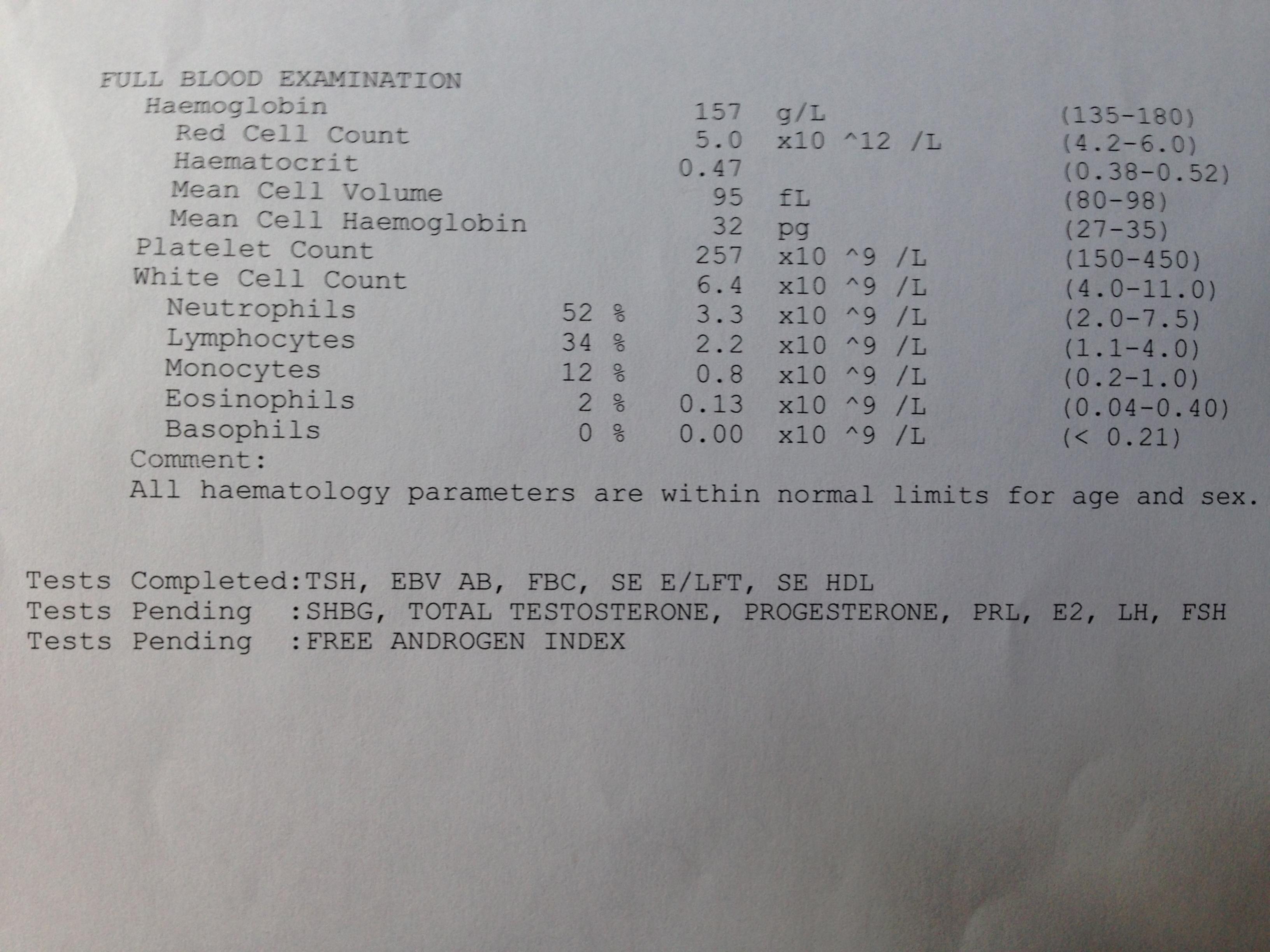
What does mid mean in a blood test?
In terms of a blood test, MID stands for mid-sized cells. This value is common in blood tests that check WBC or white blood cell count.
How is ABS absolute monocyte test done?
Absolute monocyte test is done by drawing the sample of blood. A laboratory specialist puts a drop of blood from your sample on a clear glass slide and smears it to spread the blood around. Then, they stain the blood smear with a dye that helps to differentiate the types of white blood cells in the sample.
What does MXD blood test mean?
MXD Blood Test : Normal Range, Low And High Levels. The mxd blood test stands for Mixed Cell Count, and it forms a part of a complete blood count test or a WBC differential count.
Why are absolute counts important in blood work?
The reason to consider absolute counts is very vital because if you just have a look at percentages, you could not have a clear idea. Let’s say, there are 61% neutrophils in a particular patient.
What is mid in complete blood count?
The five types include lymphocytes (LYM), neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils (GRA). MID cells and percentage: (MID) cells include less frequently occurring and rare cells correlating to monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, blasts and other precursor white cells that fall in a particular size range.
What is normal range mid in blood test?
Red blood cells: 4.5 million to 5.9 million cells/mcL for men; 4.1 million to 5.1 million cells/mcL for women. Hemoglobin: 14 to 17.5 grams per deciliter (gm/dL) for men; 12.3 to 15.3 gm/dL for women. Hematocrit: 41.5% to 50.4% for men; 35.9% to 44.6% for women. Mean corpuscular volume: 80 to 96.
What is absolute count in blood?
White blood cells (WBCs) The most important infection-fighting WBC is the neutrophil . The number doctors look at is called your absolute neutrophil count (ANC). A healthy person has an ANC between 2,500 and 6,000. The ANC is found by multiplying the WBC count by the percent of neutrophils in the blood.
Should I be worried if my absolute monocytes are high?
A high monocyte count is a potential sign of many different medical conditions. It's often linked to infectious diseases like mononucleosis or an autoimmune disease like lupus. Some medications can cause monocytosis. It's also linked to conditions such as blood disorders and certain cancers.
Why are absolute lymphocytes high?
If your doctor determines that your lymphocyte count is high, the test result might be evidence of one of the following conditions: Infection (bacterial, viral, other) Cancer of the blood or lymphatic system. An autoimmune disorder causing ongoing (chronic) inflammation.
What is the normal range for absolute lymphocytes?
In adults, the normal range of lymphocytes is between 1,000 and 4,800 lymphocytes in every 1 microliter of blood. In children, the normal range of lymphocytes is between 3,000 and 9,500 lymphocytes in every 1 microliter of blood. About 20% to 40% of your white blood cells are lymphocytes.
What does it mean when your absolute lymphocytes are low?
Lymphocytopenia, also referred to as lymphopenia, occurs when your lymphocyte count in your bloodstream is lower than normal. Severe or chronic low counts can indicate a possible infection or other signficant illness and should be investigated by your doctor. Lymphocytes are a kind of white blood cell.
What is the difference between differential count and absolute count?
It can be expressed as a percentage (relative numbers of each type of WBC in relationship to the total WBC) or as an absolute value (percentage x total WBC). Of these, the absolute value is much more important than the relative value....White Blood Cell Differential Count (Differential, Diff)Bands/Stabs%Pregnancy0-3%2 more rows
What does it mean when your absolute neutrophils are high?
Neutrophilia: Neutrophilia, also known as neutrophilic leukocytosis, occurs when your neutrophil count is too high, which is often the result of a bacterial infection. To combat the infection, immature neutrophils leave your bone marrow too soon and enter into your bloodstream.
What cancers cause high monocytes?
The most common sign of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is having too many monocytes (seen on a blood test). Having too many monocytes also causes many of the symptoms of CMML.
What is the most common cause of high monocytes?
Common causes of a high monocyte count include infections, leukemia, polycythemia vera (an increase in all blood cells, especially red blood cells), and primary myelofibrosis (buildup of scar tissue in the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced).
What causes absolute monocytes to be high?
A heightened percentage of monocytes in your blood can be caused by: chronic inflammatory disease, such as inflammatory bowel disease. a parasitic or viral infection. a bacterial infection in your heart.
What does MID test mean?
Noun. midtest (plural midtests) A test administered partway through a course of instruction.
What is a normal range?
Listen to pronunciation. (NOR-mul raynj) In medicine, a set of values that a doctor uses to interpret a patient's test results. The normal range for a given test is based on the results that are seen in 95% of the healthy population.
What is a normal reference range?
Lab results are often shown as a set of numbers known as a reference range. A reference range may also be called "normal values." You may see something like this on your results: "normal: 77-99mg/dL" (milligrams per deciliter). Reference ranges are based on the normal test results of a large group of healthy people.
What is a normal value?
Normal values are defined as references for the evaluation of measured parameters (eg. lab values). Commonly, they are given as limit value ranges (normal or reference ranges), within which the measured values of around 95% of a representative population can be found. see also: laboratory medicine, normal distribution.
Why is absolute count important?
The reason to consider absolute counts is very vital because if you just have a look at percentages, you could not have a clear idea. Let’s say, there are 61% neutrophils in a particular patient. You might take a glimpse at that and think, okay, that lookspretty fine.
Which is better, absolute or relative numbers?
Therefore, it may be concluded that absolute numbers are better indicators to diagnose, understand and treat precise disease and relative numbers do not give a clear idea about the patient’s actual pathology.
What percentage of WBC is relative?
Lymphocytes are the only exception as it can be divided into relative lymphocytes and absolute lymphocytes. Normally 20%–40% of human WBC are lymphocytes. When the percentage exceeds 40%, it is known as relative lymphocytes.
What is the relative value of basophils in chronic myeloid leukemia?
In a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia, the increase in basophil concentration is a vital diagnostic criterion. A relative value of 1% basophils with an aggregate WBC count of 100,000 cells/μL may give off an impression of being normal, but when considering the absolute value, this shows pathological basophilia with a high count of 1,000 cells/μL.
What is CBC in medical?
A complete blood count (CBC) is a panel test that gives information about the cells in a patient’s blood. It is generally requested by a doctor or another medical practitioner to diagnose specific diseases and to confirm the health status of the patient.A study reveals that a great number of clinical decisions and diagnoses are supported by laboratory medicine and clinical information obtained from laboratory tests, which plays a vital role in the diagnosis of various pathologies. Some studies have shown that although physicians usually request laboratory tests, they tend to misinterpret or ignore the results; such unacceptable interpretations have obvious impact on the treatment and quality of patient care.
What is the most commonly applied laboratory method?
One of the most frequently applied laboratory methods is the differentiation of cellular components of white blood cells. However, since its introduction, manual differentiation has been subject to relatively little changes over the last many years.
Is 62% of WBC a high number?
Contrarily, if the same patient has a very high WBC (assume 110), then 62% of the total WBC would be a very high number! So, by just looking at the percentage of neutrophils, you might go okay, that looks fine .But, if one consider closely, the number of neutrophils would be very high. So that’s the theory that goes in favor of the absolute numbers. In reality, most of the time you can just have a glimpse at the WBC, then further figure out the absolute numbers of the individual white cells.
Why are monocytes considered absolute?
It’s often listed as “monocytes (absolute)” because it’s presented as an absolute number. You may also see monocytes noted as a percentage of your white blood cell count, rather than an absolute number. Monocytes and other kinds of white blood cells are necessary to help the body fight disease and infection. Low levels can result ...
Why do monocytes have low absolute levels?
Causes of low absolute monocyte count include: chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which can injure bone marrow.
What is CBC in medical?
A standard complete blood count (CBC) will include a monocyte count. If you have an annual physical that includes regular blood work, a CBC is fairly standard. In addition to checking your white blood cell count (including monocytes), a CBC checks for: 1 red blood cells, which carry oxygen to your organs and other tissue 2 platelets, which help clot the blood and prevent bleeding complications 3 hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen in your red blood cells 4 hematocrit, a ratio of red blood cells to plasma in your blood
What percentage of white blood cells are monocytes?
Typically, monocytes make up 2 to 8 percent of total white blood cell count. Absolute monocyte test results can range slightly, depending on the method used for the test and other factors. According to Allina Health, a non-profit healthcare system, normal results for absolute monocytes fall into these ranges: Age range.
What is CBC in blood work?
How absolute monocyte count is determined. A standard complete blood count (CBC) will include a monocyte count. If you have an annual physical that includes regular blood work, a CBC is fairly standard. In addition to checking your white blood cell count (including monocytes), a CBC checks for:
Why do we need to check monocytes?
Monocytes are helpful at fighting infections and diseases, such as cancer. Getting your absolute monocyte levels checked as part of a routine blood test is one way to monitor the health of your immune system and your blood. If you haven’t had a complete blood count done lately, ask your doctor if it’s time to get one.
What is the monocyte count?
When you get a comprehensive blood test that includes a complete blood count, you may notice a measurement for monocytes, a type of white blood cell. It’s often listed as “monocytes (absolute)” because it’s presented as an absolute number.
What does a blood differential test detect?
This test can detect abnormal or immature cells and can diagnose an infection, leukemia, or an immune disorder. A healthcare professional may order a blood differential when someone has general signs and symptoms of infection and/or inflammation, such as: - Fever, chills. - Body aches, pains. - Headache.
What does it mean if your Monocytes (Absolute) result is too low?
Low monocyte count, called monocytopenia, is caused by anything that decreases the overall white blood cell count , such as:
What percentage of white blood cells are monocytes?
Monocytes are a large type of white blood cell but only account for 2%-8% of the total white blood cells in circulation. Once in the blood, monocytes migrate to tissues where they mature into macrophages.
What is MXD% in blood?
MXD% in the blood is a mixed cell percentage in the blood. There is a certain % of each cell type in the blood that is considered to be normal. If those proportions are out of order, your mxd% increases. A percent breakdown of each cell type tells what the exact problem is.
What does MXD stand for in blood work?
The mxd blood test stands for Mixed Cell Count blood test, and it forms a part of a complete blood count test. What is Low or high mxd in blood?
What does low MXD mean?
What Does Low or High MXD Blood Test Mean? As earlier mentioned, white blood cells form an important part of the immunity system in the body. Usually, a differential WBC count along with a physical examination is enough for a doctor to diagnose any underlying disease leading to the abnormal WBC levels.
Why is WBC count important?
As earlier mentioned, white blood cells form an important part of the immunity system in the body. Usually, a differential WBC count along with a physical examinationis enough for a doctor to diagnose any underlying disease leading to the abnormal WBC levels.
Which type of white blood cell counts are measured separately?
Out of the five types of white blood cells, the neutrophils and lymphocytes are considered the most important, and their levels are measured separately in a differential WBC count , and the levels of the remaining three types of white blood cells, i.e., the monocytes, eosinophils, and the basophils are sometimes measured together in an MXD blood test.
What is a complete blood count?
The complete blood count test is mainly used by doctors to evaluate a patient’s overall health, as mentioned earlier, and to detect a wide range of disorders that include anemia, systemic infection or the infection of a specific part of the body, and even leukemia. An abnormal rise or fall in the specific cell counts indicate an underlying disease ...
What is the measure of the proportion of the RBCs to the fluid component of the blood called?
Hematocrit, which is the measure of the proportion of the RBCs to the fluid component of the blood called the plasma