
What are the 10 signs of low magnesium?
Top 10 Signs And Symptoms Of Magnesium Deficiency In Humans
- Frequent Migraines. If you frequently suffer from a migraine, it may indicate that you have a magnesium deficiency. ...
- Anxiety, Restlessness, And Depression. Someday, when you suddenly feel lethargic, depressed, irritable, and restless but unexplained cause, you may have a deficiency of nutrition like magnesium.
- Unexplained Weakness And Fatigue. ...
- Insomnia. ...
What happens if you take too much magnesium?
Your blood pressure may drop quickly and lead to a condition called hypotension. Taking too much magnesium is also associated with problems like erratic heart rhythms or slow heartbeat. Very high levels of magnesium in the blood can also lead to cardiac arrest.
What are the symptoms of not enough magnesium?
Early signs of magnesium deficiency may include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- loss of appetite
- fatigue
- weakness
Can you take too much or overdose with magnesium?
Severe overdoses of magnesium are rare in otherwise healthy people. Getting too much magnesium from the diet is not typically a cause for concern. Occasionally, a high dosage of magnesium from supplements or medications can cause mild symptoms of an overdose, including diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps.
At what level is magnesium toxic?
Symptoms of magnesium toxicity, which usually develop after serum concentrations exceed 1.74–2.61 mmol/L, can include hypotension, nausea, vomiting, facial flushing, retention of urine, ileus, depression, and lethargy before progressing to muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, extreme hypotension, irregular heartbeat, ...
How do you know if your magnesium is toxic?
According to the Office of Dietary Supplements , symptoms of magnesium overdose may include:diarrhea.nausea and vomiting.lethargy.muscle weakness.abnormal electrical conduction in the heart.low blood pressure.urine retention.respiratory distress.More items...
What is the treatment for magnesium toxicity?
Calcium gluconate: the antidote for magnesium toxicity is calcium gluconate 1 g IV over 3 minutes. Repeat doses may be necessary. Calcium chloride can also be used in lieu of calcium gluconate.
What are the 4 cardinal physical signs of magnesium toxicity?
The patient should be assessed for signs of toxicity (e.g., visual changes, somnolence, flushing, muscle paralysis, loss of patellar reflexes) or pulmonary edema. If these signs are observed, a physician must be notified.
What should magnesium levels be?
A blood test will be ordered to check your magnesium level. Normal range is 1.3 to 2.1 mEq/L (0.65 to 1.05 mmol/L). Other blood and urine tests that may be done include: Calcium blood test.
Can too much magnesium be fatal?
Magnesium is essential for well-being, but too much can cause problems, including digestive issues, lethargy, and an irregular heartbeat. In rare cases, a magnesium overdose can be fatal. Magnesium toxicity is rare in otherwise healthy people, and levels are more likely to be low than high.
What is the fastest way to correct magnesium?
Treat with magnesium salts when magnesium deficiency is symptomatic or persistently < 1.25 mg/dL (< 0.50 mmol/L). Give oral magnesium salts unless patients have seizures or other severe symptoms, in which case, give 2 to 4 g of magnesium sulfate IV over 5 to 10 minutes.
Why is hypermagnesemia rare?
Hypermagnesemia is rare because the kidneys work to get rid of excess magnesium. Overdose with resultant hypermagnesemia is most often seen in people with poor kidney function after they take medications containing magnesium, such as laxatives or antacids.
What is the best treatment for magnesium?
A doctor can give intravenous (IV) calcium gluconate to help reverse the effects of excess magnesium. IV furosemide may be given for diuresis and excretion of magnesium if adequate kidney function is intact. Dialysis may need to be used to flush magnesium from the body if hypermagnesemia is severe or renal function is poor.
What are some examples of minerals?
cashews. peanuts. wheat cereal or bread. soymilk. black beans. peanut butter. But food isn’t the only place you’ll find this mineral. You’ll also find it in supplements and certain medications. For example, magnesium is the active ingredient in some laxatives.
What foods contain magnesium?
Magnesium is found in a variety of foods, especially those with lots of fiber. Nuts, leafy greens, legumes, and whole grains are among the best sources. Some specific foods that are high in magnesium include: almonds.
Does magnesium cause diarrhea?
It also notes that “high doses of magnesium from dietary supplements or medications often result in diarrhea that can be accom panied by nausea and abdominal cramping.”. Magnesium may be prescribed to prevent migraine headaches, with a daily dosage of more than 350 mg a day.
Can magnesium overdose cause kidney disease?
It can occur in people with chronic health conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, although it’s rare. Magnesium overdose may also result from taking too much of a supplement or medication containing magnesium.
Is magnesium overdose dangerous?
Overall, the risk of ever experiencing a magnesium overdose is extremely low for a typically healthy person. Still, it’s possible to have too much in certain cases.
How is magnesium upper limit calculated?
When it comes to upper limit oral doses set by medical authorities, they are calculated according to the diarrhea effect on an average adult and bear no relationship to how much magnesium supplementation a person may actually need for optimal nutrition.
What happens if you don't get enough magnesium?
If you don’t supply your body the daily magnesium it needs for energy metabolism, detoxification, building new cells etc., after a while you use up your stored resources and then the body can move into a ‘burn-out’ phase, which resembles Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and a heightened inflammatory response. It can lead to osteoporosis, diabetes and heart disease – basically all the degenerative diseases. This is why researchers have called magnesium ‘The Antiaging Mineral’. I have called it ‘The Master Mineral’ because we need it to do more jobs than any other mineral, and it regulates homeostasis and balance in the body. It is also our nurturing and recovery mineral and could even be called ‘The Mother Mineral’.
What is the difference between Epsom salt and magnesium chloride?
The main difference in effect of the Epsom salts compared to magnesium chloride is that Epsom salt has 9.7% elemental magnesium, whereas magnesium chloride salt has 15 to 16%. Epsom salt, having the sulfate component, is also skin drying and can cause irritation in sensitive skin, whereas magnesium chloride is gentler and more hydrating for skin.
How much magnesium is in a teaspoon of magnesium cream?
Two teaspoons of magnesium cream (enough to cover the whole body) delivers approximately 300mg magnesium, which remains available for transdermal uptake for several hours. If your body is very hungry for magnesium it will go in faster; and if not so hungry, a bit slower. Spreading out your topical magnesium applications throughout the day, as well as regularly drinking magnesium water (spring water concentration), ensures you get optimal uptake.
How much magnesium should I take a day?
Some people can need 1,000mg or more of magnesium per day to cope with and help recover from stresses, injury, sleep deprivation, arthritis, rheumatism, medications, drug or alcohol abuse, athletic performance or pregnancy. Some can also lose excessive amounts of minerals that would normally be recycled. This loss by kidneys increases with chronic stress. I call it ‘leaky kidneys’. This affects their ability to properly balance pH, leading to acidosis, which leads to increased inflammation and degenerative disease. We literally get dissolved by the free radicals of the acidity. These people need to put a lot more magnesium in (as well as other antioxidants and alkalizers), to keep up with the loss from the ‘holes in their bucket’ (leaky kidney).
Why do we need magnesium?
We need magnesium every day because the body uses so much of it to re-balance from stress and pressure. Calcium contracts; magnesium relaxes. Every second, every time your heart beats, 24/7, your body is using up magnesium resources which need to be replenished. Magnesium is the master mineral with 350 direct functions and over 1,000 indirect enzymatic functions in the body. It sparks up our electrical supply for detoxification, making proteins such as hormones, enzymes, collagen and elastin, organ function, bone and muscle building, and controlling how calcium behaves in the body. Massive tasks! And a lot can therefore go wrong if we don’t get enough magnesium.
Can you take magnesium transdermally?
You can use as much transdermal magnesium as you like without fear of excessive magnesium dose, because the amount able to be absorbed is limited by the fats and carrying capacity of the skin layer. In other words, the epidermis of the skin would fill up faster with the fats, becoming saturated so that for a while it can’ t take up anymore. In this way a toxic quantity of magnesium (2,900mg in one dose) cannot enter the inner domain, as it would be able to via intravenous injection. You couldn’t even get this much into you orally because you would be pooping it out at 360mg doses.
What is the normal magnesium level?
The body needs magnesium for more than 300 biochemical processes. Magnesium blood levels of 1.7–2.3 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) are within the normal range, while levels above 2.6 mg/dl can indicate hypermagnesemia. Having too much magnesium in the blood is uncommon. It is more likely to occur in people with existing health conditions, ...
What happens if you take too much magnesium?
If the body has absorbed too much magnesium, a person may notice any of the following symptoms, which can range from mild to very severe: lethargy. facial flushing. diarrhea. nausea. stomach cramps. vomiting. depression. muscle weakness.
How much magnesium is in milk of magnesia?
For example, 1 tablespoon of Milk of Magnesia contains 500 mg. Trusted Source. of elemental magnesium. A daily dose for adults is up to 4 tablespoons per day, but the body excretes much of the magnesium because of the medication’s laxative effects.
How to treat hypermagnesemia?
The first treatment for hypermagnesemia is to stop consuming magnesium in supplements or medications. Other treatments include:
Why do we need magnesium?
Why a person needs magnesium. Magnesium sources. Takeaway. Magnesium is an essential mineral. However, having too much magnesium in the blood can be dangerous. The medical term for this is hypermagnesemia, and a magnesium overdose is one possible cause. The body needs magnesium for more than 300 biochemical processes.
What percentage of people have low magnesium levels?
Some research indicates that 10–30 percent of people have low levels of magnesium.
What foods contain magnesium?
Magnesium is present in many foods, including: legumes, such as black beans and kidney beans. nuts, including almonds, cashews, peanuts, and peanut butter. whole grains, such as brown rice and oats. potatoes, when a person eats the skin. leafy green vegetables, such as spinach. fortified breakfast cereals.
What is magnesium overdose?
Magnesium overdose is an excess of magnesium in the body. Magnesium is an essential mineral that helps muscles function and maintain energy. In the absence of kidney disease, your body naturally removes excess magnesium. A magnesium overdose, also called magnesium toxicity or hypermagnesemia, generally occurs when magnesium is ingested in large quantities in the form of a supplement, either as a pill or a liquid. It is very rare to experience a magnesium overdose by consuming foods that have naturally occurring magnesium in them, such as fruits and vegetables or nuts and whole grains.
How is magnesium overdose treated?
Treatment for magnesium overdose will vary depending on the severity of the overdose. In an emergency setting, magnesium overdose treatment may include:
How to reduce the risk of magnesium overdose?
You may be able to lower your risk of magnesium overdose by: Avoiding magnesium-based antacids, particularly if you have kidney disease.
Can magnesium cause diarrhea?
A mild magnesium overdose is usually accompanied by temporary diarrhea and nausea. People who have impaired kidney function are at the greatest risk for magnesium overdose. Even a moderate magnesium overdose may cause a drop in blood pressure in those with kidney disease.
Can magnesium be ingested?
Your body naturally removes excess magnesium when the kidneys are functioning normally. A magnesium overdos e generally occurs when magnesium is ingested in large quantities in the form of a supplement. It is very rare to experience a magnesium overdose by consuming foods that have naturally occurring magnesium in them.
Can magnesium overdose be life threatening?
Serious symptoms that might indicate a life-threatening condition. In some cases, a magnesium overdose can be life threatening. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) if you, or someone you are with, have any of these life-threatening symptoms including: Abdominal, pelvic, or lower back pain that can be severe.
What is the normal magnesium level?
Normal serum magnesium concentrations range between 0.75 and 0.95 millimoles (mmol)/L [ 1, 5 ]. Hypomagnesemia is defined as a serum magnesium level less than 0.75 mmol/L [ 6 ]. Magnesium homeostasis is largely controlled by the kidney, which typically excretes about 120 mg magnesium into the urine each day [ 2 ].
How much magnesium is in the human body?
An adult body contains approximately 25 g magnesium, with 50% to 60% present in the bones and most of the rest in soft tissues [ 4 ]. Less than 1% of total magnesium is in blood serum, and these levels are kept under tight control.
What foods contain magnesium?
Includes a variety of vegetables; fruits; grains (at least half whole grains); fat-free and low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese; and oils. Whole grains and dark-green, leafy vegetables are good sources of magnesium. Low-fat milk and yogurt contain magnesium as well.
What is the amount of magnesium in water?
Tap, mineral, and bottled waters can also be sources of magnesium, but the amount of magnesium in water varies by source and brand (ranging from 1 mg/L to more than 120 mg/L) [ 8 ].
What is magnesium used for?
Magnesium is required for energy production, oxidative phosphorylation, and glycolysis. It contributes to the structural development of bone and is required for the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and the antioxidant glutathione.
What are the best foods to eat for magnesium?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans describes a healthy dietary pattern as one that: 1 Includes a variety of vegetables; fruits; grains (at least half whole grains); fat-free and low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese; and oils.#N#Whole grains and dark-green, leafy vegetables are good sources of magnesium. Low-fat milk and yogurt contain magnesium as well. Some ready-to-eat breakfast cereals are fortified with magnesium. 2 Includes a variety of protein foods such as lean meats; poultry; eggs; seafood; beans, peas, and lentils; nuts and seeds; and soy products.#N#Dried beans and legumes (such as soybeans, baked beans, lentils, and peanuts) and nuts (such as almonds and cashews) provide magnesium. 3 Limits foods and beverages higher in added sugars, saturated fat, and sodium. 4 Limits alcoholic beverages. 5 Stays within your daily calorie needs.
Is magnesium a laxative?
(Although such a dose of magnesium is well above the safe upper level, some of the magnesium is not absorbed because of the medication’s laxative effect.) Magnesium is also included in some remedies for heartburn and upset stomach due to acid indigestion [ 18 ]. Extra-strength Rolaids®, for example, provides 55 mg elemental magnesium (as magnesium hydroxide) per tablet [ 20 ], although Tums® is magnesium free [ 21 ].
How much magnesium is needed for indigestion?
For indigestion (dyspepsia): 400-1200 mg of magnesium hydroxide has been used up to four times daily. 800 mg of magnesium oxide daily has also been used. For low levels of magnesium in the blood (hypomagnesemia): 3 grams of magnesium sulfate, taken every 6 hours for four doses, has been used.
Why is magnesium important?
Magnesium is a mineral that is important for normal bone structure in the body. People get magnesium from their diet, but sometimes magnesium supplements are needed if magnesium levels are too low. Low magnesium levels in the body have been linked to diseases such as osteoporosis, high blood pressure, clogged arteries, hereditary heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.
How long does it take to give magnesium sulfate?
For abnormal heartbeat caused by a pacemaker, 2 grams of magnesium sulfate in 10 mL of solution has been given by IV over 1-10 minutes, followed by 5-10 grams of magnesium sulfate in 250-500 mL of solution over 5 hours. For asthma: Doses of 1-2 grams of magnesium sulfate have been given over 20 to 30 minutes.
How long before climbing a mountain can you take magnesium citrate?
Altitude sickness. Research suggests that taking magnesium citrate by mouth daily in three divided doses, beginning 3 days before climbing a mountain and continuing until going down the mountain, does not reduce the risk of altitude sickness.
What are some good sources of magnesium?
An easy way to remember foods that are good magnesium sources is to think of fiber. Foods that are high in fiber are generally high in magnesium. Dietary sources of magnesium include legumes, whole grains, vegetables (especially broccoli, squash, and green leafy vegetables), seeds, and nuts (especially almonds). Other sources include dairy products, meats, chocolate, and coffee. Water with a high mineral content, or "hard" water, is also a source of magnesium .
Does magnesium help with osteoporosis?
Weak and brittle bones (osteoporosis). Taking magnesium by mouth seems to prevent bone loss in older females with osteoporosis.
Does magnesium help with irregular heartbeat?
Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias). Giving magnesium intravenously (by IV) or by mouth seems to be helpful for treating irregular heartbeat, also called arrhythmias. It is not yet clear whether magnesium helps reduce irregular heartbeat after heart surgery.
What is a double check for IV magnesium sulfate?
Double checks. Require an independent double check of the drug, concentration, infusion rate, pump settings, line attachment, and patient before administering IV magnesium sulfate. Point-of-care bar code systems can also be used to verify the drug, strength, and patient. When transferring patients, Simpson and Knox suggest having the receiving and transferring nurse verify the drug, concentration, line attachment, and pump settings at the bedside via comparison to the original order.
What is the protocol for magnesium sulfate?
Protocols. Establish dosing and administration protocols and standard order sets for magnesium sulfate. Simpson and Knox also suggest standardizing the unit of measure used to prescribe magnesium sulfate (e.g., g, mEq) and to report lab values (e.g., mg/dL, mEq/L, mmol/L). Always require administration via an infusion pump, preferably a smart pump with operational dose range alerts. If the drug is discontinued, immediately remove the infusion bag and tubing from the patient's access site, pump, and IV pole to prevent later accidental infusion, and dispose of the bag properly.
How long did it take to deliver magnesium sulfate?
A nurse prepared a bag of magnesium sulfate (40 g/L) and began an infusion at 200 mL/hour to deliver a 4 g bolus dose (100 mL) over 30 minutes. After remaining with the patient for 20 minutes, the nurse was suddenly called away for an urgent problem. She returned 25 minutes later to find the patient had received a 6 g loading dose. The patient was flushed and nauseated, with shallow respirations and unable to move her extremities. Concerned about toxicity, the physician ordered a test of the solution, which revealed a concentration of 80 g/L. The nurse had misread the vial labels and added too much magnesium sulfate to the IV bag. The patient actually received a 12 g loading dose but subsequently recovered without permanent harm.
What are the signs of toxicity of bolus?
Assess patients for signs of toxicity (e.g., visual changes, somnolence, flushing, muscle paralysis, loss of patellar reflexes) or pulmonary edema and notify the physician if observed. When giving a bolus, remain at the bedside to monitor the patient continuously. Simpson and Knox suggest subsequent assessment intervals of 15 minutes for the first hour, 30 minutes for the second hour, and then hourly.
Is magnesium sulfate infused during preterm labor?
The magnesium sulfate infusion had been administered during preterm labor, but it remained connected at the Y-site to the patient although it had been discontinued and was no longer infusing. The oxytocin solution was connected to the patient, but the magnesium sulfate solution was actually started by mistake.
Is magnesium sulfate safe for obstetrics?
Problem: Practitioners who work in obstetrical units may feel comfortable administering IV magnesium sulfate, which is used to treat preterm labor and preeclampsia. Yet, many errors have been reported with this medication, some fatal. In our February 12, 1997, and June 30, 1999 newsletters, we described errors in which obstetrical patients suffered respiratory arrest after receiving overdoses of magnesium sulfate. Most of these errors were due to unfamiliarity with safe dosage ranges and signs of toxicity, inadequate patient monitoring, pump programming errors, and mix-ups between magnesium sulfate and oxytocin.
Is toxicity a lab test?
Assessing toxicity. If concerned about toxicity, lab testing may be needed. However, Simpson and Knox caution that toxic levels vary among people, so a clinical assessment is as important as serum magnesium levels. Teach patients and families the signs of toxicity to report.
Why is magnesium deficiency common?
A deficiency often occurs when the soil is not rich in organic matter or is fast-draining (sandy soils, for example). If heavy rainfall occurs, this can easily leach magnesium from the soil. There are several common causes of magnesium deficiency, including a wet, cold, or acidic environment.
What causes magnesium deficiency?
When there are high levels of calcium, ammonia, and potassium, this can also cause magnesium deficiency.
What Does Magnesium Do For Plants?
Magnesium plays an important role in the health of our plants. It is one of the key components in how our plants convert the energy from its light sources into energy to grow and thrive.
How does pH affect magnesium absorption?
The Relationship Between pH & Magnesium Absorption For Plants. When you attempt to add magnesium to your soil or soilless setup, pay close attention to the pH. If your pH is lower than 7.0, the magnesium you add can be easily absorbed.
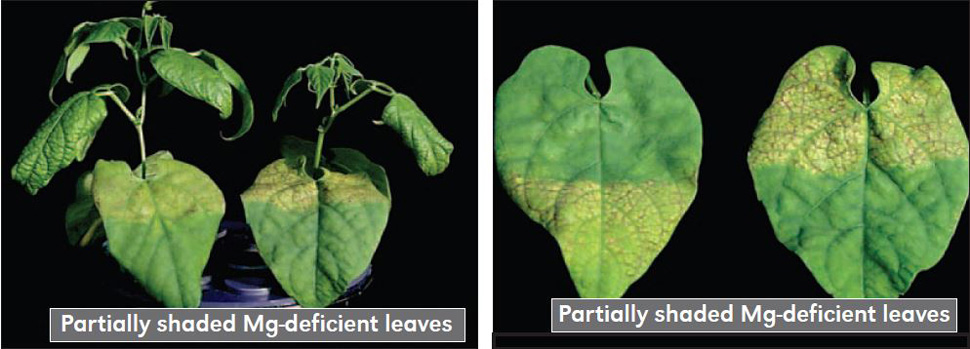
What happens when plants don't have magnesium?
When plants aren’t receiving sufficient amounts of magnesium at their roots, they will begin to degrade the chlorophyll in the oldest leaves first.
How long does it take for a plant to develop magnesium deficiency?
For the first few weeks of deficiency, you likely won’t notice any symptoms at all. However, as the plant gets older, typically around five or six weeks, you’ll notice necrosis appearing in middle-aged leaves.
How to give plants magnesium?
One of the ways to provide plants the magnesium they need is through the use of organic compost mulch and teas.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/magnesium-oxide-benefits-4184809-5c5db9f746e0fb0001442152.png)