
What is BI-RADS birads?
BIRADS BIRADS or ‘BI-RADS stands for Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System and was established by the American College of Radiology. BI-RADS is a scheme for putting the findings from mammogram screening (for breast cancer diagnosis) into a small number of well-defined categories.
What is ACR reporting and Data Systems (rads)?
ACR Reporting and Data Systems (RADS) provide standardized imaging findings terminology, report organization, assessment structure and classification for reporting and data collection in patient imaging. What are ACR Reporting And Data Systems (RADS)?
What is ACR BI-RADS Atlas 5th edition?
ACR BI-RADS Atlas® 5th Edition. The BI-RADS ® atlas provides standardized breast imaging terminology, report organization, assessment structure and a classification system for mammography, ultrasound and MRI of the breast. BI-RADS reporting enables radiologists to communicate results to the referring physician clearly and consistently,...
Who is the team at ACR BI-RADS Atlas?
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing. American College of Radiology. ACR BI-RADS ATLAS – Mammography.
What does ACR mean in mammogram?
The American College of Radiology (ACR) is a vigorous advocate of quality breast imaging. Before there was a federal mandate for breast imaging accreditation, the College established a voluntary mammography accreditation program promoting standards for quality assurance and quality control.
What is ACR type?
The American College of Radiology (ACR) type refers to different parenchymal densities of the breast, implying a more or less high diagnostic accuracy.
What is ACR Breast density B?
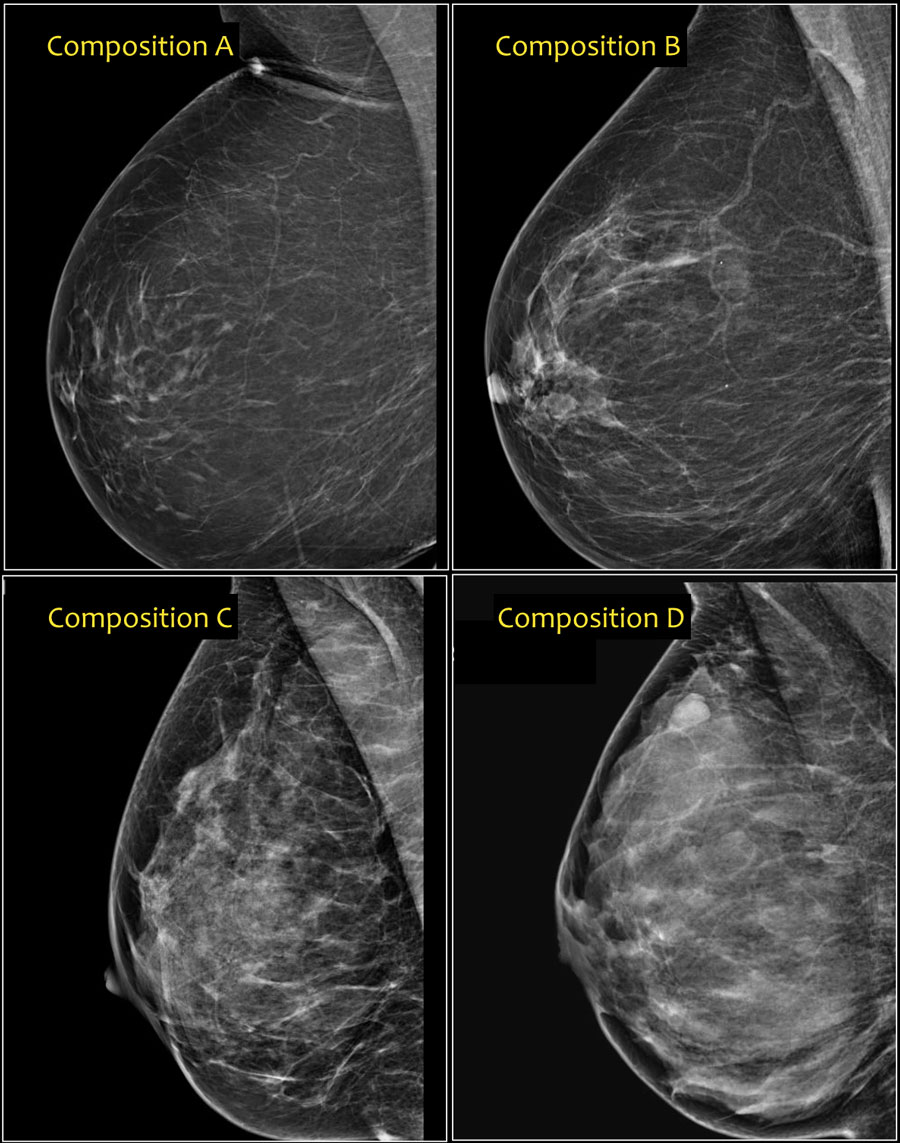
Breast density — The four levels According to the BI-RADS reporting system, the levels are (from left to right) A: almost entirely fatty, B: scattered areas of fibroglandular density, C: heterogeneously dense, and D: extremely dense.
What does ACR 2 benign mean?
A BI-RADS category 2 at the end of your report means that the mammogram, breast ultrasound and/or MRI breast show benign findings, not suspicious findings for cancer.
What does ACR 1 negative mean?
Follow-up: Additional imaging needed before a category can be assigned. Category 1. Advertisement. Assessment: Negative: means that there is no significant or noticeable abnormality to report.
Should I worry about dense breast tissue?
Dense breast tissue is common and is not abnormal. However, dense breast tissue can make it harder to evaluate the results of your mammogram and may also be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
What is ACR type C?
Type C (heterogeneously dense): another 40% of women have this type of mammographic density, which is considered dense and may obscure small cancers. Type D (extremely dense): around 10% of women have extremely dense breasts, which lowers the sensitivity of mammography.
Is it better to have fatty or dense breasts?
Pettersson and colleagues [1] report that the greater the non-dense breast area (regardless of the dense breast area), the lower the breast cancer risk. In other words, fatty breasts have a protective effect on breast cancer risk.
Can Fibroglandular be cancerous?
Scattered fibroglandular breast tissue is a noncancerous condition that can cause lumps in the breasts. It is not a disease, and it does not require treatment. This type of tissue does not cause breast cancer, but it can make cancerous lumps harder to find.
What is suspicious malignancy?
• Suspicious for malignancy (SFM) is a diagnostic category utilized in a small percentage of thyroid FNA cases, when a malignant diagnosis is suspected but cannot be definitively made.
What is Category 4 Suspicious abnormality breast?
A category 4 result means the radiologist has found something that needs to be further evaluated and could be cancer. Other benign, non-cancerous changes can look suspicious.
What does Birad 4 Suspicious mean?
4. Suspicious abnormality – Biopsy should be considered. These findings do not definitely look like cancer but could be cancer. The radiologist is concerned enough to recommend a biopsy. The findings in this category can have a wide range of suspicion levels.
What is the clinical significance of BI-RADS category 4?
Generally speaking, as we move further into categories A,B, and finally C, the chances of the breast lesion being diagnosed as Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) increases.
What is the BI-RADS category?
Up to 9% of breast cancer screening mammograms receive a BI-RADS category of 3, 4 or 5, which implies that there is cause for concern and further investigations will be necessary. BIRADS 3 is rarely used nowadays, because BIRADS 4 and 5 are categories that lead to biopsies, and breast biopsy to give a definitive diagnosis.
What is BI-RADS in mammography?
BI-RADS is a scheme for putting the findings from mammogram screening (for breast cancer diagnosis) into a small number of well-defined categories. Although BIRADS started out for use with breast screening mammography, it was later adapted for use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and breast ultrasound (US) as well.
What is the predictive value of a bi-rads score of 4?
A BI-RADS category 4 mammogram has a positive predictive value of about 30% . A category 5 mammogram is almost certainly predictive of breast cancer with a positive predictive value of about 95%. So, a birads score of 4 means I need a biopsy but there is a 30% chance of cancer and a 70% chance of something benign?
How long does it take for a BI-RADS to show up on a mammogram?
With BI-RADS category 3, your radiologist will recommend a follow-up at 6 months. Sometimes on a breast cancer screening mammogram there may be a finding of some kind, but no palpable lesion is present.
What is the risk of breast cancer in 4C?
So, this means that category 4C indicates a high risk for breast cancer. A birads 4a has 13% chance of malignancy. And for birads 4b there is a 36% chance of malignancy. Finally, a birads 4c has 79% chance of malignancy.
What is a BI-RADS classification?
BI-RADS classifications have also helped in monitoring breast cancer treatment and supporting breast cancer research again by making statistics easier to calculate. Following mammogram, a woman will usually see the BI-RADS assessment on the pathology report.
What is BI-RADS score?
The BI-RADS score is an acronym for the Breast Imaging Reporting and Database System score. It’s a scoring system radiologists use to describe mammogram results. A mammogram is an X-ray imaging test that examines breast health. It’s the most efficient tool to help detect breast cancer, especially at its earliest stage.
What is a category 4 score?
Category 4. A category 4 score indicates a suspicious finding or abnormality. In this instance, there is a 20 to 35 percent chance of cancer. To confirm, your doctor will need to perform a biopsy to test a small tissue sample.
Can a BI-RADS score be used to diagnose breast cancer?
Remember that a BI-RADS score doesn’t provide a diagnosis. If you receive a higher score that indicates the presence of cancer, you must have a follow-up appointment to confirm your doctor’s findings and to receive a proper diagnosis. An early diagnosis can increase your chances of beating breast cancer. Last medically reviewed on November 10, 2017.
What is a BI-RAD score?
BI-RADS Classifications and What They Mean. Your BI-RAD score is a number between 0 and 6. Each number corresponds to a classification that estimates your breast cancer risk based on the imaging test. 2. There is nothing to comment on; routine screening recommended.
What does a BI-RADS score of 3 mean?
A BI-RADS score of 3, or "probably benign" means that there is something suspicious on your mammogram, but that it is most likely not cancer. A follow-up mammogram may be recommended in a few months to see if something has changed.
What is BI-RADS 2021?
Updated on June 10, 2021. The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System ( BI-RADS) is a numerical scale ranging between 0 and 6 that is used in mammogram, breast ultrasound, and breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reports. It is a standardized way to report the risk of breast cancer based on diagnostic tests and was developed by ...
Why do doctors need a BI-RADS number?
A BI-RADS number helps your doctors communicate if anything in an image looks abnormal and how concerning the finding is to them. A change in the number from test to test can, likewise, help your physicians more clearly convey the difference between one image and the next. 1. andresr / Getty Images.
Is the BI-RADS score reliable?
For younger women, children, and adolescents, the BI-RADS score may not be reliable. It's also important to note that your BI-RADS score doesn't replace your physician or radiologist's opinion and insight about your imaging tests, and the number is not a substitute for a clinical exam.
What is ACR reporting and data systems?
What are ACR Reporting And Data Systems (RADS)? ACR Reporting and Data Systems (RADS) provide a standardized framework for reporting on imaging findings. The goal of the ACR RADS is to reduce the variability of terminology in reports and to ease communication between radiologists and referring physicians. Most RADS include standard terminology ...
What is a RADS?
Generally the RADS are modality dependent, contain rules to assess the probability of disease, and may include management recommendations. RADS are developed by committees of member radiologists, and relevant referring physician consultants.
What is the goal of O-RADS?
The goal of O-RADS is to create a standardized Ultrasound and MRI lexicon for describing the imaging characteristics of ovarian and adnexal masses and applying it to a risk stratification and management system for evaluation of malignancy.
What is a BI-RADS report?
BI-RADS reporting breast density. Your mammogram report will also include an assessment of your breast density, which is a description of how much fibrous and glandular tissue is in your breasts, as compared to fatty tissue. The denser your breasts, the harder it can be to see abnormal areas on mammograms.
What is a 4C finding?
4C: Finding with a high likelihood of being cancer (more than 50% but less than 95%), but not as high as Category 5. 5. Highly suggestive of malignancy – Appropriate action should be taken. The findings look like cancer and have a high chance (at least 95%) of being cancer. Biopsy is very strongly recommended.
What does BI-RADS mean?
While BI RADS categories have no specific meanings they do provide a benchmark for the radiologist to monitor the accuracy of their own diagnoses. Generally speaking, if a radiologist feels that a mammogram corresponds to BI-RADS category 4, it probably means, in their own mind, that they think the chances of the lesion being ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), invasive ductal carcinoma or lobular breast carcinoma are about 80%.
How many different BI RADS categories are there?
Each BI RADS category reflects an increased suspicion in the interpretation of the radiologist for the likelihood of being diagnosed with breast cancer . So, there are seven different mammograms, ultrasound and MRI BI RADS assessment categories. However, there are really only four possible outcomes.
What is the purpose of a biopsy with BI-RADS?
The main goal of any biopsy with BI-RADS category 5 is to confirm the diagnosis and extent of an obviously malignant lesion. Additional diagnostic procedures, particularly imaging and possibly biopsy of the axillary lymph nodes, will almost always be necessary.
Can a BI-RADS 3 be biopsied?
BI-RADS category 3 lesions should not be biopsied. For a Category 3 BI RADS on a mammogram, specialists will usually not advise a breast biopsy. Nonetheless, a great number of BI-RADS 3 cases do end up having a biopsy.
What does a bi-rads 6 mean?
Bi-RADS 6: known biopsy proven cancer – appropriate action should be taken. To be perfectly honest, if a patient has a rating of 6, it means that cancer is present. Now, a 6 does not mean what stage of cancer a patient is in, and the stages have a great impact on the treatment experience.
What is category 6 imaging?
Imaging following category 6 by can be done for multiple reasons. At times it is used for evaluating the breast tissue for a follow-up after a biopsy or surgery. Mammography is used post-biopsy for assessment of biopsy marker placement if one is deployed at time of biopsy.
What is BI-RADS in medical terms?
BI-RADS ( Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System ) is a risk assessment and quality assurance tool developed by American College of Radiology that provides a widely accepted lexicon and reporting schema for imaging of the breast. It applies to mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. This article reflects the 5th edition, published in 2013 1.
What is the highest category for breast imaging?
Breast imaging studies are assigned one of seven assessment categories: When there are multiple findings, the BI-RADS category for the exam is assigned the highest category in the following hierarchy, from lowest to highest: 1, 2, 3, 6, 0, 4, 5. The vast majority of screening mammograms fall into BI-RADS 1 or 2 4.