
What can a vacuole be compared to?
What can a vacuole be compared by in a house? The vacuole is like a refrigerator because the vacuole stores materials for later use in the same way a refrigerator stores food. If babies are consistently placed on their backs without any restrictions, what will happen to their development?
What would a vacuole be in a factory?
Vacuoles (Storage Compartments) In a factory, there are many materials that must be stored until they’re ready to be used. Or, in case of trash, it gets stored until it’s ready to be thrown in the dumpster outside. Cells have storage compartments, too. They are called vacuoles. Vacuoles can hold food and water that the cell is not using yet.
What does a vacuole do inside of a cell?
Vacuoles maintain the acidic internal pH of the cell. What the vacuole does in the cell is mainly to export unwanted substances from the cell. As a result of the turgor pressure of the central vacuole, plants are able to support structures such as leaves and flowers.
What is a good analogy for a vacuole?
What are 3 examples of cells?
- Epithelial Cells. These cells are tightly attached to one another.
- Nerve Cells. These cells are specialized for communication.
- Muscle Cells. These cells are specialized for contraction.
- Connective Tissue Cells.
How are vacuoles made?
Vacuoles are formed when vesicles, released by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex, merge together. Newly developing plant cells typically contain a number of smaller vacuoles. As the cell matures, a large central vacuole forms from the fusion of smaller vacuoles.
What is the structure of a vacuole?
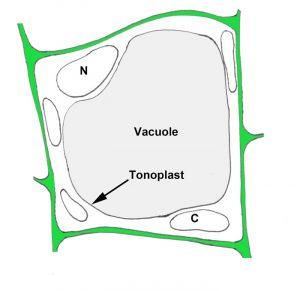
Structure of Vacuole A vacuole is a membrane bound structure found in the cytoplasmic matrix of a cell. The membrane surrounding the vacuole is known as tonoplast. The components of the vacuole, known as the cell sap, differ from that of the surrounding cytoplasm. The membranes are composed of phospholipids.
How many membranes are present in vacuoles?
Answer. Each vacuole is separated from the cytoplasm by a single unit membrane, called the tonoplast.
What do vacuoles look like?
A vacuole looks a lot like a water balloon. There's a thin outer layer, called a membrane, holding everything in. Vacuoles collect and hold onto all sorts of materials for a cell, including food and water.
What is the structure and function of the central vacuole?
The central vacuole is a cellular organelle found in plant cells. It is often the largest organelle in the cell. It is surrounded by a membrane and functions to hold materials and wastes. It also functions to maintain the proper pressure within the plant cells to provide structure and support for the growing plant.
What is the structure of the organelle?
An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell, much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei, which store genetic information; mitochondria, which produce chemical energy; and ribosomes, which assemble proteins.
What is the structure of a vesicle?
A vesicle is a self-contained structure consisting of fluid or gas surrounded and enclosed by an outer membrane called the lipid bilayer. This is made up of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails that cluster together.
What is the main function of the vacuole?
Summary: Vacuole Definition A vacuole is an organelle that is found in many types of cells, including animal, plant, fungi, bacteria, and protist cells. The main vacuole function is to store substances, typically either waste or harmful substances, or useful substances the cell will need later on.
Vacuole Definition
A vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials. This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted, and those that have been phagocytized, or engulfed, by the cell.
Vacuole Structure
A vacuole has a broad definition, and includes a variety of membrane-bound sacs. The membranes are composed of phospholipids, but each organism may use slightly different phospholipids. Embedded in the membranes are proteins, which can function to transport molecules across the membrane or give it structure.
Functions of a Vacuole
In plants, a large vacuole occupies the majority of the cell. This vacuole is surrounded by the tonoplast, a type of cytoplasmic membrane that can stretch and fills itself with a solution known as cell sap. The vacuole also fill itself with protons from the cytosol, creating an acid environment inside of the cell.
Related Biology Terms
Vesicle – A smaller version of a membrane-bound vacuole, many of which can converge to make a vacuole.
Quiz
1. In some photosynthetic bacteria, known as cyanobacteria, a large portion of the cell in taken up by a gaseous space. The membrane surrounding the space is only permeable to gases, and as such, no cytosol can enter the space. This accumulates gas in the space, and helps the cyanobacteria float.
What Is a Vacuole? Understanding the 4 Main Functions
What is a vacuole and what does it do? A vacuole is a structure found in animal, plant, bacteria, protist, and fungi cells. It’s one of the largest organelles found in cells, and it’s shaped like a large sac. Vacuoles have a simple structure: they are surrounded by a thin membrane and filled with fluid and any molecules they take in.
The 4 Main Vacuole Functions
What does the vacuole do? The main function of vacuoles is to hold various substances and molecules; they basically act like the storage unit of the cell. Below are some key vacuole functions, many of which relate to storing materials that the cell will need later on or which can damage the cell and therefore need to be removed:
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Animal Cells
Vacuoles in animal cells mostly store substances; they aren’t needed as much for breaking down substances because lysosomes, another organelle in animal cells, do that. Animal cell vacuoles are typically small, and each cell can contain multiple vacuoles. Vacuoles can store different substances depending on the type of cell they are in.
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Plant and Fungi Cells
Unlike animal cells, plant cells typically contain only one vacuole per cell (often referred to as a “central vacuole”), and the vacuole they contain is much larger than those in animal cells. Plant cell central vacuoles take up an enormous percentage of the cell, sometimes over 90% of cell space, although 30-50% is more common.
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Bacteria Cells
Not all types of bacteria have cells that contain vacuoles, but for those that do, they are mostly used for storage. Vacuoles are especially large in some species of sulfur bacteria; in these bacteria the vacuoles can take up as much space or more as vacuoles in plant cells do, up to 98% percent of the cell’s area.
Structure and Function of Vacuoles in Protist Cells
Protists contain a specific type of vacuole called a contractile vacuole. Instead of being used for storage, this vacuole regulates the amount of water in a cell (known as “osmoregulation”). Protists that live in freshwater can take too much water into their cells, causing them to rupture.
Summary: Vacuole Definition
A vacuole is an organelle that is found in many types of cells, including animal, plant, fungi, bacteria, and protist cells. The main vacuole function is to store substances, typically either waste or harmful substances, or useful substances the cell will need later on.
