What is the recommended percentage of voltage drop?
the maximum conductor voltage drop recommended for both the feeder and branch circuit is fi ve percent of the voltage source, the total conductor voltage drop should not exceed (120V x 5%) or no more than 6V less than the source. So, the operating voltage should be no less than (120V – 6V) or 114V. Reducing Voltage Drop
What is the maximum voltage drop allowed?
- Due to forward static resistance voltage drop
- Due to forward dynamic resistance voltage drop
- Voltage at which the diode starts conducting is called as cut in voltage or forward breakdown voltage.
What is the recommended voltage drop?
the maximum conductor voltage drop recommended for both the feeder and branch circuit is fi ve percent of the voltage source, the total conductor voltage drop should not exceed (120V x 5%) or no more than 6V less than the source. So, the operating voltage should be no less than (120V – 6V) or 114V. Reducing Voltage Drop
What is the difference between voltage drop and low voltage?
- It is a loss in the system, an inefficiency. ...
- Voltage drop can lead to malfunction or poor performance.
- Voltage drop is occasionally designed into some elements of vehicle designs, as voltage drop does reduce inrush current to motors and reduce some stress on relays and contactors controlling motor ...
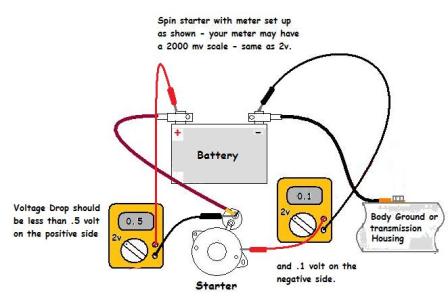
Is 8% voltage drop too much?
The NEC recommends that the maximum combined voltage drop for both the feeder and branch circuit shouldn't exceed 5%, and the maximum on the feeder or branch circuit shouldn't exceed 3% (Fig. 1). This recommendation is a performance issue, not a safety issue.
Is 2% voltage drop acceptable?
In the solar industry lexicon, 2% voltage drop has been known to system integrators as a hard rule that, when sizing conductors, the DC voltage drop should be limited to no higher than 2%.
What is ideal voltage drop?
It is based on the fact that a diode that is said to be "forward conducting" has a voltage drop that fluctuates a small amount between around 0.6 to 0.8V. This constant voltage drop model assumes that the voltage value is at a constant 0.7V.
What is acceptable voltage range?
The nominal voltage in the United States is 120 volts, but the National Electrical Code [NEC 210.19 (A)] specifies an acceptable drop of 5% to fartherest outlet, which is 114 volts. The NEC does not specify maximum voltage, but plus 5% is the accepted standard.
How much voltage drop is acceptable 12V?
Conductors in electrical systems should not be sized with voltage drops exceeding 3%. For a 12V system the maximum voltage drop should be less than (12 V) x 3% = 0.36 V.
What should be the voltage drop for 240 volts supply?
If the supply is single-phase at the usual level of 240 V, this means a maximum volt drop of 4% of 240 V which is 9.6 V, giving (in simple terms) a load voltage as low as 230.4 V. For a 415 V three-phase system, allowable volt drop will be 16.6 V with a line load voltage as low as 398.4 V.
What happens if voltage drop is too high?
Excessive voltage drop in a circuit can cause lights to flicker or burn dimly, heaters to heat poorly, and motors to run hotter than normal and burn out. This condition causes the load to work harder with less voltage pushing the current.
How do you fix voltage drop?
Four practical approaches can be used to minimize voltage drop problems:Increasing the number or size of conductors.Reducing the load current on the circuit.Decreasing conductor length, and.Decreasing conductor temperature.
Why voltage drop is important?
Voltage Drop Needs to be Determined on Long Cord Assemblies For long cord assemblies (over 50 feet), it's important to calculate voltage drop due to potential safety risks. Reasons include: loss of power to equipment, potential damage to cords and wires, and safety issues.
What is acceptable voltage fluctuation?
In the real world, the tolerance for voltage fluctuations is between 5% and 5%. You can get a voltage range from 114V to 126V from your outlet and from 228V to252V for your full-phase appliances.
What is normal voltage in a house?
110 voltThe most common electrical outlet in any home is a 110 volt.
What is normal line voltage in a house?
In North America, most of your electrical appliances are rated to operate with a voltage of 120 volts alternating current (VAC), and allow plus or minus a few volts for variations in load and resistive losses in the electrical wires.
How to reduce voltage drop?
There are two ways to do this, either reduce the length of the wire or use a thicker gauge wire. Most likely, reducing the length won’t be an option so sizing up your wiring is likely the best option.
How much voltage drop at the farthest source?
In fact, the National Electric Code (NEC) recommends that the voltage drop at your furthest device be less than 5% of the source. This an excellent guideline to work within and will help ensure the safety of your circuit and the proper functionality of your system.
How many volts does an inverter need?
Most electronics can operate within a small range around their rated voltage. For example, a 24-volt inverter doesn’t necessarily need exactly 24 volts. However, an excessive voltage drop will cause your devices to stop working or malfunction and could even cause damage.
What is the law of ohms?
Ohm’s Law states that voltage equals current multiplied by resistance (V = I*R). Therefore, a small amount of voltage is lost in the wires as current flows through your electrical system. This is known as voltage drop. More current flowing or higher resistance wire will result in a higher voltage drop.
What is the resistance of a wire?
The resistance is the resistance of the wire. The resistance of a wire depends mainly on the diameter and length of the wire.
Do electronics have voltages?
Some electronics have a wide range of operating voltages and are very forgiving. Others are not. Refer to the operating manuals of your electronics to determine your specific voltage requirements. The biggest concern is not that your devices may not work but rather the safety of your system and preventing a fire.
