What is a Lun and why do we need one?
What is a LUN and why do we need storage LUNs? What is a LUN and why do we need storage LUNs? What is a LUN, and why do we need one? In simple terms, a logical unit number (LUN) is a slice or portion of a configured set of disks that is presentable to a host and mounted as a volume within the OS.
What is the difference between datastore and Lun?
A datastore is a partition on a disk or LUN which is formatted with VMware's VMFS filesystem. 01-18-2012 11:33 AM May be helpful. A logical unit number (LUN) is a unique identifier used to designate individual or collections of hard disk devices for address by a protocol associated with a SCSI, iSCSI, Fibre Channel (FC) or similar interface.
What is VMware Virtual Volumes?
VMware Virtual Volumes is an integration and management framework for external storage that provides finer control at the VM-level, streamlines storage operation and offers flexibility of choice. VMware Virtual Volumes eliminates physical containers and enables more flexible consumption of resources.
What is VMware VVols?
This virtual disk becomes the primary unit of data management, eliminating pre-allocated LUNs/Volumes. vVols enables storage operations with VM granularity, leveraging native array-based data services and software-based data services.
See more
What's a LUN in VMware?
A logical unit number (LUN) is a unique identifier for designating an individual or collection of physical or virtual storage devices that execute input/output (I/O) commands with a host computer, as defined by the Small System Computer Interface (SCSI) standard.
What is LUN in virtualization?
What is a virtual LUN (virtual logical unit number)? A virtual LUN (virtual logical unit number) is a representation of a storage area that is not tied to any physical storage allocation. Virtual LUNs are used in thin provisioning (also known as virtual provisioning) for storage area network (SAN) management.
What is the difference between LUN and volume?
A LUN is a logical volume from the point of view of the storage. From the client point of view the LUN it is a disc volume that can be partitioned. Volume is a generic term. It means a contiguous storage area.
Where is the LUN number in VMware?
To obtain LUN multipathing information from the ESXi host command line: Log in to the ESXi host console. Type esxcli storage core path list to get detailed information regarding the paths. Type esxcli storage core path list -d naaID to list the detailed information of the corresponding paths for a specific device.
Is LUN and Datastore same?
what is the difference between LUN and datastore? A LUN is a logical volume on a storage system, which usually is presented to one ore more hosts. A datastore is a partition on a disk or LUN which is formatted with VMware's VMFS filesystem.
How many types of LUN are there?
LUN Types. VDS supports five LUN types: simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and striped with parity. Simple, spanned, and striped LUNs are non-fault tolerant; mirrored and parity LUNs are fault tolerant.
What does LUN stand for?
logical unit numberIn computer storage, a logical unit number, or LUN, is a number used to identify a logical unit, which is a device addressed by the SCSI protocol or by Storage Area Network protocols that encapsulate SCSI, such as Fibre Channel or iSCSI.
What is LUN size?
Supported sizes are from 1 to 16 TiB in increments of 1 GiB. The supported ESS LUN sizes are limited to the exact sizes that are specified from 0.1 to 982.2 GB (decimal) in increments of 0.1 GB and are rounded up to the next larger 32 K byte boundary.
What is LUN mapping?
LUN mapping is the process of controlling which hosts have access to specific logical units (LUs) within the disk controllers. LUN mapping is typically done at the storage system level. Host mapping is done at the software level.
How do I find my LUN details?
Using Disk ManagerAccess Disk Manager under "Computer Management" in "Server Manager" or in the command prompt with diskmgmt.msc.Right-Click on the side-bar of the disk you wich to view and select "Properties"You will see the LUN number and the target name. In this example it's "LUN 3" and "PURE FlashArray"
How do you present a LUN to a host?
Click the LUN that you want to map. Click Map LUN. Click Add Groups to Map. Select the name of the host or initiator group from the list and click Add.
How do you add a LUN?
Add a LUN to an iSCSI TargetNavigate to the vSAN cluster.Click the Configure tab. Option. Description. vSphere Client. Under vSAN, click iSCSI Target Service. Click the iSCSI Targets tab, and select a target. In the vSAN iSCSI LUNs section, click Add. The Add LUN to Target dialog box is displayed. ... Click Add.
What is LUN migration?
LUN Migration is an important feature for use in storage system tuning. LUN Migration moves data from a source LUN to a destination LUN (of the same or larger size) within a single storage system. This migration is accomplished without disruption to applications running on the host.
How do I configure LUN?
ProcedureUnder vSAN, click iSCSI Target Service.Click the iSCSI Targets tab, and select a target.In the vSAN iSCSI LUNs section, click Add. The Add LUN to Target dialog box is displayed.Enter the size of the LUN. The vSAN Storage Policy configured for the iSCSI target service is assigned automatically.
What is thick and thin LUN?
A Thin Provisioned LUN takes up actual used space and asks for more only when you write data to it. For example, if you create a Thin Provisioned 100GB LUN and store 20GB files, the space it consumes on the volume is 20 GB, whereas a Thick Provisioned LUN would take up 100 GB right from the start.
What is English LUN?
lun {adjective} snug {adj.} lun (also: hyggelig) cozy {adj.}
How to open a VMDK file?
First, connect via SSH (if necessary). Then open the disk (it can be a local disk or SSH). After scanning (it can take a while), find the files you need. The next step is to mount the VMDK file and open it with the left mouse button. Next, preview the files to verify their integrity.
What is a LUN in iSCSI?
What is an iSCSI LUN? Logical Unit (LUN) is a logical device, an iSCSI network drive. iSCSI, in turn, is network-attached storage and network protocol in which disk images available on the network are stored in EXT.
What is the final step in exporting data?
The final step is to acquire a license to complete the export of data .
Can I use DiskInternals RAID Recovery on iSCSI?
That is, there is one basic file system for the operating system. In this case, you can use DiskInternals RAID Recovery to return data.
Does VM recovery take place in real time?
All action takes place in real-time without needing to turn off the VM. Without exception, all recovered files and folders are exported to local or remote locations (including FTP). Unicode file names and multilevel folders are supported.
What is Virtual Volumes (vVols)?
vVols uniquely shares a common storage operational model with vSAN, the market leading hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) solution. Both solutions use storage policy-based management (SPBM) to eliminate storage provisioning, and use descriptive policies at the VM or VMDK level that can be applied or changed in minutes. SPBM accelerates storage operations and reduces the need for specialized skills for storage infrastructure.
What is SPBM in storage?
Storage Policy-Based Management (SPBM) allows capturing storage service levels requirements (capacity, performance, availability, etc.) in the form of logical templates (policies) to which VMs are associated. SPBM automates VM placement by identifying available datastores that meet policy requirements and coupled with vVols, it dynamically instantiates necessary data services.
What is vVols in VMware?
vVols represents the collaboration of VMware and the storage ecosystem towards a new storage operational model centered on the VM. Major vendors participated in the design of vVols. The ecosystem continues to grow and strengthen with solutions ready for vVols.
What is vVols in IT?
vVols is an industry-wide initiative that will allow IT organizations to leverage the unique capabilities of their current storage investments and transition without disruption to a simpler and more efficient operational model. IT organizations can also manage heterogeneous storage using a common control plane.
Why is VVols important?
With vVols, it is much simpler to deliver and enable the right storage service levels according to the specific requirements of individual VMs. By having finer control over storage resources and data services down to the VM level, the VI administrator can create exact combinations and precisely deliver storage service levels. Over-provisioning is eliminated because each VM will consume the exact resources needed – nothing less, nothing more.
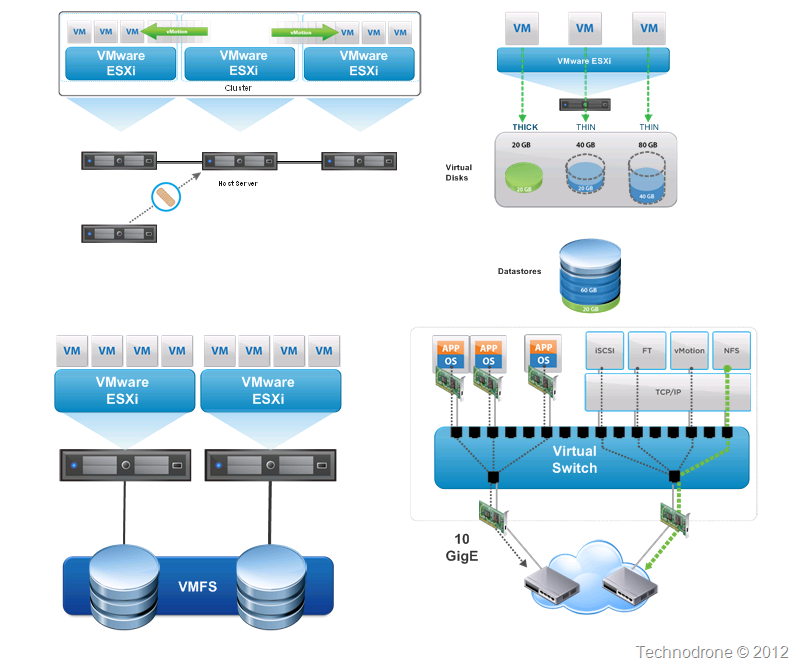
How LUNs work
LUN setup varies by system. A logical unit number is assigned when a host scans an SCSI device and discovers a logical unit. The LUN identifies the specific logical unit to the SCSI initiator when combined with information such as the target port identifier.
Types of LUNs
The underlying storage structure and logical unit type play a role in performance and reliability. Some examples include:
LUN uses
The primary use case of a LUN is to act as an identifier for designating a storage device; however, the use case may be different per type of LUN. For example, a simple LUN is used as a designator for one portion of or one whole physical disk. Spanned LUNs are designators that signify a LUN that spans over two or more physical disks.
LUN zoning and masking
Storage area networks will control host access to LUNs in order to enforce data security and integrity. LUN masking and switch -based zoning manage the SAN resources accessible to the attached hosts.
LUNS and virtualization
A LUN constitutes a form of virtualization in the sense that it abstracts the hardware devices behind it with a standard SCSI method of identification and communication. The storage object represented by the LUN can be provisioned, compressed or deduplicated as long as the representation to the host does not change.
Managing LUNs
After LUN creation, the LUN can be managed through a software program that specifies the path between LUNs and hosts. LUNs can be managed by controlling LUN availability, increasing LUN size, and by deleting or securing the LUN. Management best practices will differ depending on the environment.
LUN challenges
Common challenges related to LUNs often involve the use of the term as the logical unit/storage device itself. When referring to LUN in this sense, common challenges that appear tend to be related to resource management, multipath I/O and provisioning. For example, oversizing LUNs can quickly lead to wasted disk resources.