Are municipal bonds a good investment?
On the plus side, highly-rated municipal bonds are generally very safe investments compared to almost any other investment. The default rate is tiny. As with any bond, there is interest rate risk. If your money is tied up for 10 or 20 years and interest rates rise, you'll be stuck with a poor performer.
What are the best municipal bonds?
iShares National Muni Bond ETF (ticker: MUB) This national municipal bond fund is one of the most popular, with access to more than 4,800 U.S. muni bonds. With MUB's $23.7 billion in assets under...
What is the value of a bond at maturity?
When a bond matures, the bond issuer repays the investor the full face value of the bond. For corporate bonds, the face value of a bond is usually $1,000 and for government bonds, the face value is...
What are municipal bonds?
Municipal bonds are issued by states and local municipalities to finance the construction of roads, schools and other infrastructure. The interest they earn is usually exempt from federal income taxes, and if issued in the town or state you reside may be exempt from state and local taxes as well.

What is the average rate of return on municipal bonds?
With yields as high as they are, municipal bond funds offer a buffer against yields rising even further. A muni bond fund with a yield of 2.79% and a duration of 6 years, would still provide a positive return for the next 12 months even if yields were to rise another 40 basis points across the curve.
What is a good municipal bond rating?
Generally, BBB- or higher are investment grade ratings (for less risky bonds), while lower than BBB- are non-investment grade ratings (for riskier bonds). The terms “speculative” or “high yield” might be used instead of non-investment grade. Some of the ratings above may be modified with a “+”, “-” or a number.
What happens when a municipal bond matures?
When you buy a municipal bond, you are loaning money to the issuer in exchange for a set number of interest payments over a predetermined period. At the end of that period, the bond reaches its maturity date, and the full amount of your original investment is returned to you.
What is the downside of municipal bonds?
The only real disadvantage of municipal bonds is that they carry relatively low interest rates compared to other types of securities. This is particularly true when the economy is strong and interest rates for Treasury bills and CDs rise.
Are municipal bonds a good investment?
Municipal or corporate bonds are a great alternative for investors who want to create a reliable stream of income, particularly during their retirement years. Highly-rated bonds are by their nature very safe investments compared to almost any other alternative and especially compared to stocks.
How often do municipal bonds pay interest?
every six monthsMunicipal Bonds and Their Tax Advantages Bond interest typically is paid every six months (though some types of bonds work differently); interest on notes is usually paid at maturity.
How long do you have to hold municipal bonds?
Most munis are sold in minimum increments of $5,000 and have maturities that range from short term (2 – 5 years) to very long term (30 years)....Municipal Securities Snapshot.IssuerStates, cities, counties and other governmental entitiesMinimum InvestmentGenerally $5,0006 more rows
When a bond matures How much is it worth?
When a bond matures, the bond issuer repays the investor the full face value of the bond. For corporate bonds, the face value of a bond is usually $1,000 and for government bonds, the face value is $10,000.
What happens to municipal bonds when interest rates rise?
Bonds and interest rates have an inverse correlation: as interest rates increase, bond prices fall.
Can you lose money on municipal bonds?
The Bottom Line. If you are investing for income, either municipal bonds or money market funds will pay you interest. Just know that bonds can lose value and money market funds most likely won't. Note also that since municipal bonds are income-tax free, you are actually making more than the interest rate would indicate ...
Can I cash out municipal bonds?
You can redeem a matured bond at your local financial institution or through the municipality itself. You also have the option to sell the bond before it matures on a secondary market, and you may be forced to redeem the bond if the municipality calls it.
Do you pay federal tax on municipal bonds?
Income from bonds issued by state, city, and local governments (municipal bonds, or munis) is generally free from federal taxes.
What are AAA rated municipal bonds?
“Aaa” - Issuers or issues rated Aaa demonstrate the strongest creditworthiness relative to other U.S. municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues. “Aa” - Issuers or issues rated Aa demonstrate very strong creditworthiness relative to other U.S. municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
What are high yield municipal bonds?
High yield municipal bonds are primarily project bonds These revenue bonds tend to offer higher yields to compensate investors for the risk and uncertainty associated with the project's revenue stream.
Which of the following ratings would be the highest rating for a municipal note?
MIG stands for Moody's Investment Grade and refers to ratings given municipal notes. There are three MIG ratings, with the best rating being MIG 1 and the lowest rating being MIG 3. Aaa is Moody's best rating for bonds, and C is its lowest rating for bonds.
What type of bond has an AA+ or Aa1 rating?
How bond ratings workMoody'sStandard & Poor'sFitchAaaAAAAAAAa1AA+AA+Aa2AAAAAa3AA-AA-6 more rows
What are some of the risks of investing in municipal bonds?
As with any investment, investing in municipal bonds entails risk. Investors in municipal bonds face a number of risks, specifically including:
What is call risk on a bond?
Call risk. Call risk refers to the potential for an issuer to repay a bond before its maturity date, something that an issuer may do if interest rates decline -- much as a homeowner might refinance a mortgage loan to benefit from lower interest rates. Bond calls are less likely when interest rates are stable or moving higher. Many municipal bonds are “callable,” so investors who want to hold a municipal bond to maturity should research the bond’s call provisions before making a purchase.
What is credit risk?
Credit risk. This is the risk that the bond issuer may experience financial problems that make it difficult or impossible to pay interest and principal in full (the failure to pay interest or principal is referred to as “default”). Credit ratings are available for many bonds.
How long does a municipal bond last?
Short-term bonds mature in one to three years, while long-term bonds won’t mature for more than a decade. Generally, the interest on municipal bonds is exempt from federal income tax. The interest may also be exempt ...
What are the different types of municipal bonds?
The two most common types of municipal bonds are the following: 1 General obligation bonds are issued by states, cities or counties and not secured by any assets. Instead, general obligation are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the issuer, which has the power to tax residents to pay bondholders. 2 Revenue bonds are not backed by government’s taxing power but by revenues from a specific project or source, such as highway tolls or lease fees. Some revenue bonds are “non-recourse”, meaning that if the revenue stream dries up, the bondholders do not have a claim on the underlying revenue source.
What does a credit rating mean?
Credit ratings seek to estimate the relative credit risk of a bond as compared with other bonds, although a high rating does not reflect a prediction that the bond has no chance of defaulting. Interest rate risk. Bonds have a fixed face value, known as the “par” value.
What is revenue bond?
Revenue bonds are not backed by government’s taxing power but by revenues from a specific project or source, such as highway tolls or lease fees. Some revenue bonds are “non-recourse”, meaning that if the revenue stream dries up, the bondholders do not have a claim on the underlying revenue source.
What Are Municipal Bonds?
Municipal bonds (munis) are debt obligations issued by government entities. When you buy a municipal bond, you are loaning money to the issuer in exchange for a set number of interest payments over a predetermined period. At the end of that period, the bond reaches its maturity date, and the full amount of your original investment is returned to you.
What is the default rate on municipal bonds?
The most recent study covers defaults from 1970 to 2020. 5 Over the past 10 years, the average default rate for investment grade municipal bonds was 0.10%, compared with a default rate of 2.25% for similarly rated corporate bonds. 6
How many municipal bonds were defaulted in 2017?
Nevertheless, municipal bonds defaults are not uncommon. There were 10 defaults in 2017, seven of which were associated with Puerto Rican debt crisis. A record $31.15 billion in bonds were in default that year, up 15% from 2016. 7
How to generate income from bond portfolio?
Investors seeking to generate both income and capital appreciation from their bond portfolio may choose an active portfolio management approach, whereby bonds are bought and sold instead of held to maturity. This approach seeks to generate income from yields and capital gains from selling at a premium.
What is a BBB bond?
Bonds rated 'BBB', 'Baa', or better are generally considered appropriate investments when capital preservation is the primary objective . To reduce investor concern, many municipal bonds are backed by insurance policies guaranteeing repayment in the event of default .
What is a ladder bond?
A ladder consists of a series of bonds, each with a different interest rate and maturity date. As each rung on the ladder matures, the principal is reinvested into a new bond. Both of these strategies are categorized as passive strategies because the bonds are bought and held until maturity.
What are the factors that affect the price of municipal bonds?
Changes in interest rates and interest rate expectations are generally the primary factors involved in municipal bond secondary market prices. When interest rates fall, newly issued bonds will pay a lower yield than existing issues, which makes the older bonds more attractive.
What happens when a conduit borrower fails to pay?
In cases where the conduit borrower fails to make a payment, the issuer usually is not required to pay the bondholders. INTRODUCTION TO THE MUNICIPAL BOND MARKET.
What are the different types of municipal bonds?
The two most common types of municipal bonds are the following: 1 General obligation bonds are issued by states, cities or counties and not secured by any assets. Instead, general obligation are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the issuer, which has the power to tax residents to pay bondholders. 2 Revenue bonds are not backed by government’s taxing power but by revenues from a specific project or source, such as highway tolls or lease fees. Some revenue bonds are “non-recourse”, meaning that if the revenue stream dries up, the bondholders do not have a claim on the underlying revenue source.
How long does a municipal bond last?
Short-term bonds mature in one to three years, while long-term bonds won’t mature for more than a decade. Generally, the interest on municipal bonds is exempt from federal income tax. The interest may also be exempt ...
What happens when you buy municipal bonds?
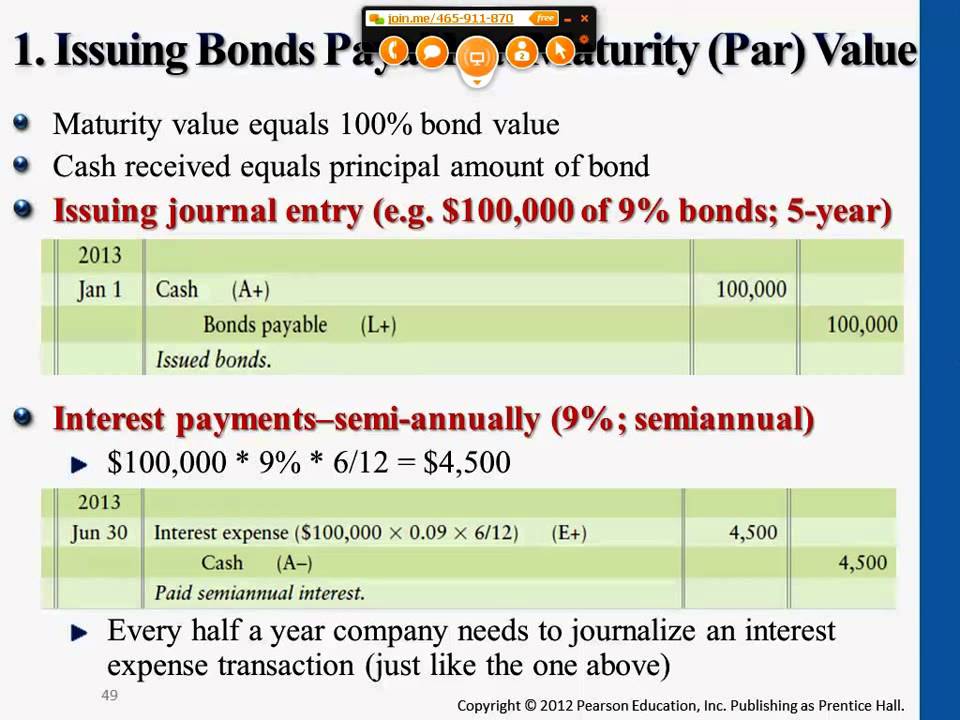
By purchasing municipal bonds, you are in effect lending money to the bond issuer in exchange for a promise of regular interest payments, usually semi-annually, and the return of the original investment, or “principal.”.
What is a general obligation bond?
General obligation bonds are issued by states, cities or counties and not secured by any assets. Instead, general obligation are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the issuer, which has the power to tax residents to pay bondholders.
What is revenue bond?
Revenue bonds are not backed by government’s taxing power but by revenues from a specific project or source, such as highway tolls or lease fees. Some revenue bonds are “non-recourse”, meaning that if the revenue stream dries up, the bondholders do not have a claim on the underlying revenue source.
Is municipal bond interest taxable?
Generally, the interest on municipal bonds is exempt from federal income tax. The interest may also be exempt from state and local taxes if you reside in the state where the bond is issued. Bond investors typically seek a steady stream of income payments and, compared to stock investors, may be more risk-averse and more focused on preserving, rather than increasing, wealth. Given the tax benefits, the interest rate for municipal bonds is usually lower than on taxable fixed-income securities such as corporate bonds.
Why is the bond markup ruling controversial?
One reason why this new ruling could cause controversy is that bond investors never knew how much markup is actually bundled into their purchase price. Unlike stock commissions that have a flat fixed rate, bond markups can be adjusted up or down and have no real guideline.
What happens if there are no trades of the same security?
If there are no trades of the same security, then the dealer must look at similar securities that are of the same credit quality, issue size or comparable yield.
Why is it important to know the price of a bond?
It becomes especially important for muni bond transactions wherein, because of the large number of issues and liquidity concerns, retail investors rely on their brokers to a large extent on pricing their securities.
What is confirmation of trade?
In the past, every time a retail client would buy or sell a municipal bond, the confirmation of trade would include the final aggregate price for the transaction. This price would include the markup or commission the broker would receive. With the new changes, confirmations are required to show the total dollar amount of the markup and the percentage of the markup in relation to the bond purchase price. In addition to the markup information, the new rule requires the time of the trade and a reference or hyperlink to the Electronic Municipal Market Access ( EMMA )’s website.
What does a dealer do when there are no similar trades?
If there are no similar trades, then the dealer must expand its search to look at interdealer trades, deals done between other dealers and institutions, or trades on electronic trading platforms.
What is the waterfall method?
In the new rule, the SEC discloses the layout of how a dealer is to determine what the Prevailing Market Price of a particular bond is. This analysis is called the Waterfall method and is described through three steps.
How does the bond ruling affect retail investors?
A key impact for retail investors that this ruling will have is that dealers should be much more inclined to give the best possible pricing for the bond, knowing that clients can easily research it for themselves. This will most likely also limit the amount of markup that dealers add to bond transactions, and eventually, to a much more uniform amount. For example, prior to this ruling, clients had no idea how much markup they were getting on bond deals. Now that the information is transparent, this should provide a more fair and reasonable markup amount.
What Is Average Effective Maturity?
For a single bond, the average effective maturity (AEM) is a measure of maturity that takes into account the possibility that a bond might be called back by the issuer.
How long does a bond portfolio last?
A bond portfolio consists of several bonds with different maturities. One bond in the portfolio could have a maturity date of 20 years, while another could have a maturity date of 13 years. The maturity at the time of issuance will decline as the maturity date approaches.
What is callable bond?
Callable bonds allow the issuer to redeem them prior to the stated maturity, thus having lower average effective maturities than stated. Knowing the likelihood that a bond may be called is crucial to computing average effective maturity.
What is AEM in bond?
For a single bond, the average effective maturity (AEM) is a measure of maturity that takes into account the possibility that a bond might be called back by the issuer. For a portfolio of bonds, average effective maturity is the weighted average of the maturities of the underlying bonds.
How long does a bond last in 2018?
In 2018, the maturity date of the bond will decline to 12 years. Over the years, the maturity of the bonds in a portfolio will decline, assuming the bonds are not swapped for newer issues. The average effective maturity is computed by weighting each bond's maturity by its market value with respect to the portfolio and the likelihood of any ...
Why is weighted average maturity important?
The weighted average maturity of the portfolio is essential to knowing the interest rate risks faced by that portfolio. For instance, longer-maturity funds are generally considered more interest-rate sensitive than their shorter counterparts.
How long does it take for a bond to mature?
On average, the bonds in the portfolio will mature in 14.5 years.