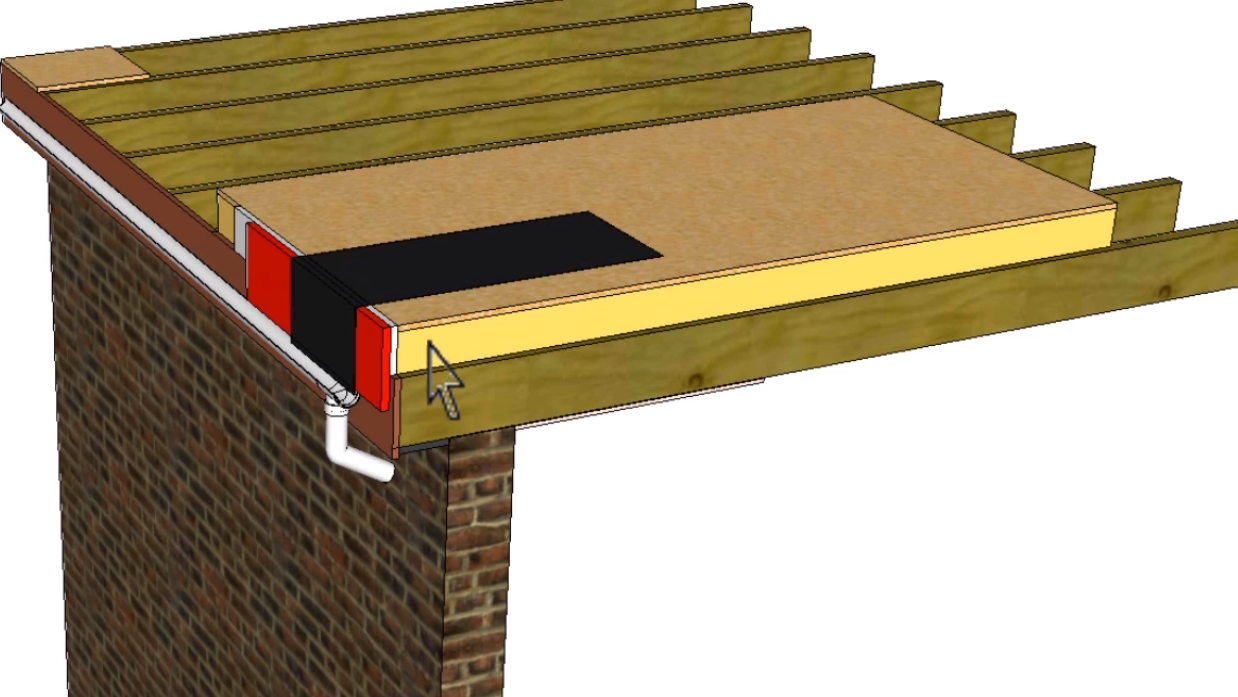
A vapour control layer or VCL on a warm flat roof sits between the roof decking and the insulation. A vapour control layer helps you shield your building from the consequences of condensation. Condensation is generated when warm moist air rises and condenses into a liquid on contact with the cooler areas above the insulation.
What is damplas vapour control layer?
Damplas Vapour Control Layer (VCL) is intended for use within Flat Roof structures to prevent the penetration of moisture into structure surfaces and to improve the airtightness of buildings. The VCL also restricts the movement of warm moist air and improves building insulation. The Vapour Barrier is suitable for both warm and cold Deck designs
What is a VCL on a flat roof?
A VCL on a warm flat roof sits between the roof decking and the insulation. A polythene vapour control layer limits the movement of air and water vapour through a membrane, so a vapour control layer is air permeable, or vapour permeable.
What is a vapour control layer?
A vapour control layer helps you protect your building from the consequences of condensation. Condensation is formed when warm moist air penetrates the building fabric and then condenses into a liquid on contact with the colder surfaces outside the insulation layer.
Do I need a vapour barrier for my roof?
Vapour barriers can still be useful though. One of the few places above ground level where a complete vapour barrier should be used is in flat roofing when using foil-faced PIR insulation. In this case, you need to lay a full vapour barrier on top of your flat roof deck before you lay the insulation and your flat roof covering.
What is a vapour control layer (VCL)?
How do I maintain my vapour control layer when installing services in a wall with Celotex PL4000?
Do Celotex make vapour control layers?
Do I need a VCL in solid ground floors?
What is the purpose of scrim tape on plasterboard?
What are the advantages of VCL?
Why is VCL important?
See 4 more

Do you need a vapour barrier on a flat roof?
Vapour barriers are especially important as a part of flat roof construction on commercial buildings. Water vapour that penetrates roof materials can cause considerable damage, including: Corrosion of steel materials.
What is a vapor control layer?
A Vapour Control Layer, or VCL for short, is a plastic layer that restricts the movement of warm, moist air from inside a property into the fabric of the building. VCLs prevent excess moisture entering a wall's cavity, behind the insulation.
How do I fix the vapour control layer?
0:201:29How do you install a Vapour Control Layer? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe're going to overlap another piece over the top. And all the joints have to be taped. Well sealedMoreWe're going to overlap another piece over the top. And all the joints have to be taped. Well sealed so we're using the amber cold tape.
Do you need a vapour control layer?
Vapour control layers are always required whenever you insulate, irrespective of the insulation used. They should be used to form a continuous airtight layer and so all the joints and any penetrations must always be sealed with the appropriate airtightness tapes.
How thick is a vapour control layer?
The thickness of VCLs ranges from a simple single layer polythene VCL at 500 gauge, which is 125 microns or 0.125mm thick, to high performance, multi layered, bitumen lined, foil faced VCLs.
Is a vapour control layer waterproof?
A vapour barrier is typically sheet with a waterproof film which prevents warm, humid indoor air from condensing by keeping it from touching the cooler outer layer.
How do you stop condensation on a flat roof?
Preventing condensation with multifoil insulation Installing a good vapour barrier underneath the rafters in a roof will prevent warm air from entering the roof void from below. Multifoil insulation has shiny, reflective layers to keep heat inside the building, ensuring no risk of condensation.
Is vapour barrier same as DPM?
While vapour barriers and vapour checks stop or control the moisture inside a building from creeping into the walls, a damp-proof membrane has a different job. DPM is used under floors to prevent damp from rising up into the building and causing rising damp.
Will a vapour barrier stop condensation?
In order to prevent condensation from forming, a vapor barrier should be placed on the warm side of your insulation to stop warm, moist air from condensing on a cold surface inside your wall.
Is vapour control layer breathable?
VCL is a collective term for materials used to control the passage of moisture So in theory, it can be used to describe both breathable membranes and Vapour Barriers which are 2 very different materials. However, you will usually find that VCL is used specifically to describe a vapour barrier.
Is the foil on PIR insulation a vapour barrier?
Assuming it's foil faced PIR boards then the foil is a vapour barrier in itself, just tape the joins with foil tape.
Does foil insulation stop condensation?
Foil insulation helps prevent condensation by blocking warm air from entering a space. Condensation is caused when hot air meets cold air and particles can no longer hold onto water molecules. Because foil insulation reflects warm air from entering, a mixture of hot air and cold air cannot create condensation.
What is the difference between a vapour control layer and a breather membrane?
The answers in the names: vapour control layer stops water vapour getting into the wall from the inside of the structure. Breather membrane keeps water from getting into the wall from the outside but allows any water vapour that is in there to escape.
Is vapour control layer breathable?
VCL is a collective term for materials used to control the passage of moisture So in theory, it can be used to describe both breathable membranes and Vapour Barriers which are 2 very different materials. However, you will usually find that VCL is used specifically to describe a vapour barrier.
Is foil backed plasterboard a vapour barrier?
Foil Backed Plasterboard utilises a thin foil backing to provide excellent vapour resistance. The foil acts as a powerful barrier that limits moisture diffusion and prevents creeping damp.
Does insulated plasterboard have a vapour barrier?
Moisture resistant Insulated Plasterboard is backed with rigid polyisocyanurate foam and two vapour barriers which are specially designed to use in wall linens and internal wall partitions.
When to Use Vapour Control Layers - Knowledge Hub - Fast Build
A vapour control layer (VCL) is a plastic layer or membrane that restricts the transition of warm, moist air from inside a property into the fabric of the building.
6.2.12 Vapour control layers - NHBC Standards 2022
500 gauge (120 micron) polyethylene sheet, vapour control plasterboard or a product assessed in accordance with Technical Requirement R3; adequately fixed to the warm side of the insulation and frame (framing timbers should have a moisture content of less than 20%)
VCL with insulated plasterboard - Damp & DPCs - BuildHub.org.uk
It's OK behind the insulated PB, as the main thing is to position the VCL to stop vapour from inside the house reaching parts of the structure where it could drop below dew point, and so allow interstitial condensation from water vapour movement from inside the house.
Is A Vapour Control Layer Needed For A Flat Roof?
The need for a vapour control layer; whether a vapour barrier or vapour check is dependent on the way in which the building in question is to be used. Below we will look at a variety of different buildings and discuss how their typical conditions impact the need of a vapour control layer for a flat roof.
Changing The Use Of A Building
Moisture gain analysis will help guide those who want to make allowances for a building which is changing its purpose to be something involving high humidity conditions. Installing an efficient vapour barrier is an expensive precaution, but in most conditions a vapour check is unlikely to be adequate.
Installing A Vapour Control Layer
An efficient vapour barrier needs to have bonded overlaps and penetrations should be effectively sealed. Precautions should be taken to make sure the vapour barrier is isolated from the buildings movements to ensure its integrity remains throughout it's surface life. Sometimes this will mean a partially-bonded two-layer barrier is required.
Choosing A Vapour Control Layer
The material used to form the vapour check or barrier, and their method of attachment will depend upon the substrate which they are to be used on. The types of decks are as follows:
Want To Know More About Vapour Control Layers?
If you would like RJ Evans to provide any information related to vapour control layers, please contact us or call us now on 01277 375 511. One of our friendly flat roofing specialists will be delighted to help.
What are the Layers in a Flat Roof?
The answer that we give is usually fairly generic: It consists of multiple layers from the ceiling to insulation to vapour control layer to insulation to the final top membrane. In this article, we will try to break it down to a more detailed version for you. Remember though that each flat roofing system has different layers. That means an EPDM flat roof will have a slightly different layering methodology than a tar and gravel one.
What is the waterproofing layer on a roof?
1) On the very top you have the waterproof membrane. This is the EPDM, TPO, Mod Bit, PVC, Tar and Gravel or whatever layer you choose on. It is the primary waterproofing layer and is the only layer you should see on your roof.
Why are vapour control layers used?
Vapour control layers are also airtight and generally used as an airtight layer to make buildings airtight.
Why do we need a vapour barrier?
In the UK until relatively recently an impervious full vapour barrier was used on the inner face of a timber frame and was thought to prevent condensation formation by simply blocking the flow of moisture-laden air through the wall. However, it has since been found that not only are vapour barriers regularly full of holes which let moisture through during the winter months, they also cause the accumulation of moisture inside the wall during the summer months by preventing moisture escaping towards the interior of the building.
Why do we use VCLs?
A VCL is always used as close to the inner face of a wall as possible and reduces the amount of moisture passing through the layer to low levels, ensuring only insignificant amounts of condensation occur within the structure. Additionally, VCLs will allow moisture that is driven towards the interior in the summer months to slowly pass back inside ...
How to keep a timber frame roof dry?
The answer to keeping timber-framed walls and roofs dry is to use a layer to restrict the flow of moisture but not to try and stop it. This is known as a vapour control layer (VCL) or a vapour retarder. A VCL is always used as close to the inner face of a wall as possible and reduces the amount of moisture passing through the layer to low levels, ensuring only insignificant amounts of condensation occur within the structure. Additionally, VCLs will allow moisture that is driven towards the interior in the summer months to slowly pass back inside the building. This prevents the conditions for mould forming and ensures the longevity of the structure.
Why is it important to prevent condensation in walls?
It is therefore very important to prevent this condensation process occurring in walls, for the longevity of the building. During the summer months, the temperature gradient is reversed and the higher temperature is found on the outside of the wall and the lower temperature on the inside. This creates a situation where moisture is driven inwards ...
What is the purpose of the inner face of a building?
In simple terms, this is a layer on the inner face of the building which is used to reduce moisture flow into and through the walls, roof or floor. This is to prevent damaging levels of condensation occurring in the fabric of the building which in turn would cause decay in timber, corrosion in metals or frost damage in masonry.
Why is mould a problem in a timber building?
The high humidity levels and warm temperatures found in these walls combined to form perfect conditions for mould and rot to thrive. This was problematic to both the timber structure, as it rots, but also to the inhabitants of the building as mould spores are well known to cause respiratory problems and ill health.
How do you insulate an unvented roof?
Two acceptable methods for insulating an unvented attic assembly in all climates are as follows:
Where should vapor barrier be installed?
Vapor barriers are usually best installed on the side of the wall that experiences the hotter temperature and moister conditions: the inner surface in colder climates and the outer surface in hot, humid climates. In existing spaces, oil-based paints or vapor-barrier latex paints offer an effective moisture barrier.
Does a warm roof need ventilation?
The enclosed void of a warm pitched roof does not require to be ventilated. … Rather than actively ventilating to the outside, entrapped water vapour diffuses through the vapour permeable underlay; negating the need for forming cavities or voids below the underlay.
Can roofing felt be used as a Vapour barrier?
Plastic housewraps have largely replaced asphalt felt as the water-resistive barrier required by codes. … Fortunately a number of materials, including traditional asphalt felt (tar paper) have this ability to stop liquid water while remaining “permeable” to water vapor.
Can I use plastic sheeting as a vapor barrier?
In simple terms, a vapor barrier is a material that won’t allow moisture to pass through it, such as plastic sheeting. A very simple experiment to show how a vapor barrier works is to lay a plastic garbage bag down on some damp soil. … There are two basic types of vapor barriers used with exterior wall insulation.
Does vapor barrier need to be taped?
Installing vapor barriers on wall surfaces is important to prevent moisture transfer and should always include sealing air gaps in walls, ceilings, and floor surfaces. … Vapor bond tape is essential in creating the most effective vapor barriers.
Can you staple vapor barrier?
Tug and smooth the vapor barrier to ensure a completely smooth surface lacking wrinkles or gaps through which moisture and air may escape, defeating the vapor barrier’s purpose. Staple through the plastic into the sole plate — the horizontal board running under the studs — at bottom.
Vapour Control for Flat Roofs
A vapour control layer helps to shield the building from the consequences of condensation. Condensation is generated when warm moist air rises and condenses into a liquid on contact with the cooler areas above the insulation.
Differences between Vapour Control Layers and Vapour Barrier
A polythene vapour control layer limits the movement of air and water vapour through a membrane, so a vapour control layer is air permeable, or vapour permeable. Comparatively, a vapour barrier prevents any movement of vapour or air occurring through the building, instead of just limiting it to a controlled level.
CARLISLE Construction Materials
For more information from CARLISLE Construction Materials, please visit their CPD Member Directory page. Alternatively please visit the CPD Industry Hubs for more CPD articles, courses and events relevant to your Continuing Professional Development requirements.
Where are vapour barriers used?from iko.com
Department of Energy .) Combined vapour/air barriers are also appropriate in any place where both the air barrier and vapour barrier are both located on the warm side of the building assembly.
What materials are used for a flat roof?from roofingsuperstore.co.uk
Including fibreglass roof kits, torch-on felt, and liquid rubber products, everything you need for flat roofing is in one place. Whether you’re repairing a flat roof or laying a new one from scratch, you’ll find all the materials you need here. Including flat roof vapour barrier for extra secure roofing solutions. Looking for pitched roof materials? You’ll find pitched roofing products here.
How does condensation occur in insulation?from londonflatroofing.co.uk
Condensation is generated when warm moist air rises and condenses into a liquid on contact with the cooler areas above the insulation. The notion behind a vapour control layer is to install it on the room side of the insulation so it stops the passage of warm moist air entering the structure.
What type of retarder should I use on my house?from iko.com
The IRC recommends builders install a Class-I or -II vapour retarder on the interior side of homes in climate zones 5 (Cold) and north, and in the Marine 4 zone. However, if you air-condition your house in the summer, your might trap condensation in your roof or walls for part of the year. If this is the case, be sure to use a Class-II vapour retarder on the interior of the wall. You also can use a Class-III vapour retarder on the interior paired with spray foam insulation on the interior of the wall or roof. When building in hot, humid climates (zones 1 to 3), you shouldn’t have a vapour retarder on the interior side of the wall. (Source: Fine Home Building .)
Why use a vapour retarder?from iko.com
Vapour retarders frequently are used in flat roof construction to prevent moist air from the inside of the building condensing onto the roof assembly and potentially causing damage to materials . (Source: NRCA .) These products are an important way to preserve the thermal efficiency of roof insulation, and so make up a crucial part of protecting the comfort and energy efficiency of a home or commercial building. In most cases, when installing a vapour retarder on a roof deck, it should have a perm rating of 0.5 or less.
Why is a VCL important?from londonflatroofing.co.uk
A VCL is a very important component in your build up acting as one of the protective layers that minimises the amount of warm moist air that comes into a construction aspect. A VCL in conjunction with the correct use of venting and membranes will essentially eradicate the risk of interstitial condensation.
Why do we need an air barrier?from iko.com
In a lot of cases you may not need a vapour barrier, but instead use an air barrier to prevent water vapour from migrating through air currents. This is the number one way for water vapour to travel into homes and assemblies (such as walls or roofs). In fact, air flowing through holes and cracks is 30 times more likely to transport water vapour through building assemblies than through simple diffusion of the water vapour. (Source: CMHC, “Canadian Wood-Frame House Construction”, p.18 .)
What is a vapour control layer (VCL)?
A vapour control layer helps you protect your building from the consequences of condensation. Condensation is formed when warm moist air penetrates the building fabric and then condenses into a liquid on contact with the colder surfaces outside the insulation layer. The idea behind a vapour control layer is to install it on the room (i.e. warm) side of the insulation so it blocks the passage of warm moist air entering the structure.
How do I maintain my vapour control layer when installing services in a wall with Celotex PL4000?
Services should be kept to a minimum. Where necessary, a continuous bead of adhesive should be applied around these services.
Do Celotex make vapour control layers?
Although Insulation UK don’t manufacture vapour control layer products, Celotex PL4000 features a vapour control layer built in. It is positioned between the plasterboard and Celotex foam insulation. When the boards are tightly butted together, the tapered edges of the plasterboard are sealed with scrim tape and jointing compound to form an effective vapour control layer with a high vapour resistance.
Do I need a VCL in solid ground floors?
In solid ground floor applications , such as concrete slab and beam and block, a VCL is required to the warm side of the insulation. This membrane also serves as a protective barrier for the insulation, avoiding liquid screed migration and damage to the facer from wet screed or concrete.
What is the purpose of scrim tape on plasterboard?
When the boards are tightly butted together, the tapered edges of the plasterboard are sealed with scrim tape and jointing compound to form an effective vapour control layer with a high vapour resistance.
What are the advantages of VCL?
An advantage of the VCL is that it will help prevent installed insulation getting damp and losing its thermal properties. A VCL can also help prevent the occurrence of damp and mould, which can also cause structural problems, weakening timber framed buildings and corroding other construction materials.
Why is VCL important?
A VCL is a vitally important component in your build up acting as one of the protective layers that minimises the amount of warm moist air that enters the building fabric. A VCL in conjunction with the correct use of ventilation and membranes will effectively eliminate the risk of interstitial condensation.