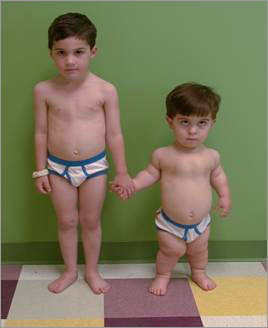
Symptoms
What causes dwarfism?
- Achondroplasia. Though achondroplasia is a genetic condition, four out of five people who have it also have two parents who are average sized.
- Turner syndrome. This condition affects only females. ...
- Growth hormone deficiency. The reasons for growth hormone deficiency aren’t always clear. ...
- Hypothyroidism. ...
- Intrauterine growth retardation. ...
Causes
The majority of people living with achondroplasia have a normal life span and normal intelligence, regardless of delayed development in infancy. Though complications from achondroplasia are a possibility, taking care of symptoms can help prevent serious health problems from occurring later in life.
Prevention
[1] [2] The condition occurs in 1 in 15,000 to 40,000 newborns worldwide. [1] [4] [5] Some populations appear to have a higher incidence of achondroplasia. For instance, it is estimated to occur in about 1 case in 6400 births in Denmark and about 1 case in 10,000 births in Latin America.
Complications
While achondroplasia does come with a set of possible complications and the risk of a shortened lifespan, just like other causes of dwarfism can have an impact on life expectancy, many people with achondroplasia can lead normal, fulfilling lives. Being aware of possible complications and what you can do to minimize your risk of developing them could be a step in the direction of a longer and healthier life with achondroplasia.
What are the causes of dwarfism?
What is the prognosis for achondroplasia?
How many people in the world have achondroplasia?
Does dwarfism affect lifespan?

What type of genetic disorder is achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is a form of short-limbed dwarfism. The word achondroplasia literally means "without cartilage formation." Cartilage is a tough but flexible tissue that makes up much of the skeleton during early development.
Is achondroplasia a chromosomal abnormality?
Achondroplasia is a single gene disorder? caused by mutations? in the FGFR3 gene? on chromosome? 4. Two different mutations in the FGFR3 gene cause more than 99 per cent of cases of achondroplasia. It is a dominant? genetic disease so only one copy of the FGFR3 gene needs to be mutated for symptoms to develop.
Is achondroplasia a birth defect?
Achondroplasia is a birth defect that affects a baby's bone growth. Birth defects are health conditions that are present at birth. Birth defects change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body.
Is dwarfism a gene mutation or chromosomal?
Dwarfism is usually the result of a genetic mutation. But having a gene or genes responsible for dwarfism can occur in a couple of ways. In some cases, it can happen spontaneously. You may not be born with mutated genes inherited from a parent.
Is dwarfism autosomal or Sexlinked?
In later years, subse- quent matings showed clearly that the dwarfism is caused by a sex-linked gene which is apparently completely recessive in heterozygous males.
What are 3 examples of genetic mutations that are caused by external factors?
Summary. Mutations are caused by environmental factors known as mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents.
What gene causes dwarfism?
The most common form of dwarfism is due to a DNA difference in the FGFR3 gene on chromosome 4. This has a couple of important implications for you. First off, if your father's dwarfism is due to this dominant cause, he must have one copy of this gene that leads to dwarfism and one copy that does not.
How is achondroplasia dwarfism inherited?
Achondroplasia may be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. This means that if a child gets the defective gene from one parent, the child will have the disorder. If one parent has achondroplasia, the infant has a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder.
Can achondroplasia be cured?
Currently there are no treatments able to reverse achondroplasia, which is caused by mutations in a gene — called FGFR3 — that result in the excess production of proteins that slow bone growth, nor are there ways to treat the genetic culprit itself.
Is achondroplasia a substitution mutation?
Virtually all cases of achondroplasia are caused by a single nucleotide substitution in the FGFR3 gene, which alters one amino acid in the FGR3 protein (Gly380Arg). Other mutations in this gene cause other skeletal disorders in humans. Very few genetic disorders are as mutation-specific as in achondroplasia.
Is achondroplasia a point mutation?
Achondroplasia comes from the genetic point mutations in the fibroblastic growth factor receptor 3 gene (FGFR3), which enables abnormal cartilage growth-plate differentiation and insufficient bony development.
Is achondroplasia a mutation?
Achondroplasia impairs the growth of bone in the limbs and causes abnormal growth in the spine and skull. Although the cause is a genetic mutation, only about one out of five cases is hereditary (passed down by a parent).
What chromosome is involved in achondroplasia?
Although this condition can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, 80% of cases are due to new, sporadic mutations. Mutations involve the gene encoding fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), situated on chromosome 4.
Is Turner syndrome a mutation or chromosomal abnormality?
Turner syndrome is a chromosomal condition that affects development in females. The most common feature of Turner syndrome is short stature, which becomes evident by about age 5. An early loss of ovarian function (ovarian hypofunction or premature ovarian failure) is also very common.
How is achondroplasia dwarfism inherited?
Achondroplasia may be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. This means that if a child gets the defective gene from one parent, the child will have the disorder. If one parent has achondroplasia, the infant has a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder.
What chromosome is the FGFR3 gene on?
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGFR3 gene. FGFR3 has also been designated as CD333 (cluster of differentiation 333). The gene, which is located on chromosome 4, location p16. 3, is expressed in tissues such as the cartilage, brain, intestine, and kidneys.
What is achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is a genetic (inherited) condition that results in abnormally short stature and is the most common cause of short stature with disproportionately short limbs. The average height of an adult with achondroplasia is 131 cm (52 inches, or 4 foot 4 inches) in males and 124 cm (49 inches, or 4 foot 1 inch) in females.
What are the characteristics of achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is a distinctive condition that usually can be noted at birth.
How is achondroplasia diagnosed?
The diagnosis of achondroplasia can be based on the typical physical features, the hallmarks of achondroplasia, evident at birth. Characteristic features are also seen by X-rays, ultrasound, and other imaging techniques. With ultrasound imaging, the diagnosis can sometimes be strongly suspected before birth.
What can be done for patients with achondroplasia?
Considerations in monitoring children with achondroplasia include careful measurements of growth (length/height and weight) and head circumference using curves specially standardized for those with achondroplasia. Knowledgeable pediatric care and periodic orthopedic and neurologic examinations are critical.
What if two people with achondroplasia have children?
Thus, with each conception, there is a 25% chance for an average-size child, a 50% chance for a child (like them) with achondroplasia and a 25% chance for a conception with two achondroplasia genes. The combined presence of two genes for achondroplasia (called homozygous achondroplasia) causes a grievous skeletal disorder that leads to early death from breathing failure due to constriction by a tiny chest cage and neurologic problems from hydrocephalus.
Why do achondroplasia occur sporadically?
This means that most cases of achondroplasia occur sporadically (out of the blue) and are the result of a new mutation in a sperm or ovum of one of the normal- appearing parents.
What is the oldest birth defect?
Achondroplasia is one of the oldest known birth defects. The frequency of achondroplasia is estimated to range from about 1 in 10,000 births in Latin America to about 12 in 77,000 in Denmark. An average figure worldwide is approximately 1 in 25,000 births.
What is achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is a disorder of bone growth that prevents the changing of cartilage (particularly in the long bones of the arms and legs) to bone. It is characterized by dwarfism, limited range of motion at the elbows, large head size (macrocephaly), small fingers, and normal intelligence. Achondroplasia can cause health complications such as interruption of breathing ( apnea ), obesity, recurrent ear infections, an exaggerated inward curve of the lumbar spine ( lordosis ). More serious problems include a narrowing of the spinal canal that can pinch (compress) the upper part of the spinal cord (spinal stenosis) and a buildup of fluid in the brain ( hydrocephalus ). [1] [2] Some people with achondroplasia may have delayed motor development early on, but cognition is normal. [3] Achondroplasia is caused by mutations in the FGFR3 gene. Inheritance is autosomal dominant. [1] [2] Treatment may include medication with growth hormone, and surgery aimed to correct the spine, or bone problems, as well, as to reduce the pressure inside the brain in cases of hydrocephaly. [2] Prognosis with achondroplasia is good except in cases of spinal compression at the neck. [3]
What is the inheritance pattern of achondroplasia?
When it is inherited, it follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. About 80% of individuals who have achondroplasia have parents with average stature and are born with the condition as a result of a new ( de novo) gene alteration ( mutation ). [1] [2] [4] Each individual with achondroplasia has a 50% chance, with each pregnancy, ...
How many cases of achondroplasia are there in Latin America?
For instance, it is estimated to occur in about 1 case in 6400 births in Denmark and about 1 case in 10,000 births in Latin America. No particular race has been documented to be more commonly affected. [5]
How to make a diagnosis for a genetic disorder?
Healthcare professionals typically look at a person’s medical history, symptoms, physical exam, and laboratory test results in order to make a diagnosis. The following resources provide information relating to diagnosis and testing for this condition. If you have questions about getting a diagnosis, you should contact a healthcare professional.
Can achondroplasia cause a slow motor development?
[1] [2] Some people with achondroplasia may have delayed motor development early on, but cognition is normal. [3] .
What is the genetic cause of achondroplasia?
Most children with achondroplasia (80%) are born to parents of average stature as the result of a change in the gene (a mutation) that causes it to not function properly.
When is achondroplasia diagnosed?
Sometimes achondroplasia is diagnosed before birth based on physical features during a prenatal ultrasound. Radiology (medical imaging) may be used to confirm the diagnosis. In other cases, it isn’t diagnosed until after birth.
What receptors are used to slow down bone growth?
Some signals, like the signals from FGFR3 receptors (fibroblast growth factor receptor 3), tell the bones to slow down growth. Others, like the signals from NPRB receptors (natriuretic peptide receptor B), block those signals and allow bones to grow. FGFR3 receptors are usually only “turned on” when the body needs to stop changing cartilage ...
Why does FGFR3 slow bone growth?
In achondroplasia, a change in the structure of the FGFR3 gene causes the body to continuously send out signals to slow bone growth. Because FGFR3 receptors are always “turned on,” the signals to slow bone growth are stronger than the signals that tell bones to grow (which come from the NPRB receptors). As a result, the chondrocytes have trouble ...
Does achondroplasia hold you back?
The widespread impact of this condition can cause serious, progressive, and lifelong complications. Despite these complications, achondroplasia does not have to hold people back from living happy and fulfilling lives. The more you know, the more prepared you can be for the future.
What is achondroplasia?
Achondroplasia is caused by a gene alteration (mutation) in the FGFR3 gene. The FGFR3 gene makes a protein called fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 that is involved in converting cartilage to bone. FGFR3 is the only gene known to be associated with achondroplasia. All people who have only a single copy of the normal FGFR3 gene and a single copy of the FGFR3 gene mutation have achondroplasia.
Why does achondroplasia cause delays in walking?
Because of the hypotonia, there may be delays in walking and other motor skills. Compression of the spinal cord and/or upper airway obstruction increases the risk of death in infancy. People with achondroplasia commonly have breathing problems in which breathing stops or slows down for short periods (apnea).
What are the symptoms of achondroplasia?
People who have achondroplasia have abnormal bone growth that causes the following clinical symptoms: short stature with disproportionately short arms and legs, short fingers, a large head (macrocephaly) and specific facial features with a prominent forehead (frontal bossing) and mid-face hypoplasia.
How is achondroplasia diagnosed?
Achondroplasia is diagnosed by characteristic clinical and X-ray findings in most affected individuals . In individuals who may be too young to make a diagnosis with certainty or in individuals who do not have the typical symptoms, genetic testing can be used to identify a mutation in the FGFR3 gene.
What is the chance of having a child with achondroplasia?
A person who has achondroplasia who is planning to have children with a partner who does not have achondroplasia has a 50 percent chance, with each pregnancy, of having a child with achondroplasia. When both parents have achondroplasia, the chance for them, together, to have a child with normal stature is 25 percent.
Do people with achondroplasia have average size parents?
Most people who have achondroplasia have average-size parents. In this situation, the FGFR3 gene mutation occurs in one parent's egg or sperm cell before conception. Other people with achondroplasia inherit the condition from a parent who has achondroplasia.
Is achondroplasia inherited?
Most cases of achondroplasia are not inherited. When achondroplasia is inherited, it is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Testing in adults
Any adult can ask for genetic testing to see if they carry an altered FGFR3 gene. For the test, a doctor or technician collects a sample of hair, blood, or saliva.
Testing during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a doctor may be able to diagnose achondroplasia in a fetus using an ultrasound scan. This may show characteristics of the condition, such as shortened humerus and femur bones.
Testing in children
Doctors can often diagnose achondroplasia based on physical signs, but if a child is very young or the characteristics are not typical, a doctor may recommend genetic testing.
Daily life
Achondroplasia does not affect a person’s intelligence or necessarily prevent someone from doing typical things, such as going to school, working, or having a family.
Long-term health
People with achondroplasia have a higher risk of certain health complications. Doctors can treat or manage many of these. Some of the most common are orthopedic, and may include:
