/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/68882603/1300144836.0.jpg)
An ACL consists of several components central to its function:
- Sequence number: The sequence number identifies the ACL entry with a specific number.
- ACL name: The ACL name defines the ACL entry using a name assigned to it as opposed to numbers. ...
- Remark: On some routers, you can input comments, which can be used to include more detailed descriptions.
What is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a band of dense connective tissue which courses from the femur to the tibia. The ACL is a key structure in the knee joint, as it resists anterior tibial translation and rotational loads.
What is the ACL and what does it do?
The ACL is a key structure in the knee joint, as it resists anterior tibial translation and rotational loads. When the knee is extended, the ACL has a mean length of 32 mm and a width of 7-12 mm. There are two components of the ACL, the anteromedial bundle (AMB) and the posterolateral bundle (PLB).
What is an ACL knee brace?
An ACL knee brace is a high level support brace used following ACL tears and ruptures. They may be used instead of surgery, whilst awaiting surgery, or once recovering from surgery. ACL braces are a great way to provide extra stability to the knee, give it time to heal and prevent further injury.
What are the common ACL injuries?
ACL injuries often happen during sports and fitness activities that can put stress on the knee: 1 Suddenly slowing down and changing direction (cutting). 2 Pivoting with your foot firmly planted. 3 Landing awkwardly from a jump. 4 Stopping suddenly. 5 Receiving a direct blow to the knee or collision, such as a football tackle.
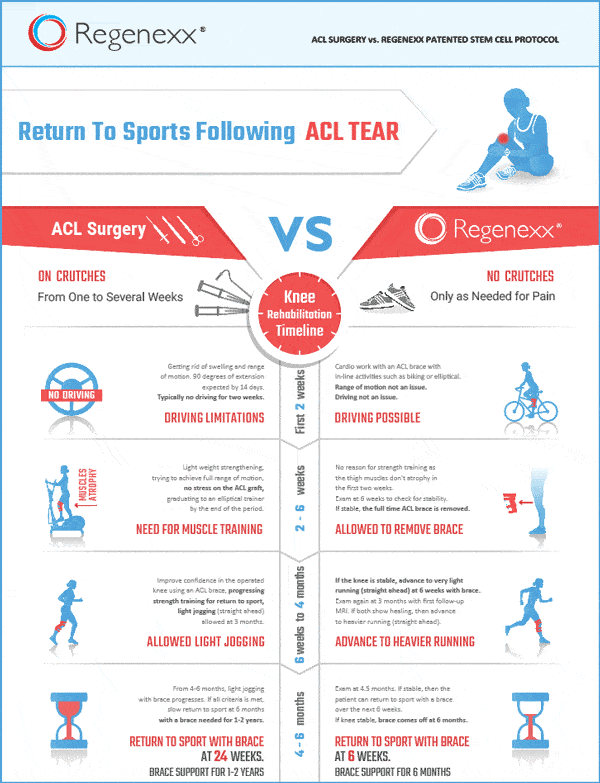
Is the ACL a cartilage?
During ACL repair, the cartilage can be smoothed using arthroscopic surgical techniques. However, some cartilage injuries lend themselves to further treatment with procedures that stimulate cartilage growth or replace the injured areas with new cartilage.
What material is used for ACL surgery?
Synthetic grafts made of different materials such as carbon fibers, polypropylene, Dacron and polyester have been utilised either as a prosthesis or as an augmentation for a biological ACL graft substitute.
Does ACL surgery have metal?
In ACL reconstruction, a replacement ligament (graft) is attached to tunnels drilled into the end of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). Often screws are used to attach the graft to the bone. Traditionally, metal screws have been used.
What ligaments make up the ACL?
Cruciate ligaments: The two cruciate ligaments are inside your knee joint and connect your femur to your tibia. They cross each other to create an X. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is located toward the front of the knee. The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is behind the ACL.
Do ACL screws dissolve?
However, the evidence on the use of biodegradable interference screws in anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction is still scarce. Although the screws promise to degrade within approximately 12-24 months after surgery, several cases have been reported in which this did not happen [1, 10, 15].
Can ACL screws come out?
We use specialized screws or pins to hold that ligament in the bone tunnels until it heals, which takes about six or eight weeks. Those screws or pins are either permanent, made out of titanium or made out of a substance that will be reabsorbed by the body over the course of one or two years.
Will my knee ever be the same after ACL surgery?
In some patients, their knee is not the same. In some patients, ten years later their knee is not the same. Some people do very well with ACL reconstruction surgery, some do very well with second or revision ACL surgery. Some do well with the third ACL reconstruction/revision surgery.
How many screws are used in ACL surgery?
In addition, in the double-bundle technique, we used four interference screws for the fixation, while in the single-bundle technique only two interference screws were used. All these factors could explain the superiority of the double-bundle ACL comparing to the single-bundle ACL even at the 10-year follow-up.
Are the screws in ACL surgery metal?
In ACL reconstruction, a replacement ligament (graft) is attached to tunnels drilled into the end of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). Often screws are used to attach the graft to the bone. Traditionally, metal screws have been used.
Can you bend knee with ACL tear?
Some people find that the knee joint feels looser than it should. Less range of motion. After you damage your ACL, it's very likely that you won't be able to bend and flex your knee like you normally would.
How thick is an ACL ligament?
The mean thickness in the middle third of the ACL was 4.5 mm in the sagittal plane (range: 3.1–7.2 mm) and 4.3 mm in the frontal plane (range: 2.9–6.2 mm). The mean size of the lateral femoral condyle was 62.2 mm (range: 48.1–74.7 mm), while the mean size of the medial femoral condyle was 55.7 mm (range: 43.2–67.4 mm).
How painful is a torn ACL?
Moderate-to-severe pain is very common. Initially, the pain is sharp and then becomes more of an ache or throbbing sensation as the knee swells. Since the ACL is the major knee stabilizer, an injury to it will cause the knee to give out or buckle when a person tries to walk or change direction.
What tools are used for ACL reconstruction?
The Inion® ACL instrument set is a compact and easy-to-use system for ACL reconstruction. The system combines the instruments and the Graft preparation station in one autoclavable case. The Inion® ACL instrument set offers instruments required for both interference screw and button-type of fixation.
What hardware is used in ACL reconstruction?
Commonly used fixation devices include interference screws (metallic and bioabsorbable), suspensory fixation (the Endobutton [Acufex Microsurgical, Mansfield, Massachusetts], RetroButton [Arthrex, Naples, Florida], ACL TightRope [Arthrex, Naples, Florida]), and cross-pins.
How many screws are used in ACL surgery?
In addition, in the double-bundle technique, we used four interference screws for the fixation, while in the single-bundle technique only two interference screws were used. All these factors could explain the superiority of the double-bundle ACL comparing to the single-bundle ACL even at the 10-year follow-up.
How is an ACL graft attached?
Your surgeon will drill sockets or tunnels into your thighbone and shinbone to accurately position the graft, which is then secured to your bones with screws or other devices. The graft will serve as scaffolding on which new ligament tissue can grow.
What is the ACL made of?
The ACL has a microstructure of collagen bundles of multiple types (mostly type I) and a matrix made of a network of proteins, glycoproteins, elastic systems, and glycosaminoglycans with multiple functional interactions.
What is the ACL length?
When the knee is extended, the ACL has a mean length of 32 mm and a width …. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a band of dense connective tissue which courses from the femur to the tibia. The ACL is a key structure in the knee joint, as it resists anterior tibial translation and rotational loads. When the knee is extended, the ACL has ...
What Are The Components of An ACL?
The implementation for ACLs is pretty similar in most routing platforms, all of which have general guidelines for configuring them.
What is an ACL?
Summary. ACLs are the packet filters of a network. They can restrict, permit, or deny traffic which is essential for security. An ACL allows you to control the flow of packets for a single or group of IP address or different for protocols, such as TCP, UDP, ICMP, etc.
How to Implement An ACL On your Router?
Understanding ingress and egress traffic (or inbound and outbound) in a router, is critical for proper ACL implementation.
What is ACL in routing?
When you define an ACL on a routing device for a specific interface, all the traffic flowing through will be compared with the ACL statement which will either block it or allow it.
How to identify an ACL entry?
Identify an ACL entry using a number. Define an ACL entry using a name. Instead of using a sequence of numbers, some routers allow a combination of letters and numbers. Some Routers allow you to add comments into an ACL, which can help you to add detailed descriptions.
What is dynamic ACL?
Dynamic ACL. Dynamic ACLs, rely upon extended ACLs, Telnet, and authentication. This type of ACLs are often referred to as “Lock and Key” and can be used for specific timeframes. These lists permit access to a user to a source or destination only if the user authenticates to the device via Telnet.
What is ACL in Access Control?
An Access Control Lists “ ACL ” is a function that watches incoming and outgoing traffic and compares it with a set of defined statements.
What is the sensitivity of ACL?
MRI is the primary modality to diagnose ACL pathology with a sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 95%. Diagnosis may also be made with knee arthroscopy to differentiate complete from partial tears and chronic tears. Arthrography is considered the gold standard as it is 92% to 100% sensitive and 95% to 100% specific; however, it is rarely used as the initial step in diagnosis as it is invasive and requires anesthesia.
How to tell if ACL is torn?
On MR, ACL tears have primary and secondary signs. Primary signs will indicate changes associated directly with the ligamentous injury, while secondary signs are those changes closely related to the ACL injury. Primary signs include edema, an increased signal of the anterior cruciate ligament on T2 weighted or proton density images, discontinuity of the fibers, and a change in the expected course of the ACL (alteration of Blumensaat’s line). Tears usually occur within the midportion of the ligament, and signal changes are most often seen here and appear hyperintense. Secondary signs include bone marrow edema (secondary to bone contusion), a second fracture (as discussed below), associated medial collateral ligament injury, or anterior tibial translation of greater than 7 mm of the tibia relative to the femur (best seen on lateral view).
Why do women have a higher risk of ACL injury?
Some studies suggest that females may have weaker hamstrings and preferential utilize the quadriceps muscle group while decelerating. When engaging the quadriceps musculature while slowing down, this places abnormally increased stress on the ACL, as the quadriceps muscles are less effective at preventing anterior tibial translation versus the hamstring muscles. A second factor that may increase the risk of ACL injury is the increased valgus angulation of the knee. [4][5] One study utilizing video analysis demonstrated that female athletes are more likely to place their knees in increased valgus angulations when changing directions suddenly, which increased the stress on the ACL ligament. Lastly, it has been suggested that estrogenic effects on the strength and flexibility of tissues such as ligaments may play a role and predispose females to injury; however, this remains controversial and has yet to be proven.
What is non-operative treatment for ACL tear?
Nonoperative treatment is typically reserved for those with low functional demands, type and severity of ACL tear, time of injury, and subsequent assessment . Continued monitoring and treatment by an orthopedist and physical therapist is necessary and will only improve their functional status and stability post-injury. Of note, about half of the patients who initially choose the non-operative pathway will later choose to undergo surgical repair.
Can a radiograph show ACL fracture?
Radiographs are generally non-contributory for ACL injuries but help rule out fractures or other associated osseous injuries. In younger patients, avulsion of the tibial attachment may be seen. Other non-specific features that can be seen on radiographs include:
Can an ACL injury be managed?
ACL injuries, depending upon their severity, can be managed nonoperatively or operatively. The patient with an anterior cruciate ligament injury should be referred to the orthopedic physician to discuss treatment options and a physical therapist (PT) for rehabilitation.
Why is the ACL so important?
It helps maintain the knee's rotational stability and prevents the tibia (shinbone) from slipping in front of the femur (thighbone). The ACL is particularly vulnerable to injury during athletic activity or as the result of impact, and a torn ACL is a common injury in athletes of all levels. It is especially common in sports with a lot ...
What is an ACL tear?
An ACL tear is when the anterior cruciate ligament becomes partially or completely ruptured. Once torn, an ACL cannot regrow or heal on its own.
Who tears their ACL?
People of all ages, physical conditions and abilities can tear an ACL. Active women experience a higher incidence of ACL injuries than men because their biomechanics tend to put more stress on their knees.
How is a torn ACL diagnosed?
A doctor can usually diagnose a torn ACL from a physical exam, although magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) is helpful. Getting an MRI is also important to find out if other parts of the knee have been injured.
When is ACL surgery necessary?
The choice to have surgery is usually based on the patient's lifestyle. In athletes and other people of any age who wish to continue doing physically demanding activity , an ACL reconstruction surgery is often needed.
Why is ACL surgery so common in children?
This was because tradtional ACL surgery techniques could cause growing children to develop a leg length discrepancy or growth deformity.
How to treat ACL injury?
The doctor will determine how bad the ACL injury is and review whether nonsurgical treatment and rehabilitation will be enough or if orthopedic surgery is necessary. Whether or not surgery is performed, physical therapy will be critical to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee and improve its range of motion.
What is the ACL?
Overview. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the key ligaments that help stabilize your knee joint. The ACL connects your thighbone (femur) to your shinbone (tibia). It's most commonly torn during sports that involve sudden stops and changes in direction — such as basketball, soccer, tennis and volleyball.
How to reduce the risk of ACL injury?
Proper training and exercise can help reduce the risk of ACL injury. A sports medicine physician, physical therapist, athletic trainer or other specialist in sports medicine can provide assessment, instruction and feedback that can help you reduce risks.
Why does my knee have a ligament?
Causes. Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect one bone to another. The ACL, one of two ligaments that cross in the middle of the knee, connects your thighbone to your shinbone and helps stabilize your knee joint. ACL injuries often happen during sports and fitness activities that can put stress on the knee:
How to prevent ACL injury in female athletes?
Training to strengthen muscles of the legs, hips and core — as well as training to improve jumping and landing techniques and to prevent inward movement of the knee — may help to reduce the higher ACL injury risk in female athletes.
Why do women have higher risk of ACL injury?
There are a number of factors that increase your risk of an ACL injury, including: Being female — possibly due to differences in anatomy, muscle strength and hormonal influences. Participating in certain sports, such as soccer, football, basketball, gymnastics and downhill skiing. Poor conditioning.
What to do if you have an ACL injury?
Seek immediate care if any injury to your knee causes signs or symptoms of an ACL injury. The knee joint is a complex structure of bones, ligaments, tendons and other tissues that work together. It's important to get a prompt and accurate diagnosis to determine the severity of the injury and get proper treatment.
How to tell if you have an ACL injury?
Signs and symptoms of an ACL injury usually include: A loud pop or a "popping" sensation in the knee. Severe pain and inability to continue activity. Rapid swelling. Loss of range of motion. A feeling of instability or "giving way" with weight bearing.
What is the function of the ACL?
During activity, the ACL controls how far forward the tibia can "slide" relative to the femur: it essentially acts to prevent too much forward movement. While some degree of motion or sliding is normal and is required for knee function, too much motion may damage other structures in the knee which can lead to long term problems in some patients.
What are the grades of ACL injuries?
ACL injuries are classified by grades 1, 2, and 3. Depending on the grade of ACL injury, the patient’s age, and level of athleticism, non-operative or surgical treatments may be recommended.
How is an ACL injury diagnosed?
An ACL tear can be diagnosed by a physician through a history and physical examination. On physical examination, the physician can specifically assess the amount of motion present and determine if the ACL is torn. Additionally, evaluation of other structures within the knee is done also, as ACL tears are often found in association with injury to other structures within the knee, such as the cartilage and collateral ligaments.
What is the anterior cruciate ligament?
There is a ligament on each side of the knee (the collateral ligaments) and two ligaments deep inside the knee. The two ligaments inside the knee that “cross” each other are called the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). Both ligaments attach on one side to the end of the thighbone (femur) and on the other to the top of the shinbone (tibia). [Figure 1].
How is the ACL injured? What are the symptoms?
The ACL can be injured or torn in a number of different ways. The most common mechanism is that of a sudden pivoting or cutting maneuver during sporting activity , which is commonly seen in football, basketball and soccer. The ligament can also tear due to work injuries or automobile accidents.
How to tell if you have an ACL tear?
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury or tear? 1 A “pop” in the knee at the time of injury 2 Swelling of the knee 3 Inability to bear weight on leg (though some have little or no pain) 4 Instability of the knee
Why do you need a knee scan for ACL tear?
The scan is also useful for evaluating the cartilage or meniscus tissue in the knee if this information is necessary to make decisions regarding the best treatment for a specific patient.
What is an ACL brace?
ACL Knee Brace Guide. An ACL knee brace is a high level support brace used following ACL tears and ruptures. They may be used instead of surgery, whilst awaiting surgery, or once recovering from surgery. ACL braces are a great way to provide extra stability to the knee, give it time to heal and prevent further injury.
What happens if your ACL is damaged?
When it is damaged, the stability of the knee is reduced and can lead to the knee giving way during normal daily activities or when playing sport. If the knee is repeatedly giving way, it can cause more damage to the knee, especially the cartilage.
What is the best knee brace for ACL?
Donjoy is the leading manufacturer of ACL knee braces and they are the best at providing support and protection. Donjoy ACL braces are specially designed to reduce that force and strain on the ACL. They are expensive, but they work really well for everything from everyday use to professional athletes.
What material is used to help knee pain?
The neoprene material provides soothing heat and compression which relieves knee pain and knee swelling and promotes healing
What is McDavid Pro II made of?
It is made of lightweight materials including aircraft grade aluminium gears that accommodate the natural gliding action of the knee. The McDavid Pro II has a sewn in patellar support buttress which helps improve patellar tracking. The fully adjustable Velcro straps ensure a perfect fit for your knee.
Can you get ACL damage from knee brace?
If the knee is repeatedly giving way, it can cause more damage to the knee, especially the cartilage. Some people can overcome the problem through strengthening and stability exercises, but many benefit from an ACL knee brace.
Why is the ACL important?
As such, the ACL is essential in making sure the knee joint remains stable. Many different scenarios may cause an ACL injury. For instance, it can happen as a result of landing on a bent knee from jumping up high or landing on an over-extended knee.
What does ACL mean in sports?
The ACL stands for Anterior Cruciate Ligament, and it’s a tear in a knee muscle that causes the ligament to completely change the way it turns and its general direction. ACL tears happen a lot in professional sports; in the knee joint which connects the shin bone to the thigh bone.
What is the best knee brace for torn ACL?
The UFlex Athletics Knee Com pression Sleeve Support expertly combines style and practicality. That’s why it’s considered to be one of the best knee braces for torn ACL, especially if you plan to wear it on a daily basis.
Why is my ACL sore?
There are lots of high impact sports and activities that can cause a tear in your ACL. The result is usually painful swelling followed by an inability to remain stable. That’s why it’s important to use a well-fitting knee brace that provides you with the support you need.
Can you get an ACL tear in 2021?
A torn ACL is one of the most common injuries among professional athletes. An ACL tear can happen to anyone, including casual distance runners and anyone who maintains an active lifestyle. The good news is there are valid safety measures to help quickly recover from this common knee injury.
Does Lycra fit behind knees?
Lycra, in particular, has a luxurious feel to it. It’s soft, breathable, moisture-wicking, stays well in place, and doesn’t bunch up behind your knee.
Can you wear knee braces for ACL?
The good news is there are valid safety measures to help quickly recover from this common knee injury. Knee braces designed specifically for ACL injuries are the most effective solution against this problem, and they’re a 100% risk-free solution.

Introduction
Attachments
- Origin
Arises from the posteromedial corner of medial aspect of lateral femoral condyle in the intercondylar notch. This femoral attachment of ACL is on posterior part of medial surface of lateral condyle well posterior to longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft. The attachment is actuall… - Orientation
It runs inferiorly, medially and anteriorly.
Nerve Supply
- The ACL receives nerve fibers from the posterior articular branches of the tibial nerve. These fibers penetrate the posterior joint capsule and run along with the synovial and periligamentous vessels surrounding the ligament to reach as far anterior to the infrapatellar fat pad. Most of the fibers are associated with the endoligamentous vasculature and have a vasomotor function. Th…
Vascular Supply
- The major blood supply of the cruciate ligaments arises from the middle geniculate artery. The distal part of both cruciate ligaments is vascularized by branches of the lateral and medial inferior geniculate artery. The ligament is surrounded by a synovial fold where the terminal branches of the middle and inferior arteries form a periligamentous network. From the synovial sheath bloo…
Composition
- The ACL has a microstructure of collagen bundles of multiple types (mostly type I) and a matrix made of a network of proteins, glycoproteins, elastic systems, and glycosaminoglycans with multiple functional interactions.
Bundles
- There are two components of the ACL, the smaller anteromedial bundle (AMB) and the larger posterolateral bundle (PLB), named according to where the bundles insert into the tibial plateau. The anteromedial bundle is tight in flexion and the posterolateral bundle is tight in extension. In extension both bundles are parallel; in flexion the femoral insertion site of the posterolateral bun…
Function
- The ACL provides approximately 85% of total restraining force of anterior translation. It also prevents excessive tibial medial and lateral rotation, as well as varus and valgus stresses. To a lesser degree, the ACL checks extension and hyperextension. Together with the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), the ACL guides the instantaneous center of rotation of the knee, therefore contr…