
What is the role of an Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service for use in a Windows Server environment. It is a distributed, hierarchical database structure that shares infrastructure information for locating, securing, managing, and organizing computer and network resources including files, users, groups, peripherals and network devices.
How to configure Active Directory?
Step-1: Install Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) Role
- Login to your server using administrator user account.
- Open the Server Manager dashboard.
- Click on Tools and Select Add roles and features.
- Click Next to proceed.
- Select Role-based or feature-based installation option and click on Next.
- Since I am installing AD DS server role locally I will select “Select a server from the server pool”. ...
What are the main features of Active Directory?
Major features in Active Directory Domain Services
- A domain is a group of objects, such as users or devices, that share the same AD database. ...
- A tree is one or more domains grouped together. ...
- A forest is a group of multiple trees. ...
- Organizational Units (OUs) organize users, groups and devices. ...
- Containers are similar to OUs, but Group Policy Objects cannot be applied or linked to container objects.
How are Active Directory objects defined?
Active Directory stores data as objects. An object is a single element, such as a user, group, application or device, e.g., a printer. Objects are normally defined as either resources, such as printers or computers, or security principals, such as users or groups. Active Directory categorizes directory objects by name and attributes.

What are the 3 main components of an Active Directory?
The Active Directory structure is comprised of three main components: domains, trees, and forests. Several objects, like users or devices that use the same AD database, can be grouped into a single domain.
What are the 4 types of Microsoft Active Directory?
Below we'll explain their differences in order to help you decide what you need.Active Directory (AD) ... Azure Active Directory (AAD) ... Hybrid Azure AD (Hybrid AAD) ... Azure Active Directory Domain Services (AAD DS)
What is Active Directory in simple words?
Active Directory (AD) is a database and set of services that connect users with the network resources they need to get their work done. The database (or directory) contains critical information about your environment, including what users and computers there are and who's allowed to do what.
How many types of Active Directory are there?
7 different typesThere are technically 7 different types of Active Directory. Each of them are deployed in different way, places and for different purposes.
What is example of Active Directory?
Active Directory categorizes directory objects by name and attributes. For example, the name of a user might include the name string, along with information associated with the user, such as passwords and Secure Shell keys.
What is domain in Active Directory?
An Active Directory domain is a collection of objects within a Microsoft Active Directory network. An object can be a single user or a group or it can be a hardware component, such as a computer or printer. Each domain holds a database containing object identity information.
What are the 5 roles of Active Directory?
Active Directory has five FSMO roles:Schema Master.Domain Naming Master.Infrastructure Master.Relative ID (RID) Master.PDC Emulator.
What is purpose of Active Directory?
Active Directory stores information about objects on the network and makes this information easy for administrators and users to find and use. Active Directory uses a structured data store as the basis for a logical, hierarchical organization of directory information.
What are the 4 most important benefits of Active Directory?
Benefits of Active Directory Domain ServicesYou can customize how your data is organized to meet your companies needs.You can manage AD DS from any computer on the network, if necessary.AD DS provides built in replication and redundancy: if one Domain Controller (DC) fails, another DC picks up the load.More items...•
What is difference between AD and LDAP?
AD is a directory service for Microsoft that makes important information about individuals available on a limited basis within a certain entity. Meanwhile, LDAP is a protocol not exclusive to Microsoft that allows users to query an AD and authenticate access to it.
Is Active Directory an LDAP server?
Active Directory is a directory server that uses the LDAP protocol.
What is Active Directory interview questions?
Top 25 Active Directory Interview Questions & AnswersWhat do you mean by Active Directory? ... Name the default protocol used in directory services? ... Define SYSVOL? ... Define the term FOREST in AD? ... What is Kerberos? ... What do you mean by lingering objects? ... Define Active Directory Schema? ... Name the components of AD?More items...•
What is difference between Active Directory and Azure Active Directory?
Azure AD provides managed identities to run other workloads in the cloud. The lifecycle of these identities is managed by Azure AD and is tied to the resource provider and it can't be used for other purposes to gain backdoor access. Active Directory doesn't natively support mobile devices without third-party solutions.
What are different types of AD objects?
There are two types of AD objects, which are:Container objects: These objects can contain other objects within them. Groups and organizational units (OUs) are examples of container objects.Leaf objects: Leaf objects cannot contain other objects. These objects are only representations of resources in the AD network.
What is the latest version of Windows Active Directory?
Active Directory schema version 88 is the latest schema version, and it has been around since Windows Server 2019.
Which three types of users are available in Azure AD?
There are three types of user accounts that you can have in Azure AD, federated, synchronized, and cloud, or also known as cloud-only users.
Why do organizations use Active Directory?
Organizations of all sizes all over the world use Active Directory to help manage permissions and control access to critical network resources. But what exactly is it, and how can it potentially help your business?
What is the purpose of Active Directory?
The main function of Active Directory is to enable administrators to manage permissions and control access to network resources. In Active Directory, data is stored as objects, which include users, groups, applications, and devices, and these objects are categorized according to their name and attributes.
What Are Active Directory Domain Services?
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) are a core component of Active Directory and provide the primary mechanism for authenticating users and determining which network resources they can access. AD DS also provides additional features such as Single Sign-On (SSO), security certificates, LDAP, and access rights management.
What is the difference between Windows and Azure AD?
Azure AD is said to be the backbone of Office 365 and other Azure products; however, it can also be integrated with other cloud services and platforms. Some of the differences between Windows and Azure AD are as follows. Communication: Azure AD uses a REST API, whereas Windows AD uses LDAP, as mentioned previously.
What is a domain controller?
The server that hosts AD DS is called a domain controller (DC). A domain controller can also be used to authenticate with other MS products, such as Exchange Server, SharePoint Server, SQL Server, File Server, and more.
How to access Server Manager?
Open the Server Manager, which you can access via PowerShell by logging in as administrator and typing ServerManager.exe.
What is a tree in a hierarchy?
Trees: A tree is one or more domains grouped together in a logical hierarchy. Since domains in a tree are related, they are said to “trust” each other.
What are the logical divisions of an Active Directory network?
The Active Directory framework that holds the objects can be viewed at a number of levels. The forest, tree, and domain are the logical divisions in an Active Directory network.
What is an object in Active Directory?
Each object represents a single entity— whether a user, a computer, a printer, or a group—and its attributes. Certain objects can contain other objects. An object is uniquely identified by its name and has a set of attributes—the characteristics and information that the object represents— defined by a schema, which also determines the kinds of objects that can be stored in Active Directory.
What are some examples of Active Directory services?
Other Active Directory services (excluding LDS, as described below) as well as most of Microsoft server technologies rely on or use Domain Services; examples include Group Policy, Encrypting File System, BitLocker, Domain Name Services, Remote Desktop Services, Exchange Server and SharePoint Server .
What is a domain controller?
A server running the Active Directory Domain Service (AD DS) role is called a domain controller. It authenticates and authorizes all users and computers in a Windows domain type network, assigning and enforcing security policies for all computers, and installing or updating software. For example, when a user logs into a computer that is part of a Windows domain, Active Directory checks the submitted password and determines whether the user is a system administrator or normal user. Also, it allows management and storage of information, provides authentication and authorization mechanisms, and establishes a framework to deploy other related services: Certificate Services, Active Directory Federation Services, Lightweight Directory Services, and Rights Management Services.
What is AD LDS?
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services ( AD LDS ), formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM), is an implementation of LDAP protocol for AD DS. AD LDS runs as a service on Windows Server. AD LDS shares the code base with AD DS and provides the same functionality, including an identical API, but does not require the creation of domains or domain controllers. It provides a Data Store for storage of directory data and a Directory Service with an LDAP Directory Service Interface. Unlike AD DS, however, multiple AD LDS instances can run on the same server.
How does Active Directory synchronize changes?
Active Directory synchronizes changes using multi-master replication. Replication by default is 'pull' rather than 'push', meaning that replicas pull changes from the server where the change was effected. The Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) creates a replication topology of site links using the defined sites to manage traffic. Intrasite replication is frequent and automatic as a result of change notification, which triggers peers to begin a pull replication cycle. Intersite replication intervals are typically less frequent and do not use change notification by default, although this is configurable and can be made identical to intrasite replication.
What is an AD?
Active Directory ( AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems as a set of processes and services. Initially, Active Director y was only in charge of centralized domain management. However, Active Director y became an umbrella title for a broad range of directory-based identity-related services.
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service by Microsoft that started back in 2000 and has since exploded with over 90% of organizations using it. AD is structured like a hierarchy for efficient data storage and retrieval.
What is directory server?
Directory servers make it easy for admins to store and access resources including user and device information, computers, files, server, and much more.
What is group policy?
Group Policy is a feature that network admins use to configure and enforce many different Windows settings. Admins use Group Policy to limit network access to users based on their standing in the organization.
What is AD in network?
Similar to a physical directory with contact information, AD is a digital directory service that allows admins and users to search for resources (files, printers, computers, servers) stored anywhere on the network. What Services Does AD Provide?
What is AD CS?
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) are the services provided for Microsoft environments to deploy digital certificates. Certificates need a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to operate and AD CS lays the foundation for Windows admins to build their own PKI.
Why is authentication important in AD?
Authentication is crucial for network security because it ensures that only approved users can access certain network resources. Learn how you can improve AD authentication with Cloud RADIUS.
What is each object in an organization represented by in AD?
Each object in an organization is represented by an entity in AD and assigned a name and attributes for identification.
Why is Active Directory used?
Active Directory is mostly used by system administrators to save user’s data, assigning security-related policies, and place software. Active Directory governs the security policies when a VPN connection is established and people are allowed to connect to that network.
What is the purpose of Microsoft Active Directory?
Microsoft Active Directory not just functions as a locator service, but also provides great benefits to the organizations by enabling a centralized execution of activities that take place in the network. The image below depicts the important aspects of Active Directory.
What is a domain controller?
The domain controller is a Windows server that saves information regarding all the objects which are within that domain. It is an Active Directory server that contains all the information related to objects. User accounts and computer accounts are added to Domain Controller when information is stored.
What is domain in network?
A domain is a network structure where one server or multiple servers are responsible for dealing with security and permissions on the network. It is created in order to control user’s access and permission where 50, 100, or thousands of computers are connected. The topmost domain created in the directory is the root.
What is the top part of an Active Directory tree called?
In the Active Directory structure, the top part is called a Forest. As we move down the hierarchy, it forms the tree which can be seen as a collection of domain and sub-domains. The domain is at the center of the Windows Network.
What is directory service?
Directory service allows information to be stored, classified, and retrieved. The directory service in Microsoft office is called Active Directory. It is a database that is used to store an enormous amount of information about the User, User Groups, Client computers, and Network resources like Printers and Shared folders.
What are the two main objects that need to be managed in Active Directory?
We have been talking about objects in Active Directory. Users and computer are two main objects which need to be managed in Active Directory. In this section, we will see steps that can be followed to create a new AD user account.
Why is Active Directory important?
Active Directory is vital for organizations as it helps you efficiently manage company users, computers, devices, and applications. For example, IT managers can leverage Active Directory to systematically organize company data in a hierarchy structure, which states which users or computers belong to which network, or which users have access to which network resources, and so forth.
What is directory in IT?
The directory or database stores critical information related to your IT environment, including essential details about users, user permissions, and computers. In short, it helps you control various activities going on in your IT environment. Most importantly, AD also ensures user authentication, generally via user ID and passwords, and allows them to access data they’re authorized to use.
What is domain in AD?
In the AD, the domain is the primary unit in a logical structure. The objects named under the same directory database, trust relationships, and security policies with other domains are called Domains. Each domain will store data about objects belonging to that domain only.
What is a domain controller?
A domain controller contains many computers on the network and allows the system administrators to manage them from the central place. It is a server or computer used to authenticate other computers throughout the network. It stores the login credentials of all other computers and printers in the network.
What is Active Directory 2021?
Active Directory is a Microsoft product that operates on Windows Server. A step-by-step guide on how to set it up correctly in 2021.
What is an AD DS?
One of the primary Active Directory services is the AD DS (Active Directory Domain Services), a crucial part of the Windows Server OS. The AD DS runs on servers known as Domain Controllers (DCs). An enterprise usually has multiple DCs, and each of these controllers has a copy of the main directory for the domain. Any changes made to the directory on one DC- for example, deleting a user account or changing a password are all applied to the other DCs in a domain to keep them up-to-date.
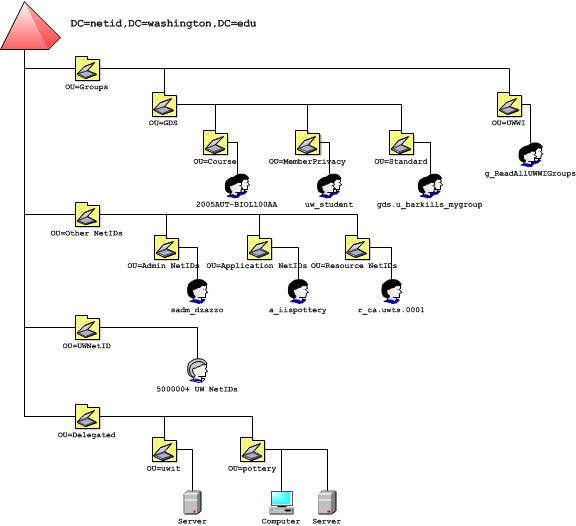
Overview
Logical structure
As a directory service, an Active Directory instance consists of a database and corresponding executable code responsible for servicing requests and maintaining the database. The executable part, known as Directory System Agent, is a collection of Windows services and processes that run on Windows 2000 and later. Objects in Active Directory databases can be accessed via LDA…
History
Like many information-technology efforts, Active Directory originated out of a democratization of design using Request for Comments (RFCs). The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), which oversees the RFC process, has accepted numerous RFCs initiated by widespread participants. For example, LDAP underpins Active Directory. Also, X.500 directories and the Organizational Unit preceded the Active Directory concept that makes use of those methods. The LDAP concept be…
Active Directory Services
Active Directory Services consist of multiple directory services. The best known is Active Directory Domain Services, commonly abbreviated as AD DS or simply AD.
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is the foundation stone of every Windows domain network. It stores information about members of the domain, including devices and users, verifies their credentials and defines their access rights. The server running this service is called a domai…
Physical structure
Sites are physical (rather than logical) groupings defined by one or more IP subnets. AD also holds the definitions of connections, distinguishing low-speed (e.g., WAN, VPN) from high-speed (e.g., LAN) links. Site definitions are independent of the domain and OU structure and are common across the forest. Sites are used to control network traffic generated by replication and also to refer clients to the nearest domain controllers (DCs). Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 uses the sit…
Implementation
In general, a network utilizing Active Directory has more than one licensed Windows server computer. Backup and restore of Active Directory is possible for a network with a single domain controller, but Microsoft recommends more than one domain controller to provide automatic failover protection of the directory. Domain controllers are also ideally single-purpose for directory operations only, and should not run any other software or role.
Database
The Active-Directory database, the directory store, in Windows 2000 Server uses the JET Blue-based Extensible Storage Engine (ESE98) and is limited to 16 terabytes and 2 billion objects (but only 1 billion security principals) in each domain controller's database. Microsoft has created NTDS databases with more than 2 billion objects. (NT4's Security Account Manager could support no more than 40,000 objects). Called NTDS.DIT, it has two main tables: the data table and the lin…
Trusting
To allow users in one domain to access resources in another, Active Directory uses trusts.
Trusts inside a forest are automatically created when domains are created. The forest sets the default boundaries of trust, and implicit, transitive trust is automatic for all domains within a forest.
One-way trust One domain allows access to users on another domain, but the other domain doe…