What is the primary treatment for vocal fold pathology?
Is voice therapy a viable option?
About this website
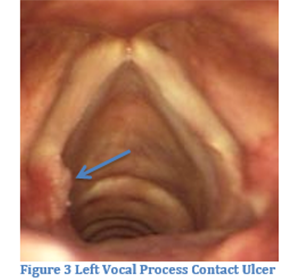
What are the symptoms of vocal disorders?
Vocal cord disorders are often caused by vocal abuse or misuse. Symptoms may include a raspy, hoarse, low, or breathy voice, or trouble swallowing or coughing. Any hoarseness or change in voice that lasts longer than 2 weeks should be brought to the attention of your healthcare provider.
What are three common voice disorders?
Some common voice disorders include: Laryngitis. Voice changes related to the brain and nervous system, known as spasmodic dysphonia (spaz-MOD-ki dis-FOE-nee-uh) Polyps, nodules or cysts on the vocal cords — growths that aren't cancer.
What are signs of damaged vocal cords?
Strained vocal cord symptoms may include:Chronic hoarseness for more than two weeks (such as a raspy or breathy voice, a voice quiver, or a strained or choppy voice)Pain or a lump in the throat when speaking.Changes in pitch.Odd sounding speech.
What happens if vocal nodules go untreated?
Left untreated, the growths can lead to voice strain as your body attempts to compensate for your injury. In many cases, voice therapy can teach you how to use your voice more efficiently and without strain so your injury can heal. In some cases, surgery is needed to remove the growths.
What is the most common symptom of all voice disorders?
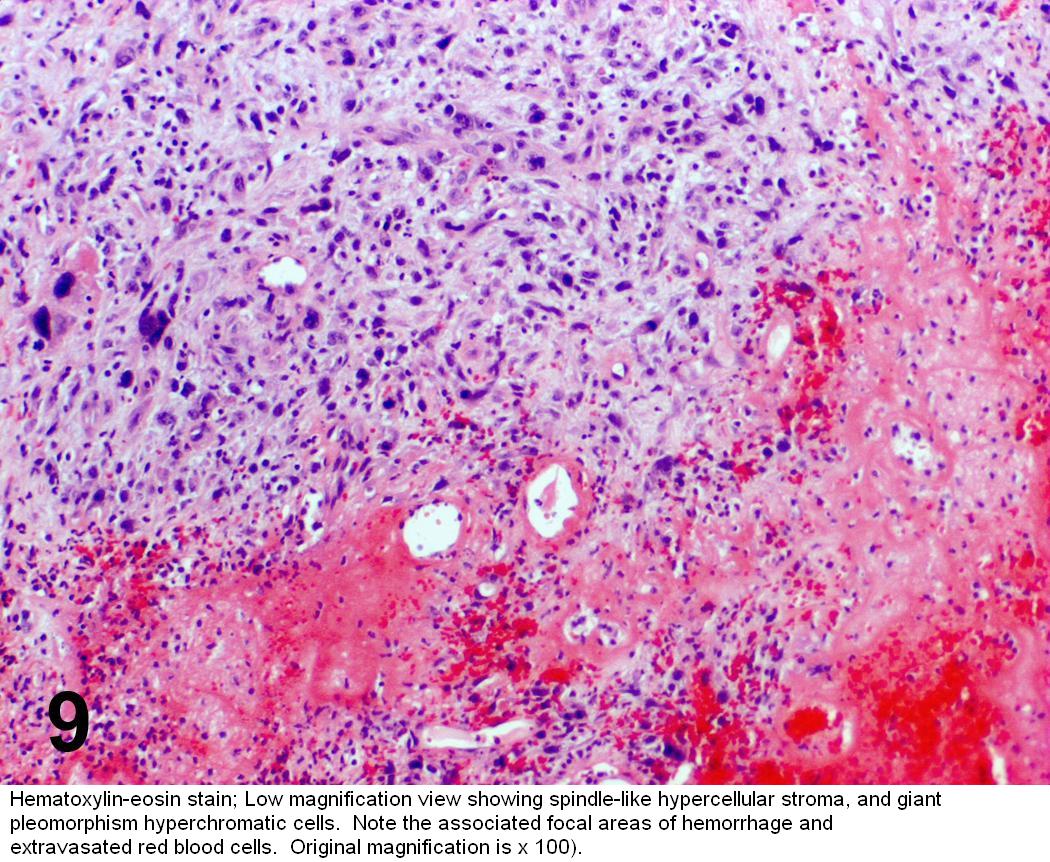
The most common symptoms are hoarseness, voice loss, and throat pain. Vocal fold lesions (such as nodules, polyps, and cysts): Benign laryngeal lesions are abnormal growths of the vocal folds or the larynx (voice box) that are NOT cancerous.
What is the most common cause of voice disorders?
What causes voice disorders?Growths. In some cases, extra tissue may form on the vocal cords. ... Inflammation and swelling. Many things can cause inflammation and swelling of the vocal cords. ... Nerve problems. Certain medical conditions can affect the nerves that control the vocal cords. ... Hormones. ... Misuse of the voice.
Can vocal damage be repaired?
While these conditions can temporarily damage our vocal cords, with a little care – such as vocal rest and good hydration – we should recover fairly quickly. Sometimes, though, vocal problems persist, and that's when you need to take action to avoid long-term or permanent damage.
Can you recover from damaged vocal cords?
Occasional vocal cord injury usually heals on its own. However, those who chronically overuse or misuse their voices run the risk of doing permanent damage, says voice care specialist Claudio Milstein, PhD.
Can a vocal cord be repaired?
Replacing the damaged nerve (reinnervation). In this surgery, a healthy nerve is moved from a different area of the neck to replace the damaged vocal cord. It can take as long as 6 to 9 months before your voice gets better. Some health care providers combine this surgery with a bulk injection.
Can you get rid of vocal nodules without surgery?
Vocal cord nodules can be surgically removed but may also be treated with non‐surgical voice therapy interventions (e.g. voice re‐training, rest or hygiene advice) or medical/pharmacological treatment of underlying infections, allergy or gastroesophageal reflux.
Does vocal nodule surgery hurt?
Most people who have microlaryngoscopy return home on the day of surgery. You may experience minor discomfort in your throat or soreness in your jaw, but pain is rarely severe. Your doctor may recommend a dose of over-the-counter pain relief medication, if necessary.
How long does it take to recover from vocal nodules surgery?
If your vocal cords were affected during the procedure, rest your voice completely for 3 days. If nodules or other lesions were removed from your vocal cords, you may have to follow total voice rest (no talking, whispering, or making any other voice sounds) for up to 2 weeks.
What is the most common voice and speech problem?
Here are four of the most common voice disorders and why you may encounter them.Laryngitis. Vocal cords can sometimes swell, causing hoarseness or a complete loss of voice. ... Lesions. Noncancerous growths can affect the vocal cords, causing voice disorders. ... Muscle tension dysphonia. ... Contact ulcers.
What neurological disorders affect voice?
Neurologic voice disorders occur as part of an underlying neurologic condition such as Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, or ALS. They can also happen as the result of a stroke. These disorders can affect the strength of the muscles of the voice box, and impact the control of the voice.
What are the main categories of voice disorders?
Organic Voice Disorders.Functional Disorders.Psychogenic Disorders.
What are benign voice disorders?
Benign vocal lesions are non-malignant growths of abnormal tissue on the vocal cords. The common benign lesions of vocal cord are singer's nodule, polyps, papilloma, polypoidal degeneration (Reinke's edema) and cysts.
What is the primary treatment for vocal fold pathology?
Voice Therapy as Primary Treatment of Vocal Fold Pathology
Is voice therapy a viable option?
Voice therapy may offer a valuable and viable option for the treatment of vocal fold pathology. This article provides an overview of the history of voice therapy within the context of treatment of laryngeal disorders, types of voice therapy, efficacy and outcome data to support the use of voice therapy, and clinical considerations and caveats.
Why does voice disorder persist?
Recognizing associations among these factors, along with patient history, may help in identifying the possible causes of the voice disorder. Even when an obvious cause is identified and treated, the voice problem may persist. For example, an upper respiratory infection could be the cause of the dysphonia, but poor or inefficient compensatory techniques may cause dysphonia to persist, even when the infection has been successfully treated.
What are the different types of voice disorders?
A number of different systems are used for classifying voice disorders. For the purposes of this document, voice disorders are categorized as follows: 1 Organic — voice disorders that are physiological in nature and result from alterations in respiratory, laryngeal, or vocal tract mechanisms 2 Structural — organic voice disorders that result from physical changes in the voice mechanism (e.g., alterations in vocal fold tissues such as edema or vocal nodules; structural changes in the larynx due to aging) 3 Neurogenic — organic voice disorders that result from problems with the central or peripheral nervous system innervation to the larynx that affect functioning of the vocal mechanism (e.g., vocal tremor, spasmodic dysphonia, or paralysis of vocal folds) 4 Functional — voice disorders that result from improper or inefficient use of the vocal mechanism when the physical structure is normal (e.g., vocal fatigue; muscle tension dysphonia or aphonia; diplophonia; ventricular phonation)
What is the name of the disorder that affects voice quality?
Voice quality can also be affected when psychological stressors lead to habitual, maladaptive aphonia or dysphonia. The resulting voice disorders are referred to as psychogenic voice disorders or psychogenic conversion aphonia/dysphonia (Stemple, Glaze, & Klaben, 2010). These voice disorders are rare.
What is voice disorder?
A voice disorder is present when an individual expresses concern about having an abnormal voice that does not meet daily needs —even if others do not perceive it as different or deviant (American Speech-Language-Hearing Association [ASHA], 1993; Colton & Casper, 1996; Stemple, Glaze, & Klaben, 2010; Verdolini & Ramig, 2001).
What is neurogenic voice disorder?
Neurogenic — organic voice disorders that result from problems with the central or peripheral nervous system innervation to the larynx that affect functioning of the vocal mechanism (e.g., vocal tremor, spasmodic dysphonia, or paralysis of vocal folds)
How prevalent is voice disorder in children?
In the pediatric population, the reported prevalence of a voice disorder has ranged from 1.4% to 6.0% (Black, Vahratian, & Hoffman, 2015; Carding et al., 2006; Duff, Proctor, & Yairi, 2004).
What is organic voice?
Organic — voice disorders that are physiological in nature and result from alterations in respiratory, laryngeal, or vocal tract mechanisms
What is the primary treatment for vocal fold pathology?
Voice Therapy as Primary Treatment of Vocal Fold Pathology
Is voice therapy a viable option?
Voice therapy may offer a valuable and viable option for the treatment of vocal fold pathology. This article provides an overview of the history of voice therapy within the context of treatment of laryngeal disorders, types of voice therapy, efficacy and outcome data to support the use of voice therapy, and clinical considerations and caveats.