient's body (Figure 4). The thickness of the fan beam may be as small as 1 millimeter or as large as 10 millimeters. In typical examinations there are several phases; each made up of 10 to 50 rotations of the x-ray tube around the patient in coordination with the table moving through the circular opening. The patient may receive an injection of a "contrast material" to facilitate visualization of vascular structure. 3 Detectors on the exit side of the patient record the x rays exiting the section of the patient's body being irradiated as an x-ray "snapshot" at one position (angle) of the source of x rays. Many different "snapshots" (angles) are collected during one complete rotation. 4 The data are sent to a computer to reconstruct all of the individual "snapshots" into a cross-sectional image (slice) of the internal organs and tissues for each complete rotation of the source of x rays.
What is chest xray?
The chest x ray (Figure 1) is the most common medical imaging examination. During this examination, an image of the heart, lungs, and other anatomy is recorded on the film. back to top.
How do x-rays affect radiation?
Depending on the amount absorbed in a particular tissue such as muscle or lung, a different amount of x rays will pass through and exit the body. The amount of x rays absorbed contributes to the radiation dose to the patient. During conventional x-ray imaging, the exiting x rays interact with a detection device (x-ray film or other image receptor) ...
Does an EBCT scanner require moving parts?
Although the principle of creating cross-sectional images is the same as for conventional CT, whether single- or multi-slice, the EBCT scanner does not require any moving parts to generate the individual "snapshots.". As a result, the EBCT scanner allows a quicker image acquisition than conventional CT scanners.
What is a CT scan?
A computed tomography scan — also called a CT or CAT scan — is an imaging test that lets doctors see inside a person’s body. As a patient lies still on a table, special X-ray equipment takes pictures from different angles to create cross-sections of the body.
How does a CT scan help with cancer?
The scan can help doctors find cancer and show a tumor’s shape, size, location and the blood vessels that feed it, according to the American Cancer Society. Doctors can compare CT scans done over time to see how a tumor is changing in response to treatment.
What can CT scans detect?
They can detect the following conditions, according to the National Institutes of Health:
How harmful is a CT scan?
The radiation exposure from a CT scan is higher than that from standard X-ray procedures, but the increase in cancer risk from one scan is small, the National Cancer Institute noted.
What is difference between a CT scan and an MRI?
Both are painless imaging tests, but a CT scan uses X-rays, while MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a large magnet and radio waves to look inside the body, so there’s no exposure to radiation.
What is the best way to see the soft tissues of the body?
An MRI is particularly good at showing soft tissues of the body, including the brain, spinal cord, muscles, ligaments and tendons.
How long does a contrast dye test last?
The test lasts anywhere from a few minutes to half an hour, depending on the size of the area being scanned.
What is a computerized tomography scan?
A computerized tomography scan (CT or CAT scan) uses computers and rotating X-ray machines to create cross-sectional images of the body. These images provide more detailed information than normal X-ray images. They can show the soft tissues, blood vessels, and bones in various parts of the body. A CT scan may be used to visualize the: head.
What can a CT scan show?
They can show the soft tissues, blood vessels, and bones in various parts of the body. A CT scan may be used to visualize the: During a CT scan, you lie in a tunnel-like machine while the inside of the machine rotates and takes a series of X-rays from different angles. These pictures are then sent to a computer, ...
How long does it take for an X-ray to be done?
You may hear clicking, buzzing, and whirring noises during the scan. The table will move a few millimeters at a time until the exam is finished. The entire procedure may take anywhere from 20 minutes to one hour.
What can imaging help with?
The imaging technique can help your doctor: diagnose infections, muscle disorders, and bone fractures. pinpoint the location of masses and tumors (including cancer) study the blood vessels and other internal structures. assess the extent of internal injuries and internal bleeding.
Why is it important to lie still during CT scan?
It’s very important to lie still while CT images are being taken because movement can result in blurry pictures. Your doctor may ask you to hold your breath for a short period during the test to prevent your chest from moving up and down.
Can you get a CT scan while pregnant?
It’s also important to tell your doctor if you’re pregnant. Though the radiation from a CT scan is unlikely to harm your baby, your doctor may recommend another exam, such as an ultrasound or MRI scan, to minimize risk.
Is it safe to have a CT scan?
There are very few risks associated with a CT scan. Though CT scans expose you to more radiation than typical X-rays, the risk of cancer caused by radiation is very small if you only have one scan. Your risk for cancer may increase over time if you have multiple X-rays or CT scans. The risk of cancer is increased in children receiving CT scans, ...

Types of Tomography in Medicine
History of Tomography Technology
- From the first documented instance of someone conceptually developing tomography, or at least thinking of tomography as a way to view a broader object utilizing cross-sections, to the development of the first CT Scan of a living subject, tomography development spanned over the years 1914 to 1974. The following list gives a brief overview of this ti...
Uses of Tomography
- Tomography is an incredibly useful tool that has applications across industries, including medicine, archeology, geology, atmospheric sciences, biology, and physics.
Conventional X-Ray Images
- Figure 1: Chest X ray Image All x-ray imaging is based on the absorption of x rays as they pass through the different parts of a patient's body. Depending on the amount absorbed in a particular tissue such as muscle or lung, a different amount of x rays will pass through and exit the body. The amount of x rays absorbed contributes to the radiation doseto the patient. During conventio…
Computed Tomography
- Figure 2: Cross-sectional Image of Abdomen Although also based on the variable absorption of x rays by different tissues, computed tomography (CT) imaging, also known as "CAT scanning" (Computerized Axial Tomography), provides a different form of imaging known as cross-sectional imaging. The origin of the word "tomography" is from the Greek word "t...
How A Ct System Works
- Figure 3: Patient in CT Imaging System 1. A motorized table moves the patient (Figure 3) through a circular opening in the CT imaging system. 2. As the patient passes through the CT imaging system, a source of x rays rotates around the inside of the circular opening. A single rotation takes about 1 second. The x-ray source produces a narrow, fan-shaped beam of x rays used to ir…
Advances in Technology and Clinical Practice
- Figure 4: CT Fan Beam Today most CT systems are capable of "spiral" (also called "helical") scanning as well as scanning in the formerly more conventional "axial" mode. In addition, many CT systems are capable of imaging multiple slices simultaneously. Such advances allow relatively larger volumes of anatomy to be imaged in relatively less time. Another advancement in the tech…
Required Reports For Industry