
What is VLAN hopping and how does it work?
In VLAN hopping, a threat actor must first breach at least one VLAN on the network. This enables cybercriminals to create a base of operations to attack other VLANs connected to the network. What is a VLAN (Virtual LAN)? How does VLAN hopping cause network security vulnerabilities?
What is virtual local area network hopping?
What is virtual local area network hopping (VLAN hopping)? Virtual local area network hopping (VLAN hopping) is a method of attacking the network resources of the VLAN by sending packets to a port not usually accessible from an end system. The main goal of this form of attack is to gain access to other VLANs on the same network.
What is a double VLAN attack?
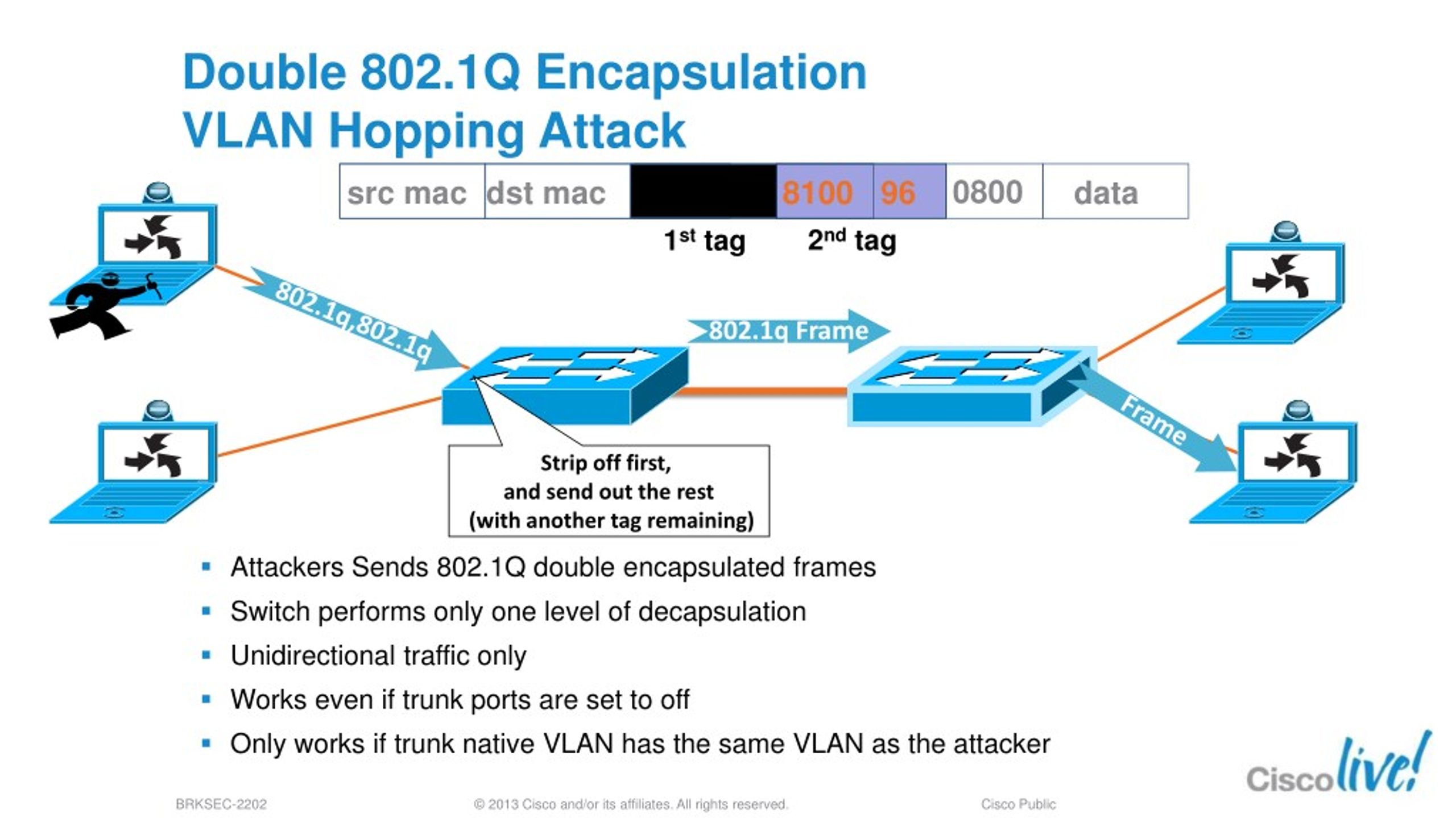
Double tags: the idea behind the attack is that the attacker is connected to an interface in access mode with the same VLAN as the native untagged VLAN on the trunk. The attacker sends a frame with two 802.1Q tags, the “inner” VLAN tag is the VLAN that we want to reach and the “outer” VLAN tag is the native VLAN.
How can an attacker jump from the native VLAN to the VLAN?
The attacker has now “jumped” from the native VLAN to the victim’s VLAN.It’s a one way trip but it could be used perhaps for a DOS attack. Switch spoofing: the attacker will send DTP packets and tries to negotiate a trunk with the switch, this is possible when you use the default “dynamic auto” or “dynamic desirable” switchport mode.
How do I stop VLAN hopping?
To prevent the VLAN hopping from being exploited, we can do the below mitigations: Ensure that ports are not set to negotiate trunks automatically by disabling DTP: NEVER use VLAN 1 at all. Disable unused ports and put them in an unused VLAN ▪ Always use a dedicated VLAN ID for all trunk ports.
What are the types of VLAN hopping?
There are two primary methods of VLAN hopping: switch spoofing and double tagging. Both attack vectors can be mitigated with proper switch port configuration.
What are three possible VLAN attacks?
Ten top threats to VLAN securityCAM Table Overflow/Media Access Control (MAC) Attack. ... Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) attack. ... Switch Spoofing/Basic VLAN Hopping Attack. ... Double Tagging/Double Encapsulation VLAN Hopping Attack. ... VLAN Management Policy Server (VMPS)/ VLAN Query Protocol (VQP) attack.More items...•
What layer is VLAN hopping?
layer 2VLAN hopping is a layer 2 network-based attack, where the user injects frames into VLAN that they are not a part of.
Can malware jump VLANs?
It is possible, but highly unlikely, that a virus could interfere with the switch to "break" the VLAN setup. If the virus causes a CAM table overflow the switch may revert to acting as a hub, and allow traffic to transverse the VLANs.
What is VLAN and why it is used?
A virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical overlay network that groups together a subset of devices that share a physical LAN, isolating the traffic for each group. A LAN is a group of computers or other devices in the same place -- e.g., the same building or campus -- that share the same physical network.
Can a VLAN be hacked?
It's even possible to transmit ARP packets to a device in a different VLAN using those forged details. It even allows the malicious user to perform a Man-in-the-middle ( MiM )attack.
Can you escape a VLAN?
Any packets sent between VLANs must go through a router or other layer 3 devices. Security is one of the many reasons network administrators configure VLANs. However, with an exploit known as 'VLAN Hopping', an attacker is able to bypass these security implementations.
How secure is a VLAN?
VLANS - not good for security But switches with VLANs are not firewalls. They operate at layer 2 (the Ethernet layer) and don't understand the “state” of the messages flowing through them. This makes the spoofing of VLAN tags trivial – there is no check to detect if a tag has been adjusted by a hacker.
Which two practices would you follow to prevent VLAN attacks on a network?
Which two practices would you follow to prevent VLAN attacks on a network? (Choose two.) Disable DTP on all ports. Change the default VLAN settings.
What are three techniques for mitigating VLAN attacks choose three?
Answers Explanation & Hints: Mitigating a VLAN attack can be done by disabling Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), manually setting ports to trunking mode, and by setting the native VLAN of trunk links to VLANs not in use.
What are Layer 2 attacks?
ARP Poisoning and DHCP snooping are layer-2 attacks, where as IP Snooping, ICMP attack, and DoS attack with fake IPs are layer-3 attacks. IP address spoofing: IP address spoofing is a technique that involves replacing the IP address of an IP packet's sender with another machine's IP address.
What is VLAN double tagging?
Double tagging occurs when an attacker adds and modifies tags on an Ethernet frame to allow the sending of packets through any VLAN. This attack takes advantage of how many switches process tags. Most switches will only remove the outer tag and forward the frame to all native VLAN ports.
What is port hopping?
Port hopping is mechanism by which a service is assigned to a random port number. After a fixed frequency of time that service is assigned to a random port and so on, so it is called hopping. This mechanism makes its difficult to attack and retain connection to a particular service.
What are the two types of VLAN hopping attacks?
There are two types of VLAN hopping attacks. They are Switch Spoofing attack and Double Tagging attack.
What is VLAN hopping?
VLAN hopping is a type of network attack where an attacker who is connected to an access port (which is attached to a particular VLAN) can gain access to network traffic from other VLAN s.
What is virtual local area network hopping (VLAN hopping)?
Virtual local area network hopping (VLAN hopping) is a method of attacking the network resources of the VLAN by sending packets to a port not usually accessible from an end system. The main goal of this form of attack is to gain access to other VLANs on the same network.
How does VLAN hopping cause network security vulnerabilities?
The vulnerabilities of VLANs relate to their key features, including the following:
Network security hacking tools
Yersinia is one of the most popular network security hacking tools for Unix -like operating systems. The primary aim of this VLAN hacking tool is to exploit weaknesses in network protocols such as:
How to prevent VLAN hopping
Good security hygiene helps reduce the risk of VLAN hopping. For example, unused interfaces should be closed and placed in a "parking lot" VLAN. Using VLANs on trunk ports should be avoided unless they are necessary. Additionally, access ports should be configured manually with the switchport mode access.
VLAN
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is used to share the physical network while creating virtual segmentations to divide specific groups. For example, a host on VLAN 1 is separated from any host on VLAN 2. Any packets sent between VLANs must go through a router or other layer 3 devices.
VLAN Hopping
This type of exploit allows an attacker to bypass any layer 2 restrictions built to divide hosts. With proper switch port configuration, an attacker would have to go through a router and any other layer 3 devices to access their target.
Switched Network
It is crucial we understand how switches operate if we would like to find and exploit their vulnerabilities. We are not necessarily exploiting the device itself, but rather the protocols and configurations instructing how they operate.
Switched Spoofing VLAN Attack
An attacker acts as a switch in order to trick a legitimate switch into creating a trunking link between them. As mentioned before, packets from any VLAN are allowed to pass through a trunking link. Once the trunk link is established, the attacker then has access to traffic from any VLAN.
Double Tagging
Double tagging occurs when an attacker adds and modifies tags on an Ethernet frame to allow the sending of packets through any VLAN. This attack takes advantage of how many switches process tags. Most switches will only remove the outer tag and forward the frame to all native VLAN ports.
VLAN Hopping Exploit
Scenario 1 - Switch Spoofing Attack In this scenario there exists the attacker, a switch, and the target server. The attacker is attached to the switch on interface FastEthernet 0/12 and the target server is attached to the switch on interface FastEthernet 0/11 and is a part of VLAN 2.
Switched Spoofing
To prevent a Switched Spoofing attack, there are a few steps you should take:
How to attack a VLAN?
VLAN Hopping is an attack where the attacker is able to send traffic from one VLAN into another. There are two different methods to accomplish this: 1 Double tags: the idea behind the attack is that the attacker is connected to an interface in access mode with the same VLAN as the native untagged VLAN on the trunk. The attacker sends a frame with two 802.1Q tags, the “inner” VLAN tag is the VLAN that we want to reach and the “outer” VLAN tag is the native VLAN. When the switch receives the frame, it will remove the first (native VLAN) 802.1Q tag and forwards the frame with the second 802.1Q tag on its trunk interface (s). The attacker has now “jumped” from the native VLAN to the victim’s VLAN.It’s a one way trip but it could be used perhaps for a DOS attack. 2 Switch spoofing: the attacker will send DTP packets and tries to negotiate a trunk with the switch, this is possible when you use the default “dynamic auto” or “dynamic desirable” switchport mode. Once you have a trunk to your computer, you will have access to all VLANs. This is basically a misconfiguration since you should never configure your interfaces to use the dynamic switchport modes.
What is spoofing in switch?
Switch spoofing: the attacker will send DTP packets and tries to negotiate a trunk with the switch, this is possible when you use the default “dynamic auto” or “dynamic desirable” switchport mode. Once you have a trunk to your computer, you will have access to all VLANs. This is basically a misconfiguration since you should never configure your interfaces to use the dynamic switchport modes.
How does a VLAN hoop attack work?
VLAN Hopping Attack is a type of network attack in which an attacker tries to gain access to a VLAN network by sending packets to it through another VLAN network with which the attacker is connected. In this kind of attack, the attacker maliciously tries to gain access to the traffic coming from other VLANs in a network or can send traffic to other VLANs in that network, to which he has no legal access. In most cases, the attacker only exploits 2 layers that segment various hosts.
What is a VLAN?
VLAN is a Virtual Local Area Network in which a physical network is divided into a group of devices to interconnect them . VLAN is normally used to segment a singular broadcast domain into numerous broadcast domains in switched layer 2 networks. To communicate between two VLAN networks, a layer 3 device is required (usually a router) such that all the packets communicated between the two VLANs must pass through the 3rd OSI layer device.
How does a spoofing attack work?
In switched spoofing VLAN Hopping Attack, the attacker tries to imitate a switch to exploit a legitimate switch by tricking it into making a trunking link between the attacker’s device and switch. A trunk link is a linking of two switches or a switch and a router. The trunk link carries traffic between the linked switches or the linked switches and routers and maintains the VLANs data.
What is a double tagging attack?
A double-tagging VLAN hopping attack can also be termed a double-encapsulated VLAN hopping attack. These types of attacks only work if the attacker is connected to an interface connected to the trunk port/link interface.
Why do I need access ports for VLAN?
In this type of network, each user is provided with an access port in order to separate VLAN’s traffic from each other, i.e., a device attached to an access port only has access to that specific VLAN’s traffic as each switch access port is connected to a particular VLAN. After getting to know the basics of what a VLAN is, let’s jump towards understanding a VLAN hopping attack and how it works.
What mode should access ports not be set to?
The configuration of access ports should not be set to any of the following modes: “ dynamic desirable “, “d ynamic auto “, or “ trunk “.
What is a network attack?
This attack allows malicious attackers to gain access to networks illegally. The attackers can then snip away passwords, personal information, or other protected data. Likewise, they can also install malware and spyware, spread trojan horses, worms, and viruses, or alter and even erase important information. The attacker can easily sniff through all the traffic coming from the network to use it for malicious purposes. It can also disrupt the traffic with unnecessary frames to an extent.
What is VLAN hopping?
VLAN hopping is a significant security threat. It lets malicious actors gain access to networks that they don’t have permission to enter. A hacker can then steal passwords or other protected information; install malware and spyware; spread Trojan horses, worms, and viruses; or corrupt, modify, or delete critical data.
How to prevent VLAN hopping?
Different techniques are used to deal with each type of VLAN hopping attack. To prevent switch spoofing, disable Dynamic Trunking Protocol to ensure that ports will not automatically negotiate trunks.
What is switch spoofing?
Switch Spoofing With a switch spoofing method, an attacker imitates a trunking switch by using the VLAN’s tagging and trunking protocol (Multi ple VLAN Registration Protocol, IEEE 802.1Q, or Dynamic Trunking Protocol). By forming a trunk link, the hacker can gain access to traffic from all of the VLANs.
Why are VLANs better than LANs?
Compared to LANs, VLANs have the advantage of reducing network traffic and collisions, as well as being more cost effective. Moreover, a VLAN can also bring added security. When devices are separated into multiple VLANs—often by department—it’s easier to prevent a compromised computer from infecting the entire network.
What is a VLAN?
In contrast, a VLAN is a group of devices on multiple LAN sections that behave as if they are on a single LAN.
How to prevent double tagging?
Double tagging can be prevented using a three-step process. First, avoid putting any hosts on the default VLAN (VLAN 1). Second, be sure that the native VLAN on every trunk port is an unused VLAN ID. Finally, enable explicit tagging of the native VLAN for all trunk ports.
What is VLAN hopping?
VLAN hopping(virtual local area network hopping) is a method of attacking a network by sending packets to a port that is not normally accessible from a given end system. (A VLAN is a local area network with a definition that maps devices on some other basis than geographic location - for example, by department, type of user, ...
What does G0/0 mean in VLAN?
We can see that the interface (G0/0) is set on trunk which means that we can jump other VLANs!
Can VLAN hopping be exploited?
VLAN Hopping can only be exploited when interfaces are set to negotiate a trunk. To prevent the VLAN hopping from being exploited, we can do the below mitigations:
