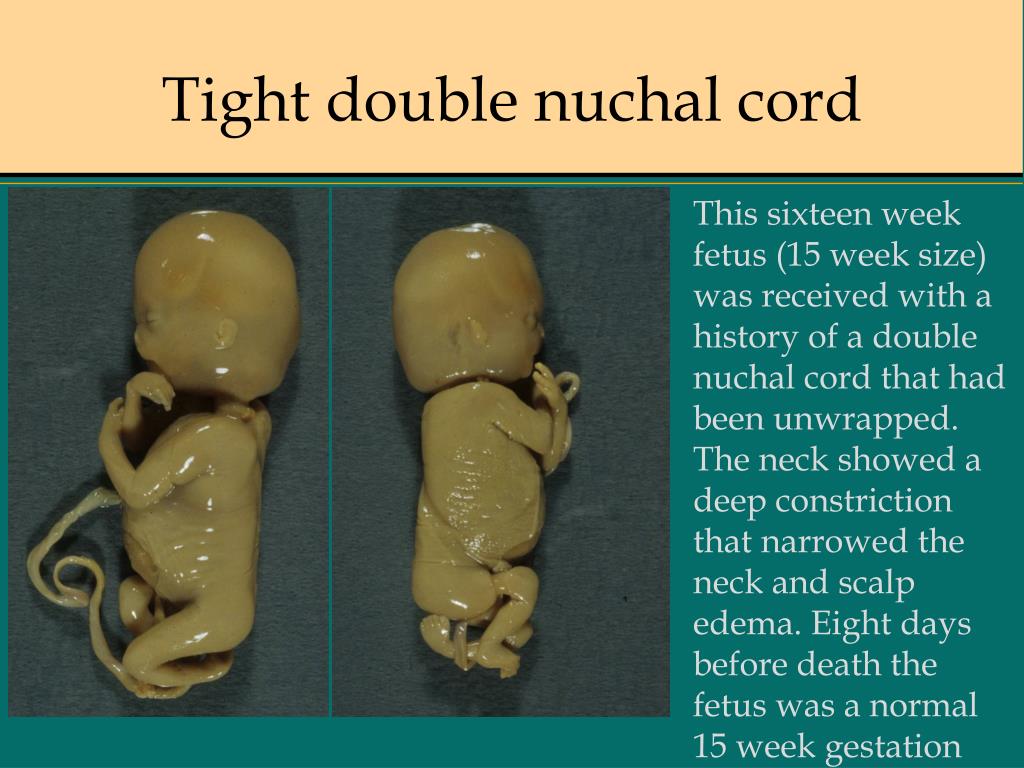
Three nuchal cords (a triple nuchal cord) occurs when three loops of umbilical cord are wrapped around the neck Nuchal cords can be qualitatively described as loose (no constriction) or as mildly, moderately or severely tight / constricting Two nuchal cords and three nuchal cords occur in 2.5% and 0.5% of term deliveries, respectively
What is a nuchal cord?
What is a nuchal cord? Nuchal cord is the term used by medical professionals when your baby has their umbilical cord wrapped around their neck. This can occur during pregnancy, labor, or birth.
Is it normal for a nuchal cord to wrap around the neck?
However, many of these babies have nuchal cords resolve on their own prior to delivery, or that doctors can easily maneuver away from the neck (i.e. not tight). Infants with nuchal cords that are wound tightly, wrapped more than once around the neck, or “locked,” are at greater risk.
How common are nuchal cords during pregnancy?
Nuchal cords are common during pregnancy with incidences recorded at around 12 percent at 24–26 weeks, reaching 37 percent at full term. When an umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the neck, the loop is referred to as the nuchal cord.
What is tight nuchal cord around the neck syndrome?
Keywords: Nuchal cords, Tight Nuchal cord around the neck syndrome (tCAN syndrome), Partial prolonged asphyxia, Adult strangulation Background In 1962, J. Selwyn Crawford [1] defined nuchal cord “360 degrees around the fetal neck.”

How common is a triple nuchal cord?
The incidence of single, double, triple or quadruple nuchal cord at delivery has been reported as 10.6%, 2.5%, 0.5% and 0.1%, respectively. The frequency of entanglement increases with gestational age, irrespective of whether the entanglement involves single or multiple loops.
Should I be worried about nuchal cord?
Should I Worry If My Baby Has a Nuchal Cord? Nuchal cords are very common and rarely cause any lasting complications or harm to your baby. Babies born with nuchal cords typically don't have any increased risk of low Apgar scores, growth and developmental problems, or stillbirth.
Can nuchal cord cause problems later in life?
Nuchal cords can reduce the flow of blood and oxygen to the baby while in utero, resulting in injuries to the brain or other organs. This can lead to life-long health conditions that can impact the quality of a baby's life.
How often is nuchal cord fatal?
Cord entanglement is a common finding in utero; however, fetal demise resulting from nuchal cord entanglement is rare (1–8).
What causes nuchal cord in pregnancy?
What causes nuchal cords? Random fetal movement is the primary cause of a nuchal cord. Other factors that might increase the risk of the umbilical cord wrapping around a baby's neck include an extra-long umbilical cord or excess amniotic fluid that allows more fetal movement.
Does nuchal cord mean C section?
Will I have to have a c-section if my baby has a nuchal cord? Absolutely not. The only reason for a c-section is extreme fetal distress. In rare cases, a nuchal cord can contribute to the distress of a baby during labor, and a c-section will be necessary.
How do you remove a nuchal cord from a baby's neck?
There's no way to prevent or treat a nuchal cord. Nothing can be done about it until delivery. Health professionals check for a cord around the neck of every single baby born, and usually it's as simple as gently slipping it off so that it doesn't tighten around the baby's neck once the baby has started to breathe.
How do you avoid nuchal cord?
In fact, 25 to 40% of babies are born with their umbilical cord wrapped around their neck (called a nuchal cord). There is nothing that can be done to prevent this.
Can a nuchal cord fix itself?
A nuchal cord might interrupt blow flow, oxygen, and nutrients to the fetus and cause complications. Fortunately, most nuchal cords will resolve before delivery.
Can a nuchal cord cause autism?
Fetal nuchal cord was not a risk factor for ASD (odds ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.66–1.57). There was homogeneity among studies that reported a risk of ASD (I2=0.0). Meaning: Fetal nuchal cord is not a risk factor for ASD.
What week is stillbirth most common?
Rates of infection and SIDS decrease with increasing gestational age at term, with the highest rates at 37 weeks. The risk of both neonatal and infant death has been shown in multiple studies to decrease with gestational age at term but then increase again at 41 weeks of gestation.
How do I prevent cords around my baby's neck?
Can you prevent umbilical cord wrapping around? There is nothing you can do to prevent the umbilical cord from wrapping around the neck of the baby. There are no symptoms or changes that indicate a cord around the baby's neck in the womb in the 9th month or even earlier.
How do you keep cord from wrapping around baby?
There's no way to prevent or treat a nuchal cord. Nothing can be done about it until delivery. Health professionals check for a cord around the neck of every single baby born, and usually it's as simple as gently slipping it off so that it doesn't tighten around the baby's neck once the baby has started to breathe.
Can a nuchal cord fix itself?
A nuchal cord might interrupt blow flow, oxygen, and nutrients to the fetus and cause complications. Fortunately, most nuchal cords will resolve before delivery.
What percent of babies have a nuchal cord?
Nuchal cord occurs when the umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the fetal neck 360 degrees. Nuchal cords occur in about 10–29% of fetuses and the incidence increases with advancing gestation age.
How do you know if the umbilical cord is wrapped around your neck?
Signs The Umbilical Cord Is Around Baby's Neck It's visible via ultrasound. Your practitioner can detect a nuchal cord about 70 percent of the time during routine ultrasounds, although it's usually not possible to determine if the cord is short or tight around the neck.
What is the nuchal cord?
. When an umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the neck, the loop is referred to as the nuchal cord. The term “nuchal” relates to the nape or back of the neck.
How many births have nuchal cords?
Tight nuchal cords occurred in about 6.6 percent of nearly 220,000 births that were analyzed by researchers from the Institute for Healthcare Delivery Research, Salt Lake City, UT. There are only rare cases where nuchal cords pose serious risks during labor and delivery.
What happens if you have a nuchal cord?
The most common risk from a nuchal cord is decreased heart rate of the baby during delivery. This is usually the result of reduced oxygen and blood flow through the entangled cord during contractions. Even if there is a decreased heart rate, most babies will still be born healthy.
Why does the umbilical cord wrap around the neck?
Excessive fetal movement may be the main cause of the umbilical cord wrapping itself around the neck. The main cause of a nuchal cord is excessive fetal movement. Other medical reasons why cords may move around the neck of a fetus or may result in loose knots include: increased the chances of complications.
What happens if you find a nuchal cord during a routine ultrasound?
If a nuchal cord is found during a routine ultrasound, it is monitored for the remainder of the pregnancy, and fetal heart rate is watched carefully during labor and delivery.
Can a birthing specialist loosen nuchal cords?
Pregnancy, labor, and delivery. Once labor has started, birthing specialists make no attempts to loosen or unloop nuchal cords, as this could do more harm than good. Moreover, researchers and doctors do not know what effect this would have, and they are careful with intervention.
Is there a connection between stillbirth and nuchal cords?
Research has found little or no connection between stillbirth and nuchal cords, although there has been some speculation about the relationship by researchers in Timisoara, Romania.
What Is a Nuchal Cord?
The umbilical cord is responsible for delivering the oxygen and nutrients your baby needs to grow, as well as for carrying away waste. It’s a flexible tube that contains two arteries and one vein and is coated in a substance called Wharton’s jelly, which helps to protect the blood vessels inside.
What Causes a Nuchal Cord?
The fetal movements your baby makes before they are born is the most common cause of nuchal cords. An extra amount of amniotic fluid, allowing your baby to move around more freely, as well as a longer than average umbilical cord, might also cause your baby to have a nuchal cord.
Are There Risks of a Nuchal Cord?
Nuchal cords happen randomly and are very common. Research suggests they happen in more than one in four births. Type B nuchal cords are less common, with about 2% to 8% of babies born with one.
What is the nuchal cord?
Nuchal cord occurs when the umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the fetal neck 360 degrees. Nuchal cords occur in about 10–29% of fetuses and the incidence increases with advancing gestation age. Most are not associated with perinatal morbidity and mortality, but a few studies have shown that nuchal cord can affect the outcome of delivery with possible long-term effects on the infants. Nuchal cords are more likely to cause problems when the cord is tightly wrapped around the neck, with effects of a tight nuchal cord conceptually similar to strangulation. Umbilical cord compression due to tight nuchal cords may cause obstruction of blood flow in thin walled umbilical vein, while infant’s blood continues to be pumped out of the baby through the thicker walled umbilical arteries causing hypovolemia, acidosis and anemia. Some of these infants have physical features secondary to tight nuchal cords that are distinct from those seen with birth asphyxia. The purpose of this article is to review the pathophysiology of tight nuchal cords and explore gaps in knowledge and research areas.
What are the effects of nuchal cords?
They found that while umbilical venous (UV) pH, pCO2, and oxygen content were not statistically different between the two groups, infants with nuchal cord had significantly lower pH, lower oxygen content, and higher PCO2 levels in their arterial cord gases. The Veno-Arterial (VA) differences in pH and PCO2 of the infants with nuchal cord were greater than that of the infants with no nuchal cords. The study concurred with other studies that Apgar score is not a sensitive indicator of acid-base changes in nuchal cord infants. Umbilical venous blood gases can be misleading in these infants, and therefore umbilical arterial blood must be sampled to detect hypercapnia and diminished oxygen content resulting from a nuchal cord. A significant umbilical arterial acidosis can occur in nuchal cord infants even in the setting of normal or near normal APGAR scores. Belai, et al. [33] showed that APGAR scores correlate very weakly with cord pH when the pH is greater than 7.0. We speculate that the physical features of tCAN syndrome may distinguish perinatal depression due to nuchal cords from other causes of birth asphyxia. Miriam Martinez-Biarge et al. [34] in 2013 in their retrospective analysis to determine whether antepartum factors alone, intrapartum factors alone, or both in combinations, are associated with term neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). A total of 405 infants >35 weeks’ gestation with early encephalopathy, were compared with 239 neurologically normal infants newborns. All cases met criteria for perinatal asphyxia, had neuroimaging findings consistent with acute hypoxia-ischemia, and had no evidence for a non–hypoxic-ischemic cause of their encephalopathy. On logistic regression analysis only 1 antepartum factor (gestation > 41 weeks) and 7 intrapartum factors (prolonged membrane rupture, abnormal cardiotocography, thick meconium, sentinel event, shoulder dystocia, tight nuchal cord, failed vacuum) remained independently associated with HIE (area under the curve 0.88; confidence interval 0.85–0.91; P, .001). Tight nuchal cord was noted in 45/396 cases and 15/237 in control group with odds ratio of 1.89 (1.03–3.5). Their results do not support HIE is attributable to antepartum factors alone, but they strongly point to the intrapartum period as the necessary factor in the development of this condition. It is our speculation that the established terminology ‘Compression Asphyxia’ in forensic medicine [35] could be applied to these infants with tight nuchal cords because of the similarities in their patho-physiological mechanisms and clinical findings. This may help in distinguishing birth asphyxia from infant with the effects of a tight nuchal cord.
What are the symptoms of a tight nuchal cord?
Infants with a tight nuchal cord may develop signs and symptoms such as hypovolemia, hypotension, decreased perfusion and mild respiratory distress. Other findings occasionally noted may include facial duskiness (Fig. 7), facial petechiae (Fig. 8), subconjuntival hemorrhage (Fig. 9), facial suffusion (Fig. 10), or skin abrasion around the neck (Fig. 11) due to tight nuchal cords. Rarely, infants become neurologically depressed or hypotonic with depressed neonatal reflexes. Based on cardio-respiratory and neurological signs and symptoms associated with a tight nuchal cord, one can group the common findings together into a possible syndrome called tight Cord Around the Neck syndrome, or ‘tCAN syndrome. We propose this term as “a cluster of cardio-respiratory and neurological signs and symptoms associated with unique physical features that occurs secondary to tight cord-round-the-neck” [20]. Rarely, there can be significant blood loss, acidosis, and anemia. A few small studies and case reports show nuchal cord as a cause of neonatal anemia. Shepherd, et al. [21] reported anemia in 5 out of 27 (19%) infants with tight nuchal cord. Three infants had hypotension requiring blood transfusion. Asymptomatic anemia as a complication of loose nuchal cords was also described. Vanhaesebroudk, et al. [22] published a case report of two neonates with acute hypovolemic shock requiring blood transfusion, low APGAR scores and umbilical arterial acidosis after tight nuchal cord. The author also noted from personal experience that if the finding in babies with a history of a loose nuchal cord include one or all of the findings such as facial petechiae and a dusky face, subconjuntival hemorrhage and low umbilical arterial cord pH, it is probably a tight nuchal cord at variable period of time prior to delivery. It is also authors’ personal observation that infants with hypermagnesemia due to maternal magnesium sulfate treatment with history of tight nuchal cord show increased risk of apneas and desaturations, possibly due to their combined effect on central nervous system. As of now, there is no scientific evidence supporting these personal experiences.
How many time points are there in nuchal cords?
The incidence of nuchal cords at the four time points studied (Courtesy from Elsevier, with permission)
Where is the congested side of the umbilical cord knot?
Umbilical Cord Knot. Notice the area of congestion to the right. The congested side is always the side between the knot and the placenta (Courtesy from University of Mo. Department of Pathology, with permission)
What causes fetal cord compression?
Nuchal cords can cause cord compression, leading to obstruction of blood flow in the thin walled umbilical vein, while blood continues to be pumped out through the thicker walled umbilical arteries causing hypovolemia, hypotension and fetal hypoxia [22]. There are only few studies that have focused on tight nuchals causing fetal hypoxia. Xu, et al. [27] investigated the value of middle cerebral artery (MCA) and umbilical artery (UA) resistance index in predicting fetal hypoxia in fetuses with umbilical cord around the neck in late pregnancy. Included in this study are measurements of MCA and UA pulsatility index (PI), resistance index (RI), peak systolic and diastolic (S/D) ratios, and resistance index ratios (RIR). RIR showed no significant difference between the no nuchal cord and the 1-loop nuchal cord group (P > 0.05). However, significant differences were noted between the no nuchal cords group and the multiple nuchals group (P < 0.01), and between the ≥2-loops nuchal cord group and the 1-loop nuchal cord group (P < 0.05). One of the conclusions of study is that MCA/UA RIR compared to PI, RI, S/D ratios is a better indicator for predicting fetal hypoxia in nuchal cord infants. Hashimoto, et al. [28] investigated evidence of fetal hypoxia by studying levels of erythropoietin (EPO) in umbilical cord blood and amniotic fluid. Tissue hypoxia is the major stimulus of erythropoietin (EPO) synthesis in fetuses and adults. Previous studies have shown that EPO does not cross the placenta [29], and that plasma EPO levels correlate with the intensity of hypoxia [30]. Cord blood EPO levels increase in acute fetal hypoxia, and amniotic fluid (AF) EPO levels increase in chronic fetal hypoxia. Hashimoto, et al., showed that in the absence of ante/intra partum complications, higher levels of AF-EPO at birth were more predictive of nuchal cord whereas cord blood EPO levels were not found to have any correlation with nuchal cord. Tightness of the nuchal cord did not affect AF or cord blood EPO concentrations. This study concluded that nuchal cords may not significantly increase the risk of acute or labor-associated fetal hypoxia, but are an independent risk factor of mild, chronic, prelabor fetal hypoxia.
What is the nuchal cord?
Nuchal cord refers an abnormal condition when umbilical cord loops around the fetal neck for 360 degrees. Nuchal cord is called single, double or triple nuchal cord depending upon the number of umbilical cord loops wrapped around the neck for ≥360 degrees.
How to diagnose nuchal cord?
In modern times, the nuchal cord can be diagnosed in the majority of the cases through the regular use of ultrasounds. Although earlier ultrasounds were not good enough, however, latest color Doppler’s can detect nuchal cord in more than 80% of cases. Once it has been diagnosed, medical specialists have to make preparations accordingly, in some cases, they may go for cesarean section (C-section) instead of natural birth. In these cases, C-section has to be performed quickly and with particular skills so that to avoid making ischemia worse. Further, after the birth, there is often the need for extra care in a child with a nuchal cord antecedent.
How Is Nuchal Cord Diagnosed?
In ultrasound, the physician would pay particular attention to the location or position of the umbilical cord, and nuchal cord would be diagnosed if it is seen encircling three-quarter of the neck. If a physician sees that umbilical cord only encircles half of the neck than the situation would be called suspicious, it means that there is a need for further investigations. It must be understood that at present there is no 100% sensitive method of nuchal cord detection. Moreover, diagnoses may be missed if nuchal cord happens late in the pregnancy. At present, the chances of nuchal cord detection in grayscale ultrasound are not more than 70%, though color Doppler’s are much more effective and may detect nuchal cord in 80-90% of situations.
What is the incidence of nuchal cord?
The incidence of nuchal cord varies with gestational age and associated risk factors. On average, its incidence is 10-29%, which increases with advancing gestation age.
Why is it so hard to predict nuchal cord?
One of the reasons why this matter is so difficult to predict is the considerable variance in length and circumference of the umbilical cord. Moreover, this situation evolves notoriously during the pregnancy. In most cases, as already mentioned, the umbilical cord is about half a meter.
How long is the umbilical cord during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, umbilical cord develops from the remnants of yolk sac and allantois by the fifth week of fetal development. On average, umbilical cord is 55 cm long with diameter of 1-2 cm. It works as a conduit or passage between fetus and placenta, comprising of two arteries and a vein.
What happens if the umbilical cord is wrapped around the neck?
If it gets too tight in wrapping the neck, it may reduce the blood flow through the veins, which means that a child would not get enough of oxygen and other vital nutrients and thus affect child’s growth. Further, as one can imagine that giving birth to a child with the umbilical cord encompassing the neck similar to a rope is not an easy task and there is a risk of severe asphyxia and damage to the brain (cerebral palsy).
What is the nuchal cord?
A nuchal cord is a complication that occurs when the umbilical cord wraps around the baby’s neck one or more times. This is common and occurs in about 15 to 35 percent of pregnancies.
How to identify nuchal cord?
To identify a nuchal cord, physicians look at multiple views of the fetal neck. A nuchal cord is diagnosed when the umbilical cord is seen encircling at least three-quarters of the fetal neck. At term, the sensitivity of ultrasound for detecting nuchal ...
What happens when medical professionals detect a nuchal cord?
During prenatal testing, a nuchal loop may be recognized with an ultrasound or it may be suspected if the baby is showing signs of distress during a nonstress test or biophysical profile.
How to prevent umbilical cord compression?
A loose nuchal cord can usually be easily slipped over the baby’s head to decrease traction during delivery of the shoulders or body. If this is not possible due to tightness, there is a technique wherein the physician may be able to slip the cord over the infant’s shoulders and deliver the baby through the loop. If this is also not possible, the physician may use the somersault technique, which allows the shoulders and body to be born in a somersault, with the cord being unwrapped after the baby is delivered.
What is the term for the cord that connects to the placenta?
When the end of the umbilical cord connected to the placenta crosses over the end connected to the baby. This may be called an “unlocked” nuchal cord , and is likely to spontaneously disentangle when the baby moves in-utero.
What is the role of the umbilical cord in the fetal body?
The umbilical cord is responsible for supplying the baby with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood, and carrying deoxygenated, nutrient depleted blood back to the placenta. If a nuchal cord interferes with these processes by compressing the umbilical cord, or restricts arteries and veins in the fetal neck, ...
How does the umbilical cord affect a baby?
Additionally, the umbilical cord may become compressed against itself or the fetal neck, which reduces the flow of oxygenated blood through the umbilical cord.
What is the nuchal cord?
Nuchal cord. A nuchal cord is when the umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the fetus 's neck. Symptoms present in the baby shortly after birth from a prior nuchal cord may include duskiness of face, facial petechia, and bleeding in the whites of the eye. Complications can include meconium, respiratory distress, anemia, and stillbirth.
How to manage a nuchal cord?
Management of a presenting nuchal cord should be tailored to prevent umbilical cord compression whenever possible. Techniques to preserve an intact nuchal cord depend on how tightly the cord is wrapped around the infant’s neck. If the cord is loose, it can easily be slipped over the infant’s head. The infant can be delivered normally and placed on maternal abdomen as desired. If the cord is too tight to go over the infant’s head, the provider may be able to slip it over the infant’s shoulders and deliver the body through the cord. The cord can then be unwrapped from around the baby after birth. Finally, if the cord is too tight to slip back over the shoulders, one may use the somersault maneuver to allow the body to be delivered. The birth attendant may also choose to clamp and cut the umbilical cord to allow for vaginal delivery if other methods of nuchal cord management are not feasible.
What to do if the umbilical cord is too tight?
Finally, if the cord is too tight to slip back over the shoulders, one may use the somersault maneuver to allow the body to be delivered. The birth attendant may also choose to clamp and cut the umbilical cord to allow for vaginal delivery if other methods of nuchal cord management are not feasible.
How many nuchal cords were detected in women?
A nuchal cord was diagnosed if the cord was visualized lying around at least 3 of the 4 sides of the neck. A cord was actually present at delivery in 52 of the 289 women. Only 18 of the 52 cords or 35% of the nuchal cords were detected on ultrasound done immediately before delivery, and 65% of nuchal cords were not detected.
What is the prognosis of a nuchal cord?
Prognosis. Usually good. Frequency. 25% of deliveries. A nuchal cord is when the umbilical cord becomes wrapped around the fetus 's neck. Symptoms present in the baby shortly after birth from a prior nuchal cord may include duskiness of face, facial petechia, and bleeding in the whites of the eye.
How to check nuchal cords?
Nuchal cords are typically checked for by running the finger over the baby's neck once the head has delivered. Ultrasound may pick up the condition before labor. If detected during delivery, management includes trying to unwrap the cord or if this is not possible clamping and cutting the cord.
What are the complications of a nuchal cord?
Complications can include meconium, respiratory disease, anemia, and still birth. Petechiae and subconjunctival bleeding due to tight nuchal cord. Petechiae on face due to tight nuchal cord. Facial duskiness due to tight nuchal cord. Abrasion from a nuchal cord.
What is the nuchal cord?
The term “nuchal cord” refers to a condition in which the umbilical cord is wrapped around the fetus’s neck. Diagnosis requires only 75 percent of the neck to have cord around it, as 360-degree imaging in utero may not be possible. There are three ways of classifying nuchal cords: First, based on how many times the cord is wrapped around ...
How common are nuchal cords?
Nuchal cords are common. At term, incidence estimates have ranged from 15 to 34 percent. Of course, most of these babies are born healthy, so it may be tempting to dismiss nuchal cords as no cause for concern. However, many of these babies have nuchal cords resolve on their own prior to delivery, or that doctors can easily maneuver away from ...
What causes oxygen deprivation in the nuchal cord?
Nuchal cords can cause oxygen deprivation/asphyxiation. One way this happens is that the cord essentially strangles the fetus, causing restriction of carotid artery blood flow and/or venous congestion. Another is that the umbilical cord itself becomes compressed (against itself or the fetus’s neck), preventing flow of oxygenated blood through the umbilical cord vessels.
How to deliver a nuchal cord?
It may also be possible to move the cord down over the shoulders and deliver the baby through the loop. If the head has already been delivered and the cord is too tight to slip over the head or shoulders, doctors may attempt a “somersault delivery.” They push the baby’s head toward the mother’s thigh (as opposed to pulling the baby straight down). This allows the shoulders and the rest of the body to be born in a somersault, and keeps the neck near the birth canal so that the nuchal cord is not stretched and further tightened. They can then unwrap the nuchal cord. If this maneuver is unsuccessful, they may have to clamp and cut the cord earlier than is generally recommended. This can put the fetus at risk of anemia and other problems. In cases where a tight nuchal cord is diagnosed prior to delivery, especially if there are accompanying signs of fetal distress, medical professionals should order an emergency C-section. Not doing so would be negligent.
What is the name of the cord that is wrapped around the fetal neck?
First, based on how many times the cord is wrapped around the fetal neck: single nuchal cord, double nuchal cord, etc.
Why do somersaults keep the neck near the birth canal?
This allows the shoulders and the rest of the body to be born in a somersault, and keeps the neck near the birth canal so that the nuchal cord is not stretched and further tightened. They can then unwrap the nuchal cord.
What are the effects of nuchal cords?
Nuchal cords can also lead to conditions such as cerebral palsy, seizures, intellectual and developmental disabilities, and more.